Exam I Acid Base Equilibrium
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
low
Is hydrogen ion concentration in body fluids usually very high or low?
weak
Are most body acids strong or weak? They exist mostly in an undissociated form with only a small amount of free hydrogen ions.
Volatile acids
acids produced from carbon dioxide which can be released via expiration
Nonvolatile acids
acids produced by the breakdown of proteins and phospholipids which can be excreted via urine.
sulfuric acid
proteins are released via this nonvolatile acid form in urine.
phosphoric acid
lipids are release via this nonvolatile acid form in urine.
Ketoacids
non-volatile acids produced in excess under abnormal conditions such as untreated diabetes where fats are used as an energy source
Lactic acid
a non-volatile acid produced in excess during very active exercise or ischemia.
Bicarbonate
HCO3-
a natural buffer of the human body that is produced when carbon dioxide is removed from the lungs, or when hydrogen ions are excreted in urine
Non bicarbonate buffer system
a buffering system of the human body resulting from the ability of various negatively charged molecules to bind free hydrogen ions. Ie) hemoglobin, organic phosphates, inorganic phosphates, plasma protein, excretion of H+ in urine, etc
excreting hydrogen ions
secreting bicarbonate buffer
the kindeys function in buffering pH by these two mechanisms.
exhaling carbon dioxide
the lungs function in buffering pH by this mechanism
Henderson-Hasselbach equation
equation used to calculate the capacity of a buffer to handle hydrogen ions relative to the concentration of dissociated ions and the dissociation constant of the acid.

bicarbonate
When using the Henderson-Hasselbach equation in relation to the body's natural buffer system, what serves as the anion/base?
dissolved carbon dioxide
When using the Henderson-Hasselbach equation in relation to the body's natural buffer system, what serves as the acid?
0.03
Because partial pressure of CO2 is reported as pressure and most CO2 in the blood is dissolved in water, the pressure must be converted to concentration by multiplying the solubility of CO2 in blood which is _____ mmol/L/mmHg, in order to be used in the Henderson/Hasselback equation.
Pulse ox machine
machine placed at the fingertip which will give the pulse rate as well as oxygen saturation. Sends infrared and red light through the finger. Oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs infrared light. The more infrared light absorbed, and not transmitted back to the machine, the higher the oxygen saturation of the blood. The red light is absorbed by deoxygenated hemoglobin.
4
what is the maximum number of oxygen molcules that can be carried by hemoglobin at a single moment?
measured
is blood pH a measured or calculate value?
measured
is partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood a measured or calculated value?
measured
is partial pressure of oxygen in the blood a measured or calculated value?
calculated (based on the partial pressure of carbon dioxide)
is the amount of bicarbonate in the blood a measured or calculated value?
calculated
is the oxygen content in the blood a measured or calculated value?
calculated
is oxygen saturation of the blood a measured or calculated value?
6.8 to 8.0
what is the range of blood pH which is compatible with life?
7.35
a patient is acidemic when their pH is below this value.
acidemic
having a measured blood pH below 7.35
Acidosis
blood pH which is trending gradually towards a pH lower than 7.35. Ie) a patient with diarrhea will excrete base, making their blood more acidic
7.45
a patient is alkalemic when their pH is above this value
Alkalosis
blood pH which is trending gradually towards a pH higher than 7.45. Ie) a patient with nausea/vomiting will excrete acid, making their blood more basic
carbon dioxide
Abnormal _____ levels during acidosis or alkylosis indicates a respiratory problem
bicarbonate
Abnormal _____ levels during acidosis or alkylosis indicates a metabolic (renal) problem
compensating
If pH remains normal while the respiratory or renal system has an abnormality, the normal system is _____ for the pH imbalance. This function is limited.
Respiratory acidosis
condition where respiration is compromised and not enough CO2 is being released (hypoventilation). PH shifts acidic, unless compensated by excretion of hydrogen and secretion of bicarbonate by the kidneys.
Respiratory alkalosis
condition where there is too much CO2 release (hyperventilation). PH shifts alkaline, unless compensated by reduction of hydrogen excretion and the retention of bicarbonate by the kidneys.
Metabolic acidosis
condition where kidney function is compromised. Not enough hydrogen ions are being excreted or not enough bicarbonate ions are being produced. PH shifts acidic, unless compensated by increased expiration of CO2 by the lungs
Metabolic alkalosis
condition where kidney function is compromised. Too many hydrogen ions are being excreted and too many bicarbonate ions are being produced. PH shifts towards alkali, unless compensated by decreased expiration of CO2 by the lungs.
lungs
are the lungs or kidneys faster at compensating for a pH change?
7.35-7.45
what is the range of normal blood pH?
35-45
what is the range of normal partial pressure of CO2 in the blood?
22-26
what is the range of normal bicarbonate levels in the blood?
acidemia
respiratory acidosis
metabolic acidosis
increased breathing (increased CO2 release)
uncompensated acidosis
What does the pH suggest?
________
What does the CO2 level suggest?
_________
What does the bicarbonate level suggest?
_________
How will the system respond?
_________
What is the diagnosis?
_________

borderline acidemia
respiratory acidosis
metabolic alkalosis
respiratory acidosis with incomplete metabolic compensation
What does the pH suggest?
________
What does the CO2 level suggest?
_________
What does the bicarbonate level suggest?
_________
What is the diagnosis?
_________

trending towards acidemia
respiratory alkalosis
metabolic acidosis
increased breathing
metabolic acidosis with complete respiratory compensation
What does the pH suggest?
________
What does the CO2 level suggest?
_________
What does the bicarbonate level suggest?
_________
How will the system respond?
_________
What is the diagnosis?
_________

alkalemia
normal
metabolic alkalosis
uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
What does the pH suggest?
________
What does the CO2 level suggest?
_________
What does the bicarbonate level suggest?
_________
What is the diagnosis?
_________

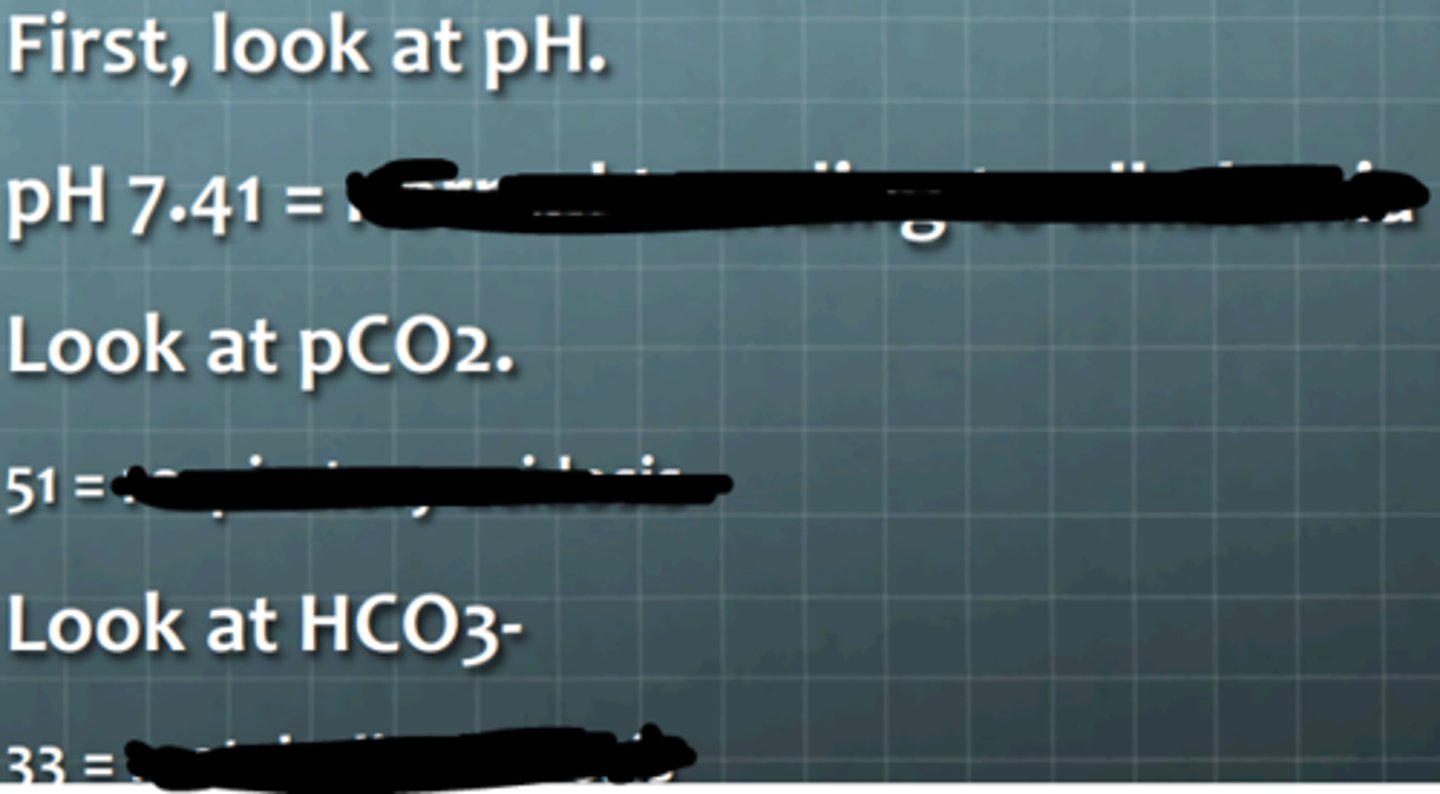
trending toward alkalemia
normal
normal
normal blood gas
What does the pH suggest?
________
What does the CO2 level suggest?
_________
What does the bicarbonate level suggest?
_________
What is the diagnosis?
_________
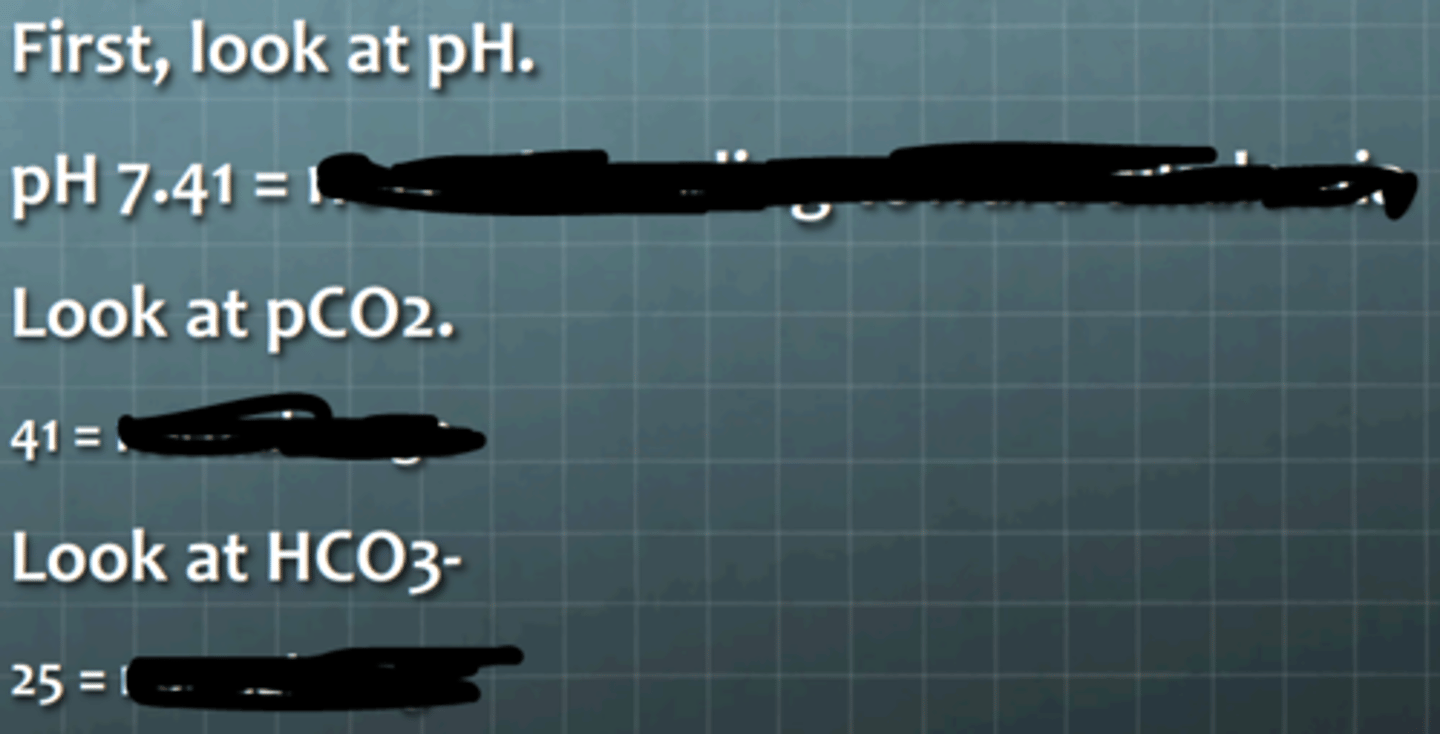
trending towards alkalemia
respiratory acidosis
metabolic alkalosis
metabolic alkalosis with complete respiratory compensation
What does the pH suggest?
________
What does the CO2 level suggest?
_________
What does the bicarbonate level suggest?
_________
What is the diagnosis?
_________
Anion gap
value used to represent the ions (mostly anions) that are not accounted for by lab measurements. These include blood serum proteins such as albumin, phosphates, citrate, and sulfate. Size of this value along with pH levels can aid in diagnosis of particular conditions which elicit relevant changes. Ie) a larger anion gap suggests metabolic acidosis where the reduced production or loss of bicarbonate is balanced by the larger anion gap
Carbonic anhydrase
an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of carbonic acid derived from carbon dioxide and water. Inhibition of this enzyme via certain drugs prevents the reuptake of bicarbonate and results in the excretion of sodium and water in urine and are useful as diuretics.
Carbonic anhydrase
Inhibitors of this enzyme can be used to decrease the production of aqueous humor production in the treatment of glaucoma.