AP Exam tips!
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
things you don't wanna miss that are all memorization! 1. when in doubt: cancel units out/always MATCH UNITS, think back to labs/equipment in class, don't justify if you don't need to, make SMART answers! it's the same test over and over again :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
to avoid getting units or SF points off
BOX OR CIRCLE YOUR FINAL ANSWER
FRQ basics strategies
pick the best, most concise answer!
only answer stem of the problem
try to immediately assign topic/unit relevant to question so you can focus brain
UNITS and SF (be careful, check for constants)
think back to in class labs and examples!
there are no negative…
equilibrium constants, Kelvin temperatures, bond energies/enthalpies (energy it takes to break a bond)
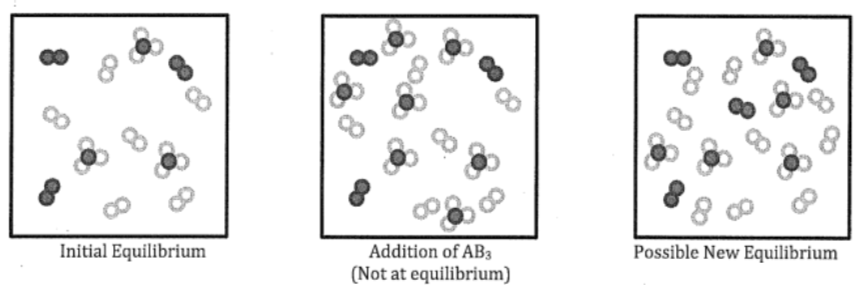
drawing/modeling particle diagrams
things to consider:
states of matter, relative amounts of particles, changes to size of container, if particles will react
remember your addition and subtraction rules
ALL ABOUT # of DECIMAL PLACES not total number of digits!!
equilibrium constant (K) rules:
when reversing the reaction, take the inverse of the K value
when multiplying the reaction by a coefficient, raise the K value to the power of that coefficient
when adding reactions with given K values, multiply their K values for overall K
@ equilibrium all reactant and product concentrations
are CONSTANT!
this is like a key characteristic/sign you’re dealing w/ equilibrium when concentration reaches constant value
never include solids/liquids in
equilibrium constant expressions or ICE tables
as acid or base strength DECREASES
its conjugate species strength INCREASES
properties of ionic compounds
form crystals (arranged in lattice of + / - ions)
HIGH melting and boiling points
low vapor pressures
hard, BRITTLE due to repulsion of like charges caused when 1 layer slides across another layer
conduct electricity when dissolved and molten
good insulators as solid
properties of metals:
metallic attractions b/c of multiple metallic cations being attracted to a delocalized sea of valence electrons
shiny/lustrous
malleable and ductile
conduct heat and electricity
when listing IMF for the first time…
don’t use any abbreviations
formal charge
valence electrons - (number of lone electrons + bonds)
dilution equation!!
ViMi = VfMf
increasing vol w water will decrease concentration, increase percent ionization
relationships between Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, entropy:
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
if -H and +S →spontaneous at ALL temperatures
if +H and -S →not spontaneous at any temp.
if both negative →only spontaneous @ low temp.
if both positive →only spontaneous @ high temp.
nernst equation
→cell potential depends on ratio of concentration/concentrations!!
Ecell = Ecell° - (0.0592/n)log Q
→Q is products over reactants
things to remember for net ionic equations
you can only break up strong electrolytes
strong acids/bases, aqueous solutions, etc.
keep everything else together!! (NEVER SEPARATE WEAK ACIDS/BASES)
cancel out common ions
write states of matter and correct rxn arrows
solubility rule must haves
group 1, nitrates, acetates, ammonium, perchlorate are always soluble
factors that affect entropy
STATE OF MATTER TAKES precedence!!
gas > liquid > solid
number of moles
temperature
units for free energy, entropy, enthalpy
ΔG and ΔH →usually kj/mol
ΔS →usually J/mol*K
when in doubt for units
see what cancels out!!
units of K per overall rxn order
M1-nt-1
any time given bond enthalpies
BIG INDICATOR FOR BONDS BROKEN - BONDS FORMED
collision theory states
for a rxn to occur: molecules must collide with sufficient energy and proper orientation
for gases: density can be found by
d = MP/RT
M is molar mass
FOR EQUILIBRIUM
set up ice tables!!! so you don’t make basic math mistakes
when to assume rxns go to completion?
precipitation, neutralization, producing water
carbonate as an acid reaction
2H+ + CO32- →CO2 + H2O
best conditions for ideal gases
HIGH temperature, LOW pressure
the only time you use 0.08206 as the value for R
is PV = nRT, otherwise check what units need to be cancelled out!
CONTAMINATION for gas collection by water displacement
either water vapor present OR other gases in the air if tube wasn’t previously evacuated
avg. KE is not the same as
avg. molecular speed!!! (molecular speed just depends on how heavy molecule is, heavier = slower)
avg. KE is directly proportional to
TEMPERATURE
key first order rxns characteristic
CONSTANT half life!! independent of concentration OR PRESSURE
0.693/k
beer’s law
absorbance = molar absorptivity*concentration*path length
usually path length/molar absorptivity are held constant, so absorbance is directly proportional to concentration
this means their ratios are also constant!
hybridization is all about
steric number!! solely based on this
definition of equilibrium
when rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal
“justify with a calculation”
puts both units and SF on the table so double triple check!
break ionic compounds apart when
assigning oxidation numbers →makes it easier!
when asked to write Ka, Kw, Kb expressions
WRITE AS EQUALITIES
STP
1.00 atm, 273 K, 22.4 L = 1 mol
when removing electrons
ALWAYS remove electrons from VALENCE (OUTERMOST) shell →esp. remember this when writing electron configurations
buffer systems = automatic sign for
HENDY HASS!!!
always check units for enthalpy for
mol/rxns or mol/g etc. because this really affects stoichiometry of answer!!!!
taking log SF rule
however many total digits there are = number of decimal places in answer
taking antilog SF rule
however many decimal places = total number of SF in answer
wavelength usually given in units of
NANOmeters, might have to convert to cancel out!!
→1 nm = 1×10-9 m
only one wavelength for maximum absorbance
every other wavelength used will give a lower absorbance!!
absorbance
how much light can be absorbed
helps us measure concentration of a colored substance
more concentrated solution = the less light that will pass through
for electromagnetic spectrum
Energy = J/photon!
be careful w/ units and alter → one of few times you may have to use avogadros number
network covalent solid
to break network covalent solid, you have to break ALL the covalent bonds which takes a lot of energy
@ equivalence point when you have to WMX
make sure you divide moles of salt by TOTAL VOLUME because you need molarities!!
calculating pH in an overtitration
treat excess titrant as strong acid/base, just get pH from this!!
[FOR ACIDS] more oxygen atoms means
a stronger acid