Honors Biology - Chapter 3 (Proteins and Nucleic Acids)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Functions of Proteins
Structural (hair, tendons, ligaments); contractile (muscle); defensive (antibodies); signaling (hormones); receptor (in cell membranes); transport (hemoglobin); storage; enzymatic (shape matters)
polypeptide vs. protein
Protein: used to refer to a molecule w/ its appropriate 3D shape (when functional)
Polypeptide (peptide): used when referring to a polymer w/ out a 3D shape
Made of Amino Acids
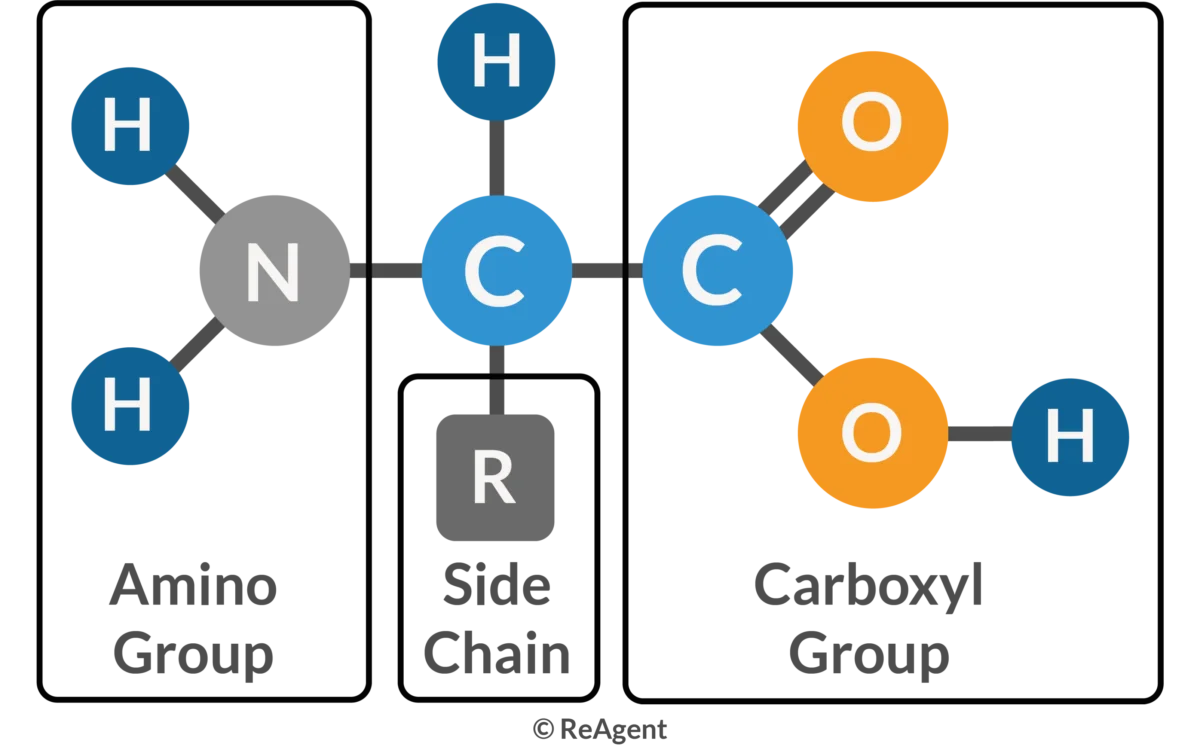
Amino Acid
Amino Acids Have Four Parts
Hydrogen w/ central carbon
Amino Group (NH2)
Carboxyl Group
R-group (variable side chain)
20 different types of R-groups/amino acids
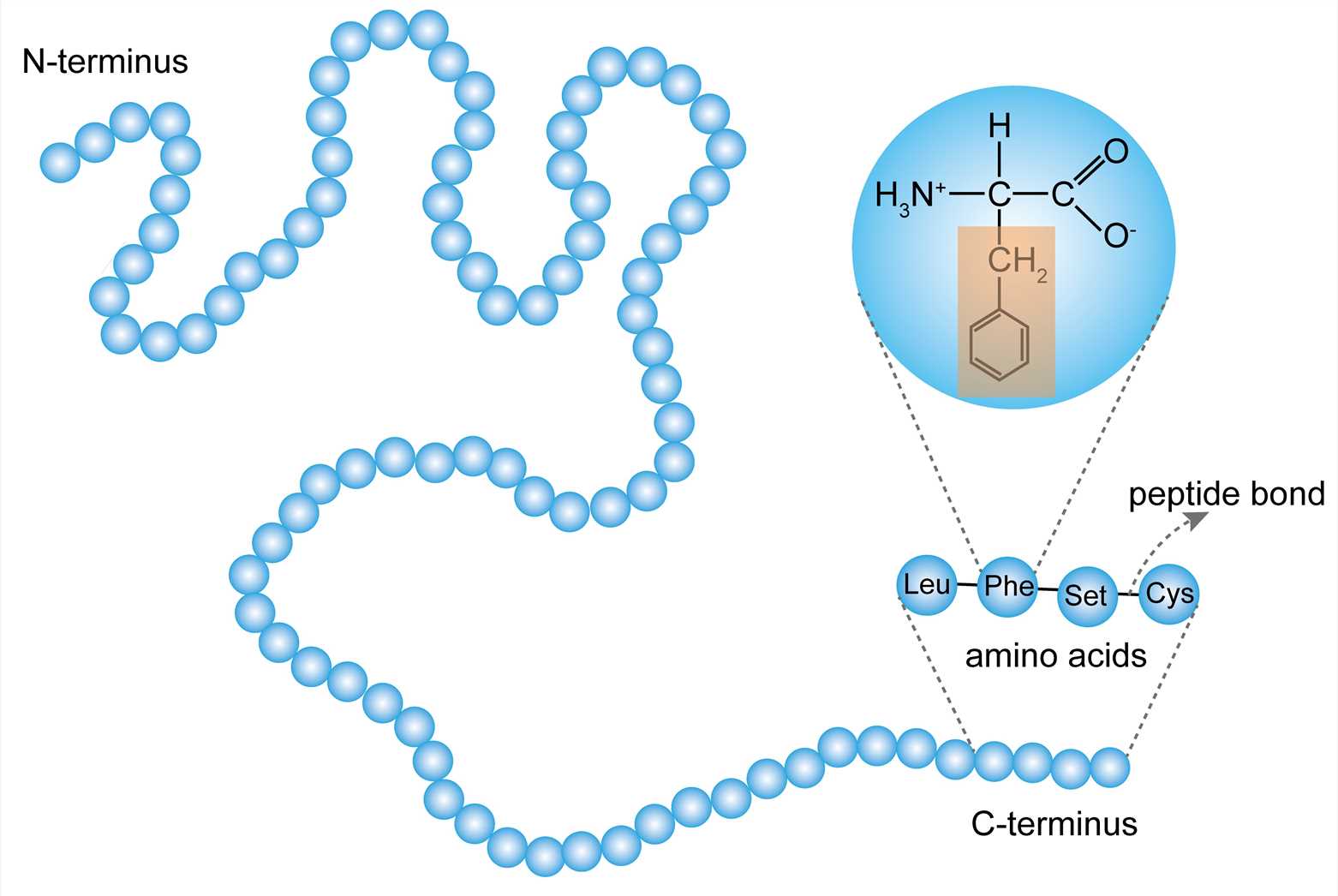
Peptide Bond
Amino acids join with a dehydration synthesis reaction, and the bonds between them are called peptide bonds (between functional groups).
A dipeptide is when two amino acids join together
A polypeptide is formed when multiple amino acids join together
R - Group Types
Electically Charged (ionized), Polar Uncharged, Hydrophobic (Nonpolar), Special Cases (small)
Primary Structure (1º)
Peptide bonds with N-C are a long chain of amino acids that help to determine the overall structure of the protein, which determines the function (animal digestion, starch vs. cellulose)
Secondary Structure (2º)
Two types: alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
held together by hydrogen bonds between functional groups
Tertiary Structure (3º)
held together by interactions between r-groups
Fully folded molecule given function by shape (some need multiple)
H-bonds help to stabilize the structure once it is made, with available H and NOF
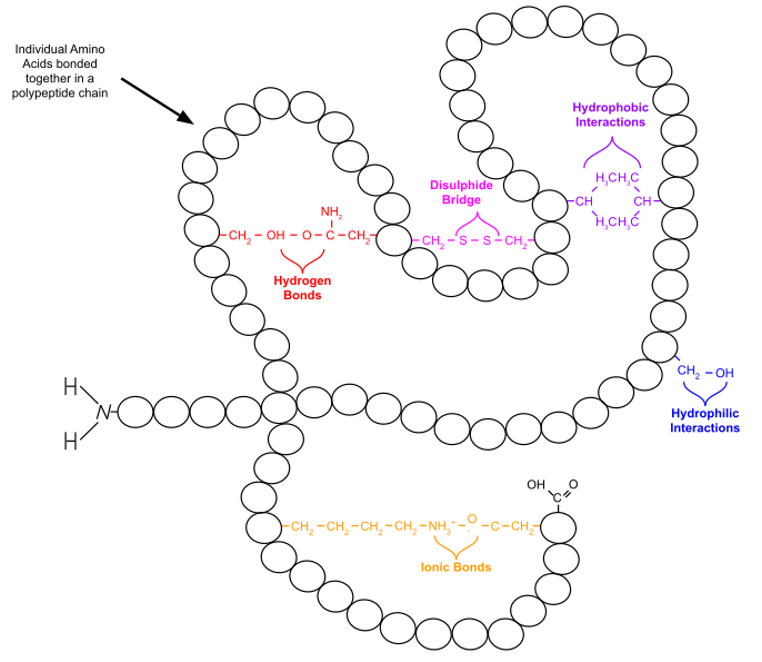
Tertiary Structure Interactions
Type of Bond | Description |
Hydrophobic Interactions | Amino acids orient toward the center to avoid water |
Hydrophilic Interactions | Form between polar R-groups (outside of molecule). Polar covalent with partial charges. |
Disulphide Bridge | Charged R groups bond together |
Ionic Bonds | Form between oppositely R – groups. |
Quarternary Structure (4º)
When a functional protein is made of multiple polypetides.
Each polypetide forms a protein subunit w/ structure but no function, only when together do they have function.
Ex. ribosome
Linked by IMFs (interaction between R- groups)
Denaturation (defenition and types)
loss of 3D structure, which results in a loss of function
Increase in temperature
Higher KE = more motion of molecules disrupting IMFS
Change in salt concentration
salt = ionic compound
add (+) and (-) ions to the solution, causing the ions in the protein to be pulled away b/c more attracted to the new ions
Change in pH
Similar to the change in salt concentration as H+ when acidic and OH- when basic, attract the negative and positive parts of the protein, respectively