Chemistry A Level OCR A; Aromatic compounds, carbonyls, organic acids and organic synthesis
1/213
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Created originally by N_Jones16 on Quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
What colour is benzene?
Colourless
Where is benzene found in naturally?
Crude oil
Is benzene a carcinogen?
Yes
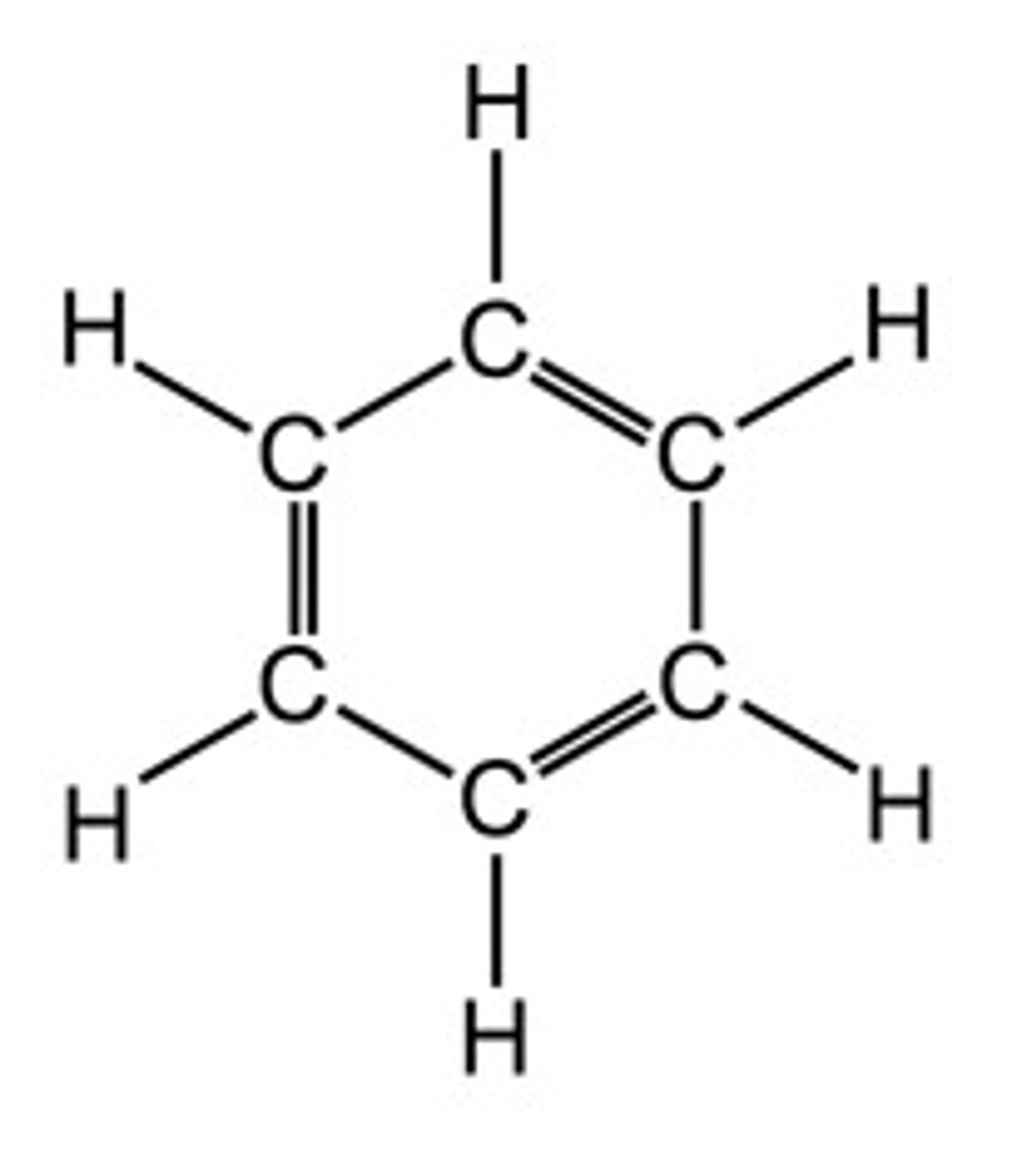
Draw the displayed structure of benzene
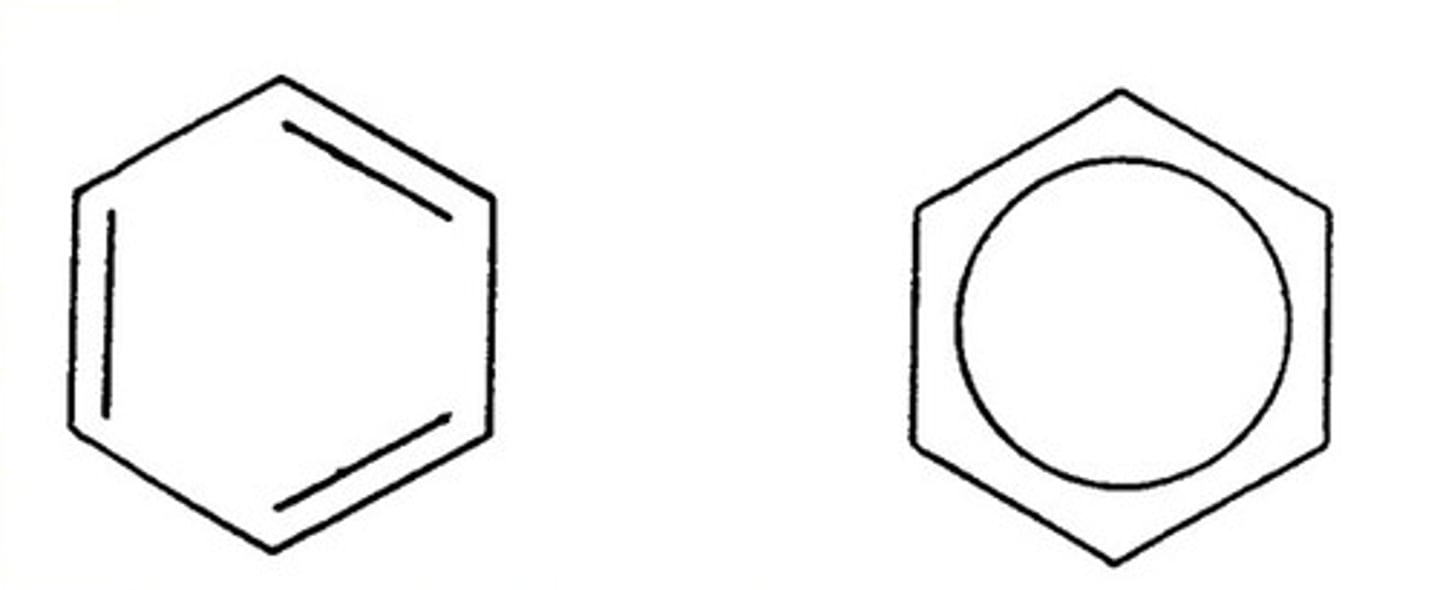
Draw the skeletal formula of benzene
Either is fine
What does the term aromatic mean?
Any organic compound that contains at least one benzenes ring
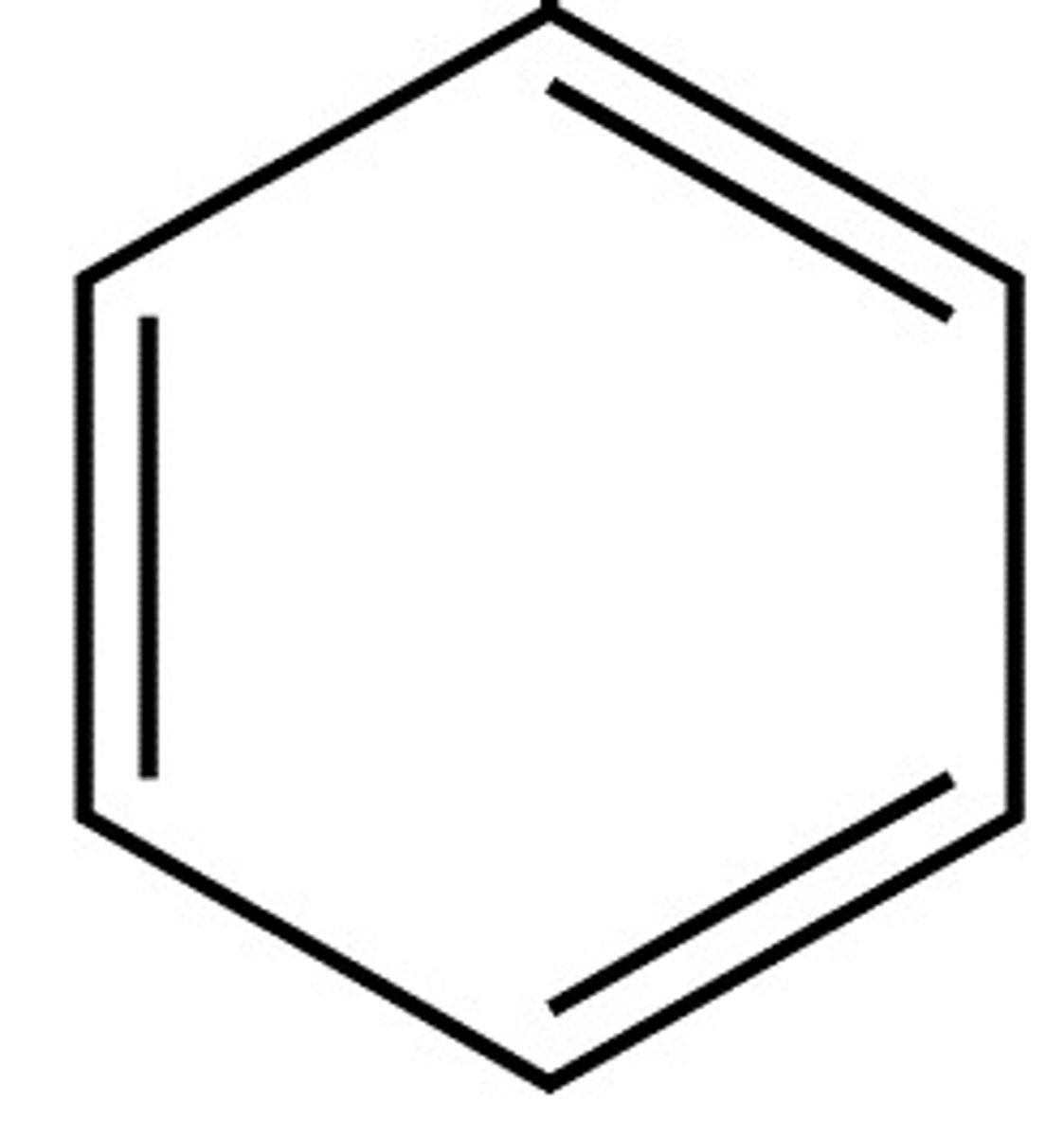
What is Kekule's structure for benzene?
What are the three pieces of evidence that disproves kekuele's structure?
1) Benzene has a lack of reactivity
2) Lengths of the carbon-carbon bonds were between a double bond and single bond
3) Hydrogenation enthalpies
What make scientists think that benzene couldn't have C=C bonds and was therefore unreactive? Disproving Kekules structure
- Benzene does not undergo electrophilic addition reactions as a organic compound having C=C bond should
- Benzene therefore doesn't decolourise bromine under normal conditions
- Therefore it was thought benzene couldn't have any C=C bonds as Kekule's structure did
What made scientists think that benzene couldn't have contained C=C bonds as the lengths were too short? Disproving Kekules structure
- X-ray diffraction proved the bond lengths were between a single bond and a double bond
- Benzene did not have the same bond lengths as kekule's structures
What made scientists think that benzene couldn't have have contained C=C bonds? Disproving Kekules structure
- Enthalpy change of hydrogenation proved to be less energy released than expected
- Benzene is therefore more stable than Kekules structure
What are the features of the delocalised model? (5)
- Benzene is a planar, cyclic hexagonal containing six carbons and six hydrogen atoms
- Each carbon atom uses three of it's available electrons to bond to the adjacent carbon atoms and one electron to bond to one hydrogen atom
- Each carbon atom has one electron in a p-orbtial at right angles
- Adjacent p-orbitals overlap sideways above and below the plane giving a ring of electron density
- Overlapping of p-orbtials creates a system of delocalised π bonds
What are the prefixes to benzene?
- Alkyl groups
- Halogens
- Nitro groups
When is benzene considered a substituent?
- When a benzene ring is attached to an alkyl chain with a functional group or alkyl chain
- NH2 group is attached
Draw the equation that shows how to form nitrobenzene, include all;
- Reagents
- Conditions
- Catalysts
- Mechanism is not required
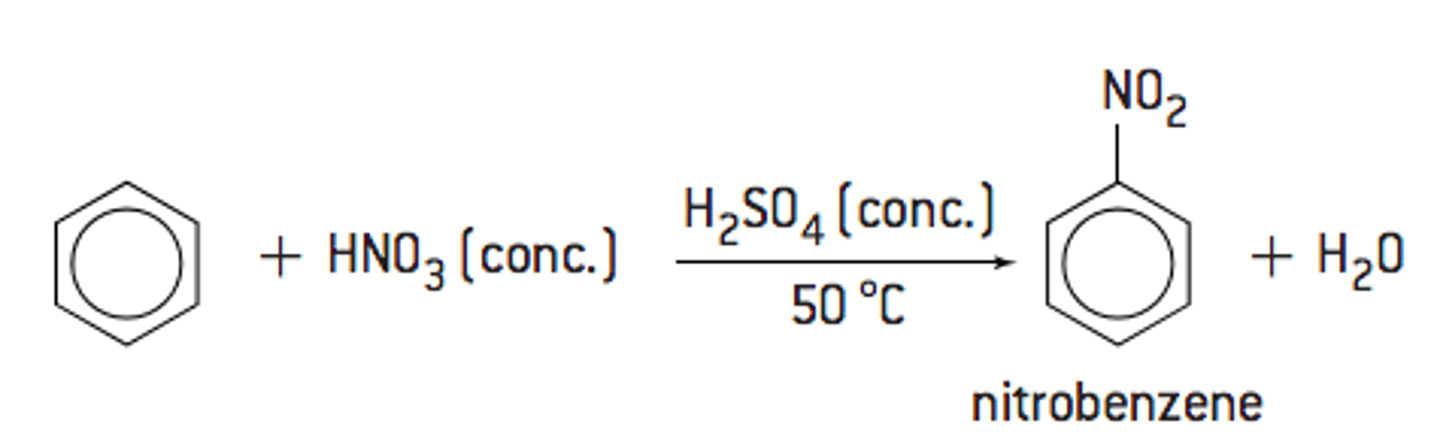
What would occur if temperature of the reaction rises above 50 ˚C?
Further substitution reactions will occur, forming dinitrobenzene
What are the uses for Nitrobenzene?
Preparation of;
- Dyes
- Pharmaceuticals
- Pesticides
- Paracetamol
What type of mechanism is the nitration of benzene?
Electrophilic substitution
Draw the mechanism for the nitration of benzene, include the formation of your electrophile from sulphuric acid and nitric acid and show the regeneration of the catalyst at the end.
Formation of electrophile HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ --> NO₂⁺ + HSO4⁻ + H₂O
Regeneration of sulphuric acid; H⁺ + HSO₄⁻ --> H₂SO₄
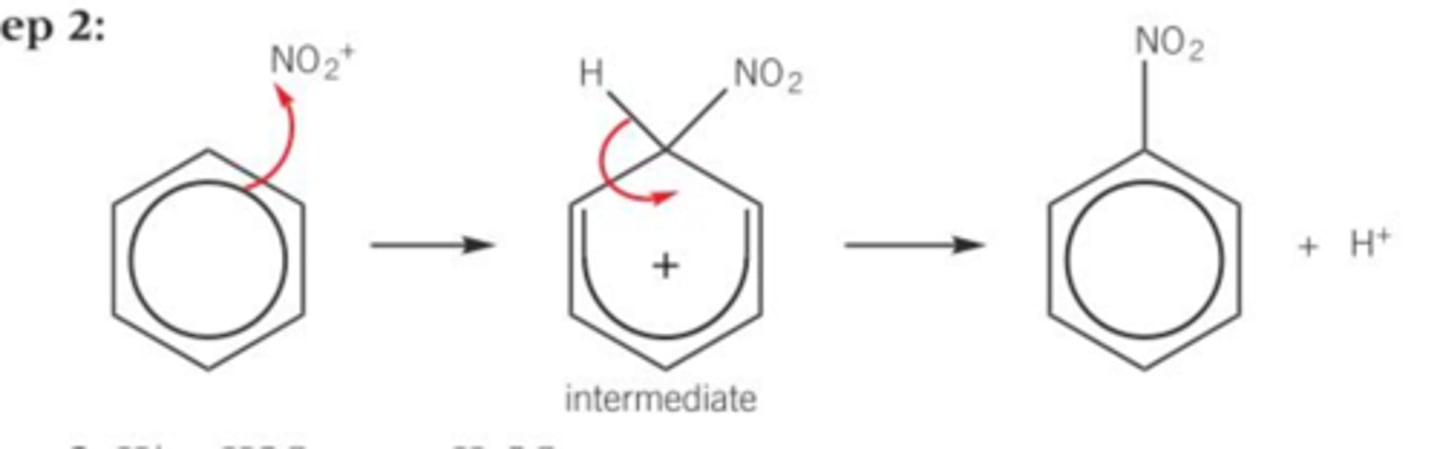
Why is sulphuric acid needed in the nitration of benzene?
- To allow the electrophile of NO₂⁺ to form to be able to be susceptible for electrophilic attack
- Benzene is too stable to react with a non-polar molecule
What is a halogen carrier?
A catalyst used to make a strong halogenated electrophile
What are three example of halogen carriers?
- FeCl₃
- AlBr₃
- FeBr₃
Draw the equation that shows how to form bromobenzene, include all;
- Reagents
- Conditions
- Catalysts
- Mechanism is not required
- Room temperature and pressure (RTP)
- Halogen carrier with Br!
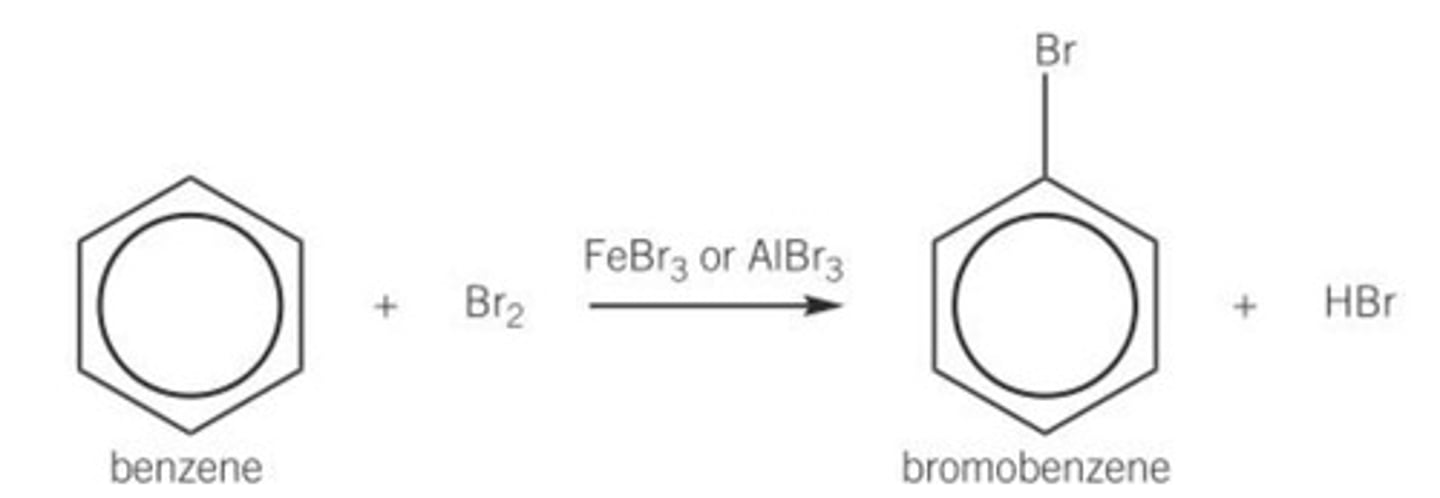
Why is a halogen carrier needed to react with benzene?
- Benzene is too stable to react with a non-polar bromine molecule
- It therefore needs a bromonium ion, Br⁺
How it the bronomium ion, Br⁺ generated?
By a reaction with a halogen carrier containing bromine
Draw the mechanism for the bromination of benzene, include the formation of your electrophile from your halogen carrier and bromine and show the regeneration of the halogen carrier at the end.
Formation of electrophile: Br₂ + FeBr₃ --> FeBr₄⁻ + Br⁺
Regeneration of halogen carrier; H⁺ + FeBr₄⁻ --> FeBr₃ + HBr
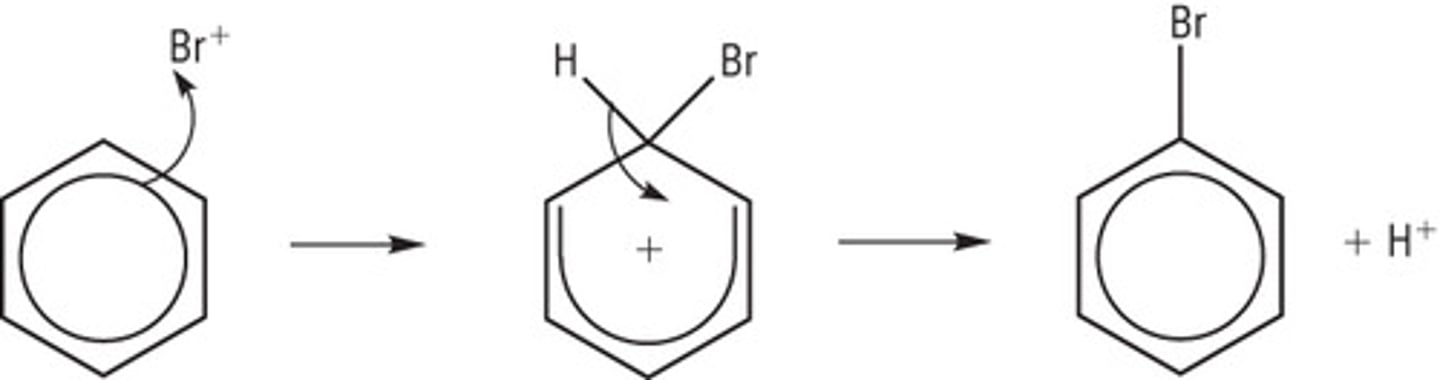
Why type of mechanism is the bromination of benzene?
Electrophilic substitution
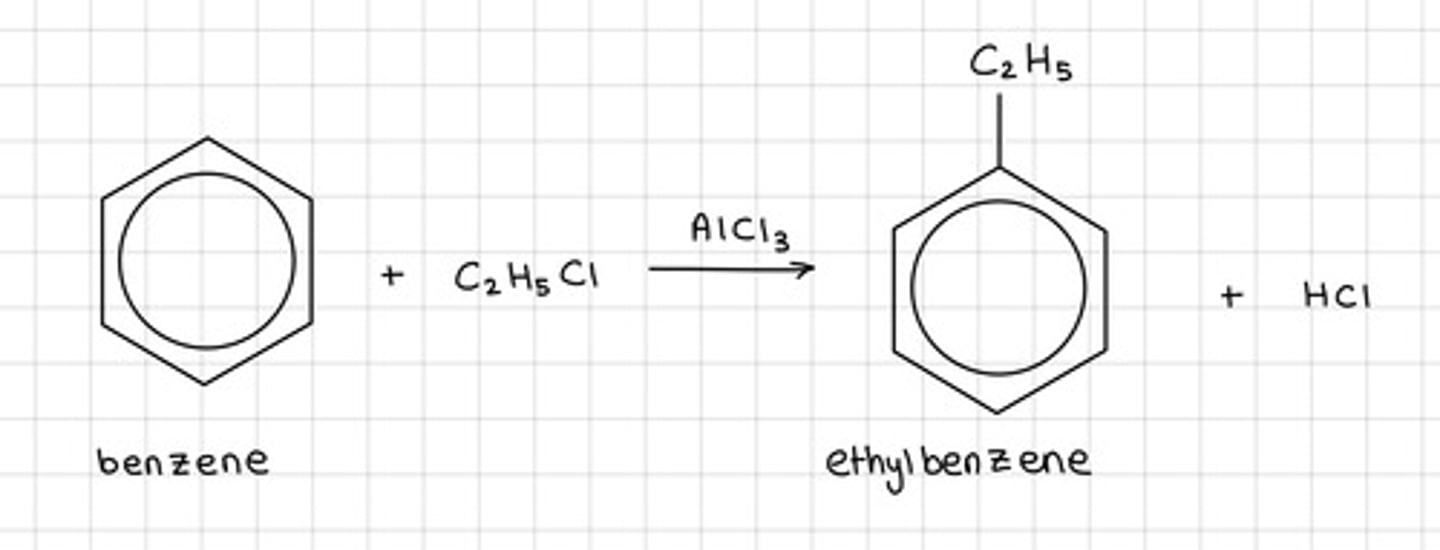
Draw the equation of what happens when a haloalkane (in this case C2H5Cl) reacts with benzene, include;
- Reagents
- Conditions
- Catalysts
This is also called the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction
- Occurs at RTP
Draw the equation of what happens when a acyl chloride reacts with benzene include;
- Show the displayed formulae for all organic compounds
- Reagents
- Conditions
- Catalysts
- RTP
- Aromatic ketone is formed
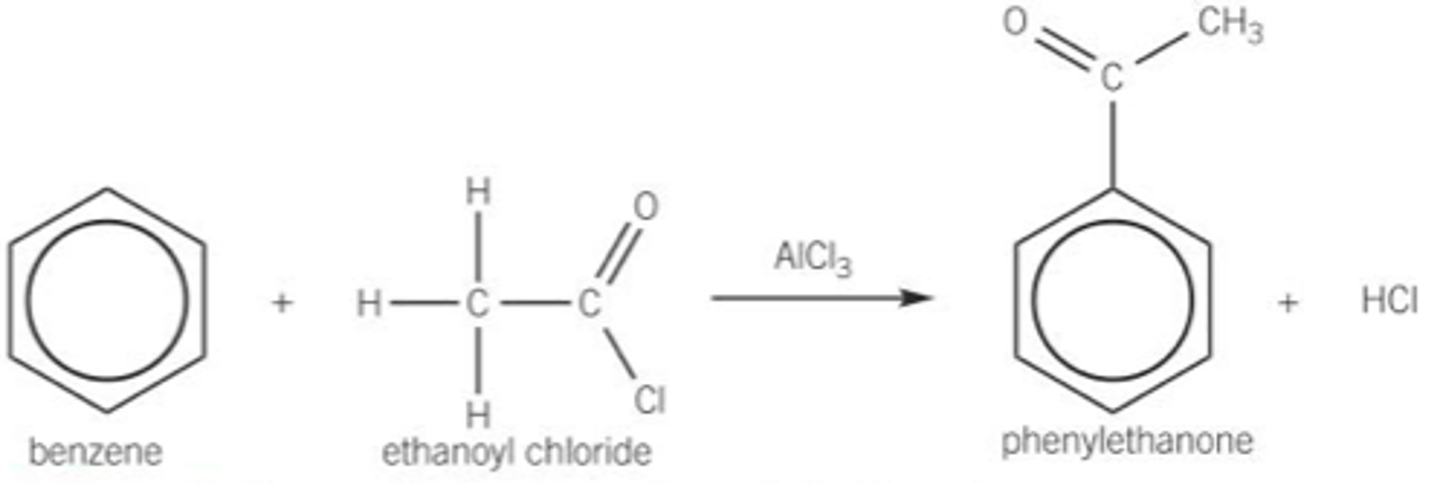
What is one use of ethanoyl chloride?
The perfume industry
What type of mechanism is the acylation reactions an example of?
Electrophilic substitution
What common organic compound can decolourise bromine?
Alkenes
What type of mechanism is the decolorisation of bromine through alkenes called?
Electrophilic addition
What occurs when bromine decolourises cyclohexene?
1) π-bond in the alkene contains localised electrons above and below the plane of the two carbon atoms in the double bond, giving high electron density
2) Localised electrons in the π-bond induce a dipole in the non-polar bromine atom causing induced dipoles
3) Slightly positive bromine atom allows bromine atom to act like an electrophile
Draw the mechanism for reaction of cyclohexene and bromine. What is the name of this reaction?
Electrophilic addition
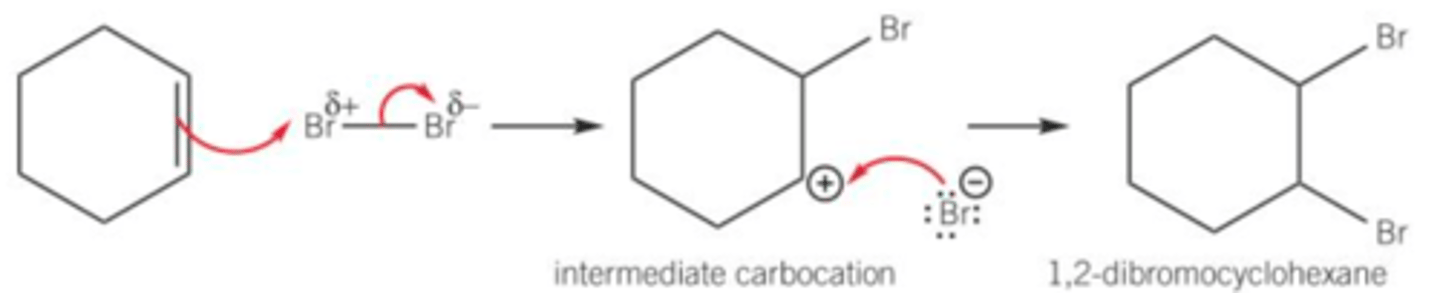
Why can't benzene also undergo electrophilic addition? (without a halogen carrier)
- Benzene has delocalised π electrons above and below the plane of the carbons in the ring structure
- Electron density is less than C=C bond in an alkene
- Insufficient π electron density around any two carbon atoms in the benzene ring
What is phenol?
An organic compound where an -OH group is attached directly to a benzene ring
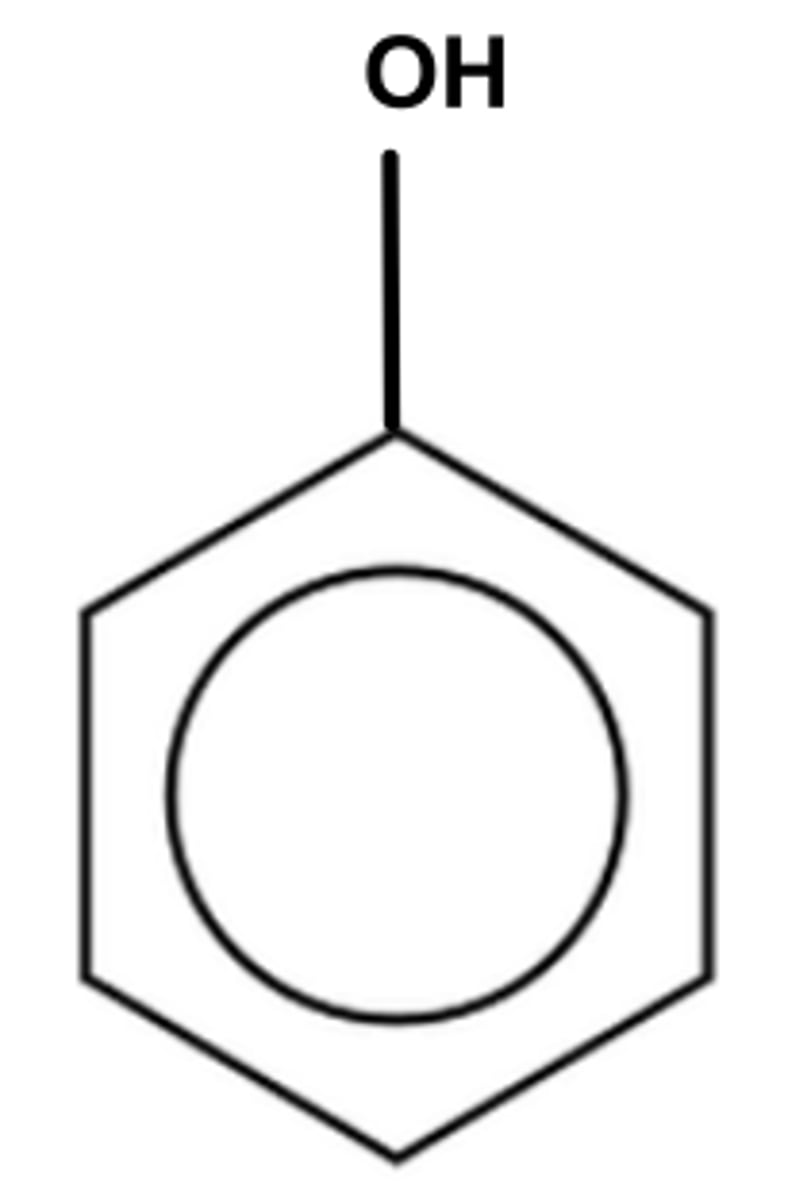
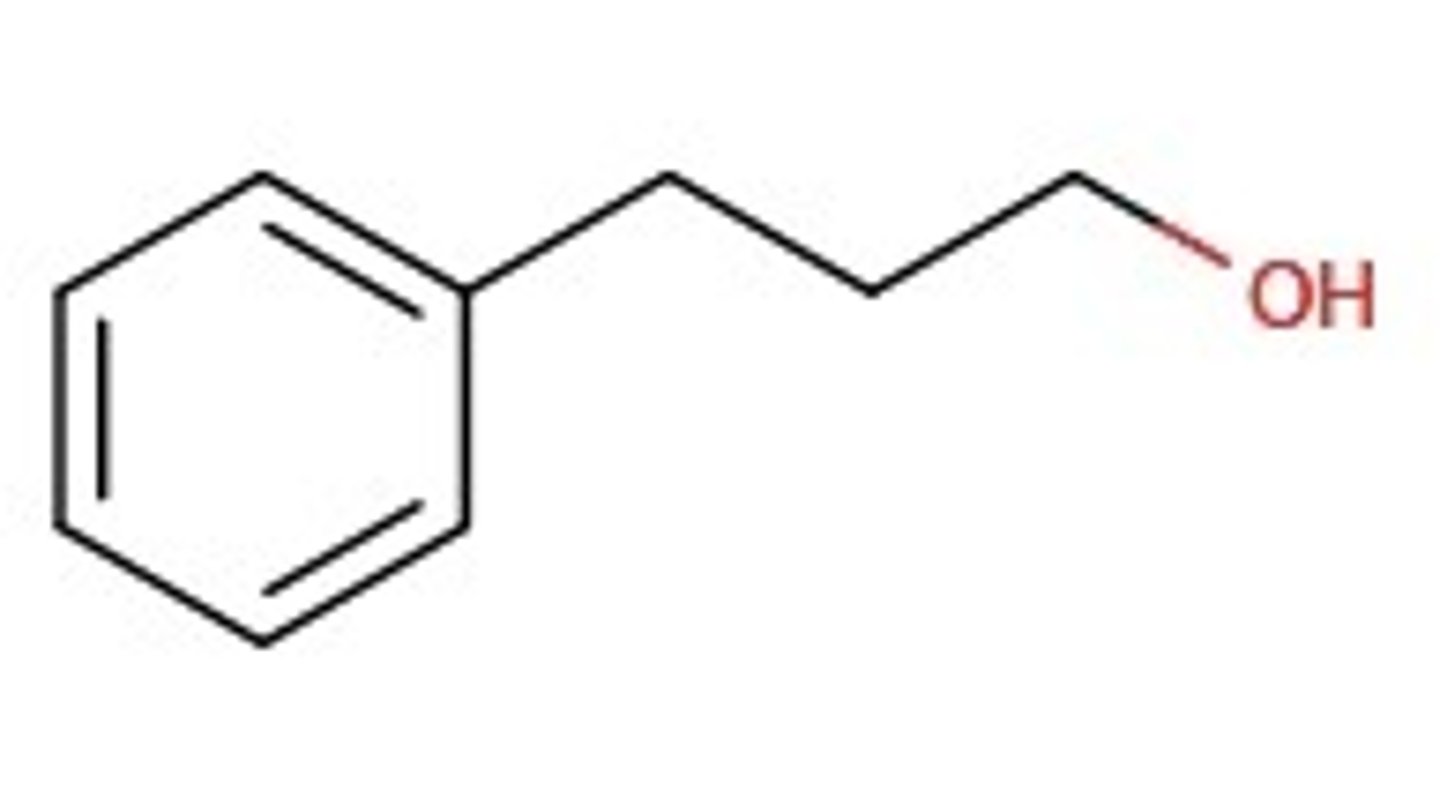
What happens if the hydroxyl group, -OH is bonded to a carbon side chain? Is it still phenol?
No, the organic compound is now an alcohol
What occurs when phenol dissolves in water? What does it act as?
- Phenol partially dissociates into an phenoxide ion + H+ (proton)
- Phenol therefore acts as a weak acid
What is the order of acidity between phenols and carboxylic acids and alcohols?
- Carboxylic acids dissociate more H+ ions than phenols
- Phenols dissociate more H+ ions than alcohols
- Therefore phenols is less acidic than a carboxylic acid but more acidic than alcohols
- Carboxylic acid > Phenols > Alcohols (acidity <--)
What types of bases can alcohols (i.e. ethanol) react with?
Neither a strong base or a weak base
What types of bases can phenols react with?
As a relatively weak acid, strong bases only, i.e. NaOH
What types of bases can carboxylic acids react with?
Strong or weak bases
What reaction can be used to distinguish between a phenol and a carboxylic acid?
Reaction with weak base sodium carbonate
Which organic compound, phenols or carboxylic acids, will react with sodium carbonate?
Only carboxylic acids
What are the observations of the reaction of carboxylic acids and sodium carbonate?
- Carbon dioxide
- Fizzing of bubbles
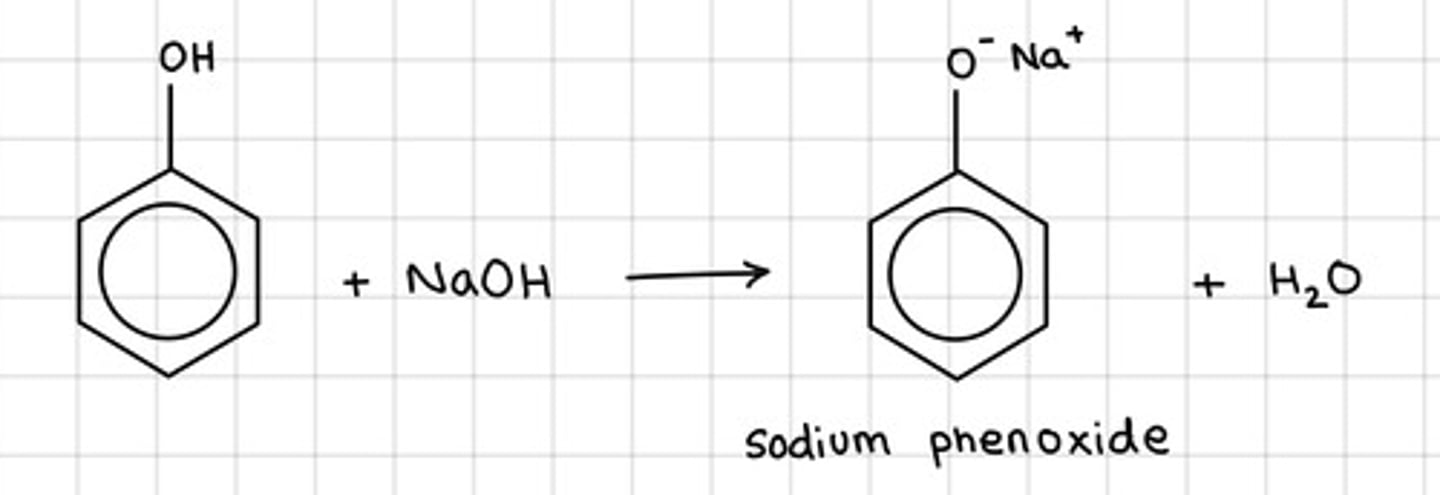
What occurs when phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide?
A neutralisation reaction occurs
Draw the equation of the reaction of sodium hydroxide with phenol, draw displayed structures for organic compounds, state symbols not required
Can the bromination and nitration of phenol also occur?
Yes
Draw the reaction of phenol with bromine, what forms and what temperature does this reaction occur at?
- A white precipitate
- Room temperature
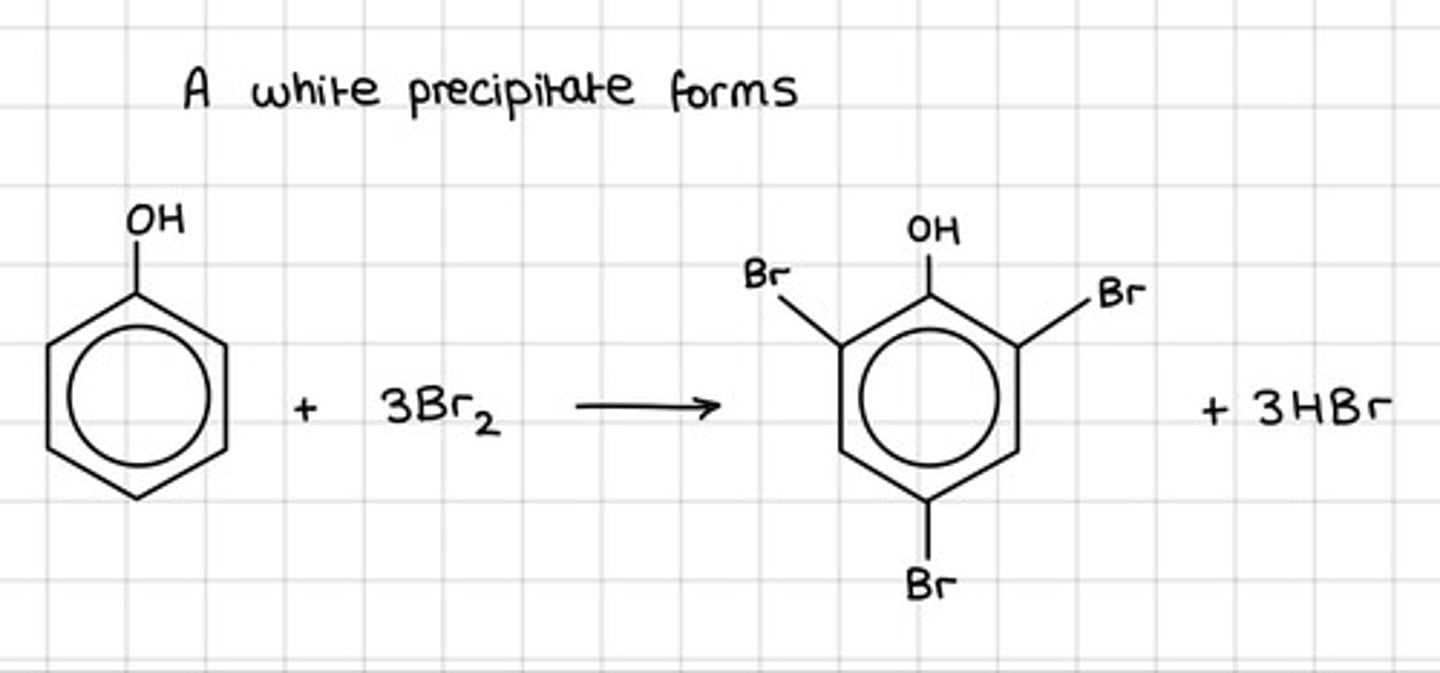
Is a halogen carrier required in the bromination of phenol?
No
What colour change occurs in the bromination of phenol?
- Bromine is decolourised
- Orange to colourless
Draw the reaction of phenol with nitric acid, what forms and at what temperature does this occur at?
Room temperature
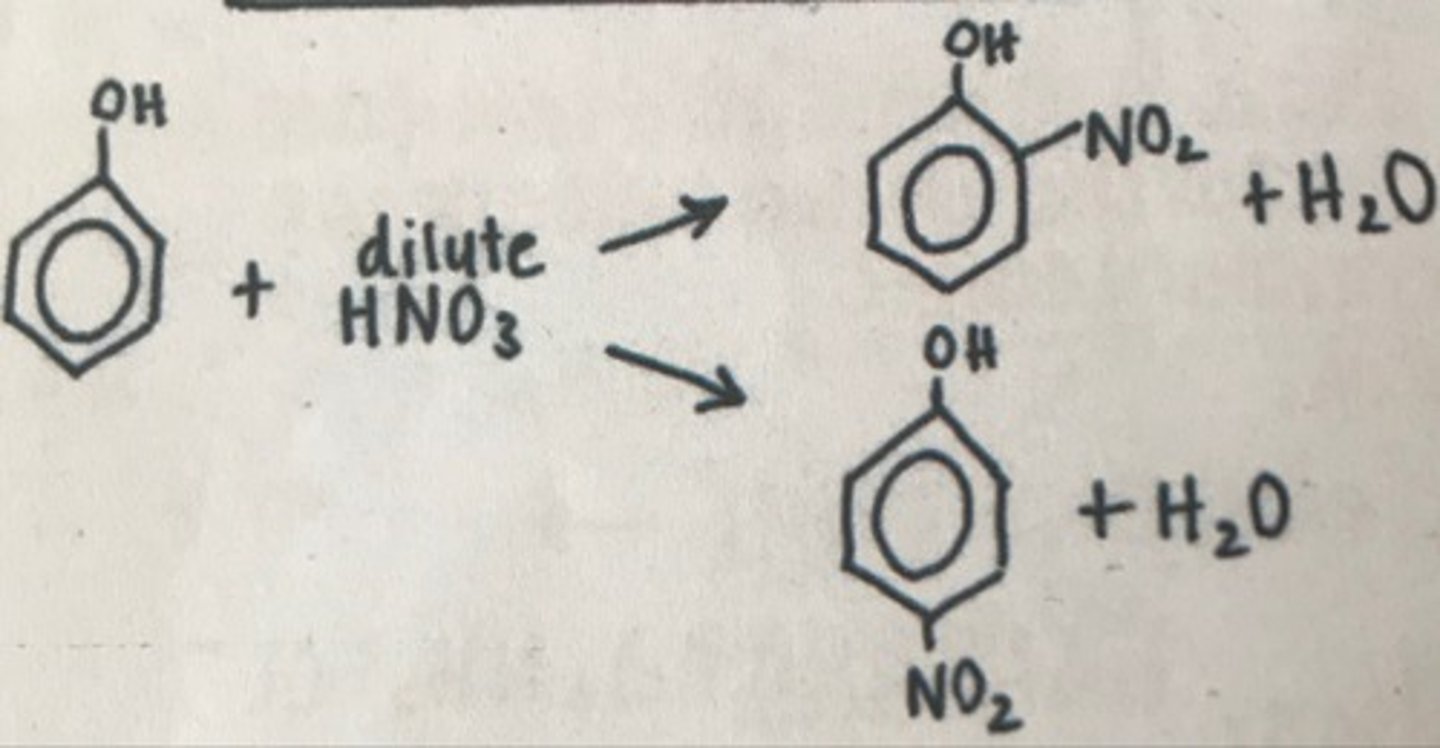
Why does phenol react more readily than benzene?
- The lone pair of electrons from the OH group (in oxygen p-orbital) in phenol is donated to the delocalised π aromatic ring system
- Therefore the electron density increases and the phenol can attract non-polar molecules more strongly than benzene
- Therefore phenol undergoes electrophilic substitution more readily than benzene as the aromatic ring in phenol is more susceptible to attack
What is activation of the benzene ring?
A functional group causes an aromatic ring to react more readily with electrophiles than a deactivating group.
What is the deactivation of the benzene ring?
A functional group causes an aromatic to react less readily with an electrophile than an activating group
In an activating group, what increases?
- Rate of reaction
- Extent of substitution
- Position of substitution on the benzene ring
What is directing effect?
How a functional group attached directly to an aromatic ring determines which carbon atoms are more likely to undergo substitution
Which functional groups causes 2, 4, 6 directing groups? (activating)
Only ortho and para (carbons 2,4,6)
- NH2 (Amine)
- OH (Phenol)
- ROR (ester)
- R (Alkyl chain)
- Halogen
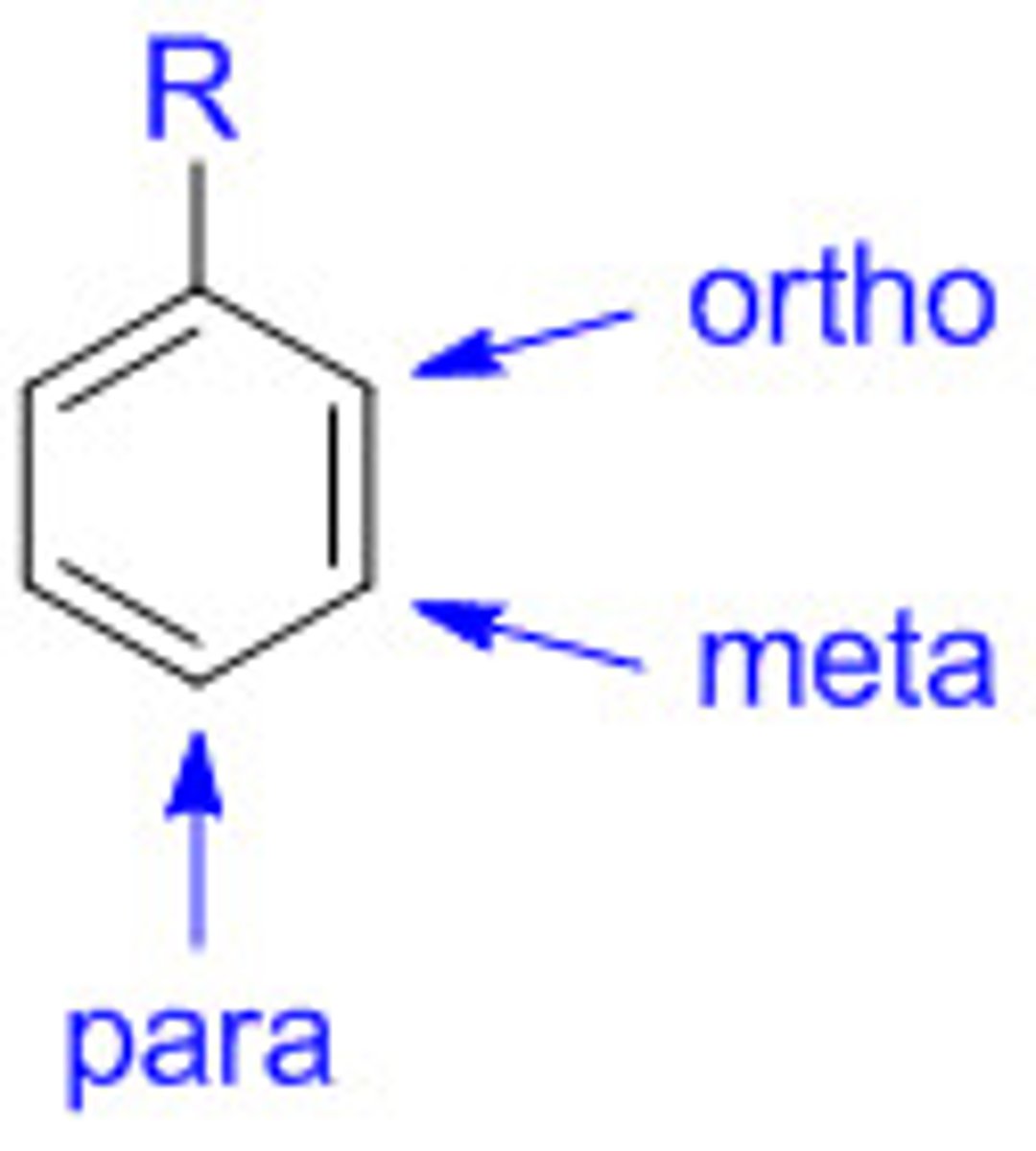
What functional groups causes 3, 5 directing groups? (deactivating)
Only Meta (carbons 3, 5);
- RCOR (ketone)
- COOR
- SO3H
- CHO (aldehyde)
- COOH (carboxylic acid)
- CN (Nitrile)
- NO2 (Nitrate)
- NR3+ (i.e. ammonia group)
What is a carbonyl group?
C=O group
What are two common carbonyl groups in chemistry A level?
- Aldehydes
- Ketones
(carboxylic acids do not count)
Draw the oxidation reaction of aldehydes,
- For organic compounds, use a displayed formulae
- Show all reagents and conditions
- Over your arrow; K2Cr2O7/H2SO4
- Under your arrow show reflux
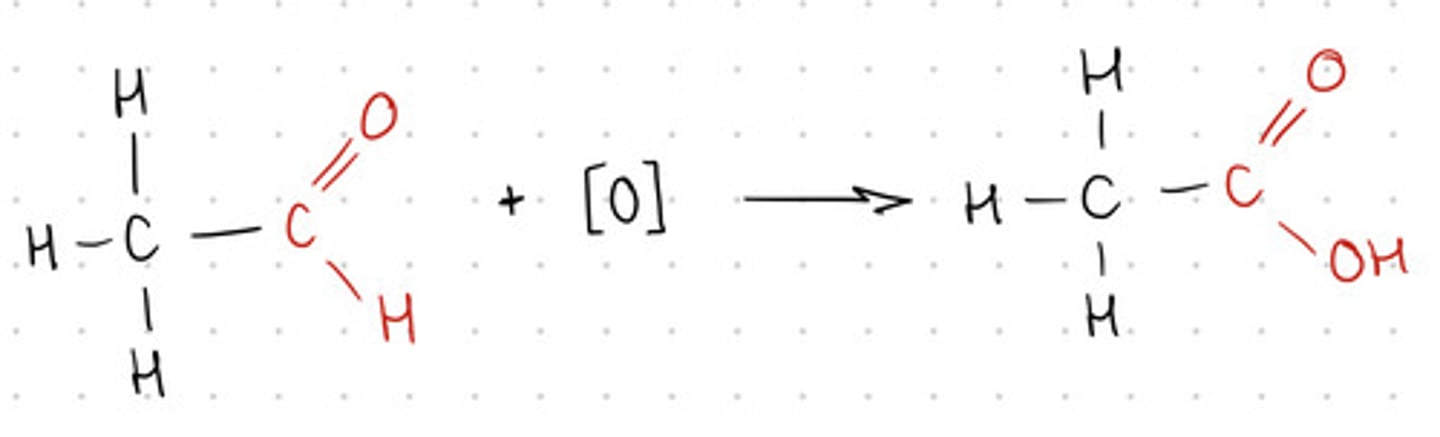
Draw the oxidation of ketones,
- For organic compounds, use a displayed formulae
- Show all reagents and conditions
Ketones do not undergo oxidation
What makes a C=O bond (carbonyl group) similar to a C=C bond?
- Both have a bond
- Both have a σ bond
What makes a a C=O bond (carbonyl group) different to a C=C bond?
- C=O bond is polar
- C=C bond is non-polar
- C=O bonds undergo nucleophilic addition
- C=C bonds undergo electrophilic addition
What does the polarity between C=O mean in terms of difference of electronegativity?
- Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon
- Therefore the electron density is closer to the oxygen atom
- Therefore oxygen is ∂- and carbon is ∂+
Due to the dipoles in a carbonyl group, what type of mechanism can carbonyls undergo?
Nucleophilic addition
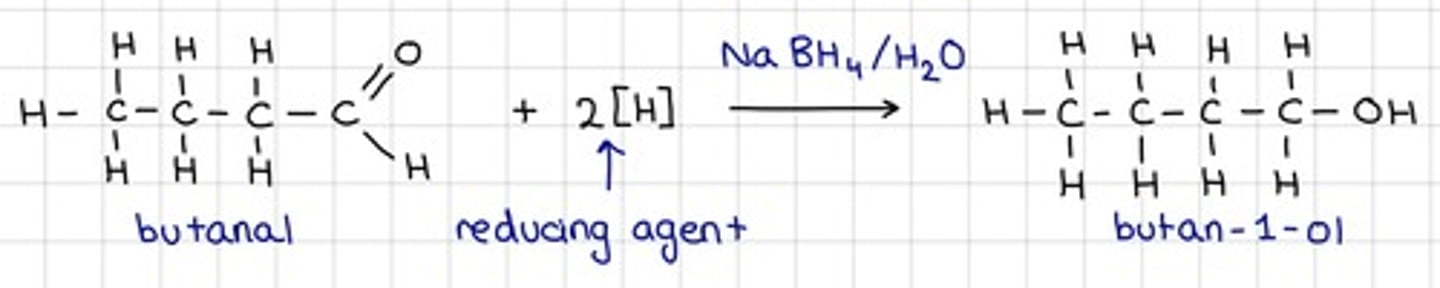
Draw the equation of the reaction of Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III), NaBH₄ with an aldehyde
- Show all reagents
- Show all conditions
- For organic structures, use displayed formulae
- No mechanism is required
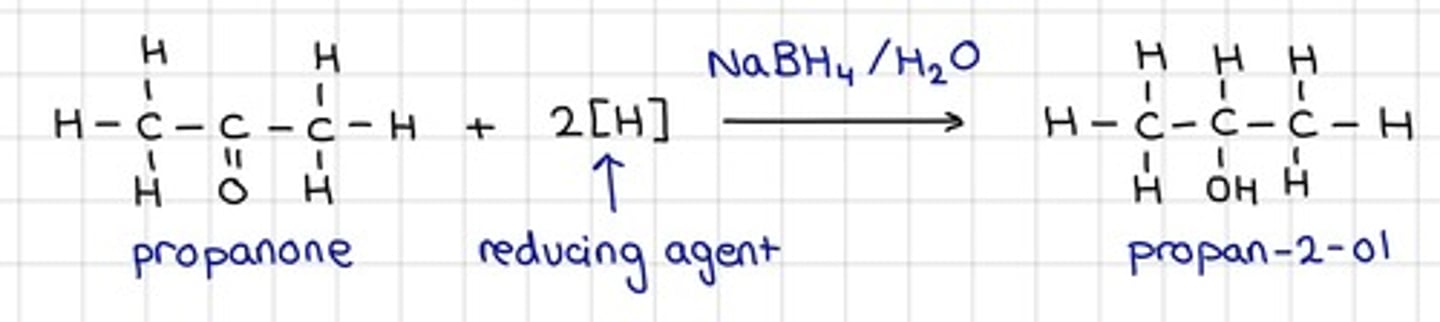
Draw the equation of the reaction of Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III), NaBH₄ with a ketone
- Show all reagents
- Show all conditions
- For organic structures, use displayed formulae
- No mechanism is required
Show the mechanism for the reduction of either carbonyl compound (ketone or carboxylic acid) to an alcohol
You may use water however show all relevant dipoles and the end product of OH- at the end
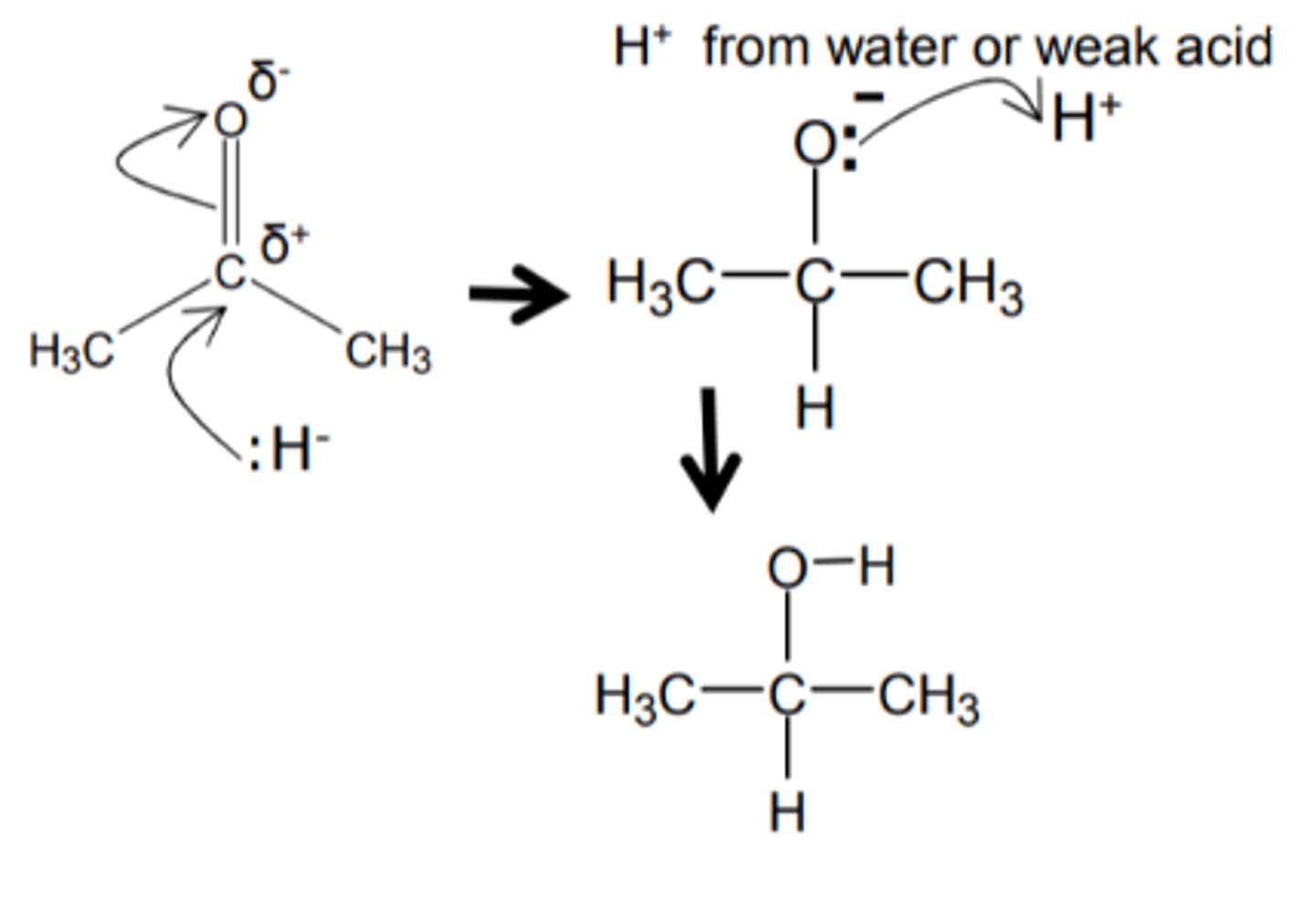
What does the hydride ion act as in the mechanism for a carbonyl?
An electron pair donor; a nucleophile
Why can't hydrogen cyanide be used in a laboratory?
Hydrogen cyanide is;
- An extremely poisonous liquid
- Boils slightly over room temperature
- Therefore unsafe
What can be used instead of hydrogen cyanide in a laboratory?
- Sodium cyanide
- Potassium cyanide
Is the use of sodium or potassium cyanide safe?
No, still hazardous
Why is the reaction with sodium or potassium cyandie useful?
It can increase the carbon chain length
Draw the equation of propanal with potassium cyanide, include;
- All reagents
- All conditions
- Show displayed formulae for organic compounds
- Mechanism is not required
- Sodium/Potassium cyanide is show as a reactant (not shown in this picture)
- H2SO4 is used to provide H+
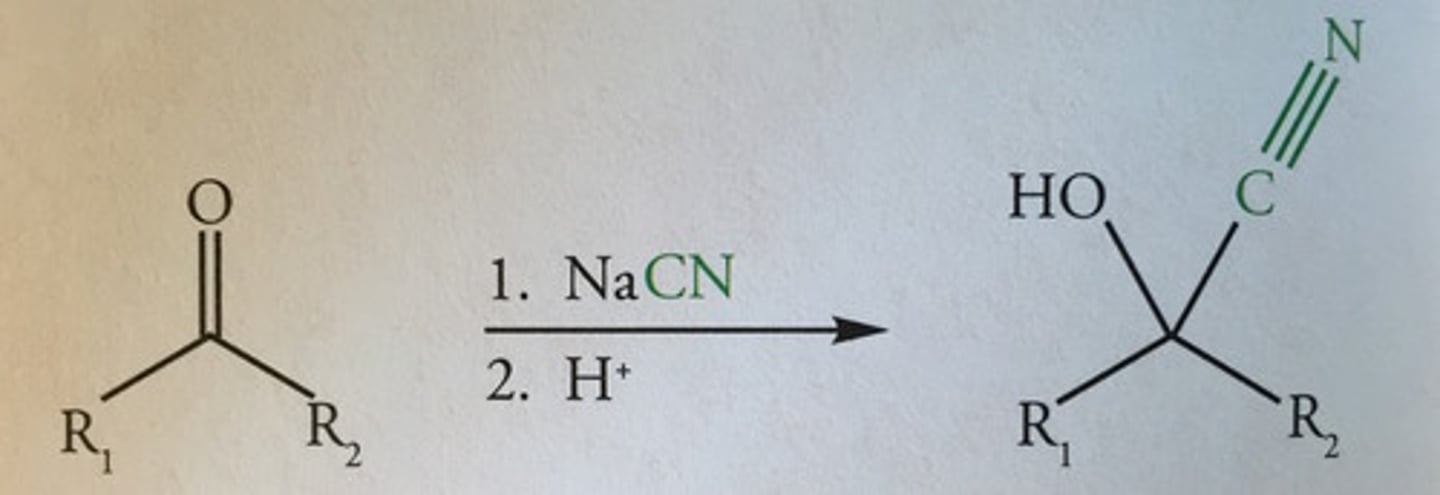
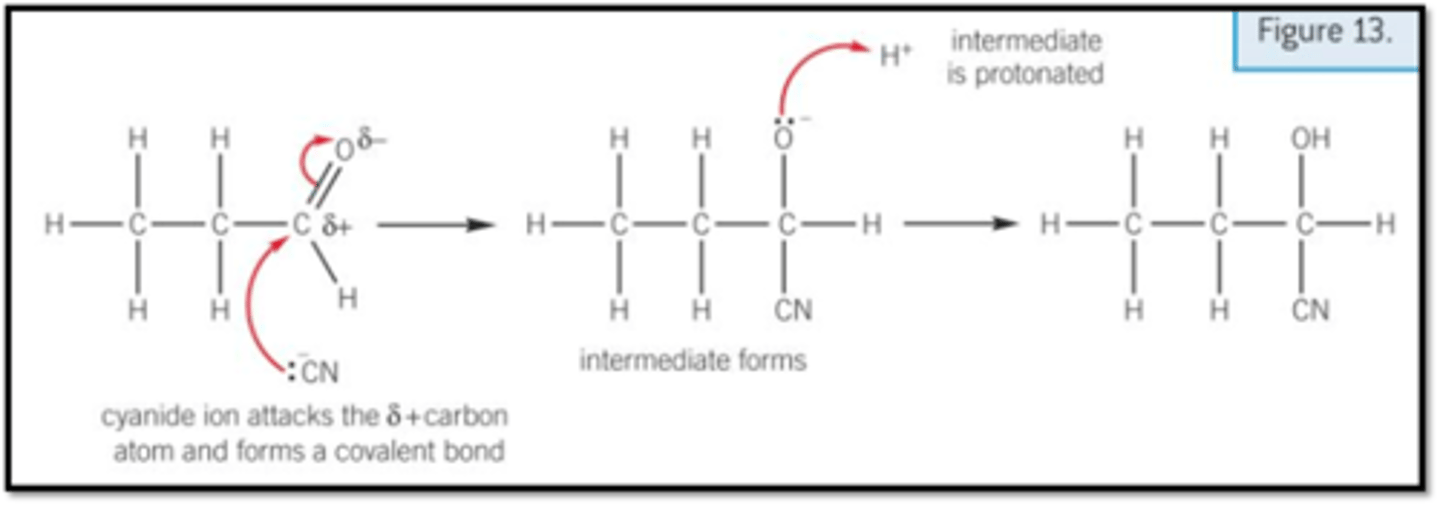
Show the mechanism for the reaction of propanal with cyanide ions to form hydroxynitrile
What is 2,4-DNP?
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
What is 2,4-DNP also known as?
Brady's reagent
What is Brady's reagent used to detect?
The presence of a carbonyl functional group of aldehydes and ketones
What is 2,4-DNP dissolved in? Why?
- Dissolved in methanol and sulphuric acid
- Solid 2,4-DNP can explode with sudden friction
Describe the process and steps of testing for a carbonyl group
1) Add 2,4-DNP to a test tube
2) Add three drops of your unknown compound to the test tube
3) If no crystal form, add a few drops of sulphuric acid
4) Orange precipitate indicated the presence of a carbonyl group
What test is used to distinguish between a ketone or aldehyde carbonyl group?
Tollens reagent
In the presence of an aldehyde, what is the observation of Tollen's reagent?
A silver mirror
When does a silver mirror of Tollen's reagent form? (repeated question)
An aldehyde
What is Tollen's reagent made up of?
Silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia
Describe the process of the preparation of Tollen's reagent
1) Add aqueous silver nitrate AgNO3(aq) to a test tube
2) Add aqueous sodium hydroxide to the silver nitrate until a brown precipitate of silver oxide Ag2O is formed
3) Add dilute ammonia solution until the brown precipitate dissolves to form a clear colourless solution, Tollens reagent
Describe the process (steps) of Tollen's reagent and all observations
1) Pour your unknown compound and your Tollen's reagent into a clean test tube
2) Put the test tube in warm water of 50 ˚C for 15 minutes,
3) Presence of silver mirror indicates an aldehyde is present
Show the half equations of oxidation and reduction between the aldehyde and silver ion
(Ag+ (aq)) + e- --> Ag(s)
RCOH + [O] --> RCOOH
What is another way, other than the combination of Brady's and Tollens reagents to identify a ketone and aldehyde?
- Use Brady's reagent to know which samples are carbonyls
- Use known melting points of 2,4-DNP derivatives to crystallise of your samples
When naming a carboxylic acid, will the carbon. of the carboxyl group always be first or last?
First
Why are carboxylic acid soluble in water?
Following the same rules applied for hydroxyl;
- ∂ negative oxygen and ∂ positive hydrogen on the carboxyl group will allow hydrogen bonding to take place
- As the non-polar carbon length increases with a singular carboxyl group, effect on solubility from the carboxyl functional group decreases
Are carboxylic acids strong or weak acids?
Weak acids, partially dissociate H+(aq) ions
As a weak acid, what can carboxylic acids react with?
- Redox reactions with metals
- Neutralisation reactions with bases
After dissociation, what does the suffix of a carboxylic acid change to?
From -oic to -ate
Show the redox reaction between propanoic acid and magnesium
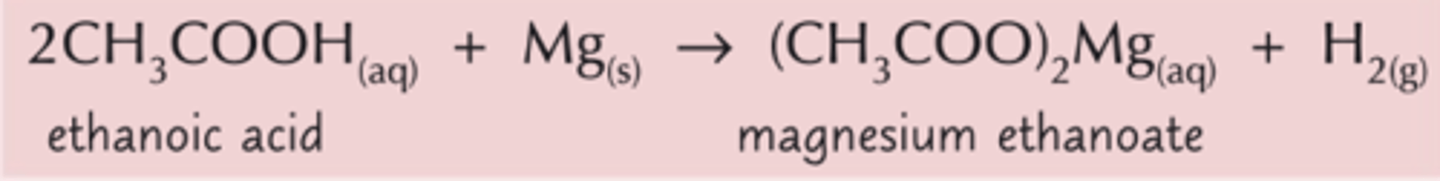
Can weak acid carboxylic acids react with weak bases?
Yes, i.e. carbonate salts
Show the reaction between ethanoic acid and calcium oxide
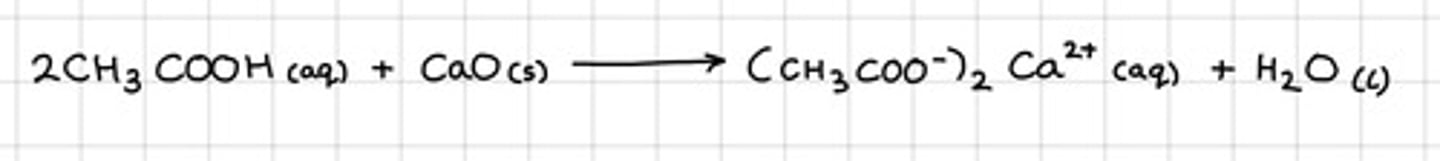
Show the reaction between methanoic acid and sodium hydroxide
