Geographic Concepts and Terms
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of key vocabulary terms and their definitions relevant to geographic concepts and practices.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
absolute location
The exact location of a point on the Earth's surface, usually expressed in coordinates like latitude and longitude.
relative location
The location of a place or point in relation to other locations.
accessibility
A measure of how easily a destination can be reached from other locations.
aerial photography
The process of taking photographs of the ground from an elevated position, often used in mapping.
environmental determinism
The theory that the physical environment predisposes human social development.
longitude
The angular distance of a point east or west of the Prime Meridian.
meridian
A line of longitude that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole.
equator
An imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres at 0 degrees latitude.
field observation
The collection of data by observing the environment or a phenomenon in its natural setting.
map
A visual representation of an area, depicting various geographic features.
mental map
An individual's own internal representation of the world or a part of it.
scale
The relationship between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
scale of the data
Refers to the level of analysis in geographic data, whether it is local, regional, or global.
sense of place
The feelings and perceptions that people associate with a specific location.
built environment
Man-made surroundings that provide the setting for human activity.
cartography
The science and art of map-making.
cartographic scale
The ratio between the dimensions of a map and the actual dimensions of the area it represents.
concentration
The spread of a phenomenon over a given area.
fieldwork
The process of collecting data or conducting research outside of a laboratory or office.
formal region
An area defined by official boundaries or marked by homogeneity.
uniform region
A region defined by common characteristics.
region
An area defined by certain unifying characteristics.
patterns
The regular arrangements or formations observed in geographic data.
physical geography
The branch of geography dealing with natural features and processes.
place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by particular characteristics.
site
The physical characteristics of a location.
situation
The location of a place relative to its surroundings.
spatial approach
An emphasis on the arrangements of phenomena across the surface of the Earth.
friction of distance
The concept that distance can create barriers to interaction and movement.
possibilism
The theory that the environment sets limits on human actions but people can adapt.
spatial association
The degree to which two or more phenomena share similar distributions.
connectivity
The relationships among people and objects across the barrier of space.
functional region
A region defined by a focal point and the surrounding area affected by it.
nodal region
A type of functional region characterized by a central node.
Prime Meridian
The meridian at 0 degrees longitude, serving as a reference point for longitude.
spatial interaction
The movement of people, goods, and ideas between different locations.
cultural ecology
The study of how cultural beliefs and practices shape and are shaped by the environment.
geographic scale
The scale at which geographical data is analyzed, such as local, regional, or global.
processes
The series of actions, changes, or functions that occur in a given system.
spatial data
Data related to physical locations and geometric information.
cultural landscape
The visible imprint of human activity on the landscape.
GIS
Geographic Information System, a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing spatial and geographic data.
projection
The method of representing the curved surface of the Earth on a flat surface.
density
The amount of a certain feature in a given area.
GPS
Global Positioning System, a satellite-based system that provides location and time information.
proximity
The nearness or closeness of a location to other locations.
diffusion
The process by which a characteristic spreads across space from one place to another.
human geography
The study of human activity and its relationship to the cultural and physical environments.
qualitative data
Descriptive, non-numerical information that provides insights into the characteristics, qualities, and experiences of places and people.
distance
The amount of space between two points.
human-environment interaction
The ways in which humans adapt to and modify their environment.
quantitative data
Numerical information that can be easily transformed into statistics and tends to be more objective.
interaction
The contact or influence between two or more entities.
distance-decay
The diminishing importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin.
reference maps
Maps that show the location of the geographic areas for which statistical data are being presented.
distortion
The alteration of the original shape or size of an area on a map.
distribution
The arrangement of a feature in space.
International Date Line
An imaginary line that runs from the North to the South Pole and defines the boundary between one day and the next.
toponym
The name given to a place or geographic feature.
landscape analysis
The study of the characteristics and features of a particular landscape.
regionalization
The process of dividing an area into smaller regions for study.
subregions
A smaller region within a larger region.
sustainability
The ability to maintain healthy environmental, economic, and social systems in balance over time.
thematic maps
Maps that depict specific themes or subjects using data represented geographically.
time-space compression
The reduction in time it takes for an idea or product to travel from one place to another.
topographic maps
Maps that use contour lines to show elevation changes in the landscape.
vernacular region
A region that is defined by the informal perceptions and identities of its inhabitants.
elevation
The height above sea level.
latitude
The angular distance north or south of the equator.
parallel
A line of latitude running parallel to the equator.
remote sensing
The acquisition of information about an object or area from a distance, typically via satellite.
location
A specific place or position.
reference map
A map that focuses on the location of various features in a given area.
cartogram
A type of map in which statistical data is shown in diagrammatic form.
isolines
Lines on a map that connect points of equal value, such as elevation.
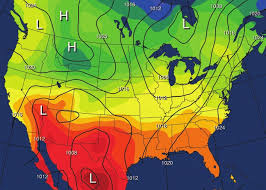
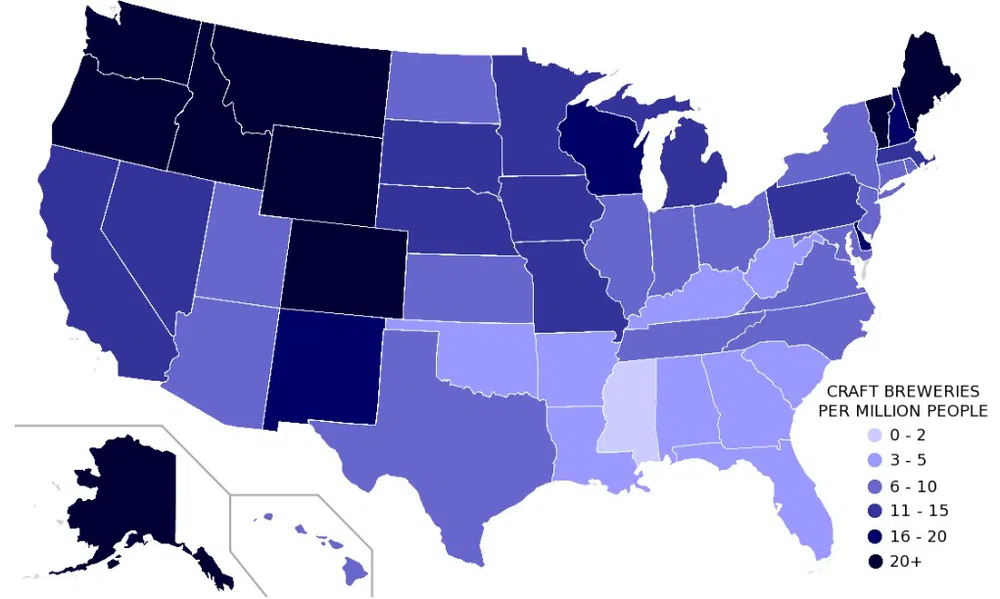
choropleth map
A thematic map where areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the value of a variable.
graduated symbol map
A thematic map that uses symbols of different sizes to represent data values.