C9 - Crude oil and fuels
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Last updated 1:50 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
1
New cards
What is crude oil?
Crude oil is a finite resource found in rocks. Crude oil is the remains of an ancient biomass consisting mainly of plankton that was buried in mud. Crude oil is a mixture of a very large number of compounds.
2
New cards
What are hydrocarbons?
Compounds made only from hydrogen and carbon atoms
3
New cards
What is an alkane?
Saturated Hydrocarbons.
1. Only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
2. Only single bonds (alkanes have no double bonds).
1. Only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
2. Only single bonds (alkanes have no double bonds).
4
New cards
What is the general formula of an alkane?
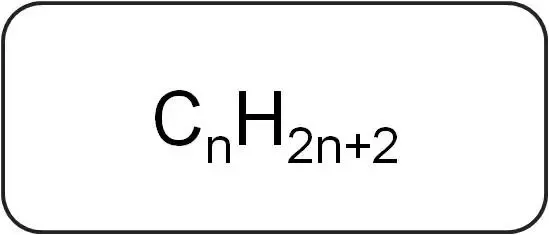
5
New cards
How is crude oil separated and by what process?
Crude oil is separated into fractions by fractional distillation
6
New cards
The properties of each fraction depends on …?
The size of hydrocarbon molecules in it
7
New cards
Why do lighter fractions make better fuel?
They ignite more easily and burn well, with cleaner (less smoky) flames
8
New cards
What do the terms viscosity and volatility mean?
viscosity - how easily it flows
volatility - the tendency to turn into a gas
volatility - the tendency to turn into a gas
9
New cards
What happens when hydrocarbons are burnt in the air?
The carbon and hydrogen in the fuel are completely oxidised.
They produce carbon dioxide and water.
They produce carbon dioxide and water.
10
New cards
How can you test for the gases formed in the complete combustion of hydrocarbon?
The carbon dioxide turns limewater cloudy
water turns blue cobalt chloride paper pink (or white anhydrous copper sulfate blue)
water turns blue cobalt chloride paper pink (or white anhydrous copper sulfate blue)
11
New cards
What does incomplete hydrocarbon combustion produce?
Carbon monoxide - a toxic gas
12
New cards
What is cracking?
A process which breaks large less useful hydrocarbons into smaller more useful hydrocarbons
13
New cards
what are the two types of Cracking?
catalytic cracking - by passing the vapours over a hot catalyst ,
steam cracking - mixing them with steam and heating them with a very high temperature.
steam cracking - mixing them with steam and heating them with a very high temperature.
14
New cards
What does cracking produce?
Saturated hydrocarbons - alkanes used for fuel
unsaturated hydrocarbons - alkenes
unsaturated hydrocarbons - alkenes
15
New cards
What is a test for an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Alkenes (and other unsaturated compounds containing carbon-carbon double bonds) react with orange bromine water turning it colourless
16
New cards
What are isomers
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas, this means they are made of the same atoms, but the atoms are arranged differently.
17
New cards
What is the definition of a homologous series?
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds that have similar chemical properties, due to them having the same functional group.
18
New cards
What is a Feedstock?
a raw material used to provide reactants for an industrial reaction
19
New cards
What is a petrochemical?
a substance made from crude oil via chemical reactions