Session 7: Ceramics; Cutting/Polishing/Abrasives
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is Finishing
For occlusal adjustment & anatomy
Improve marginal adaptation
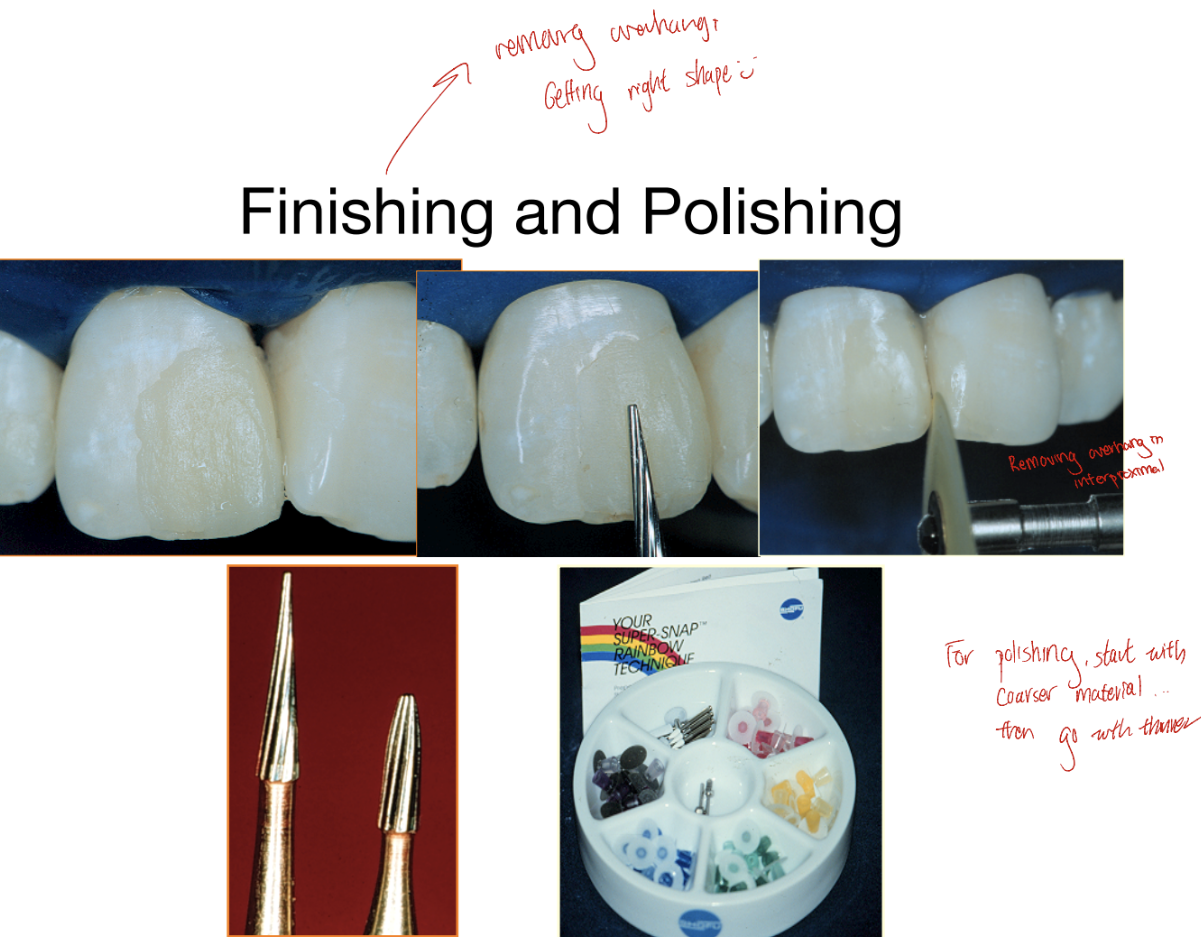
Removing overhangs, sharp edges, roughness
Removing excess material, adjust contours + smoothen rough surfaces
What is Polishing
Smooth surface to a point of high gloss or lusture
Enhance surface, smoothen + shine to reduce plaque accumulation and staining
What is the goal at the end of restorative procedures
TARGET = make restoration as smooth as enamel
What is the objective of finishing + polishing
Reduce plaque accumulation
Smooth surface accumulate less plaque
Provide more comfort to pt
Restorations should feel similar to enamel
Reduce tarnish + corrosion
Amalgam/metal…polishing removes peroxides
Improve aesthetics
Increase biocompatibility with surrounding tissue
Pt irritation from restoration rubbing on B mucosal
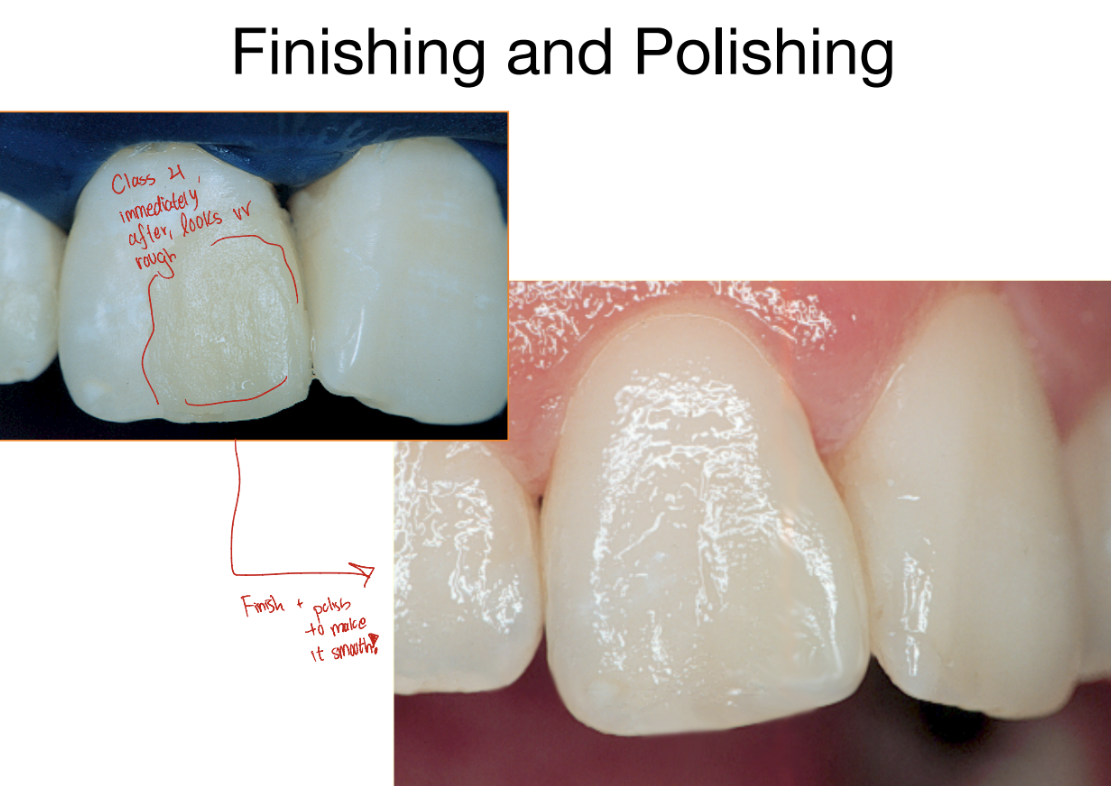
Finishing & polishing with Burs
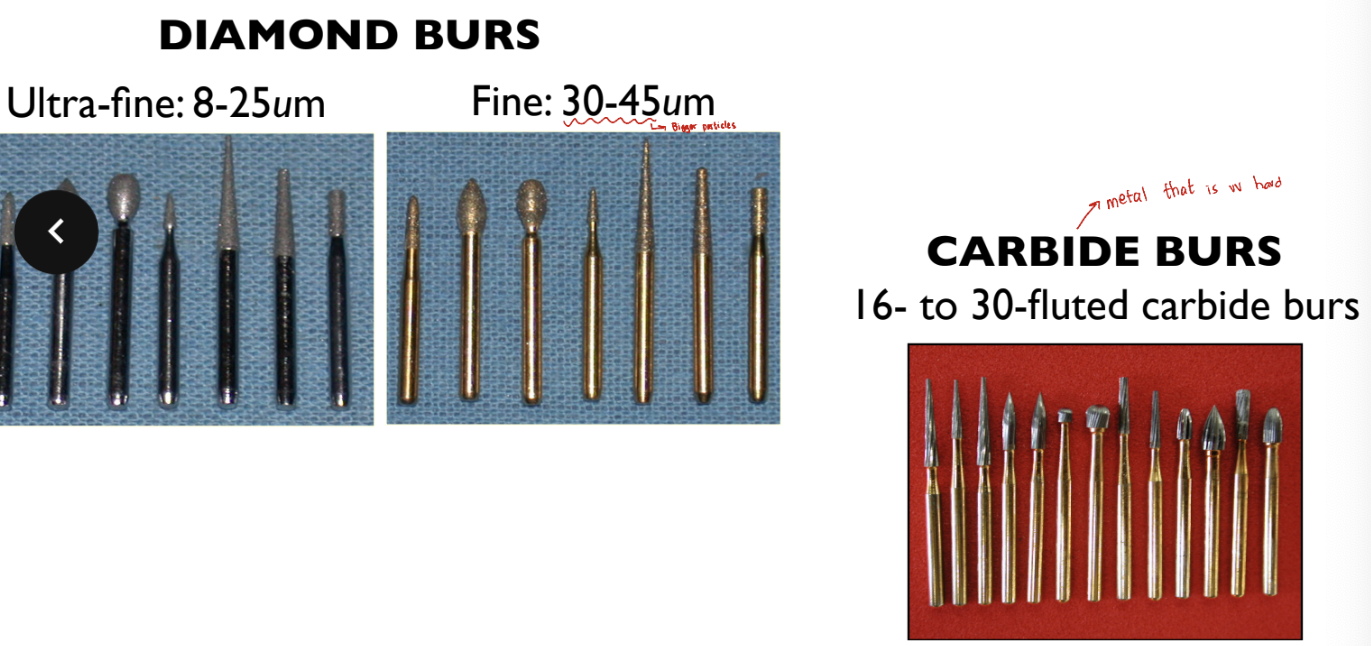
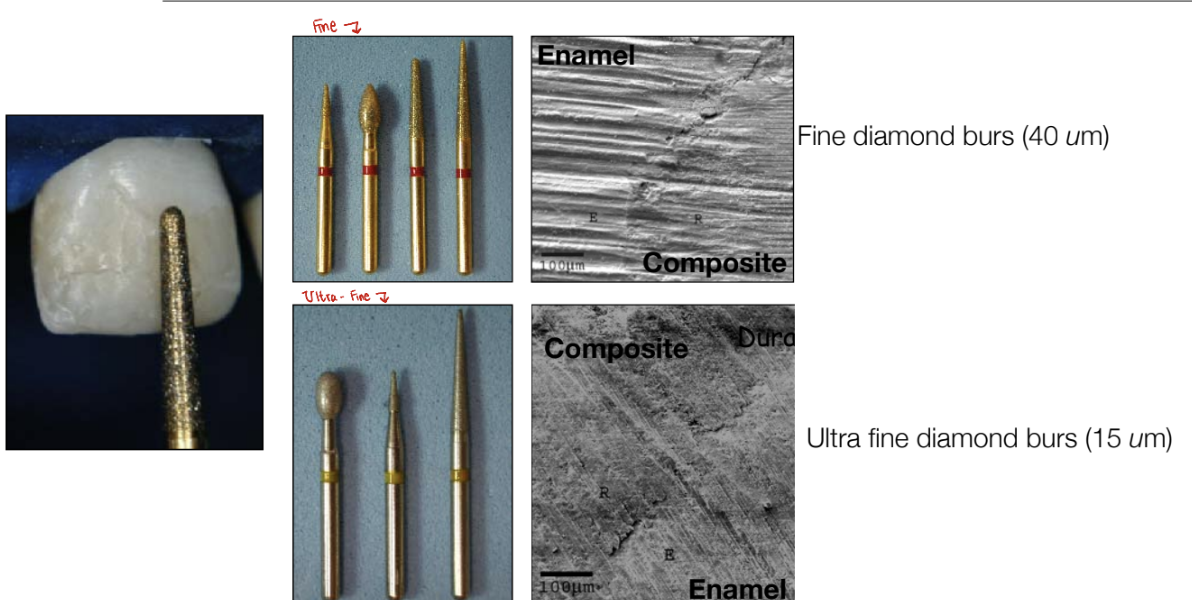
Fine vs. ultrafine diamond burs
Finishing and polishing- metal burrs
Finishing and polishing - rubber burrs
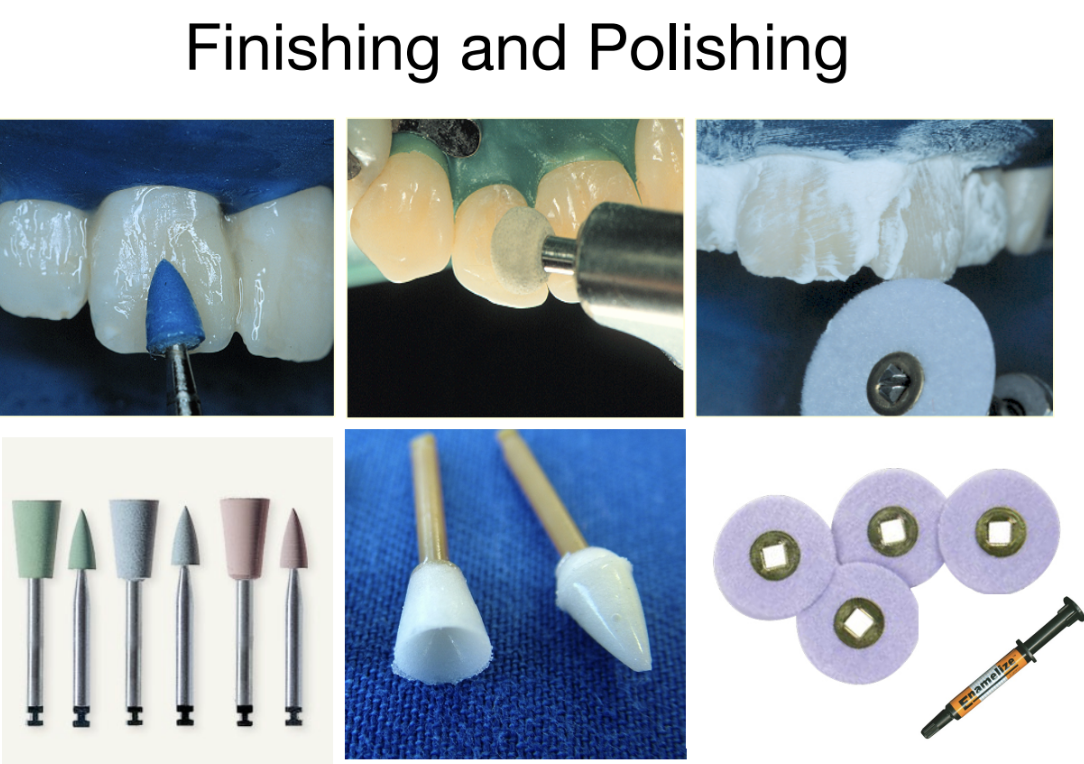


Paste for polishing

Should you keep replacing restorations
The more you replace restorations, the more harmful it is because you are removing more dental tissue
So sometimes it is possible to just smoothen and polish it!
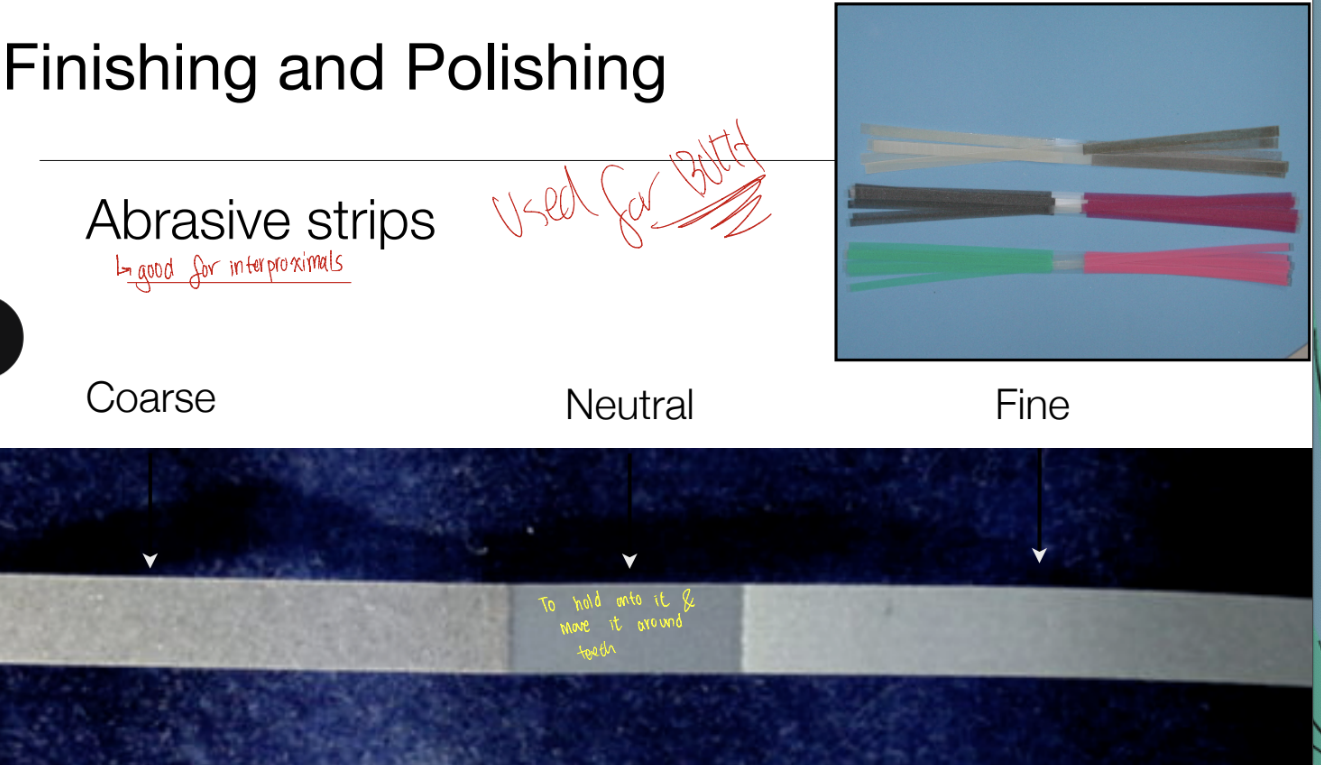
Abrasive streps
Coarse, neutral, fine —> used for both finishing and polishing
There is…
Metal-backed strips
Situation where tight proximal contacts are involved
Useful for ceramics, metals, amalgams, resin composite
More $$$
Plastic-backed strips
Used primarily for resin-composite, compomers, hybrid ionomers, and resin cements
Resin Composite Finishing
Blades
Carbide burs 12 or 16 fluted
Fine diamond burs (24-45um particle size)
Extra fine diamond burs (15-30um particle size)
Abrasive discs + strips (coarse & medium grit)
Resin composite polishing
Carbide burs 20-30 fluted
Abrasive discs + strips (fine & extra-fine grit)
Impregnated rubber wheels, points, cups ( fine & extra-fine)
Felt discs/points combined with polishing paste (alumina or diamond)
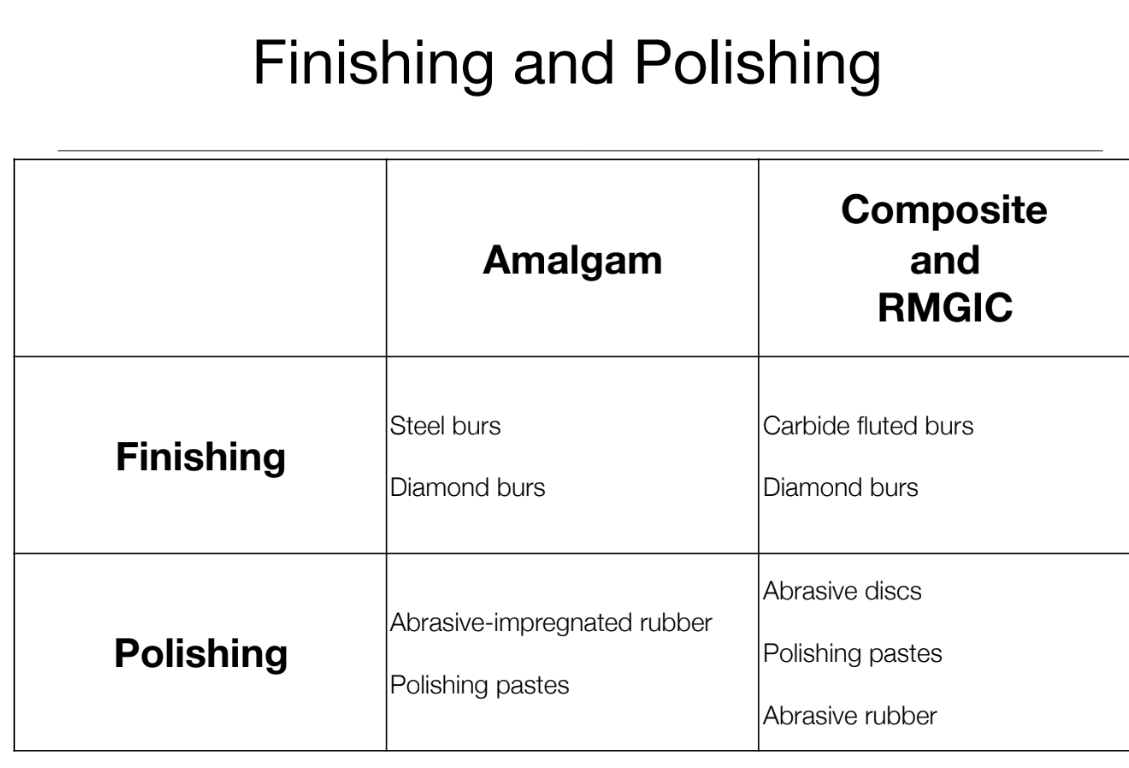
Amalgam Finishing & Polishing
Abrasive particles —> SMALLER
Amalgam finishing burs = slow-speed handpiece
Abrasive-impregnated rubber cups & points (brown, green, blue <fine>)
Pumice in water applied with rotary brush
Tin oxide in water/alcohol applied with rotary brush or felt wheel
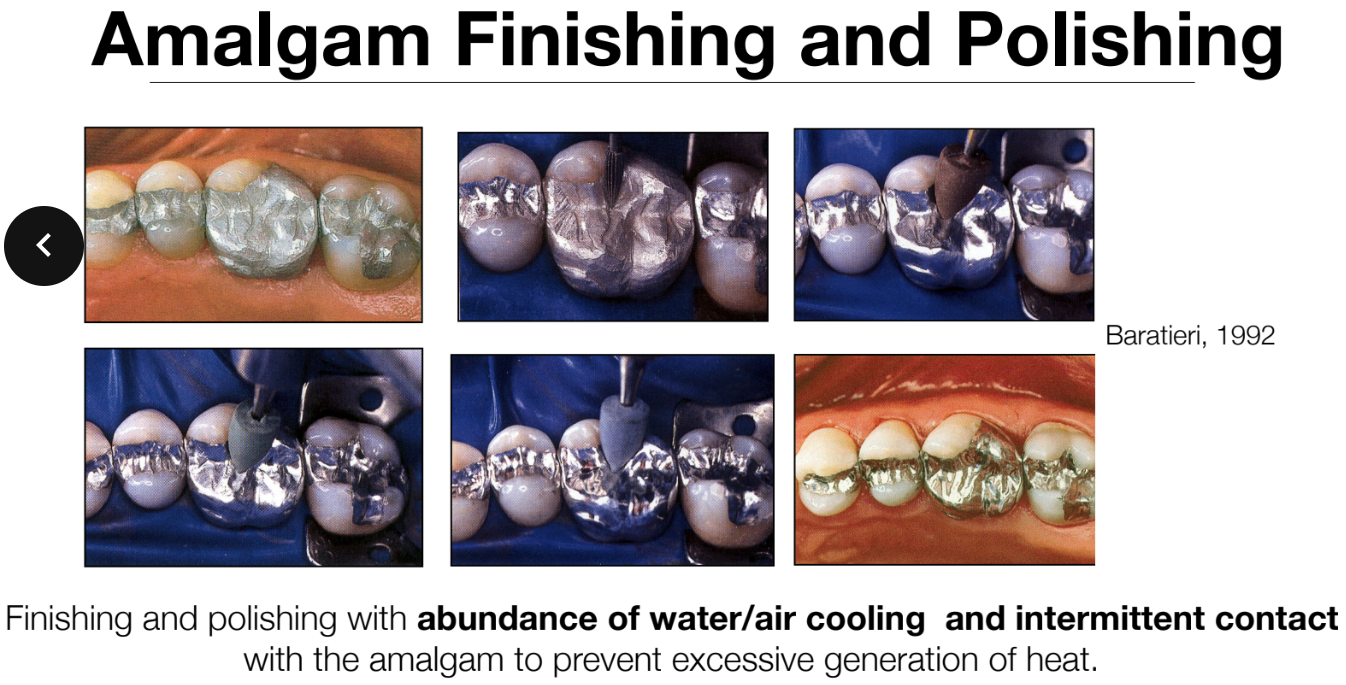
What is super important for amalgam finishing and polishing?
Using an abundance of water/air (lubricant) cooling & intermittent contact with amalgam
Prevent excessive generation of heat

Finishing and polishing - amalgam vs composite
Important for finishing and polishing
Use descending abrasiveness order
Coarse —> Medium —> Fine
Rinse b/w different abrasives
Residues can stay on restoration so RINSE
Use cooling agent
***Refurbishing restorations= part of minimally invasive dentistry
Dental Ceramics (WHERE THE LECTURE SPLITS)
Crystalline composite material, with superior aesthetics & properties adequate to replace natural dental structures
Currently material of choice for fixed prothesis (crowns & bridges) in diff forms of presentation & combination of other materials
Classification of Dental Ceramics
By application
Metal-ceramic crowns & fixed partial prosthesis
All ceramic crowns, inlays, onlays, veneers, fixed partial prostheses
By fabrication method
Sintering —> process of firing compacted ceramic powder @ high temp
Slip-casting —> “slip” = aqueous slurry of ceramic particles
Heat-pressed —> external pressure @ high temperature to sinter + shape ceramic
CAD/CAM machining —> restorations milled from ceramic blocks
COMBO OF ABOVE TECHNIQUES
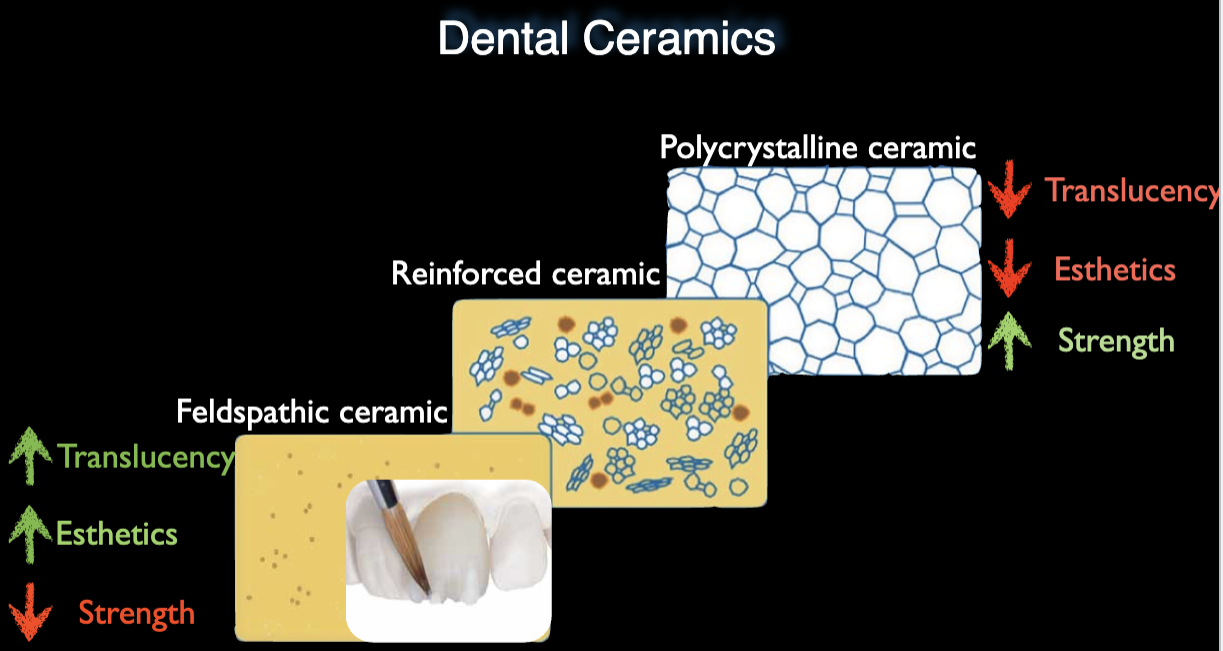
By crystalline phase
Depending on nature + amnt of crystalline phase & porosity present, mechanical + optical properties of dental ceramics vary
Increasing crystalline phase=increase resistance to crack propagation, decrease translucency
Some can have more glass, more esthetic, less strong
Some can have more crystals
Dental ceramics do not have a single composition—some are highly glassy for esthetics, while others have crystalline reinforcement for strength.
The term "crystalline composite materials" refers to ceramics that have crystals embedded in a glass matrix, making them tougher while still being categorized as ceramics.
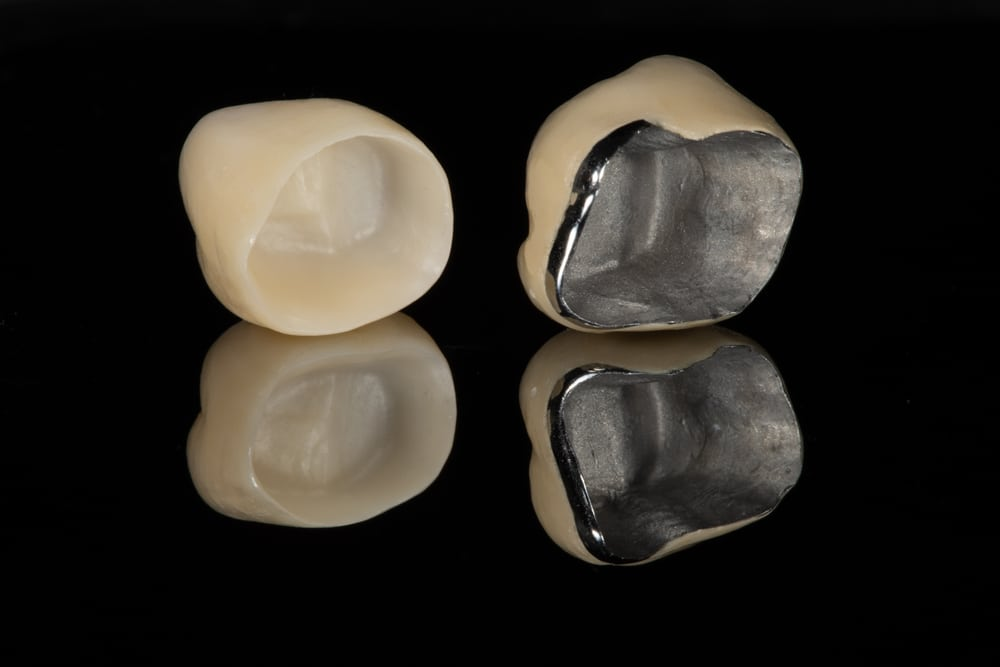
Metal Ceramic
Stil widely used
Colour stable
Tissue-friendly
Biologically inert
Chemically durable
**Survival rate of multiunit metal-ceramic fixed prostheses=considerably higher than all-ceramic systems
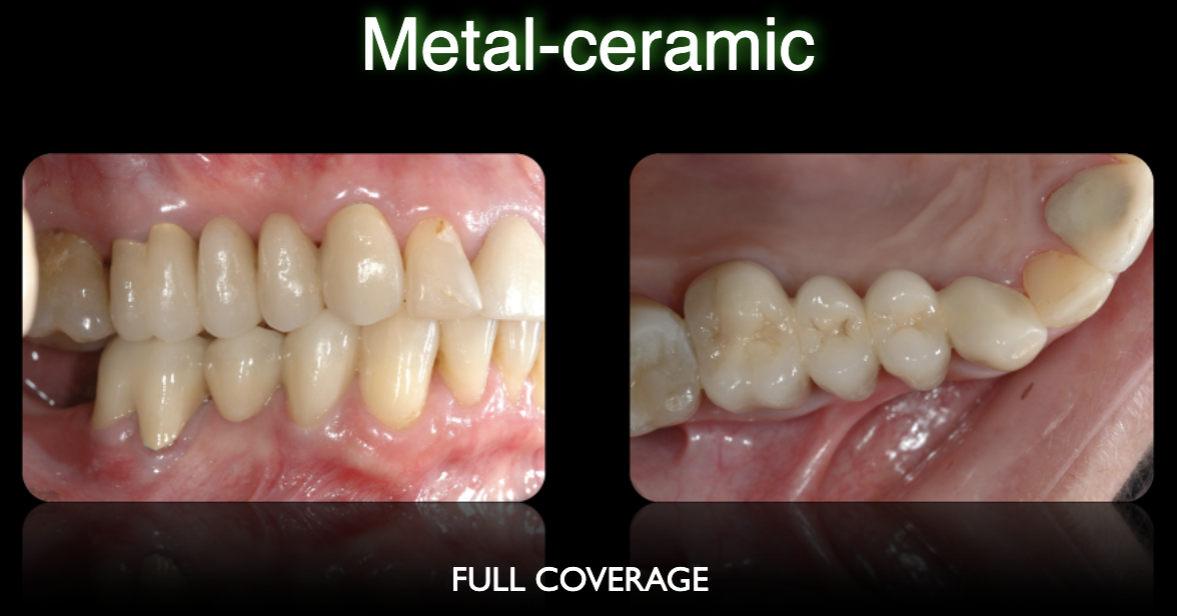
Metal-ceramic full coverage
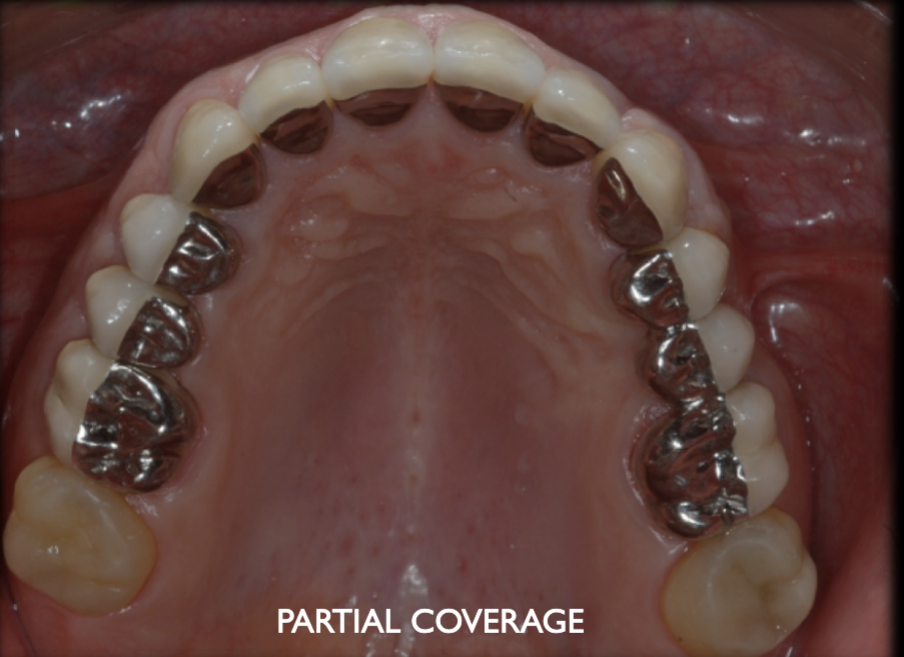
Metal ceramic partial coverage
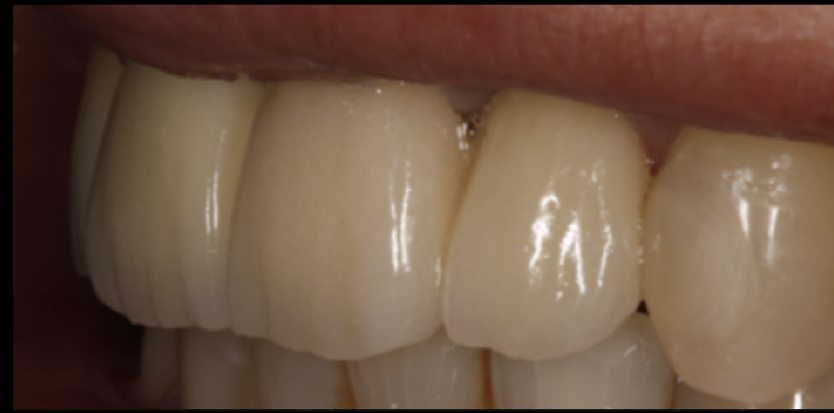
All-ceramic restorations
NO metal as infrastructure…ceramic MUST be stronger
Material for this purpose use wide variety of crystalline phases
Materials for crowns, bridges etc. use different types of crystals as reinforcement and can be made up of up to 99% crystals.
The type, amount, and size of these crystals affect how strong and how natural-looking the material is
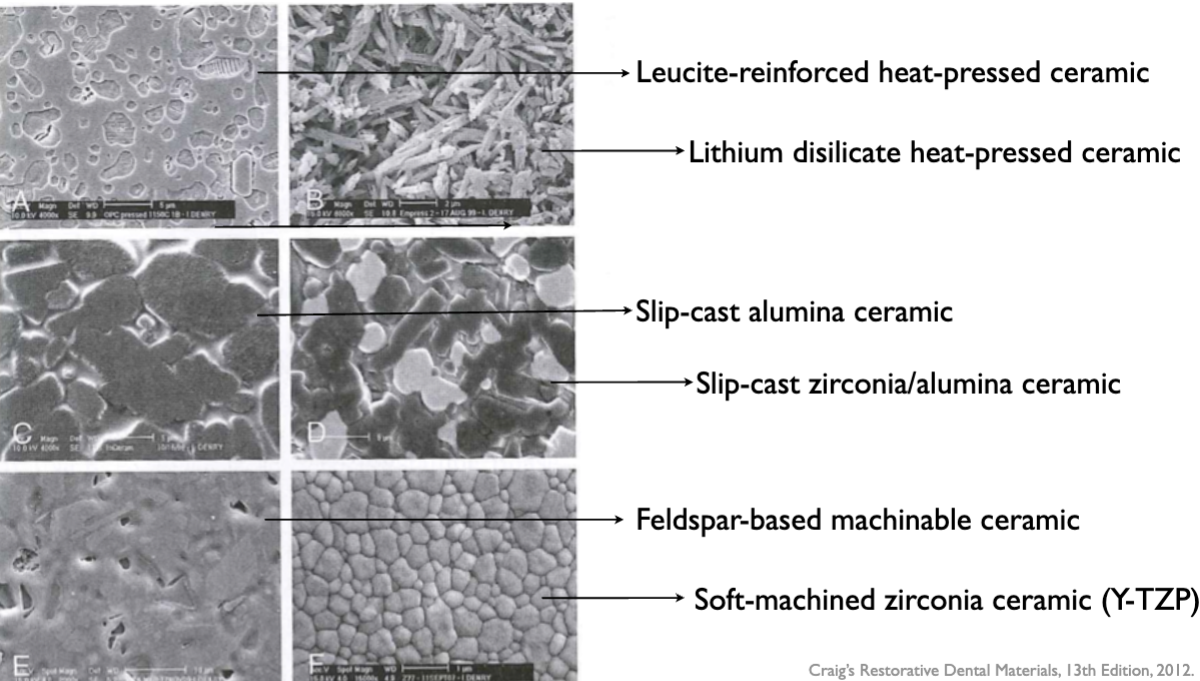
All-ceramic restorations types
Sintered All-Ceramics
Alumina-Based Ceramic
Leucite-Reinforced Ceramic
Heat-Pressed All-Ceramics
Leucite-Based Ceramic
Lithium Disilicate-Based Ceramic
Slip-Cast All-Ceramics
Alumina and Spinel-Based Ceramic
Zirconia-Toughened Alumina Ceramic
Machinable All-ceramics
Hard Machining
Soft Machining followed by sintering
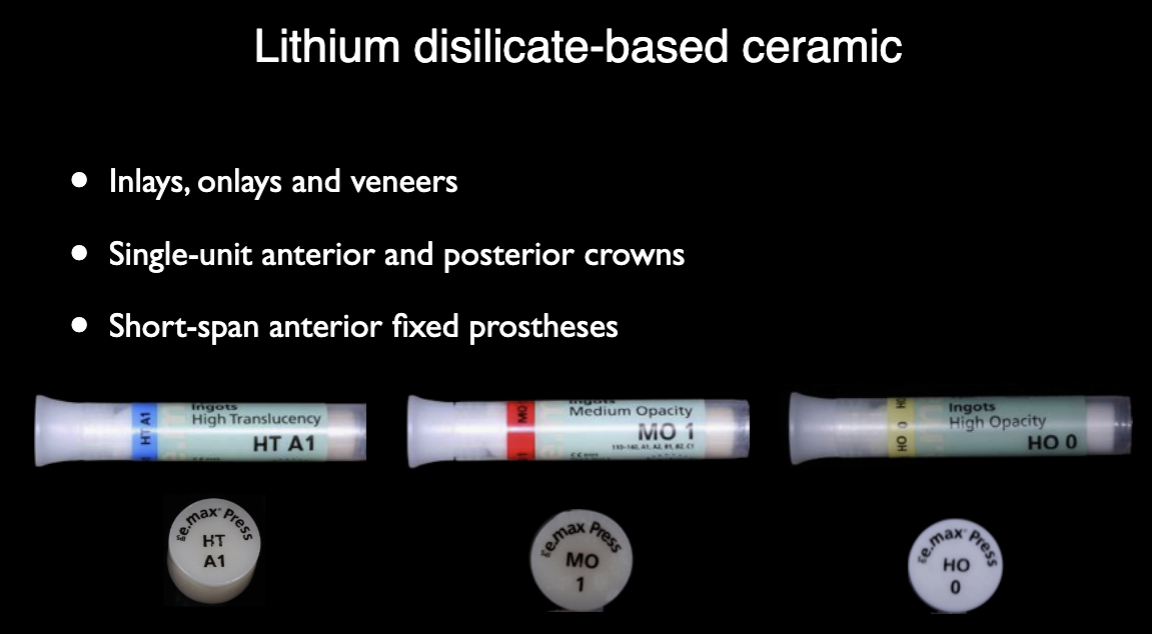
Lithium discilicate-based ceramic
Inlays, onlays, and veneers
Single-unit anterior & posterior crowns
Short-span anterior fixed prostheses
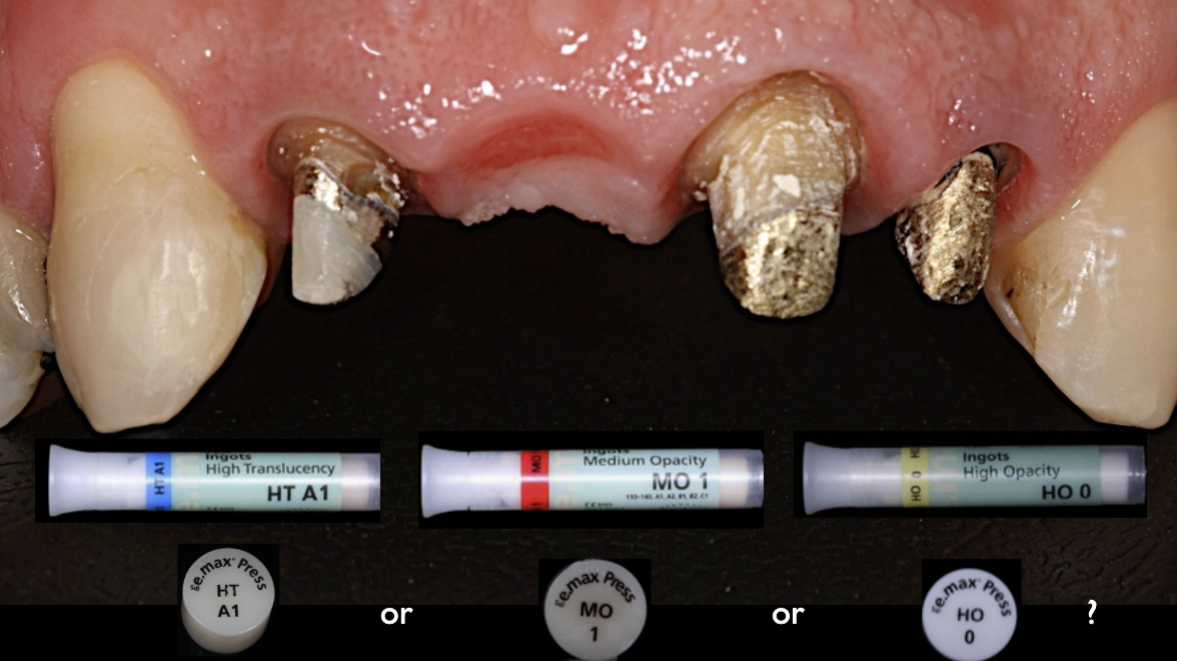
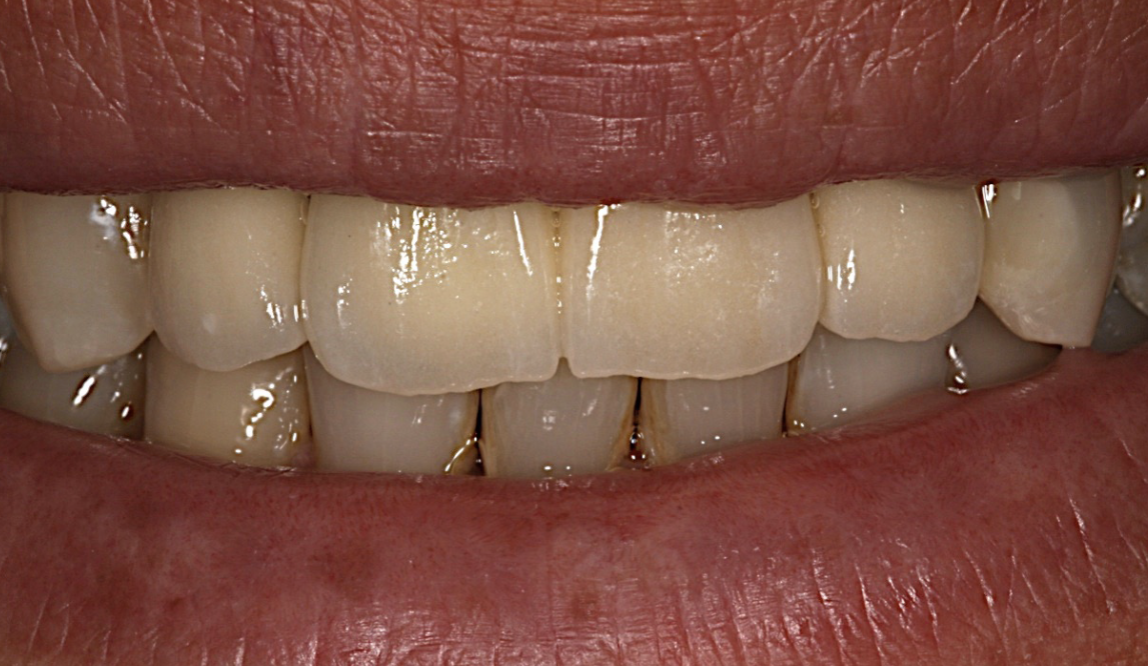
Lithium disciliate-based ceramic
Alumina-Based Slip-Cast Ceramic
Indication: Singe-units and anterior short-span fixed partial prostheses
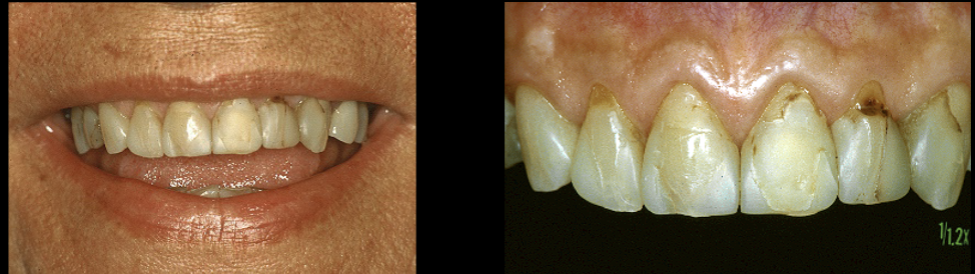
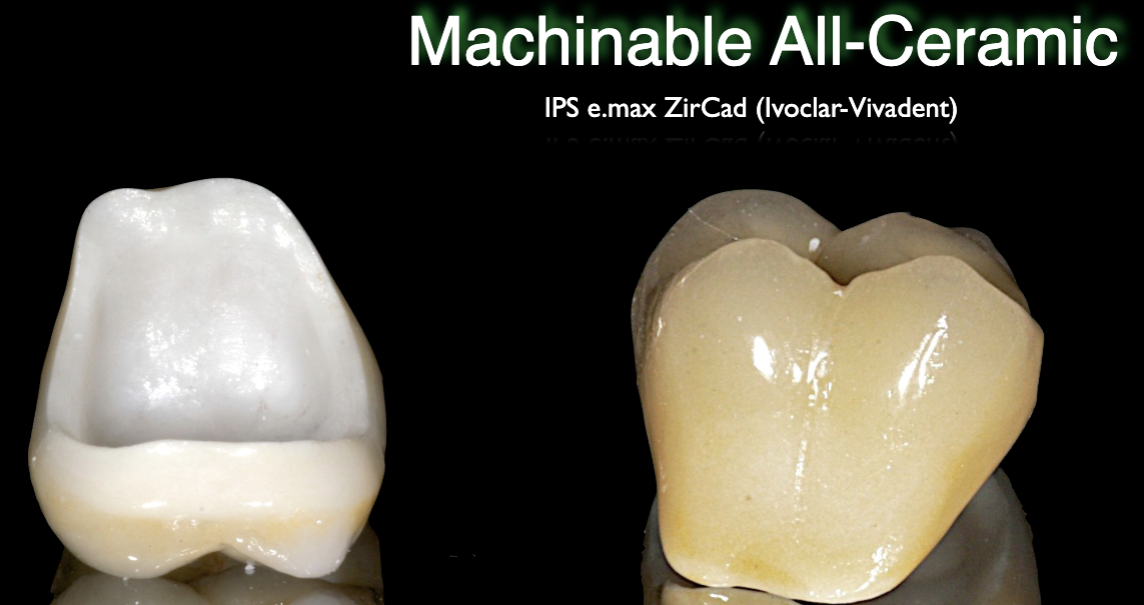
Machinable All-Ceramics
For veneers, inlays, onlays, crowns, fixed partial prostheses
Using CAD/CAM technology (Computer Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufactured)
Produce resotrations in 1 office visit=possible
Preparation=optically scanned, designed & machined from ceramic block

How do all-ceramic restorations with the machine work
