Cell Signaling and Action Potential Conduction in Neurobiology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Action Potential
Rapid change in membrane potential during neuron signaling.
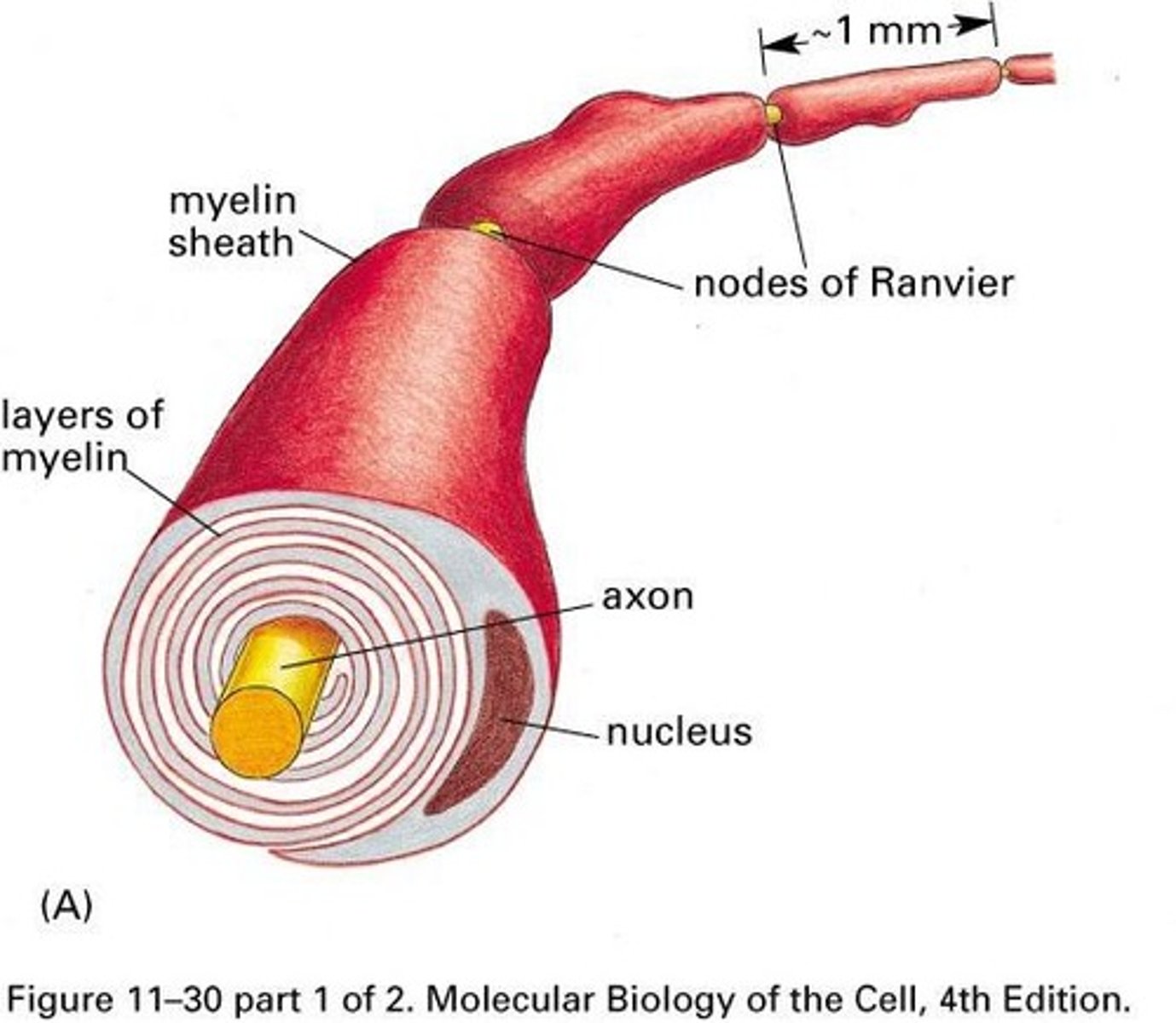
Myelinated Axons
Axons insulated with myelin for faster signal conduction.
Unmyelinated Axons
Axons without myelin, slower signal conduction.
Refractory Period
Time during which neuron cannot fire another action potential.
Absolute Refractory Period
No stimulus can trigger an action potential.
Relative Refractory Period
Only stronger stimulus can initiate action potential.
Graded Potentials
Variable changes in membrane potential, not all-or-nothing.
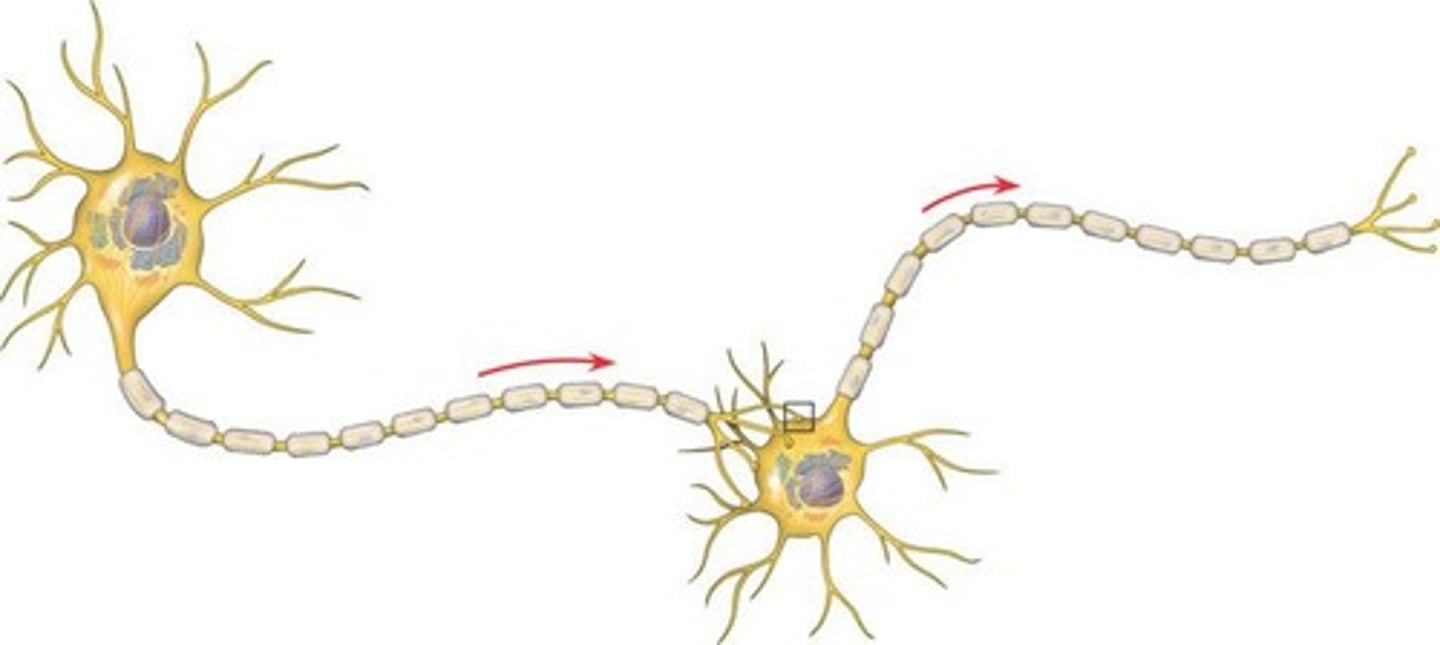
Chemical Synapse
Connection where neurotransmitters transmit signals between neurons.
Presynaptic Cell
Neuron sending the signal at a synapse.
Postsynaptic Cell
Neuron receiving the signal at a synapse.
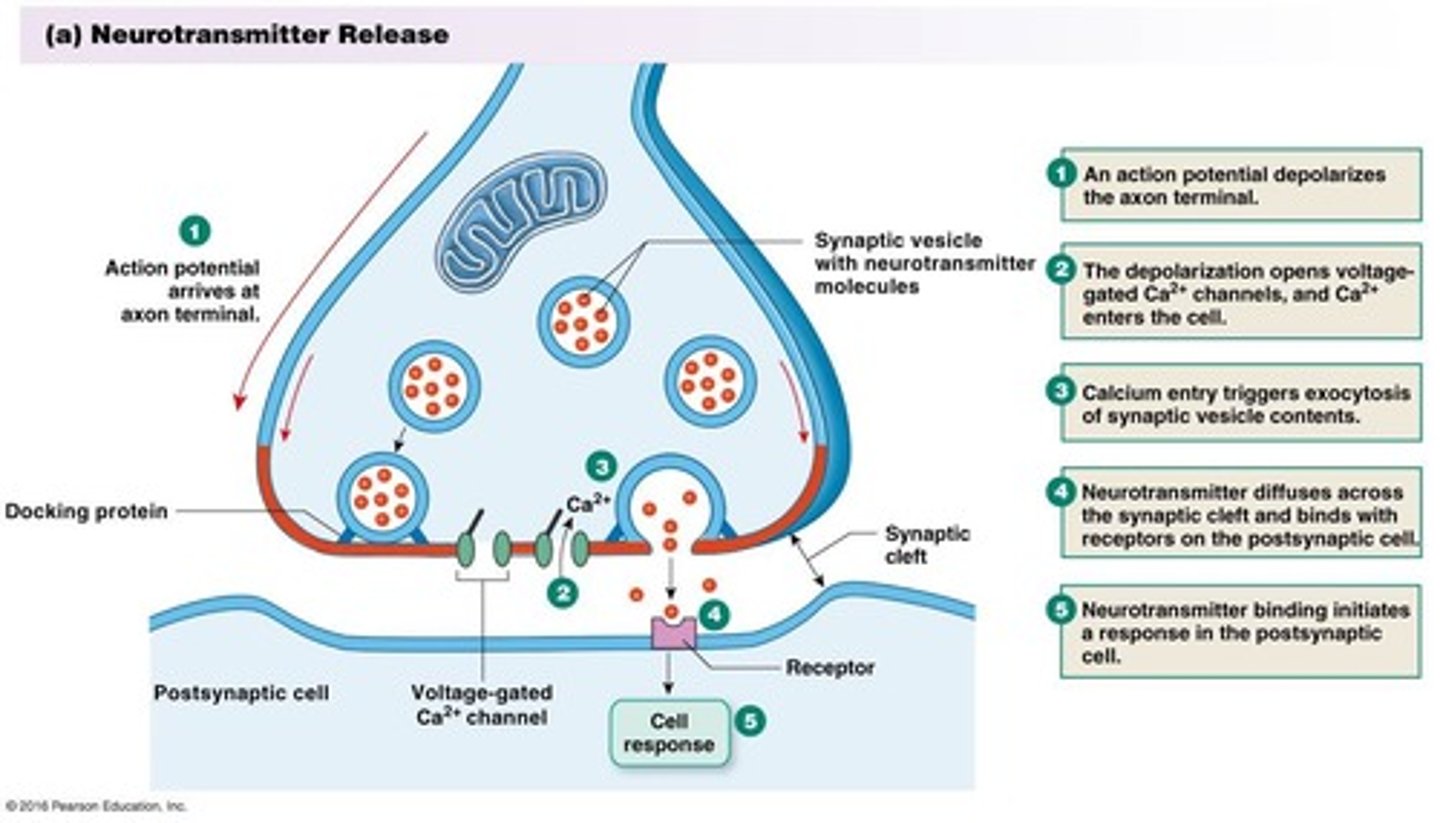
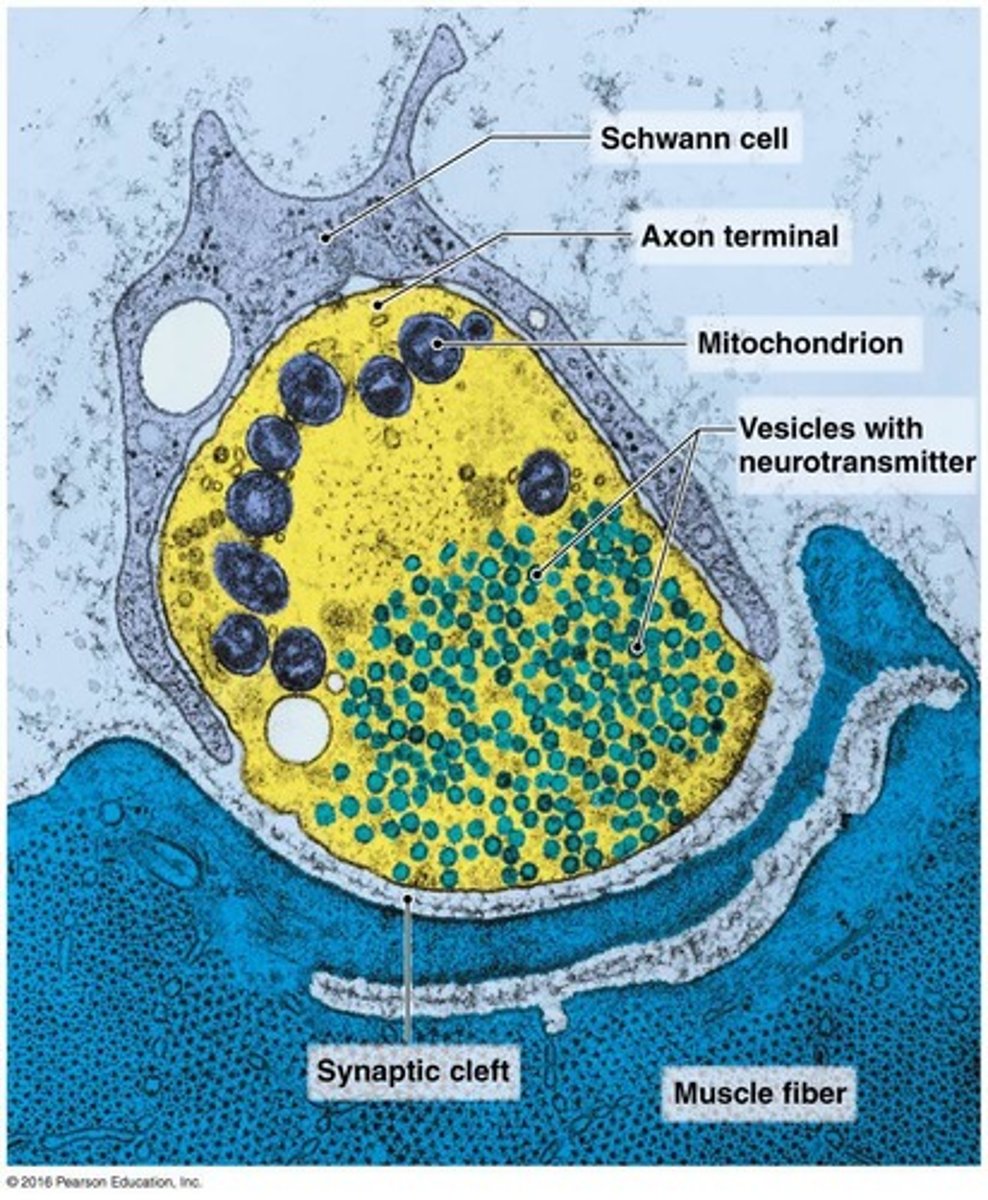
Synaptic Bouton
Terminal of presynaptic neuron releasing neurotransmitters.
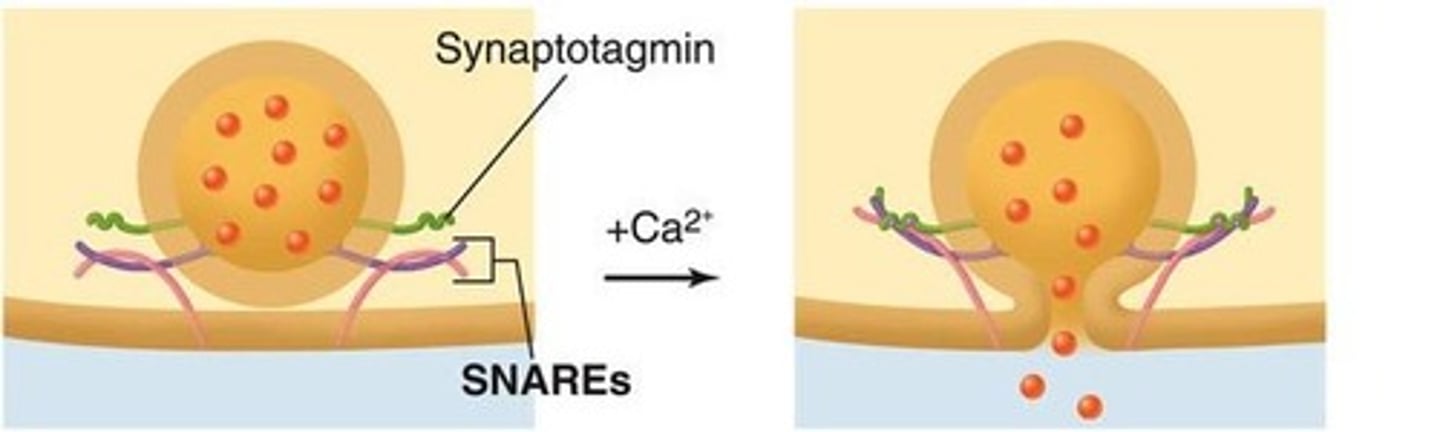
Synaptic Vesicle
Membrane-bound structure containing neurotransmitters.
Synaptic Cleft
Gap between presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons.
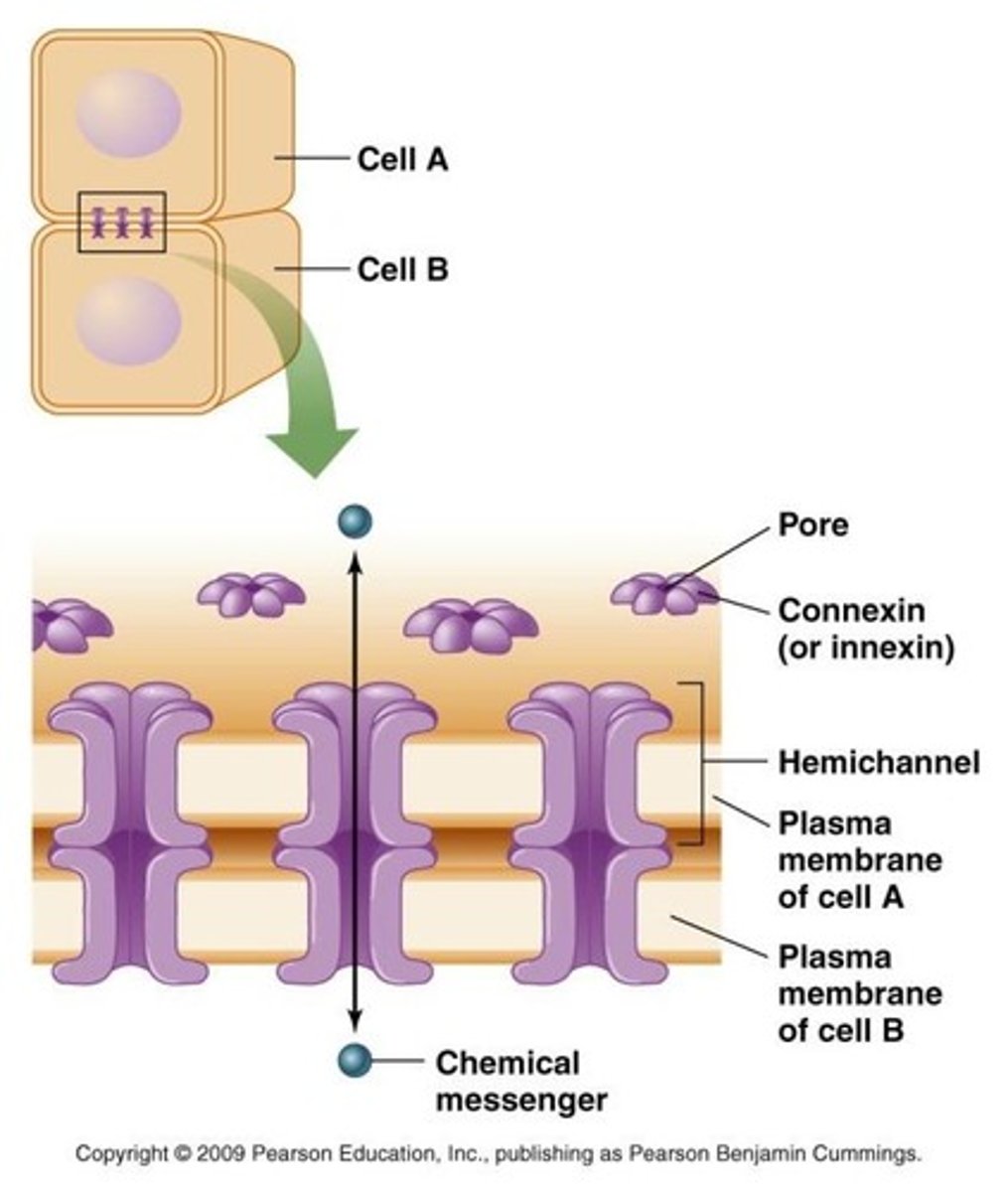
Gap Junctions
Direct cytoplasmic connections between adjacent cells.
Autocrine Signals
Signals affecting the same cell that produces them.
Paracrine Signals
Signals affecting nearby cells in the same tissue.
Endocrine Signals
Hormones released into the bloodstream affecting distant cells.
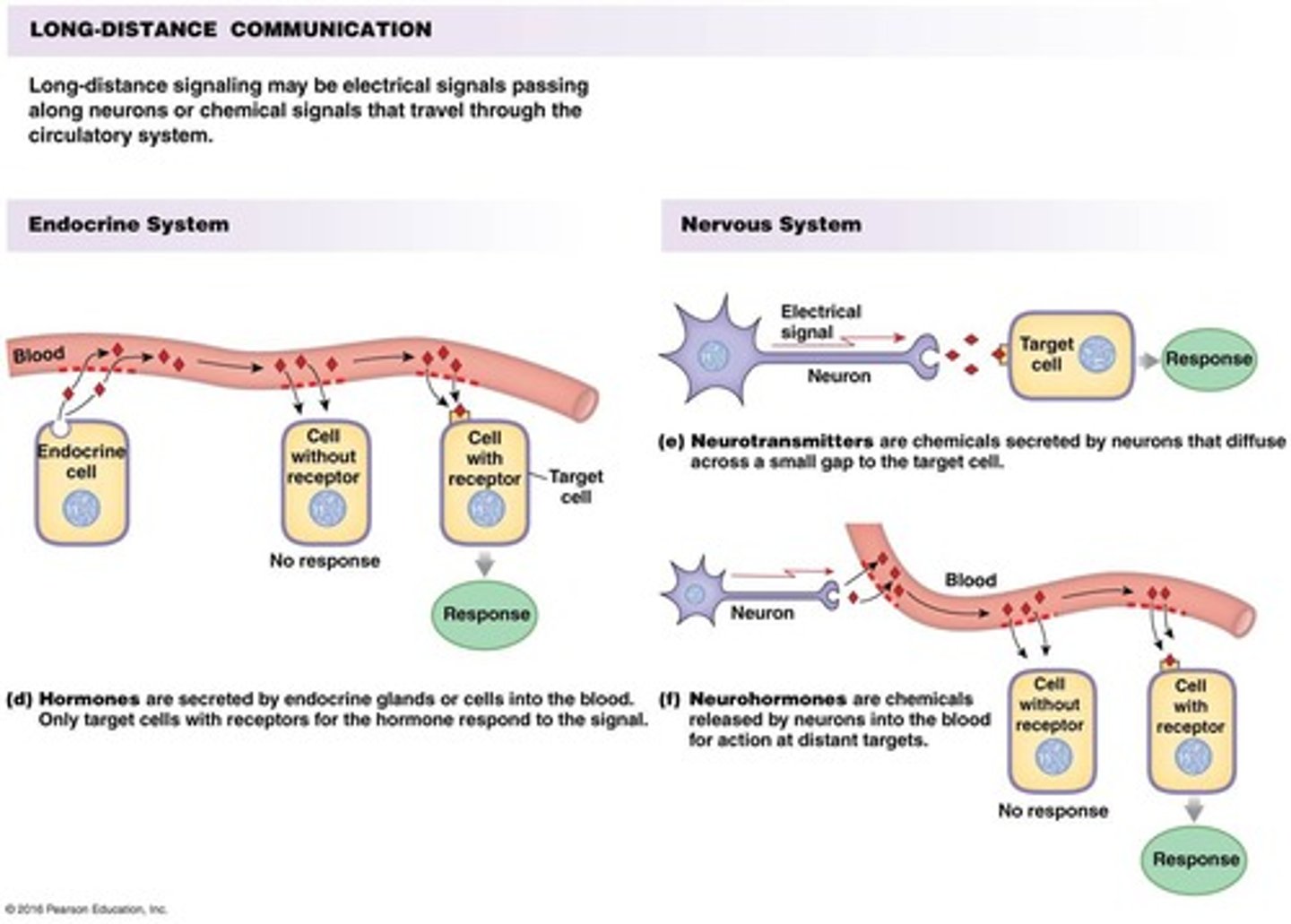
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger transmitting signals across synapses.
Neurohormone
Hormone produced by neurons, released into blood.
Second Messenger
Intracellular molecule mediating cellular response to signals.
G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
Receptor activating G-proteins to trigger signaling pathways.
Amplifier Enzyme
Enzyme that increases the concentration of second messengers.
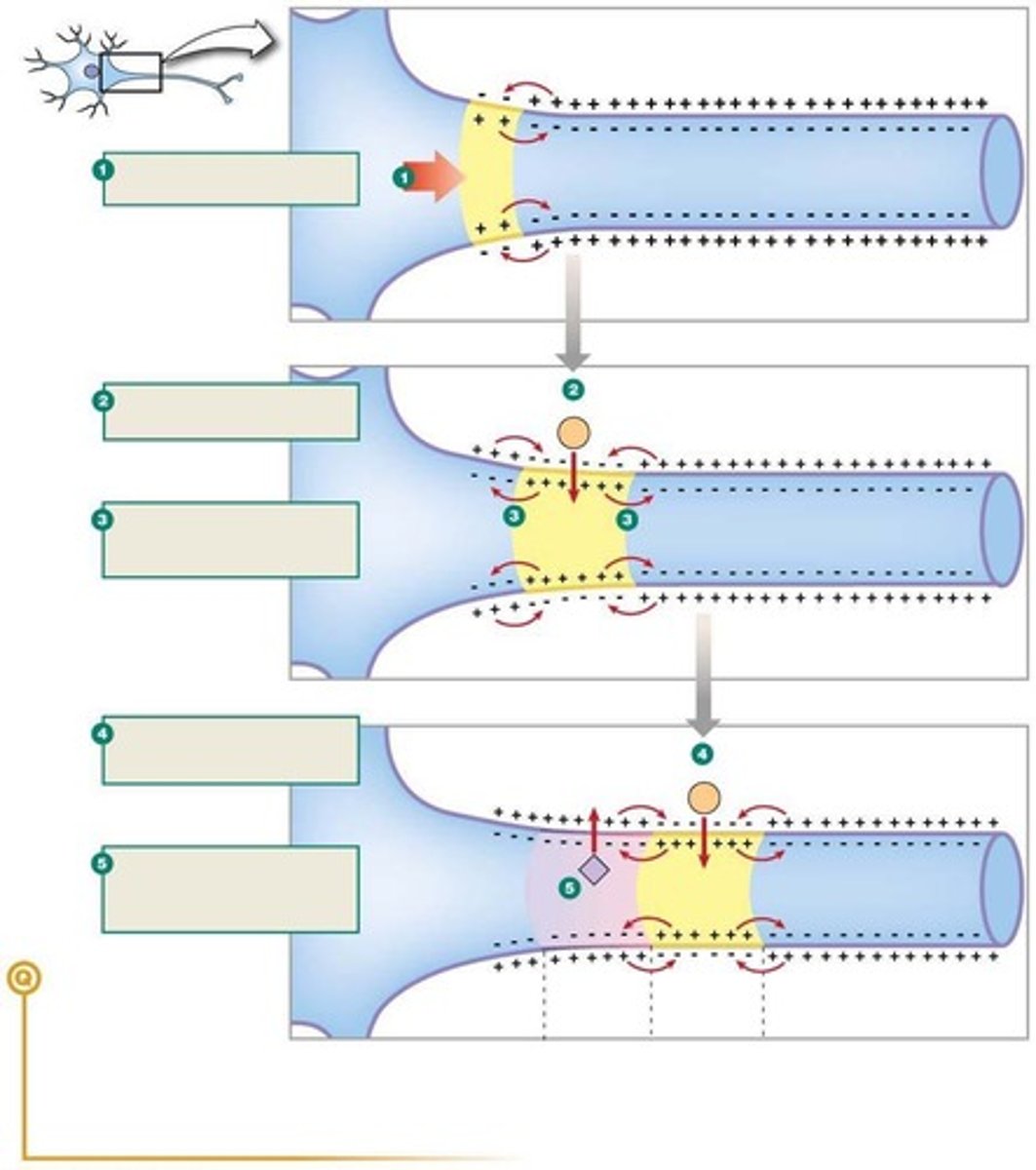
Rising phase
Initial depolarization during action potential.
Falling phase
Repolarization following action potential peak.
After-hyperpolarization
Period after action potential where membrane potential is lower.
Resting potential
Stable membrane potential before action potential initiation.
Proximal axon
Part of axon closest to cell body.
Active region
Area of axon where action potential is generated.
Distal inactive region
Part of axon farthest from cell body.
Myelin sheath
Insulating layer around axons, speeds up conduction.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath where ion channels are concentrated.
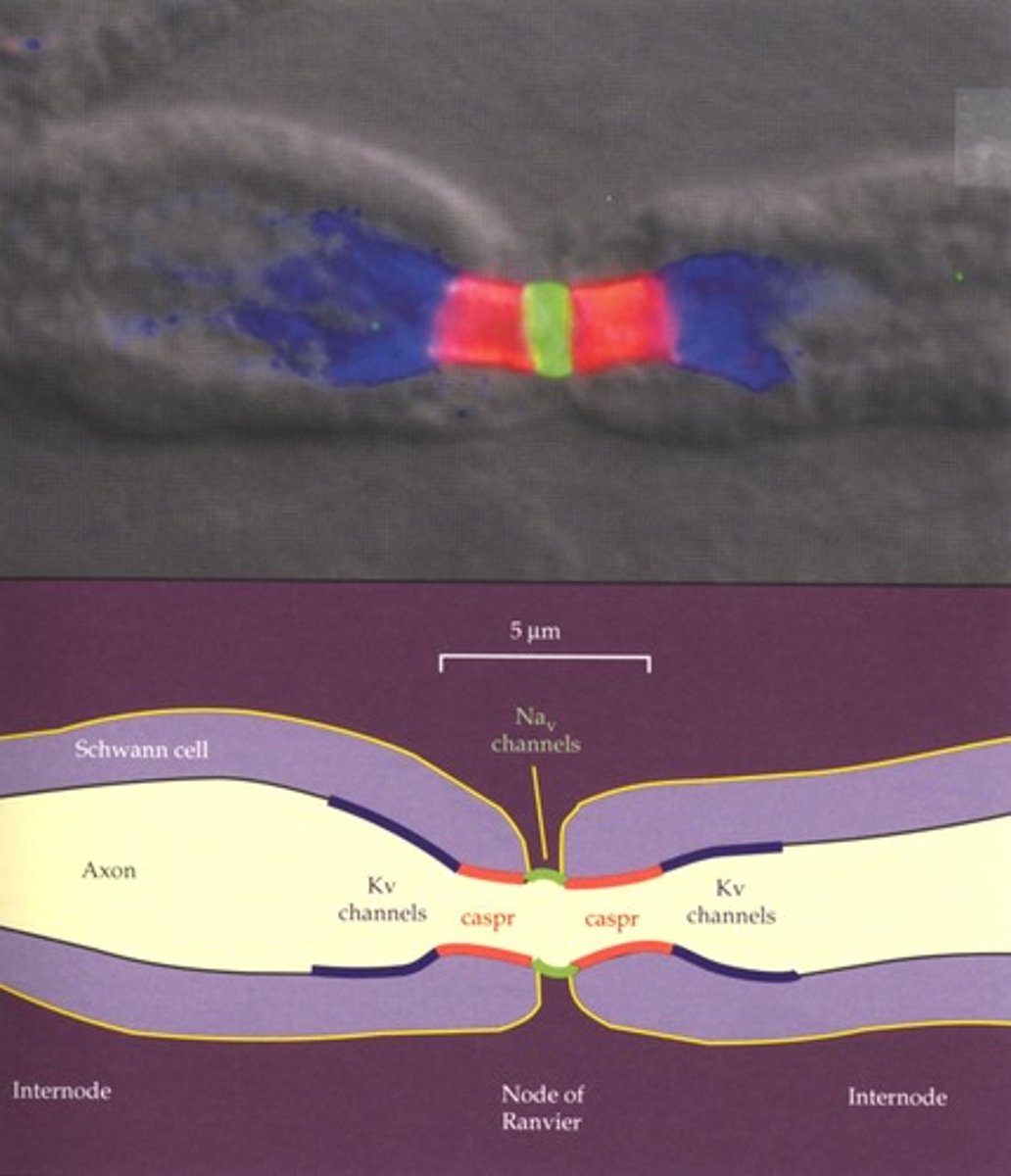
Saltatory conduction
Jumping of action potentials between nodes.
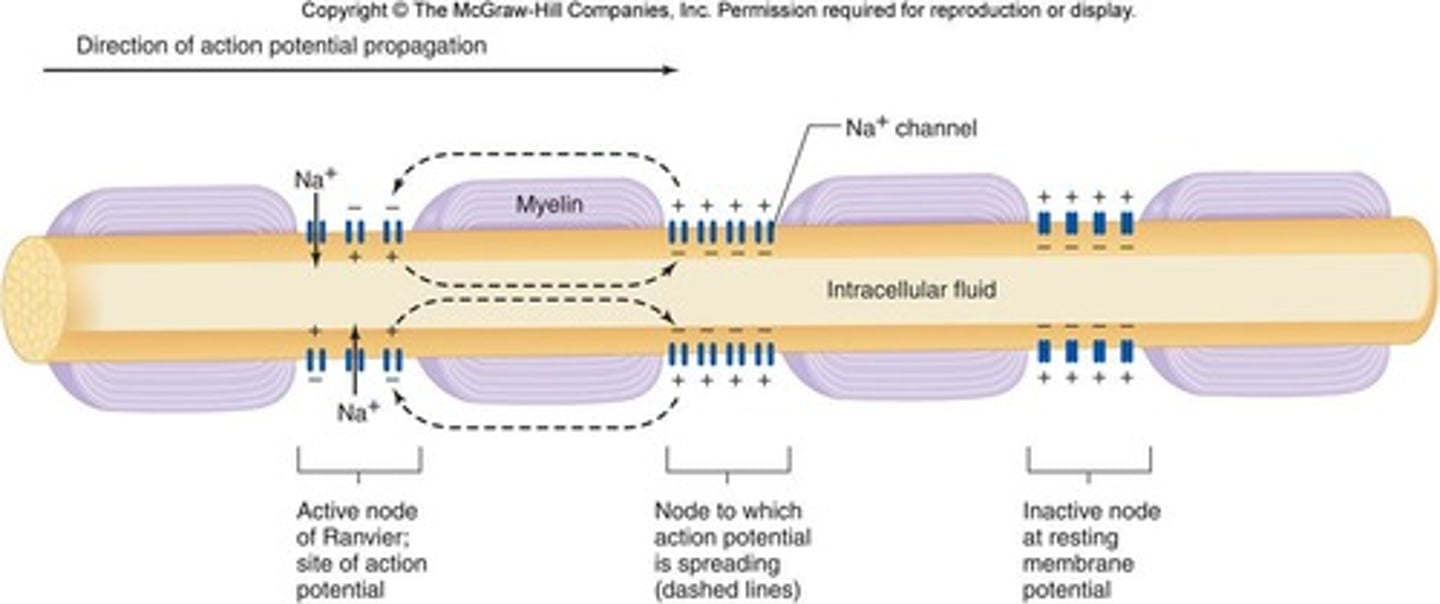
Velocity of axons
Speed of action potential propagation, e.g., 70-120 m/s.
Synaptic terminal
End of presynaptic neuron where neurotransmitter release occurs.
Graded depolarization
Change in membrane potential leading to neurotransmitter release.
Termination of synaptic transmission
Processes that stop neurotransmitter action at synapse.
Primary messenger
Molecule that initiates signal transduction pathway.
Receptor-channel
Protein that opens in response to ligand binding.
Receptor-enzyme
Receptor that has enzymatic activity upon activation.
Nicotinic receptor
Type of acetylcholine receptor that is ionotropic.
Muscarinic receptor
Type of acetylcholine receptor that is metabotropic.
Alpha receptor
Type of adrenergic receptor responsive to norepinephrine.
Beta receptor
Type of adrenergic receptor with different signaling pathways.
Action Potentials
Rapid electrical signals along neurons.
Electrical Synaptic Transmission
Direct electrical communication between neurons.
Contact-Dependent Signaling
Cell communication requiring direct contact.
Autocrine Signaling
Cell signals affecting itself.
Paracrine Signaling
Cell signals affecting nearby cells.
Endocrine System
Hormonal signaling over long distances.
Ligand
Molecule that binds to a receptor.
Receptor
Protein that binds ligands to initiate signaling.
Hydrophilic Signals
Cannot cross the cell membrane.
Lipophilic Signals
Diffuse through membranes to bind receptors.
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR)
Ion channel activated by acetylcholine.
G Proteins
Molecules that transmit signals from receptors.
G-Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
Receptor that activates G proteins upon ligand binding.
Muscarinic AChR
GPCR activated by acetylcholine, not in skeletal muscle.
Signal Amplification
Process enhancing cellular response to signals.
Second Messengers
Intracellular molecules that mediate signaling pathways.
α-bungarotoxin
Nicotinic AChR antagonist from kraite venom.
Insulin Receptor
Receptor that mediates insulin signaling.
Epinephrine
Hormone that triggers fight-or-flight response.
α-adrenergic Receptors
GPCRs responding to norepinephrine and epinephrine.
β-adrenergic Receptors
GPCRs mediating responses to epinephrine.
Chemical Synaptic Transmission
Release of neurotransmitters across synapses.