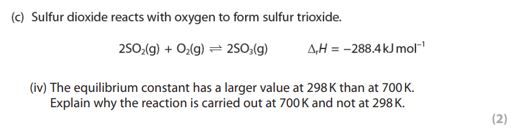Chemistry - Topics 10&11 - Equilibrium I + II
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what are the two conditions for dynamic equilibrium?
the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and both are non-zero
the concentration of the products and reactants remained unchanged
(both forward and reverse reactions are still occuring)
why does liquid water remain in the sealed container, but not in the open container?
in the open container, the reverse reaction cannot occur because the gaseous water escapes
this means dynamic equilibrium is not set up (so the amount of liquid water gradually decreases to zero rather than some non-zero value)
what is Le Chatelier’s Principle?
a chemical reaction at dynamic equilibrium will ‘respond’ to a change made to it by shifting the position of equilibrium to oppose that change
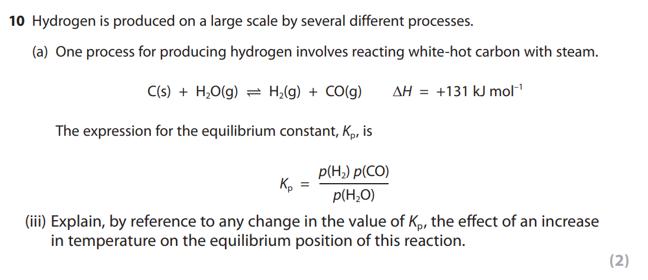
what does an increase in temperature do to the position of equilibrium?
if the temperature of the equilibrium mixture is increased, the position of equilibrium will shift in the direction of the endothermic reaction, since this leads to a decrease in temperature and hence opposes the change.
what does a decrease in temperature do to the position of equilibrium?
if the temperature of the equilibrium mixture is decreased, the position of equilibrium will shift in the direction of the exothermic reaction, since this leads to an increase in temperature and hence opposes the change.
what does the addition of a catalyst do to the position of equilibrium?
a catalyst increases the rate of the forward reaction and the rate of the reverse reaction by the same amount, so the rates remain equal. this means the system remains at equilibrium, so there is no shift in equilibrium position.
what colour is NO₂
brown
what colour is N₂O₄ gas?
colourless
what colour is solid calcium hydroxide?
white
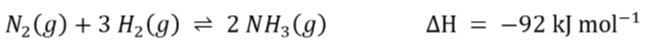
explain why a temperature of 450 degrees Celsius is used, rather than a higher or lower temperature:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g) ΔH = -92kJ/mol
rate:
higher temperature increases rate of reaction
as the particles move faster so there are more frequent successful collisions
yield:
lower temperature increases yield
because the forward reaction is exothermic (depends on question), so decreasing the temperature shifts the position of equilibrium to the right
cost:
higher temperatures are more expensive to maintain due to energy costs
so 450 degrees Celsius is a compromise temperature
explain why a pressure of 200 atm is used, rather than a higher or lower pressure:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) ⇌ 2NH₃(g) ΔH = -92kJ/mol
rate: higher pressure increases rate (more particles in same volume, more frequent collisions)
yield: higher pressure increases yield (because there are fewer moles of gas on the right, so higher pressure shifts equilibrium to the right)
higher pressures than 200atm are very expensive and dangerous to maintain
*due to hydrogen gas being present in the mixture
explain the benefits of using a catalyst in industrial processes
it increases the rate of reaction and therefore allows lower temperatures (and pressures) to be used
does not affect yield
can be reused
what is a homogenous equilibrium?
an equilibrium where all substances are in the same state/phase
there is no phase boundary
what is a heterogenous equilibrium?
an equilibrium where substances are in different states/phases
there is a phase boundary
how to write a Kc (concentration equilibrium constant) expression if this is the reaction:
a A(g) + b B(g) ⇌ c C(g) + d D(g)
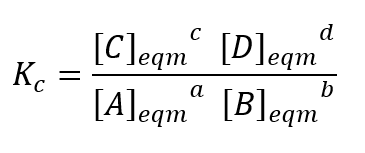
which species are not included in the Kc expression and why?
solids, because the concentration of a solid is constant (approximately)
One of the stages in the production of sulfuric acid from sulfide ores involves the oxidation of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide. The equation for the reaction is:
2SO₂(g) + O₂(g) ⇌ 2SO₃(g) ΔH = -197kJ/mol
The conditions used in one industrial process are: 420°C and a pressure of 1.7 atm together with a vanadium (V) oxide catalyst.
It is proposed to change the conditions to 600°C and 10 atm pressure, while still using the same catalyst.
* Evaluate the feasibility of each of these changes in terms of their effect on the rate, yield and economics of the reaction.
increase in temperature will increase rate of reaction as more particles have E≥Eₐ
but increase in temperature will decrease yield/move the position of equilibrium to the left/produce less SO₃ because the forward reaction is exothermic
increase in temperature increases energy costs
increase in pressure has no effect on rate (because all the active sites are already occupied on a heterogenous catalyst) OR increase in pressure will increase rate of reaction
increase in pressure will shift position of equilibrium to the right/increase yield because there are fewer moles of gas on the right
but increased pressure increases (construction and running) costs/reduces economic viability
what should you note about ICE tables?
do not do ICE tables for concentrations - ICE tables always work for moles
what can the Kc expression be equated to if Kc has no units?
replace concentrations with moles
Kc has to be unitless otherwise volumes will not cancel out
explain briefly what you could do to confirm that one week was sufficient time for equilibrium to be reached (measurement of Kc for an esterification)
repeat the experiment after 2 weeks
if 1 week was long enough, the same titre volume should be obtained and the same value of Kc should be calculated
explain what the effect of overshooting the endpoint would have on the calculated value for Kc (esterification)?
titre value too large
therefore calculated amount of ethanoic acid at equilibrium is too large
therefore calculated amount of ethanol too large and that of ester and water too low
hence calculated value of Kc too low
how to write a Kₚ (equilibrium constant expressed in terms of partial pressures) expression if this is the reaction:
a A(g) + b B(g) ⇌ c C(g) + d D(g)
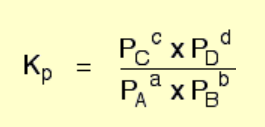
what is the mole fraction of A, xa, in the reaction mixture:
A(g) ⇌ B(g)
na/ntotal
how is the partial pressure of a gas, Pi, in a mixture related to its molar fraction in that mixture?
Pi = xiPtotal
what is the reaction quotient, Q?
the ratio of concentrations/partial pressures of products to concentrations/partial pressures of reactants (raised to the necessary power)
like Kc and Kp but not necessarily at equilibrium, just at a moment in time during the reaction
ΔG = ?
-RTlnK
what is the equilibrium constant dependent on?
only temperature
K = e-ΔG/RT
K is the same for constant temperature for a given reaction

Kₚ for a certain reaction at 298K is 2.00 × 10¹². state what the value of Kₚ suggests about the relative amounts of the components in the equilibrium mixture at 298K:
SO₂(g) + 1/2O₂(g) ⇌ SO₃(g)
the amount of SO₃ is much greater than the amounts of SO₂ and O₂
as Kₚ greater than 1 × 10 the equilibriums lies completely to the right/reaction goes to completion
explain, in terms of Kₚ, how an increase in temperature will affect the yield of sulphur trioxide in the equilibrium mixture:
SO₂(g) + 1/2O₂(g) ⇌ SO₃(g) ΔH = -98.0kJ/mol
Kₚ decreases because the forward reaction is exothermic (becauses as temperature increases Kₚ decreases - mark scheme version)
Q remains the same
Q > K
so products must be converted to reactants (so Q decreases)
so equilibrium shifts to the left until Q = K again
therefore yield of sulphur trioxide decreases
give a reason why, in industry, the reaction is carried out at a temperature of 678K:
SO₂(g) + 1/2O₂(g) ⇌ SO₃(g) ΔH = -98.0kJ/mol at 298K
the rate of reaction is increased (even though the yield is less)
the equilibrium constant has a larger value at 298K than at 700K. explain why the reaction is carried out at 700K and not at 298K.
even though the percentage yield of the product is higher at 298K
the rate of reaction is slower at 298K
The reversible reaction between hydrogen chloride and oxygen produces water vapour and chlorine.
4HCl(g) + O₂(g) ⇌ 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂(g)
ΔH = -114kJ/mol
Explain what effect, if any, each of the following changes has on the yield of chlorine at equilibrium and on the equilibrium constant, Kp:
an increase in the total pressure
an increase in total pressure will shift the position of equilibrium to the right where there are fewer moles of gas (as this shift opposes the change to the system)
therefore, the yield of chlorine at equilbrium will increase
Kp will remain unchanged because temperature is constant
The reversible reaction between hydrogen chloride and oxygen produces water vapour and chlorine.
4HCl(g) + O₂(g) ⇌ 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂(g)
ΔH = -114kJ/mol
Explain what effect, if any, each of the following changes has on the yield of chlorine at equilibrium and on the equilibrium constant, Kp:
an increase in the temperature
due to the increase in temperature, Kp will decrease, because the forward reaction is exothermic
the yield of chlorine at equilibrium will decrease because the forward reaction is exothermic (position of equilibrium shifts to the left in direction of endothermic reaction)
The reversible reaction between hydrogen chloride and oxygen produces water vapour and chlorine.
4HCl(g) + O₂(g) ⇌ 2H₂O(g) + 2Cl₂(g)
ΔH = -114kJ/mol
Explain what effect, if any, each of the following changes has on the yield of chlorine at equilibrium and on the equilibrium constant, Kp:
the use of a catalyst
using a catalyst will increase the rate of the forward and reverse reaction by the same amount
therefore, the yield of chlorine will remain unchanged
Kp will remain unchanged because temperature is constant
what is the value of the equilibrium constant not affected by?
changes in concentration
changes in pressure
the addition of a catalyst