Topic 4&5 - Reversible reactions, equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is a reversible reaction?
Reactions where the products react to form reactants.
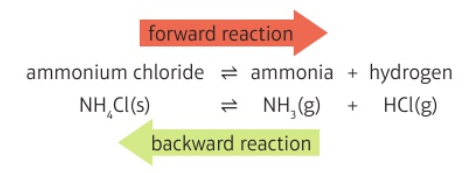
This is an example of a reversible reaction
What is the symbol used in reversible reactions?
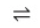
Give 3 common reversible reactions
heating hydrated copper sulphate
heating ammonium chloride
making ammonia
What are the word and symbol equations for the reaction of heating hydrated copper sulphate?
hydrated copper sulphate →←anhydrous copper sulphate + water

hydrated meaning
water of crystallisation present
anhydrous meaning
containing no water
What are the word and symbol equations for the reaction of heating ammonium chloride?
NH4Cl (s) →← NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
Ammonium chloride →← ammonia + hydrogen chloride
What is observed to form in the heating of ammonium chloride?
a white solid (NH4Cl) because it is a reversible reaction the condenses very quickly
What are the word and symbol equations for the reaction of making ammonia?
nitrogen + hydrogen →← ammonia
N2 + 3H2 →← 2NH3
What is the difference between ammonium and ammonia?
Ammonia is NH3 (a compound)
Ammonium is NH4+ (a cation derived from ammonia)
What state is ammonia at room temp?
gas
What are the features of a reaction at dynamic equilibrium?
Rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction
Concentrations of reactants and products remain unchanged
The reaction must take place in a closed system
dynamic means that the reaction is still continuing, they are still reacting
What are the factors which affect the position of equilibrium?
Changing the temp
Changing the pressure (when the reaction involves gases)
Changing the concentration of reactants or products
What effect does altering certain factor generally have on the position of equilibrium?
It causes equilibrium to shift until equilibrium is re-established
What was the purpose of Le Chatelier’s Principle?
to allow us to make predictions about which way the equilibrium reaction will shift when we change the conditions.
It tells us that equilibrium will shift to the side that will counteract the changes (such as in temp/ pressure/ concentration), and then restores equilibrium
Explain the effect of temperature of the position of equilibrium
Increasing the temperature will cause the equilibrium to shift to the side which will make the temperature decrease
The side which will make the temp decrease is the direction which is endothermic
Finish the sentences:
1.increasing the temperature shifts equilibrium to the …….. direction
2.decreases the temperature shifts equilibrium to the …….. direction
1.endothermic
2.exothermic

For the following reaction explain how an increase in temp will affect the position of equilibrium
Equilibrium will shifts to the reactants
because the reverse reaction is endothermic
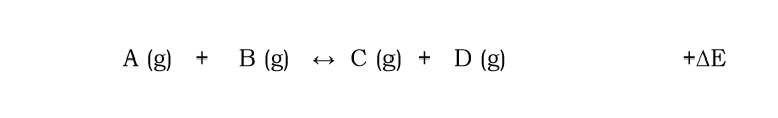
For the following reaction explain how an decrease in temp will affect the position of equilibrium
equilibrium will shift to reactants
because the reverse reaction is exothermic
What affect does pressure have on the position of equilibrium?
the greater the frequency of the collisions. or the greater the energy of the collisions, then the greater the pressure.
What will happen to the position of equilibrium generally if the pressure increases?
equilibrium will shift to the side that will make the pressure decrease
The more particles in the same volume the (greater/ lesser) the pressure
greater
What affect does increasing the pressure have on the position of equilibrium?
equilibrium shifts to the side with the least moles of gas
What affect does decreasing the pressure have on the position of equilibrium?
equilibrium shifts to the side with the most moles of a gas

Explain how decreasing the pressure of the reaction above would affect the position of equilibrium
equilibrium will shift to the products
because the products have the more moles of a gas
What can pressure be changed by ?
changing the volume of the container
What affect will decreasing the volume of a container have on the pressure?
it will increase the pressure
What affect will increasing the volume of a container have on the pressure?
It will decrease the pressure
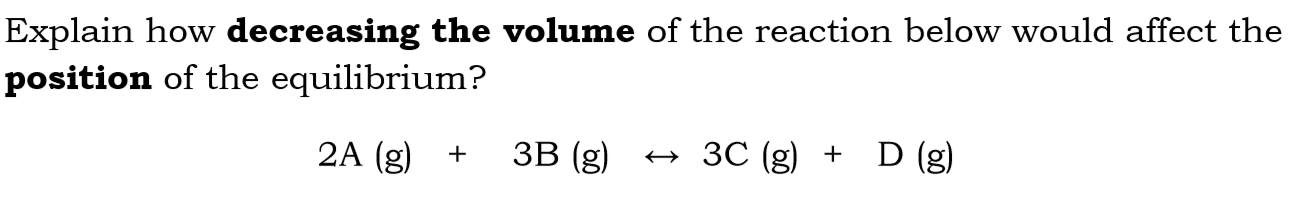
Explain how decreasing the volume of the reaction below would affect the position of equilibrium
decreasing the volume will increase the pressure
so equilibrium will shift to the products
because there are less moles of a gas in the products
What affect does concentration generally have on the position of equilibrium?
If you increase the concentration of a reactant or product at equilibrium, the reaction will shift to the opposite side (from which it was added)
What affect does concentration generally have on the position of equilibrium?
If you remove a reactant or product from a reaction at equilibrium, (decreasing the concentration), the reaction will shift towards the side from which it was removed, to try to increase its concentration again, until equilibrium is re-established
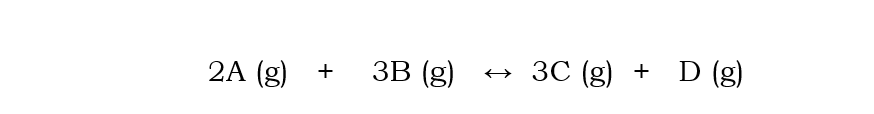
What would happen to the position of equilibrium if A is added to the reaction below?
equilibrium shifts to the products
to decrease the concentration of A
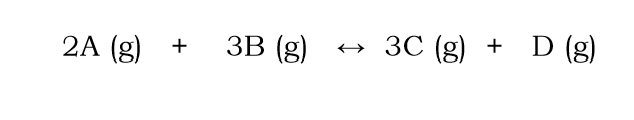
Explain what would happen to the position of equilibrium if B is removed from the following reaction
equilibrium shifts to the reactants
to increase the concentration of B
here is something else to be aware of

Question may also ask you to observe what you might see if you change certain concentrations.
How should you respond to these questions?
In response to these questions you should state what happens to the colour:
if the change made shifts equilibrium to the side with the coloured substance then the colour would darken.
if the change shifts equilibrium to the other side the colour would fade
What affect does adding a catalyse have on the position of equilibrium?
It has no affect on the position of equilibrium
What is a catalyst?
a substance which:
increases the rate of the forward and reverse reactions equally/ by the same amount
by providing an alternative reaction pathway
so more particles have energy bigger than or equal to the activation energy
catalysts only affect THE RATE OF THE REACTION AND NOT THE POSITION OF EQUALIBRIUM