Chapter 4 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
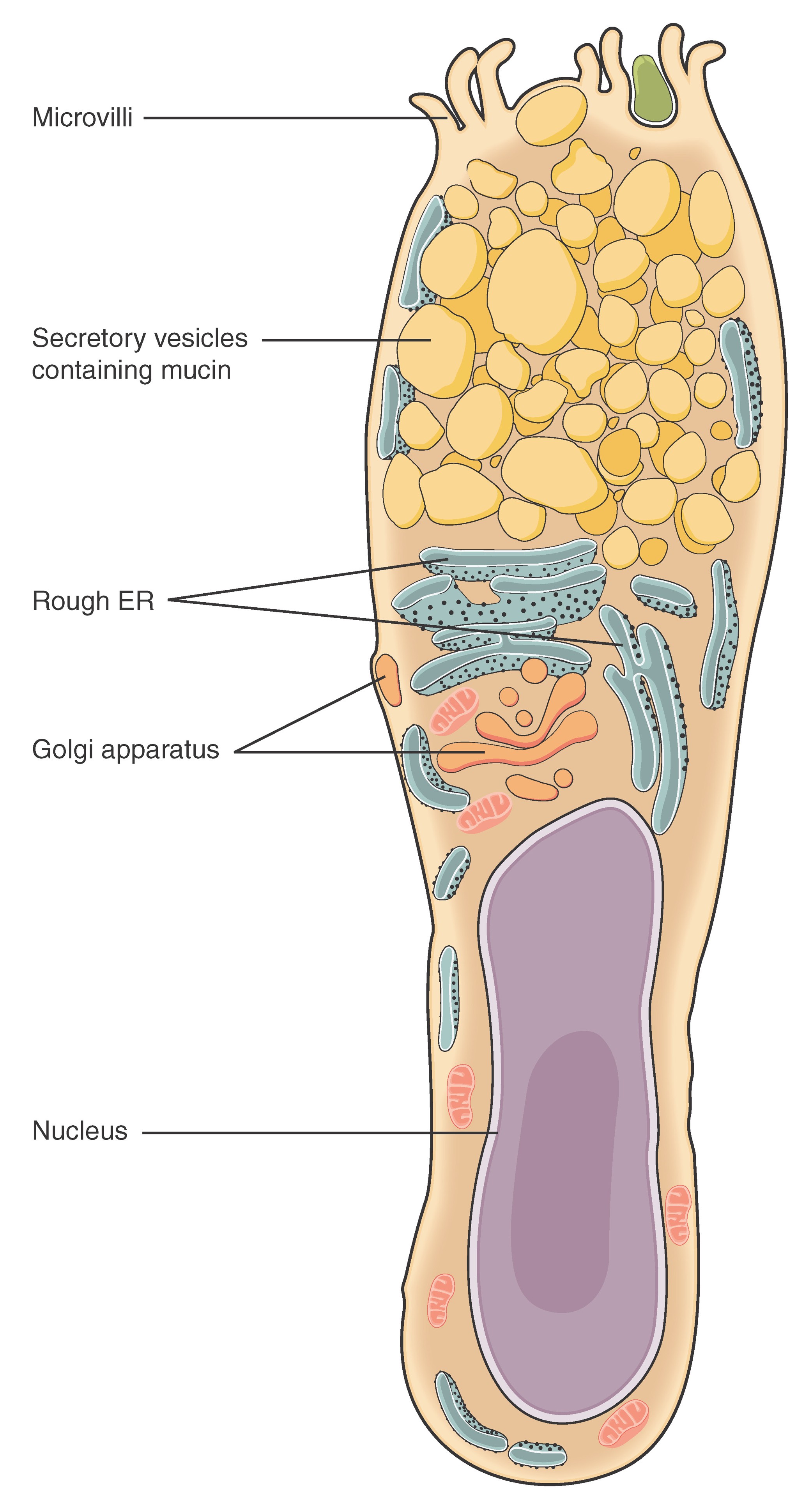
goblet cell
are specialized epithelial cells that produce and secrete mucus. They are found lining many internal surfaces of the body, such as the intestinal and respiratory tracts, where their mucus helps protect and lubricate the lining surfaces.
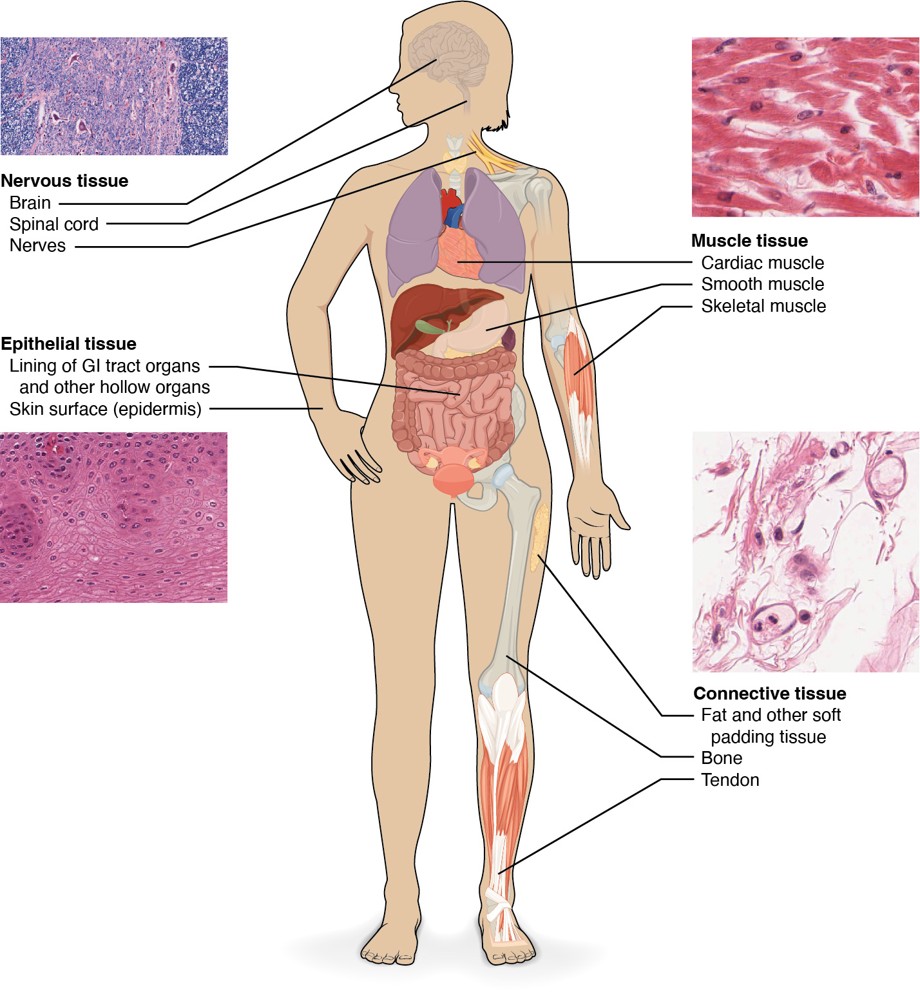
nervous tissue
is responsible for transmitting and processing information in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It includes neurons and supporting cells that help in signal transmission.
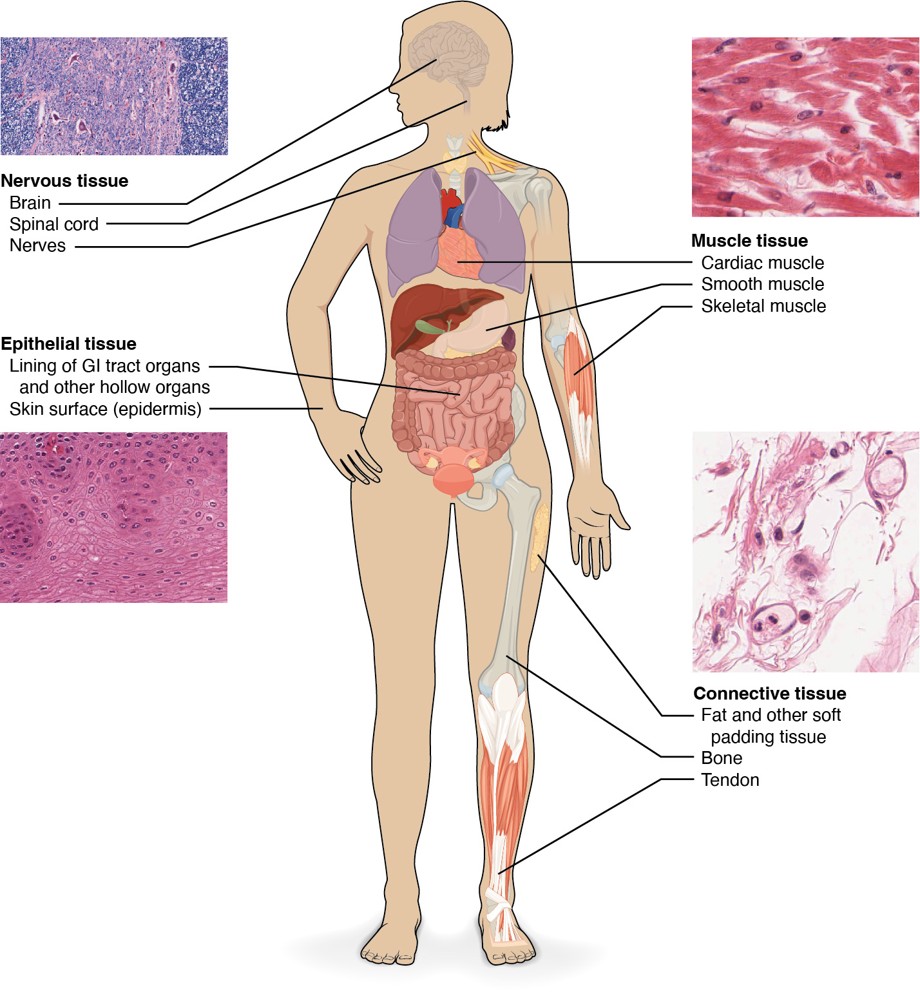
Epithelial Tissue
forms the lining of the GI tract organs and other hollow organs, as well as the skin surface (epidermis). It serves as a protective barrier and is involved in absorption, secretion, and sensation.
muscle tissue
includes three types: cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart, smooth muscle lines organs like the stomach and intestines, and skeletal muscle is connected to bones for movement.
connective tissue
supports, binds together, and protects tissues. Types include bone, tendon, fat, and other soft padding tissues that provide structure and metabolic support.
3 types: connective proper, fluid connective, supporting connective
Specific Type: Simple Squamous Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Air sacs of lungs, lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Function: Facilitates diffusion and filtration; secretes lubricating substances
Specialized Structure: Thin and flat cells to allow for easy passage of substances
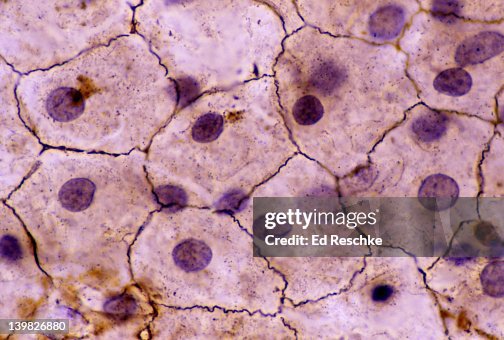
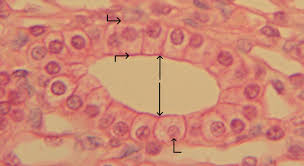
Specific Type: Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Ducts and portions of small glands, thyroid gland, and kidney tubules
Function: Secretion and absorption
Specialized Structure: Cube-shaped cells optimal for secretion and absorption functions
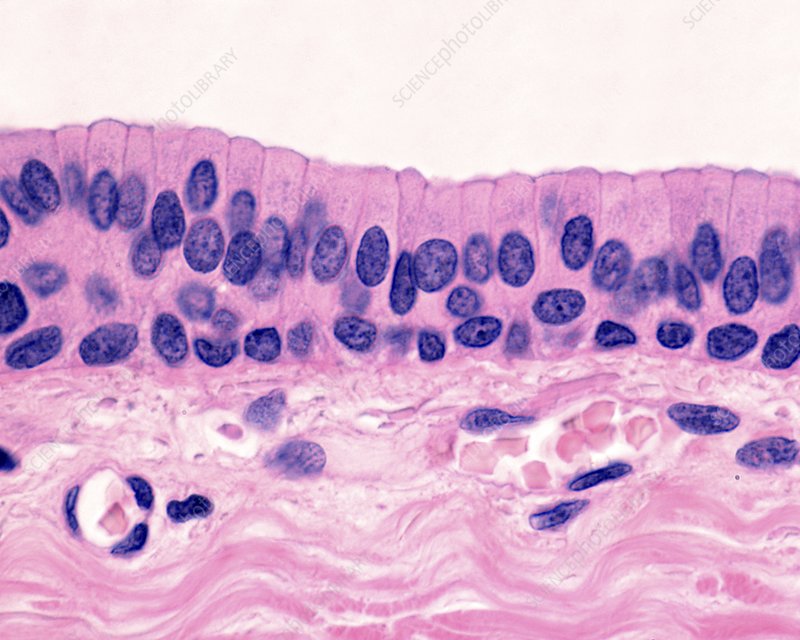
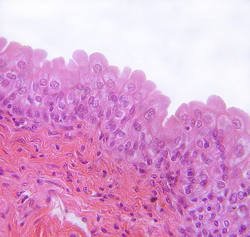
Specific Type: Simple Columnar Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Ciliated tissues in bronchioles, uterine tubes, and uterus; smooth (nonciliated) tissues in the digestive tract and bladder
Function: Absorption; secretion of mucus and enzymes
Specialized Structure: Tall, column-like cells; may feature cilia or microvilli
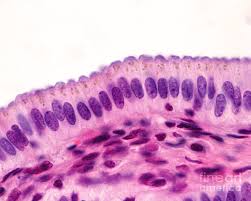
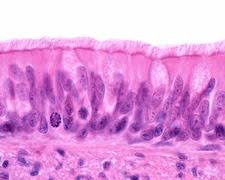
Specific Type: Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Lines the bronchi, trachea, and upper respiratory tract
Function: Secretes mucus; ciliated variety moves mucus
Specialized Structure: Cells vary in height and appear stratified but are not; often ciliated
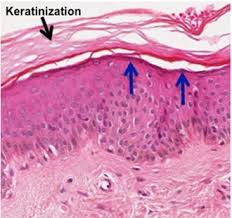
Specific Type: Stratified Squamous Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Esophagus, mouth, and vagina
Function: Protects against abrasion
Specialized Structure: Multiple layers of cells with the outermost being flat and keratinized in skin
Specific Type: Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands
Function: Protective tissue
Specialized Structure: Typically two layers of cube-shaped cells
Specific Type: Stratified Columnar Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Male and female urethra and the ducts of some glands
Function: Secretes and protects
Specialized Structure: Top layer of elongated cells over a base of shorter cells
Specific Type: Transitional Epithelium
General Type: Epithelial Tissue
Location: Lines the bladder, urethra, and the ureters
Function: Allows urinary organs to expand and stretch
Specialized Structure: Cells can change shape depending on the degree of stretch
basement membrane
Connective tissue that anchors epithelial cells, regulating molecule passage and guiding cell behavior.
apical
is the uppermost layer of an epithelial cell that faces the lumen or external environment, often specialized with structures like cilia or microvilli.
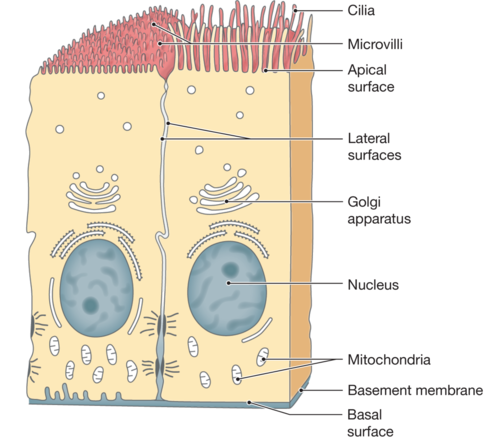
basal
refers to the bottom layer of epithelial cells that is attached to the basement membrane, anchoring the cells to underlying connective tissue.
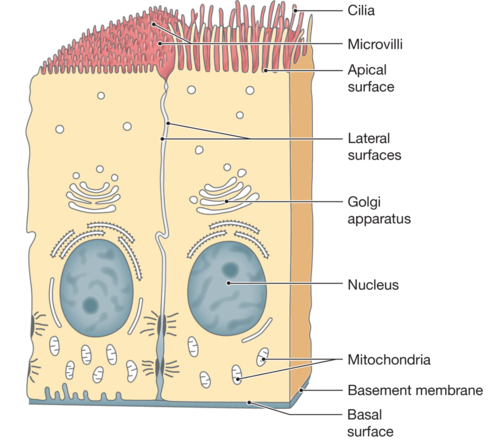
cilia
are microscopic, hair-like structures on the surface of cells that move rhythmically to propel substances across the cell surface, commonly found in respiratory and reproductive tracts.
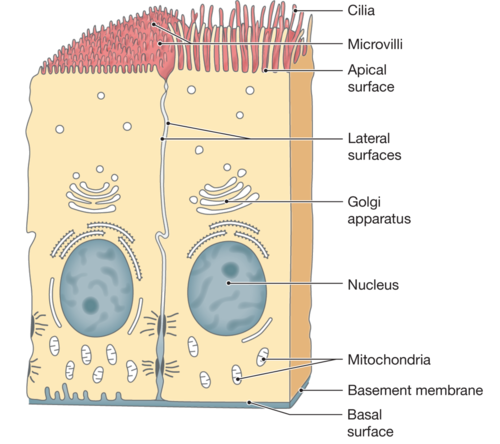
microvilli
are tiny, finger-like projections on the apical surface of epithelial cells that increase surface area for absorption, especially prominent in the intestines.
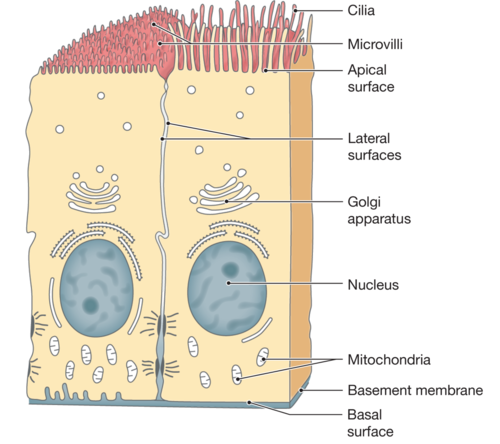
meocrine
secretion involves the release of substances from glands via exocytosis without losing any part of the cell itself, typical in sweat glands.
apocrine
secretion occurs when the upper part of the cell pinches off to release its contents, partially destroying the cell which then repairs itself, seen in mammary glands.
holocrine
secretion is when the entire glandular cell disintegrates to release its product, leading to cell death, as seen in sebaceous glands.
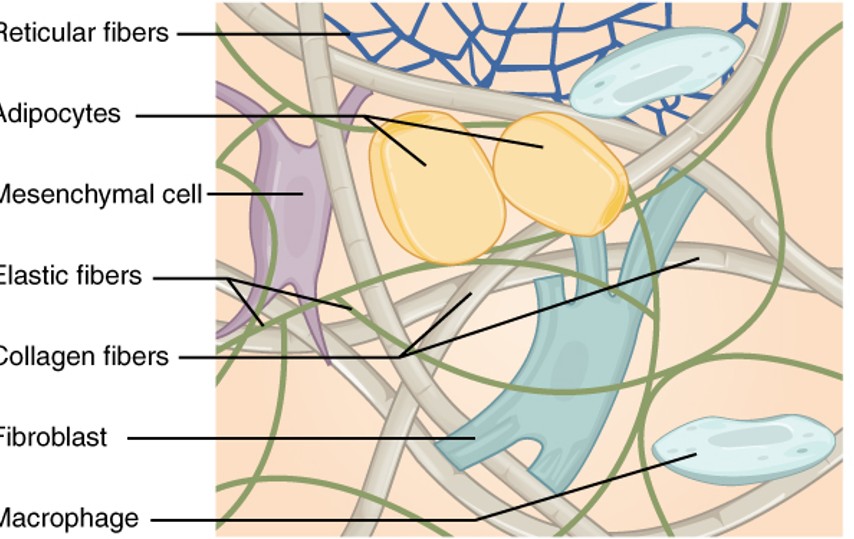
Reticular Fibers
are a type of fiber in connective tissue made from type III collagen. They form a soft, supportive mesh that structures the lymphatic tissues and bone marrow.
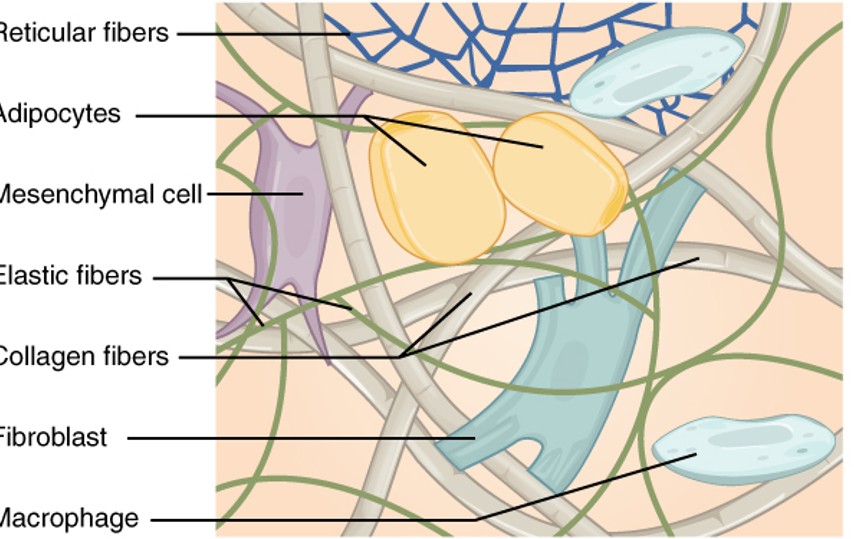
Adipocytes
also known as fat cells, are cells that specialize in storing energy as fat. They are found throughout the body, particularly in adipose tissue
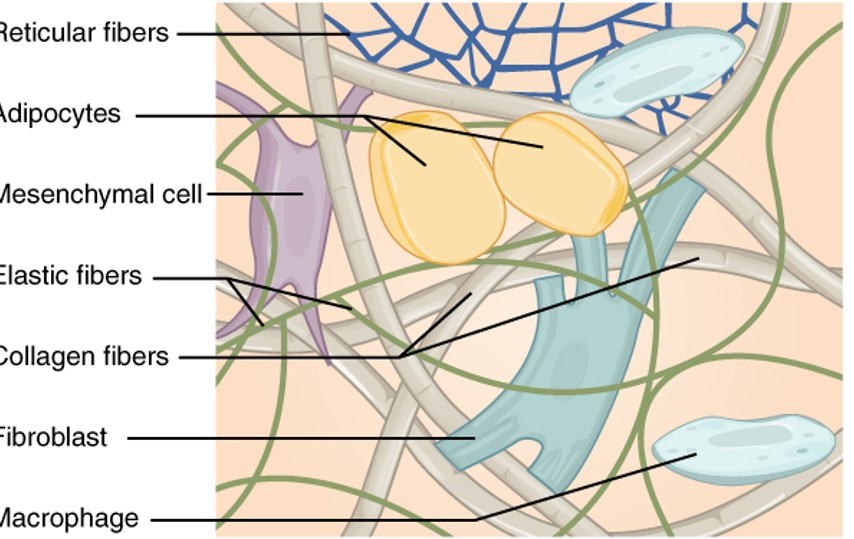
Mesenchymal Cell
are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes, among others.
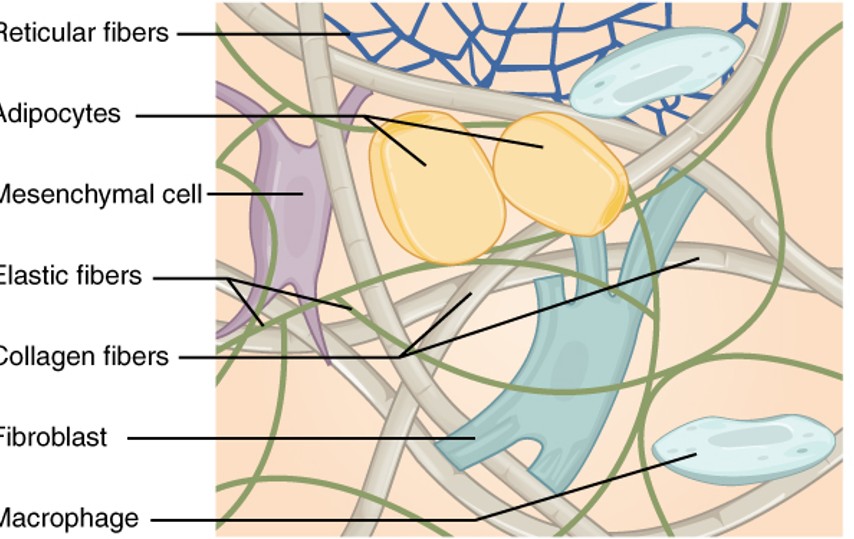
Elastic Fibers
are components of the extracellular matrix in connective tissue that provide elasticity and flexibility. They are primarily composed of elastin and fibrillin.
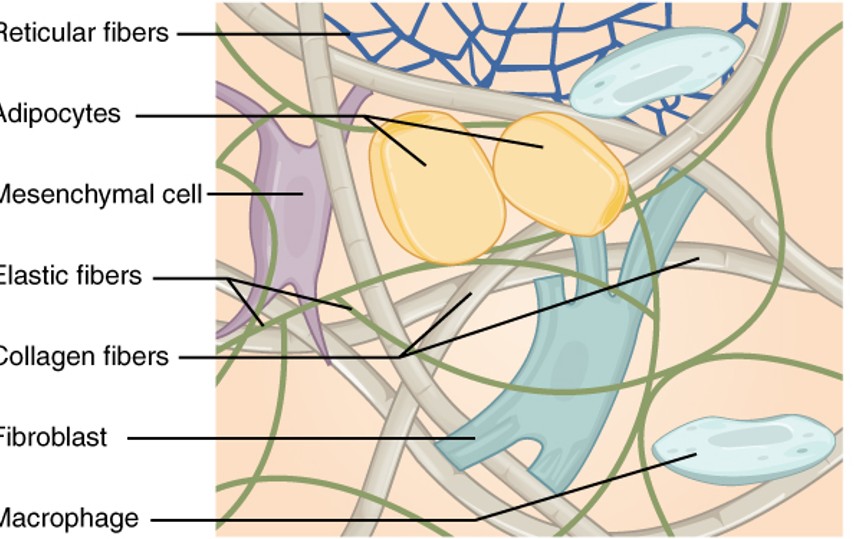
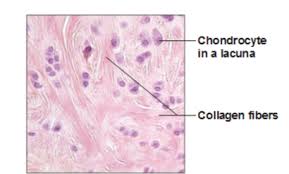
collagen fibers
are the main structural protein in the extracellular space in the various connective tissues in the body. They give tissue strength and resilience
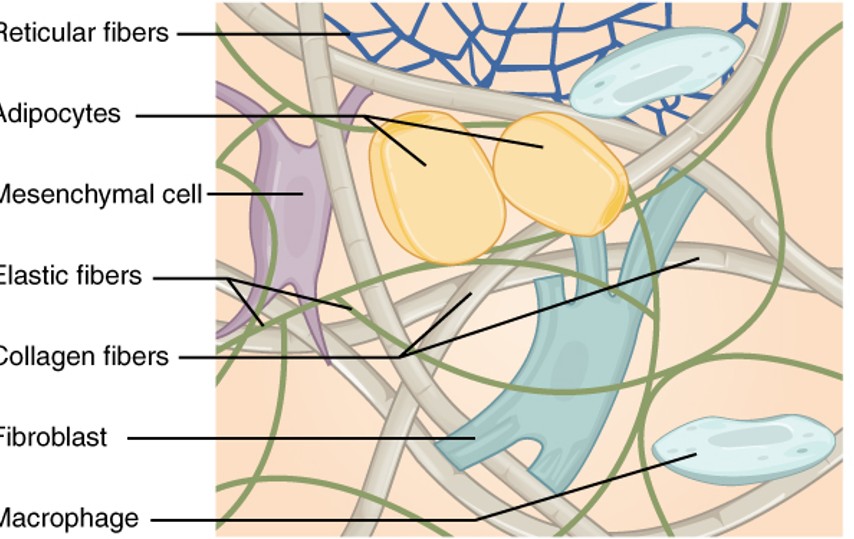
fibroblast
are the most common type of cells found in connective tissue, responsible for producing and maintaining the extracellular matrix and collagen.
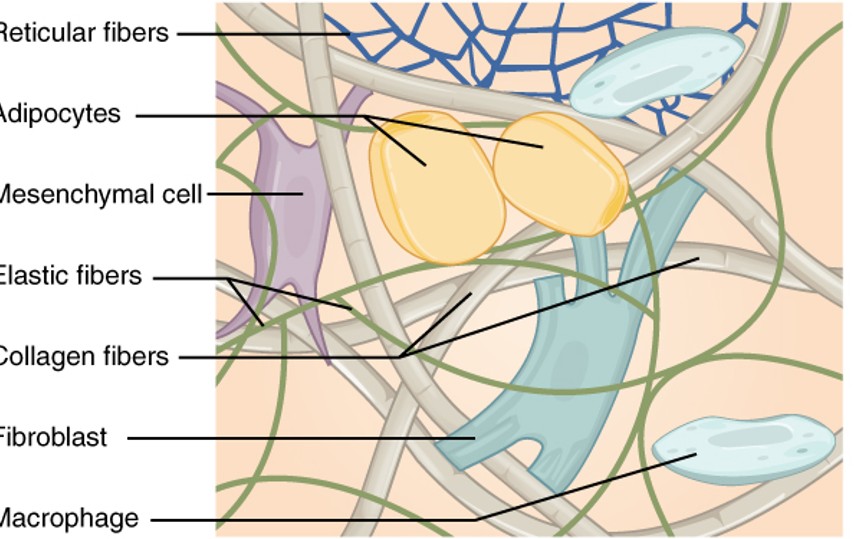
Macrophage
are a type of white blood cell that engulfs and digests cellular debris, foreign substances, microbes, and cancer cells in a process known as phagocytosis
connective tissue proper: loose
A soft, flexible tissue that holds organs in place and connects skin to underlying tissues.
connective tissue proper: dense
A tough tissue with lots of collagen fibers; helps connect muscles to bones and bones to each other.
fluid connective tissue: blood
A liquid tissue that carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste throughout the body.
fluid connective tissue: lymph
A fluid similar to blood plasma; helps fight infections and maintains body fluid levels.
Supporting Connective Tissue: Cartilage
A flexible, rubber-like tissue that cushions joints and makes up parts of the nose and ears.
Supporting Connective Tissue: bone
A hard tissue that supports and protects body parts; bones help move the body by providing attachment points for muscles.
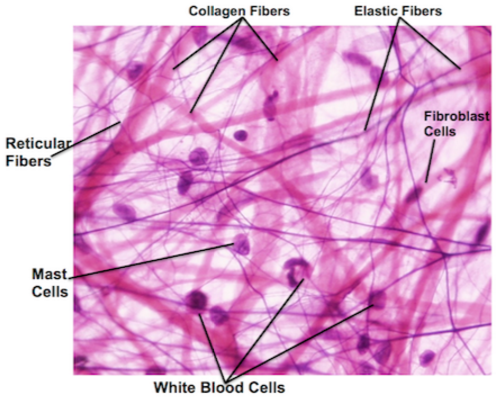
specific type: Areolar connective tissue
General: loose connective tissue.
Location: within and deep to the dermis of the skin, and covered by the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; between muscles; around blood vessels, nerves, and around joints
Function: Wraps and cushions organs; provides support but permits independent movement; phagocytic cells provide defense against pathogens
Specialized Structures: Contains fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells.
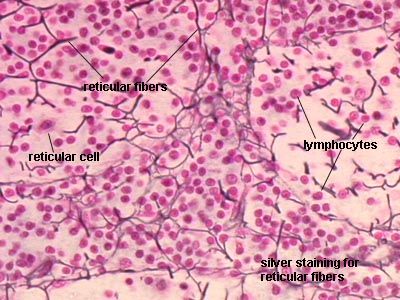
specific type: reticular tissue
General: Loose connective tissue.
Location: liver, lymph nodes kidney, bone marrow, and spleen
Function: Provides a framework that supports other cell types
Specialized Structures: Network of reticular fibers and cells.
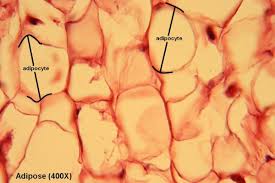
specific type: adipose tissue
General: Loose connective tissue.
Location: deep to skin, buttocks, breasts; padding around eyes and kidneys
Function: stores energy; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs.
Specialized Structures: Primarily composed of adipocytes that store fats.
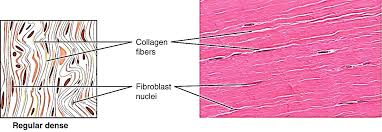
specific type: dense regular connective tissue
General: Dense connective tissue.
Location: between skeletal muscles and skeleton (tendons and aponeuroses) ; between bones or ligaments,
Function: Attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction.
Specialized Structures: Tightly packed parallel collagen fibers.
specific type: dense irregular connective tissue
General: Dense connective tissue.
Location: capsules of organs; dermis of the skin; periostea and perichondria, nerve and muscle sheaths
Function: Withstands tensions in many directions; provides structural strength
Specialized Structures: Randomly arranged collagen fibers.
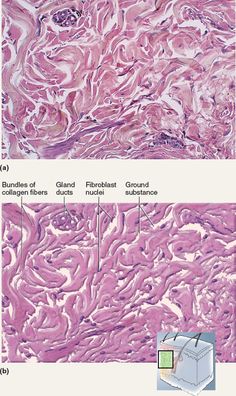
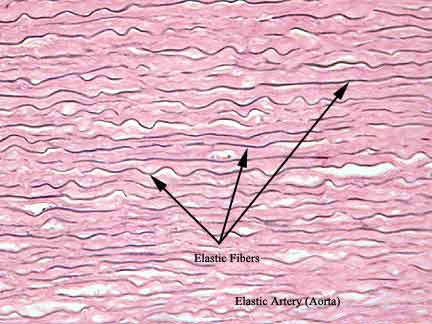
specific type: elastic tissue
General: Dense connective tissue.
Location: Walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with the vertebral column; ligaments supporting penis;
Function: stabilizes positions of vertebrae and penis; cushions shocks; permits expansion and contraction
Specialized Structures: High proportion of elastic fibers
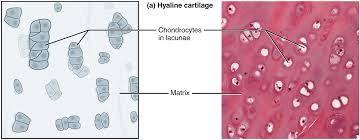
specific type: hyaline cartilage
General: Cartilage.
Location: between tips of ribs and bones of sternum; supporting larynx (voice box); trachea, and bronchi, part of nasal septum, fetal skeleton
Function: provides stiff but somewhat flexible support; reduces friction between bony surfaces
Specialized Structures: Matrix with imperceptibly fine collagen fibers
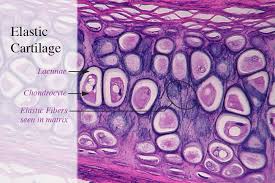
specific type: elastic cartilage
General: Cartilage.
Location: Supports the external ear and epiglottis; auditory canal, larynx
Function: Maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility.
Specialized Structures: Matrix with many elastic fibers.
specific type: fibrous cartilage
General: Cartilage.
Location: Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, pads of knee joint, minisucus.
Function: resist compression; prevents bone to bone contact; limits relative movement
Specialized Structures: Rows of chondrocytes with dense collagen fibers
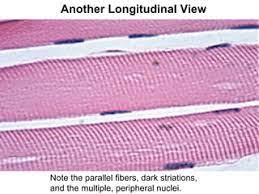
specific type: skeletal muscle tissue
General: Muscle tissue.
Location: combined with connective tissues and neural tissue in the skeletal muscles
Function: moves position of skeleton; guards entrances and exits to the to digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts; generates heat
Specialized Structures: Long cylindrical cells, striated, multinucleated
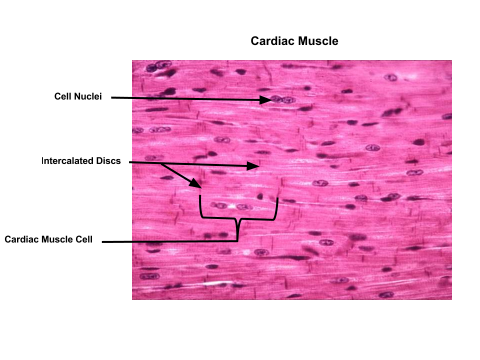
specific type: cardiac muscle tissue
General: Muscle tissue.
Location: Walls of the heart.
Function: circulates blood and maintains blood pressure; involuntary control.
Specialized Structures: Branching, striated, intercalated discs.
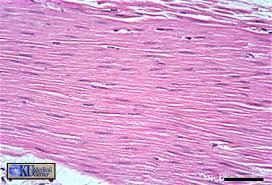
specific type: smooth muscle
General: Muscle tissue.
Location: Mostly in the walls of hollow organs and blood vescles
Function: Propels substances or objects (foods, urine, a baby) along internal passageways; involuntary control.
Specialized Structures: Spindle-shaped cells, no striations
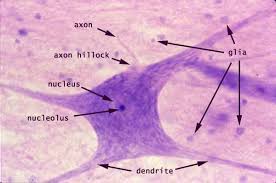
specific type: neural tissue
General: Tissue of the nervous system.
Location: Brain, spinal cord, nerves.
Function: Regulates and controls body functions.
Specialized Structures: Neurons with specialized features for rapid communication.
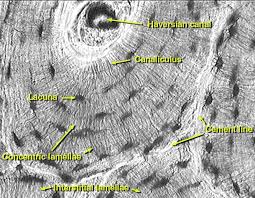
specific type: compact bone
General: Dense connective tissue.
Location: Outer layer of all bones and bulk of the diaphyses of long bones.
Function: Supports and protects; lever for muscles; stores calcium; houses bone marrow for blood cell production.
Specialized Structures: Contains osteons with central canals surrounded by concentric lamellae. Osteocytes within lacunae are connected by canaliculi
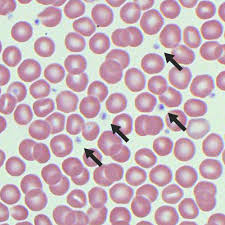
white blood cells
aka leukocytes, help defend the body from infection and disease
Never Eat Bananas Like Monkeys
neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil, lymphocytes, monocytes
platelet
aka thrombocytes, function in clotting response that seals leaks in damaged broken blood vesicles
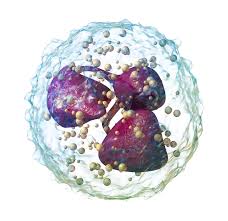
neutrophil
type of white blood cell. are phagocytes
eosinophils
type of white blood cell; is phagocyte
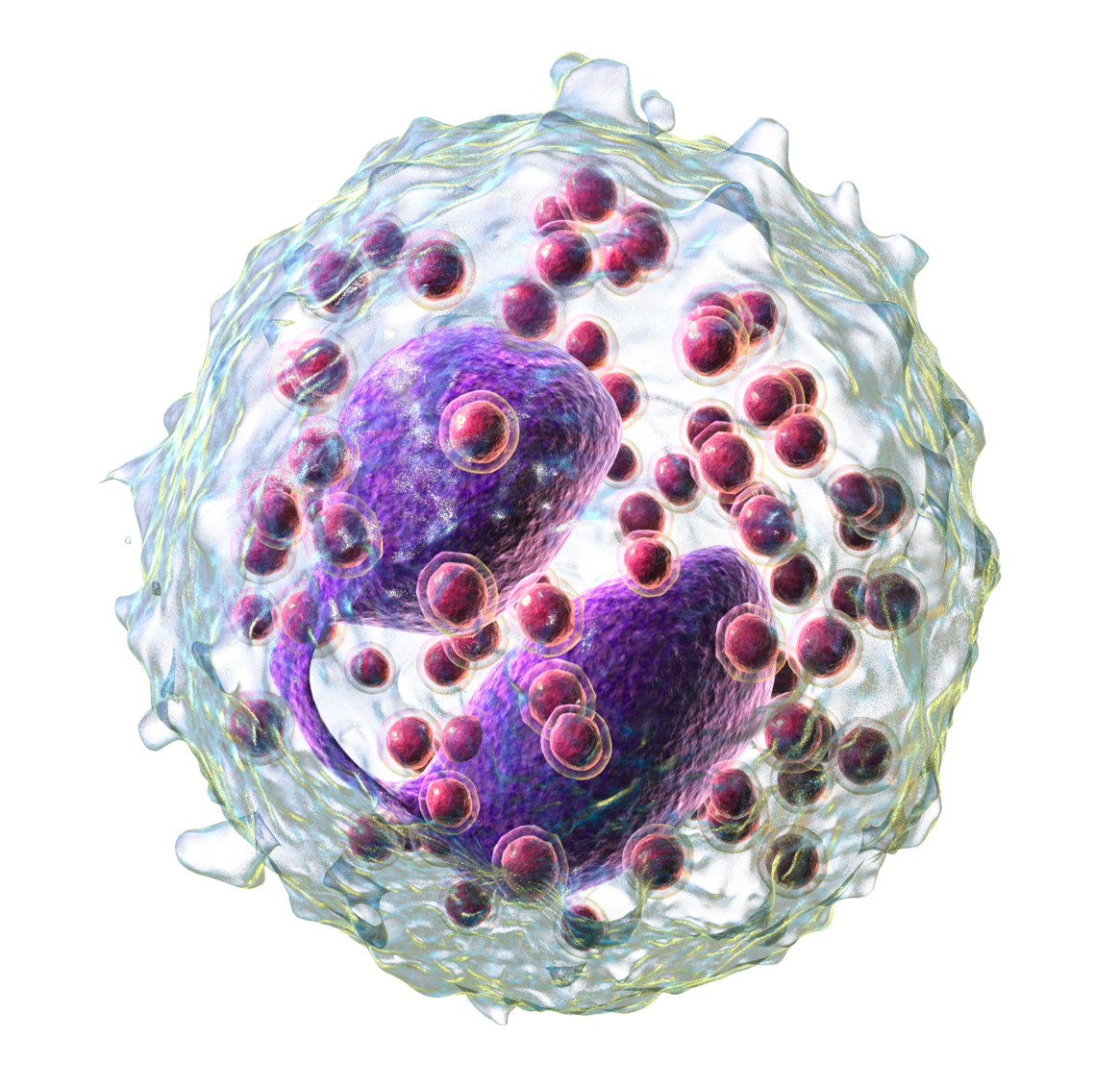
basophil
type of white blood cell; promote inflammation much like mast cells
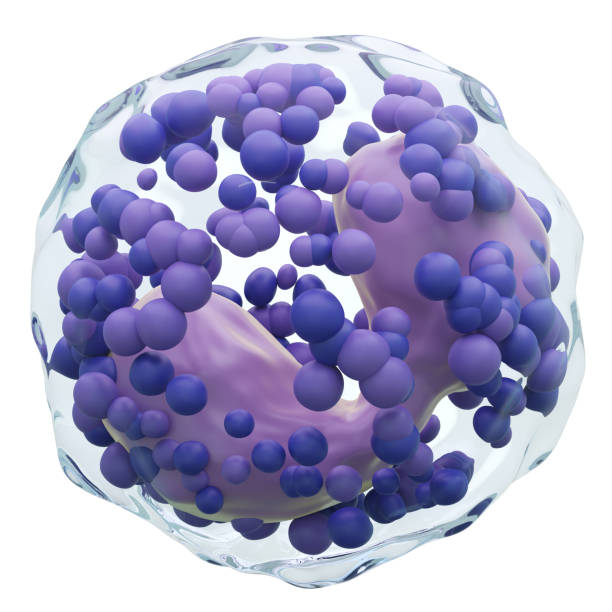
lymphocytes
type of white blood cell; relatively rare in blood but dominate in lymph
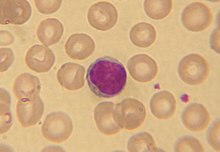
monocyte
type of white blood cell; related to free macrophages in other tissues
Chondrocyte
Mature cartilage cells that maintain the cartilage matrix.
Chondroblast
Cells that produce and secrete the extracellular matrix of cartilage, leading to its growth.
Chondroclast
Cells that break down and resorb cartilage matrix.