Earth Science: Earth Materials
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Naturally Occurring
Formed through natural geologic processes.
Solid
Only solid crystalline substances are considered minerals.
Definite Chemical Composition
Should be expressed in a chemical formula.
Generally Inorganic
Formed by inorganic processes, not derived from organic materials.
Crystalline Structure
Atoms (Ions) are arranged in an orderly.
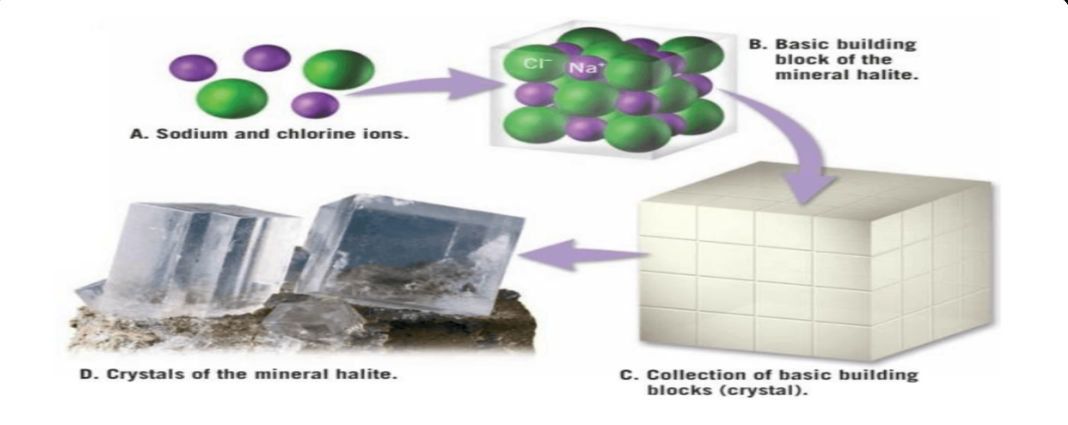
Orderly Packing of Atoms
Quartz
Consists of Silicon (Si) and Oxygen (O) atoms, (1:2).
Mineraloids
A naturally occurring, inorganic solid that does not exhibit crystallinity.
Pumice
It is ejected from the volcano in a sudden blast and cools so quickly that bubbles of gas are trapped within the amorphous glass.
Obsidian
A volcanic glass that cools so rapidly that atoms do not have time to arrange themselves into a crystalline solid.
Rock
Any solid mass of mineral, or mineral-like, matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet. Aggregate of minerals.
Atoms: Building Blocks of Minerals
Most elements join with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds.
Few minerals are made entirely of atoms of only one element. (Copper, Sulfur, Diamond)
Native Gold
Often found in stream deposits or as grains in igneous rocks.
50% of gold is used in jewelry.
40% is used for currency and investment.
10% is used in industry.
Luster
The appearance or quality of light reflected from the surface of a mineral.
Diaphaneity
The ability of mineral to transmit light. e.g. translucent, transparent, opaque.
Color
The most conspicuous characteristic of any mineral.
Streak
Color of a mineral in powdered form that is useful in identification.
Hardness
A measure of the resistance of a mineral to abrasion or scratching.
Brittle
Breaks, powders easily.
Malleable
Can be hammered into thin sheets.
Sectile
Can be cut into thin shavings with a knife.
Ductile
Can be stretched into a wire.
Flexible
Ability of being bent without breaking.
Elastic
Ability to restore in its form after deformation.
Cleavage
The tendency of a mineral to break along planes of weak bonding.
Fracture
Minerals that have chemical bonds that are equally, or nearly equally, strong in all directions.
Crystal Shape
Fibrous
Bladed
Banded
Cubic Crystals
Density / Specific Gravity
Represents the ratio of a mineral’s weight to the weight of an equal volume of water.
More Dense
More mass (matter) in a given volume.
Less Dense
Less mass (matter) in a given volume.
Other Properties of Minerals
Taste
Feel
Smell
Double Refraction
Effervescence
Silicates
Contains the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron as their building block.
Non-Silicates
Minerals that do not contain silicon or oxygen.
Natural Resources
Classified as renewable when they can be replenished over short time spans and nonrenewable when they can’t.