Psychology 101 H01 Exam 2
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
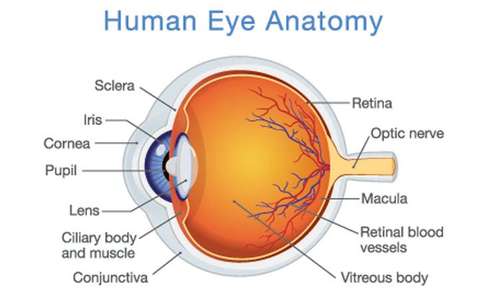
Retina
Light-sensitive layer with photoreceptors and neural circuitry; starts visual processing.
Hypnosis—dissociation theory
state where consciousness is divided into different streams, allowing for heightened suggestibility in one stream while another stream remains aware; actions outside conscious control (“hidden observer”).
Withdrawal
Opposing symptoms on stopping; reflects physiological adaptation.
Acquisition (classical)
CS–US pairing strengthens CS→CR; best when CS slightly precedes US. (ex: pavlov dog bell ringing (CS) leading to salivation (CR) when food (US) is presented.)
Extinction (classical)
(classical conditioning) conditioned response (CR) weakens when conditioned stimulus (CS) is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus (US), breaking down the association btw CS and US