IGCSE Chemistry
1/329
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
330 Terms
What is melting?
When a solid changes into a liquid

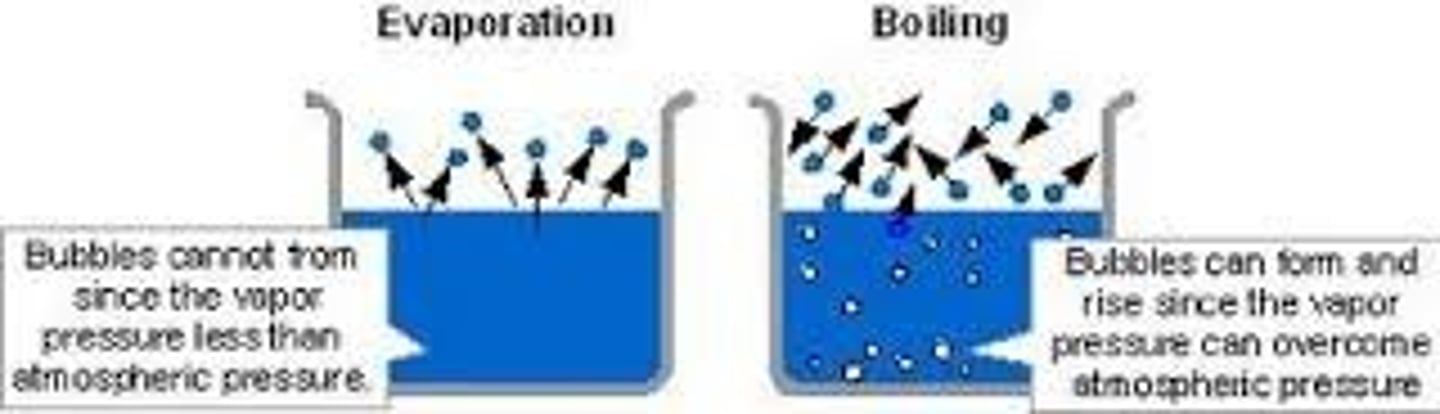
What is boiling?
When a liquid changes into a gas (from below surface as well as at surface)

What is freezing?
When a liquid changes into a solid
What is evaporation?
When a liquid changes into a gas (at surface only)

What is condensation?
When a gas changes into a liquid

What is sublimation?
When a solid changes directly into a gas

What is deposition?
When a gas changes into a solid
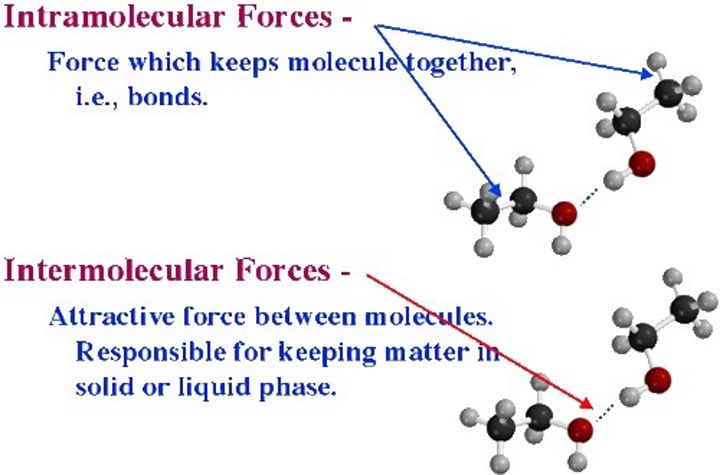
What are intermolecular forces?
Forces between molecules
What is a solution?
The mixture formed when a solute has dissolved in a solvent
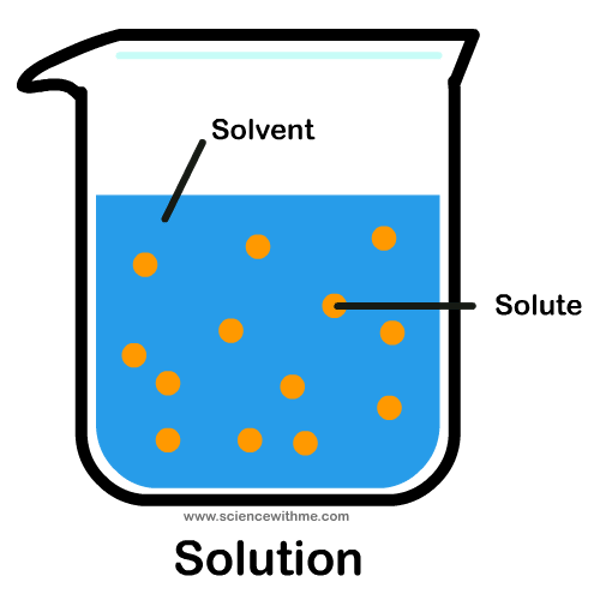
What is a solute?
Substance being dissolved
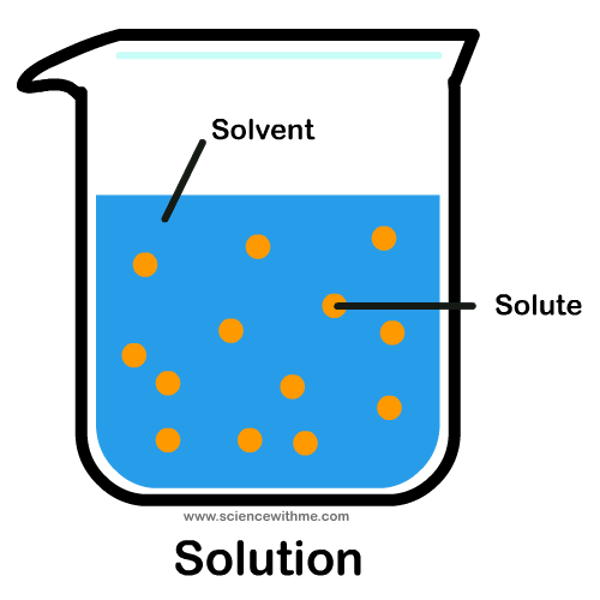
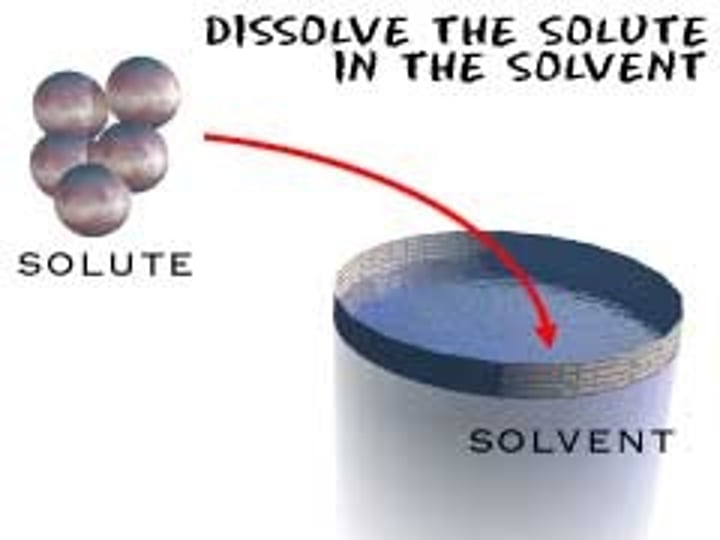
What is a solvent?
Substance where the solute is dissolved
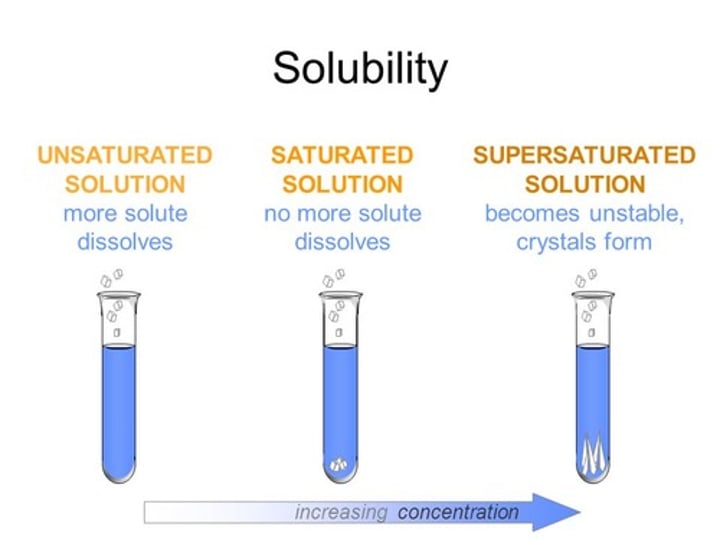
What is a saturated solution?
A solution that contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute
What is a soluble substance?
A substance that dissolves in a solvent

What is an insoluble substance?
A substance that can't be dissolved

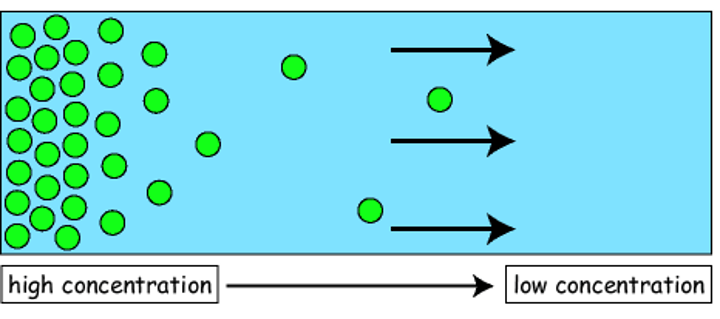
What is diffusion?
Net movement of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
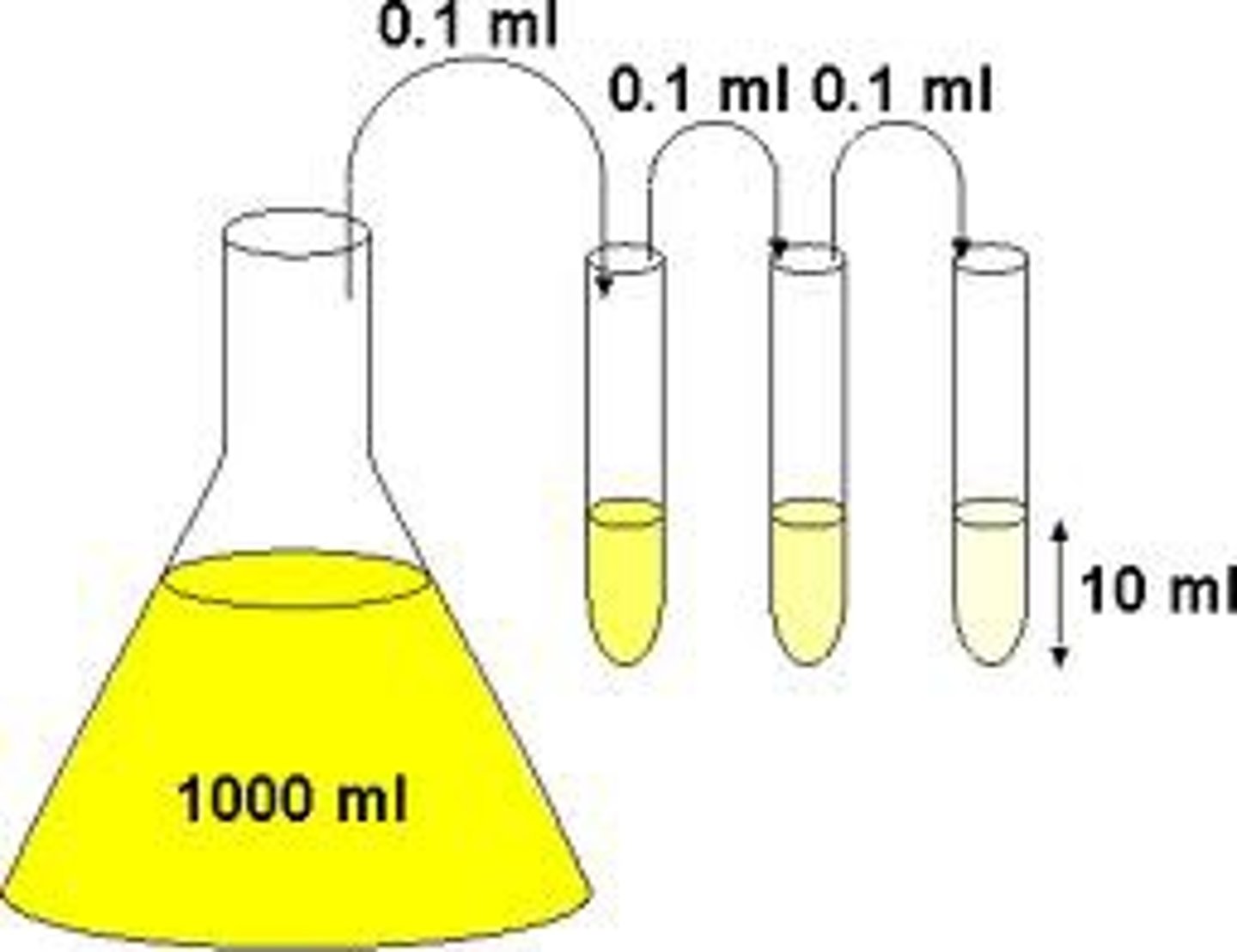
What is dilution?
Mixing a substance with a solvent to make it less concentrated
What is Brownian motion?
When particles in fluids move randomly because they are bombarded by other moving particles
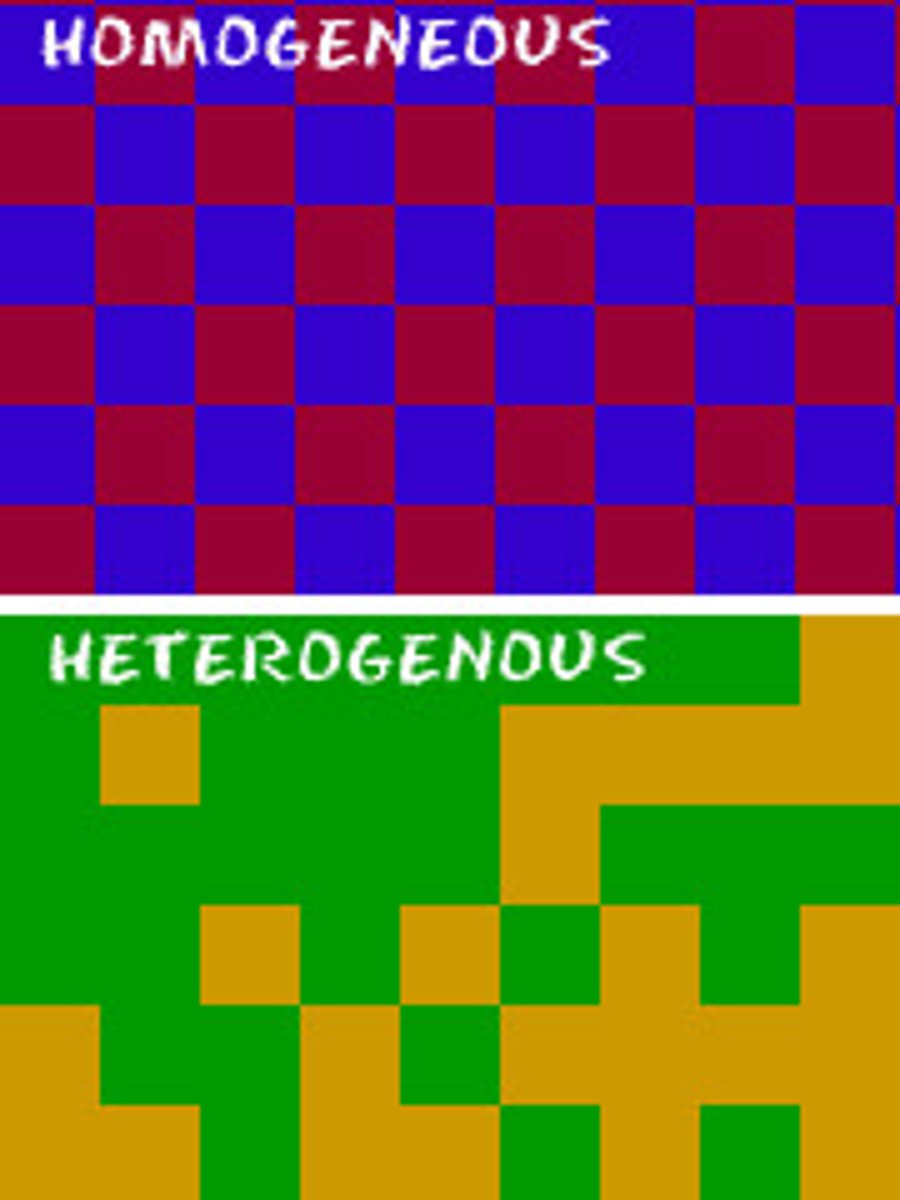
What is a homogeneous mixture?
A mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout

Why doesn't diffusion happen in solids?
Because the particles don't move
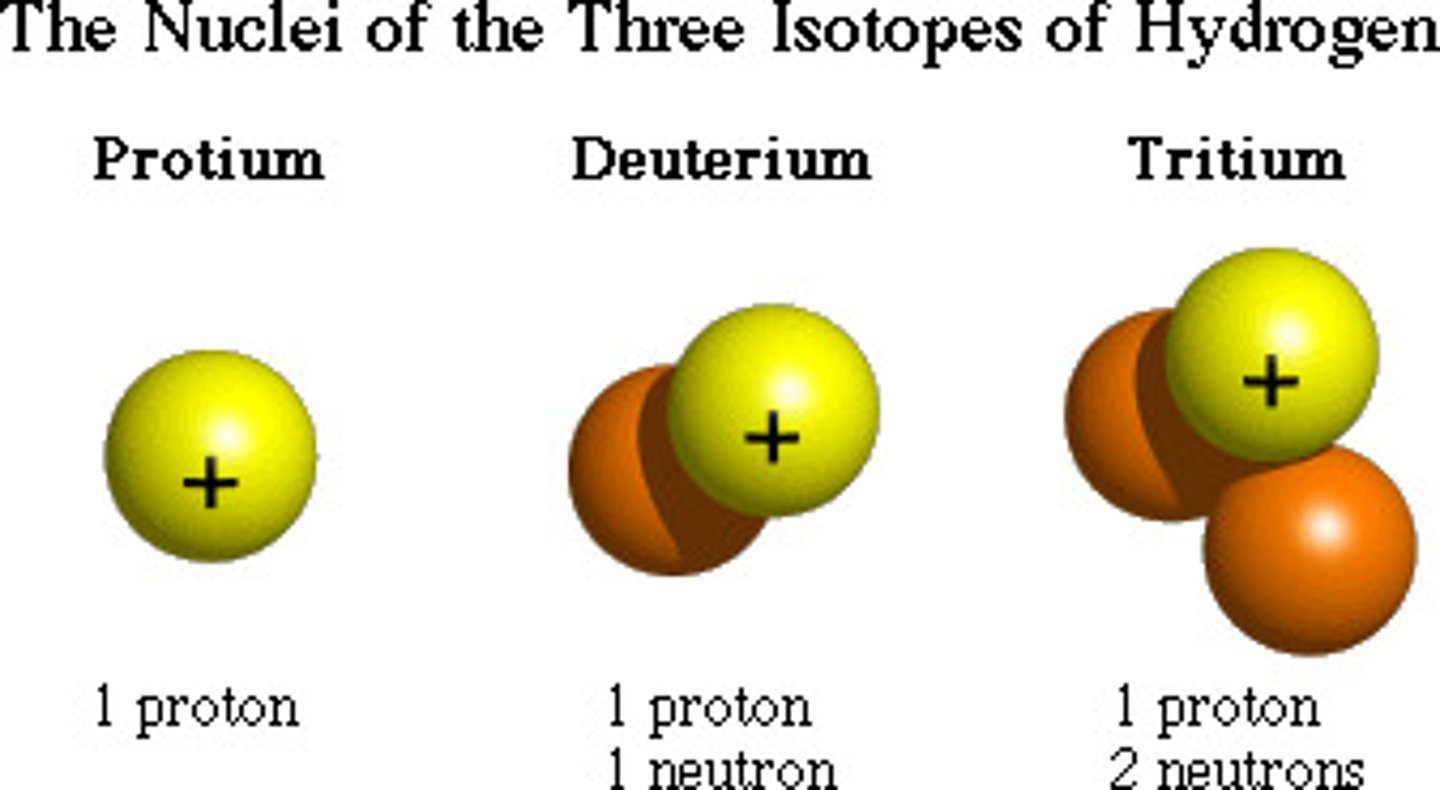
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
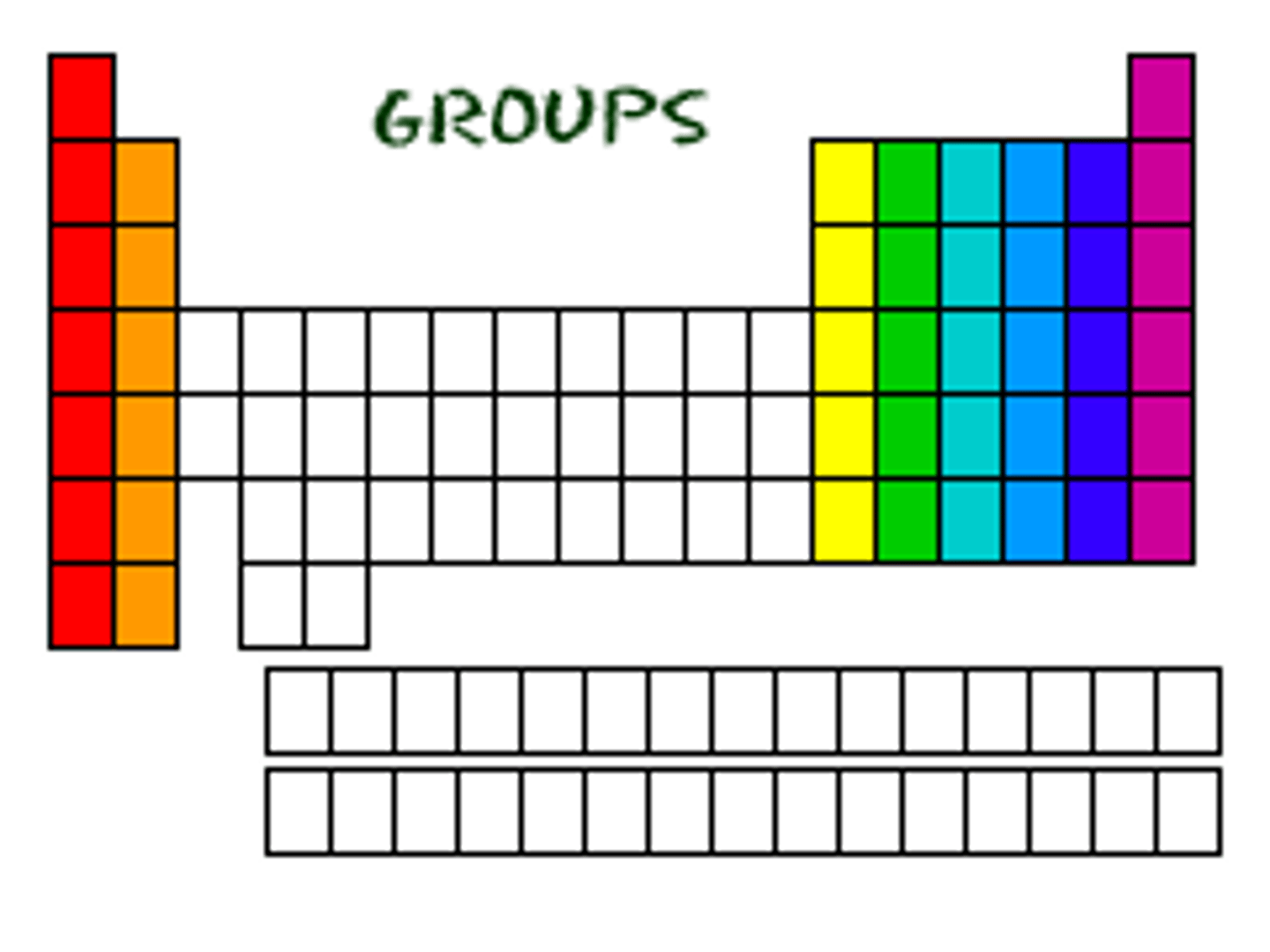
What does the group number tell you?
How many electrons are in the outer shell
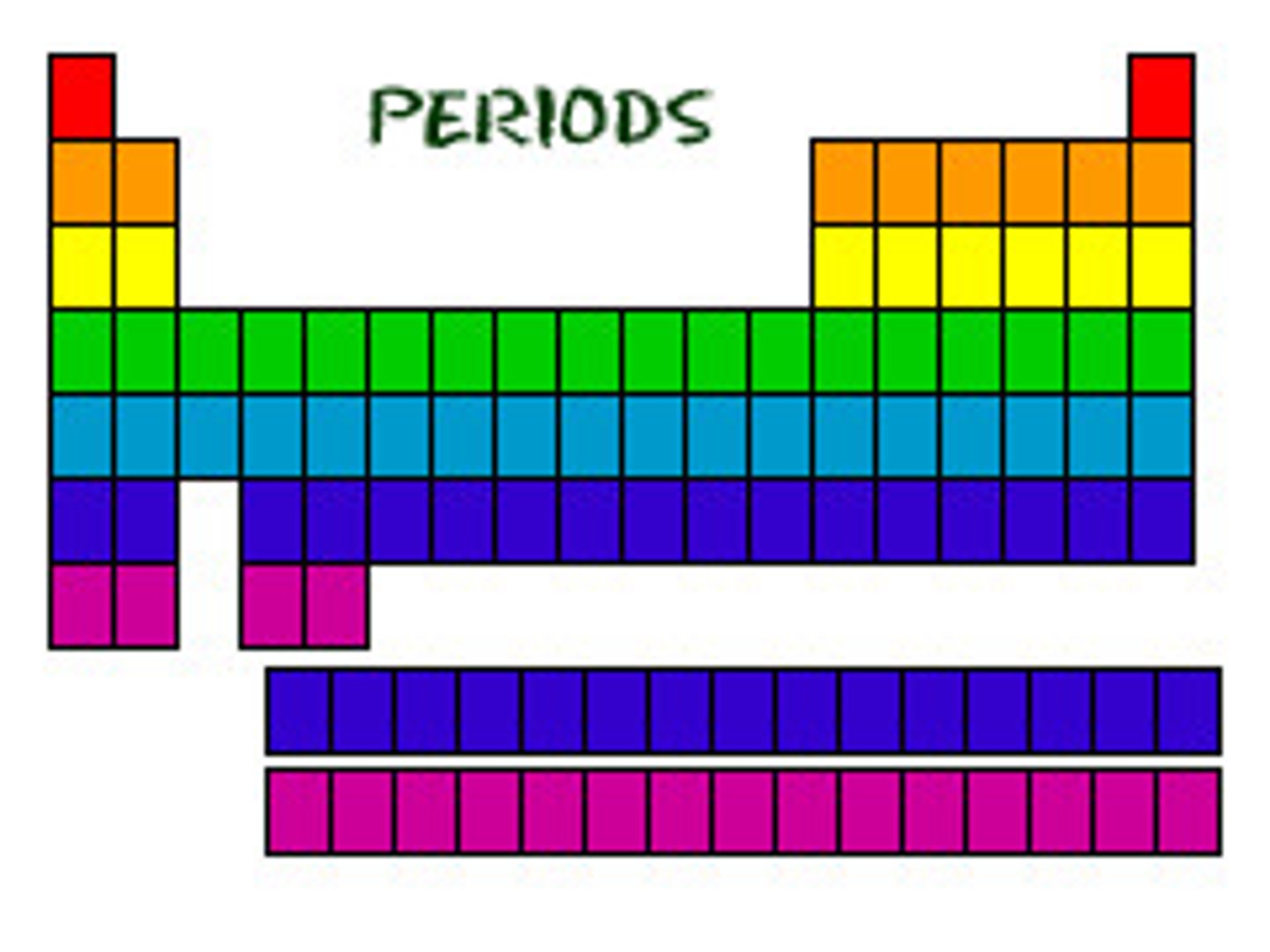
What does the period number tell you?
Number of shells
Why do atoms want a full outer shell?
So they can become more stable
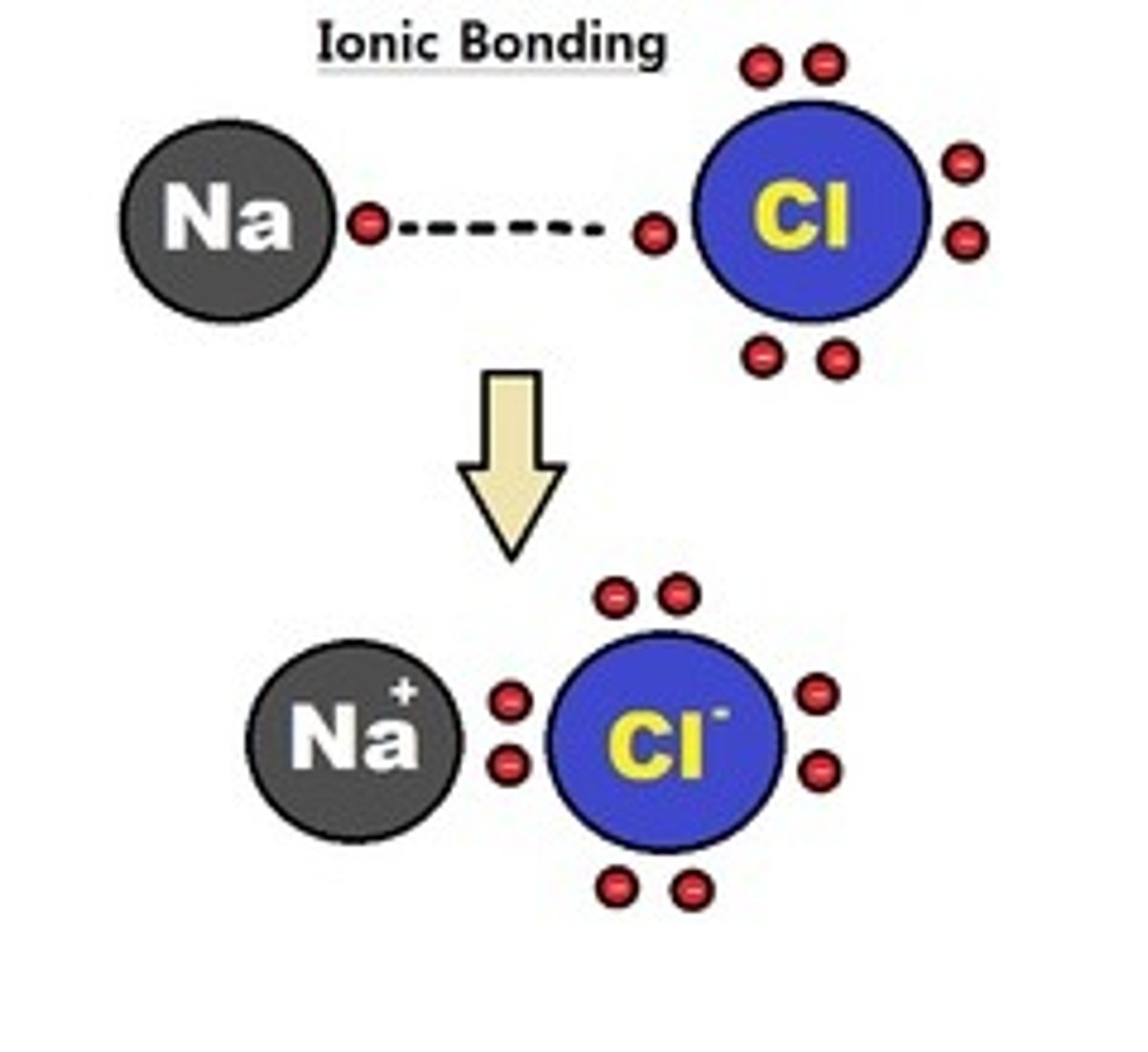
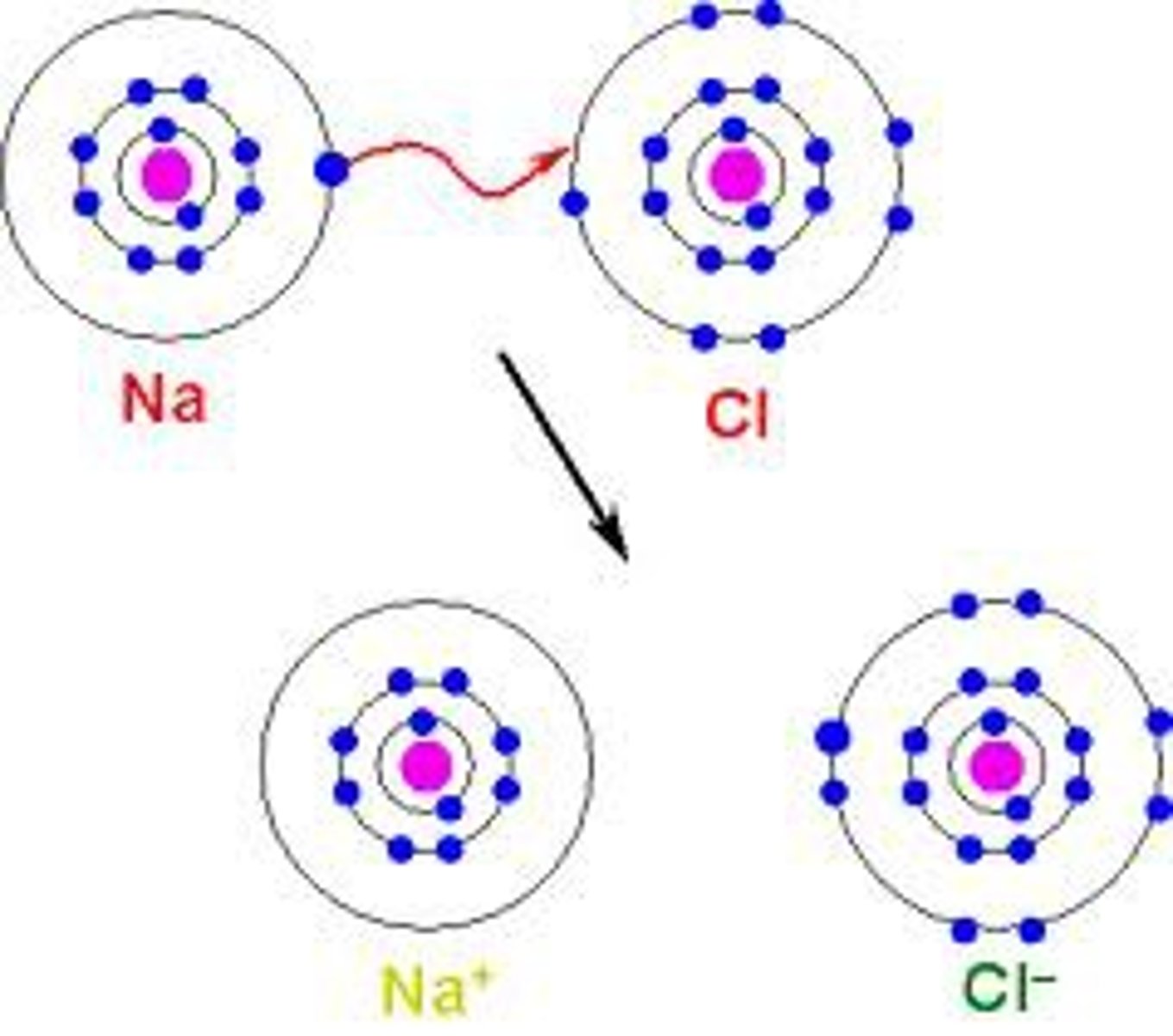
What is ionic bonding?
Transfer of electrons between a metal and a non-metal
What is electrostatic attraction?
Attraction between opposite charges
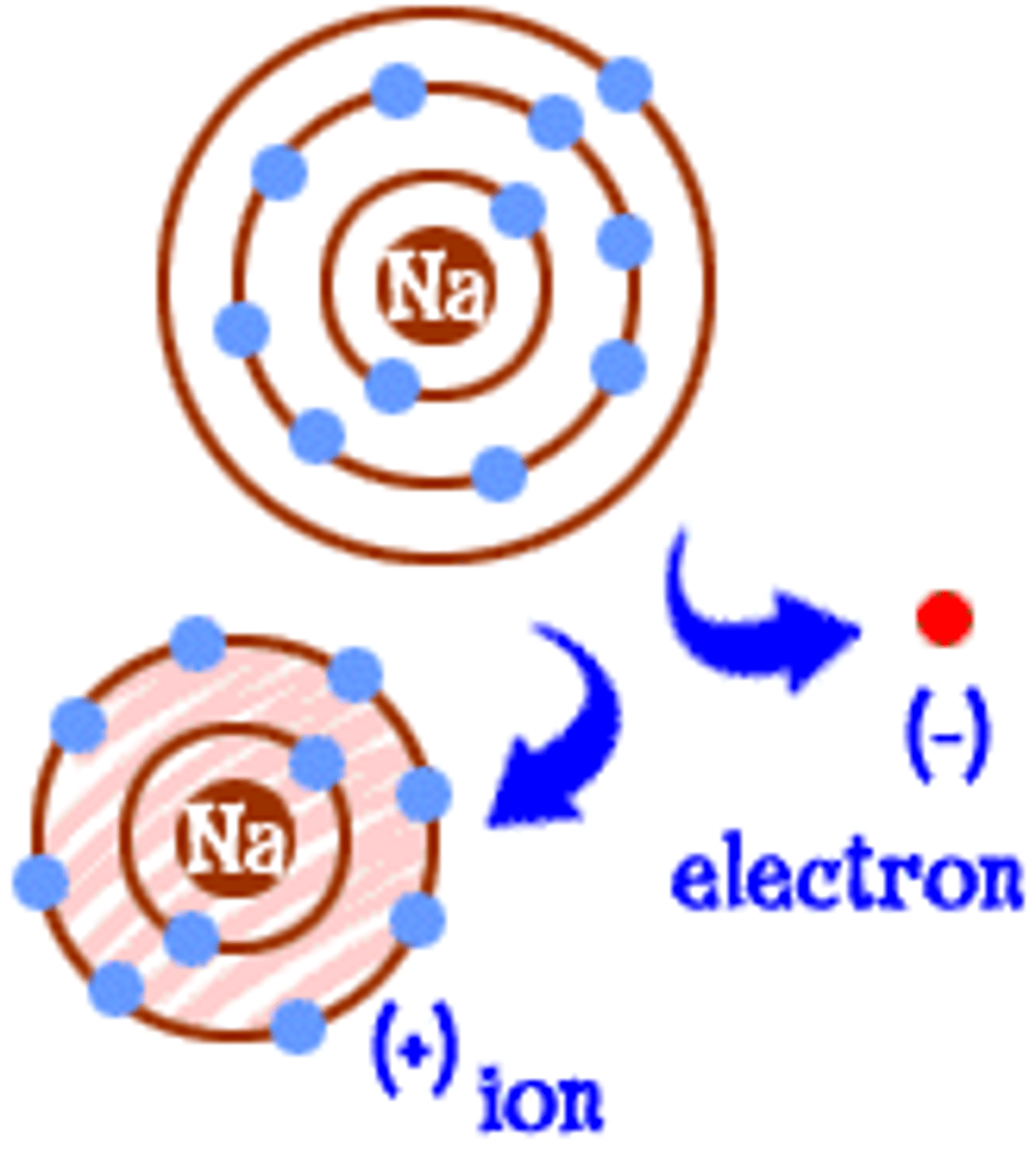
What happens when an atom loses an electron?
It becomes a positive ion because it loses a negative charge
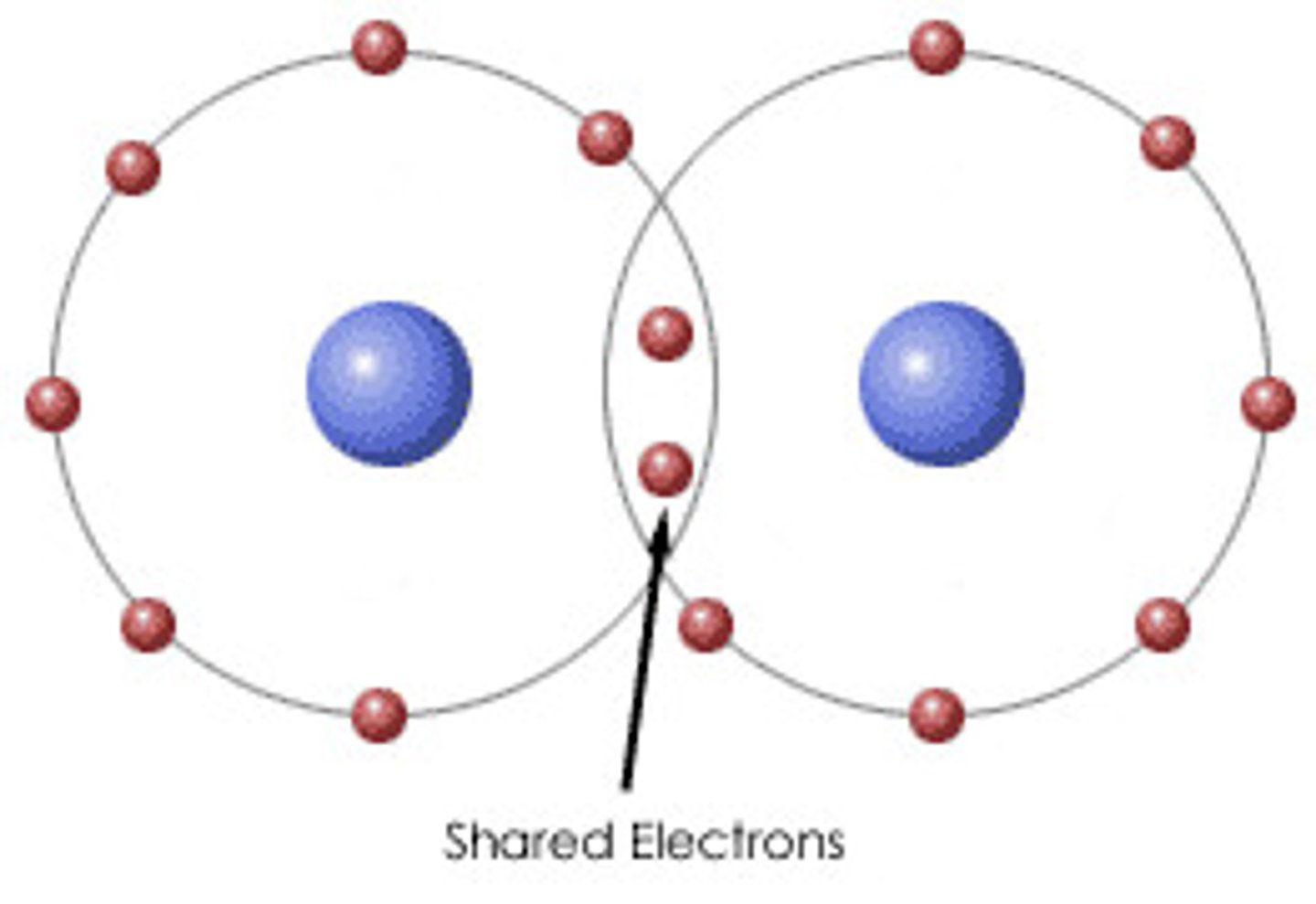
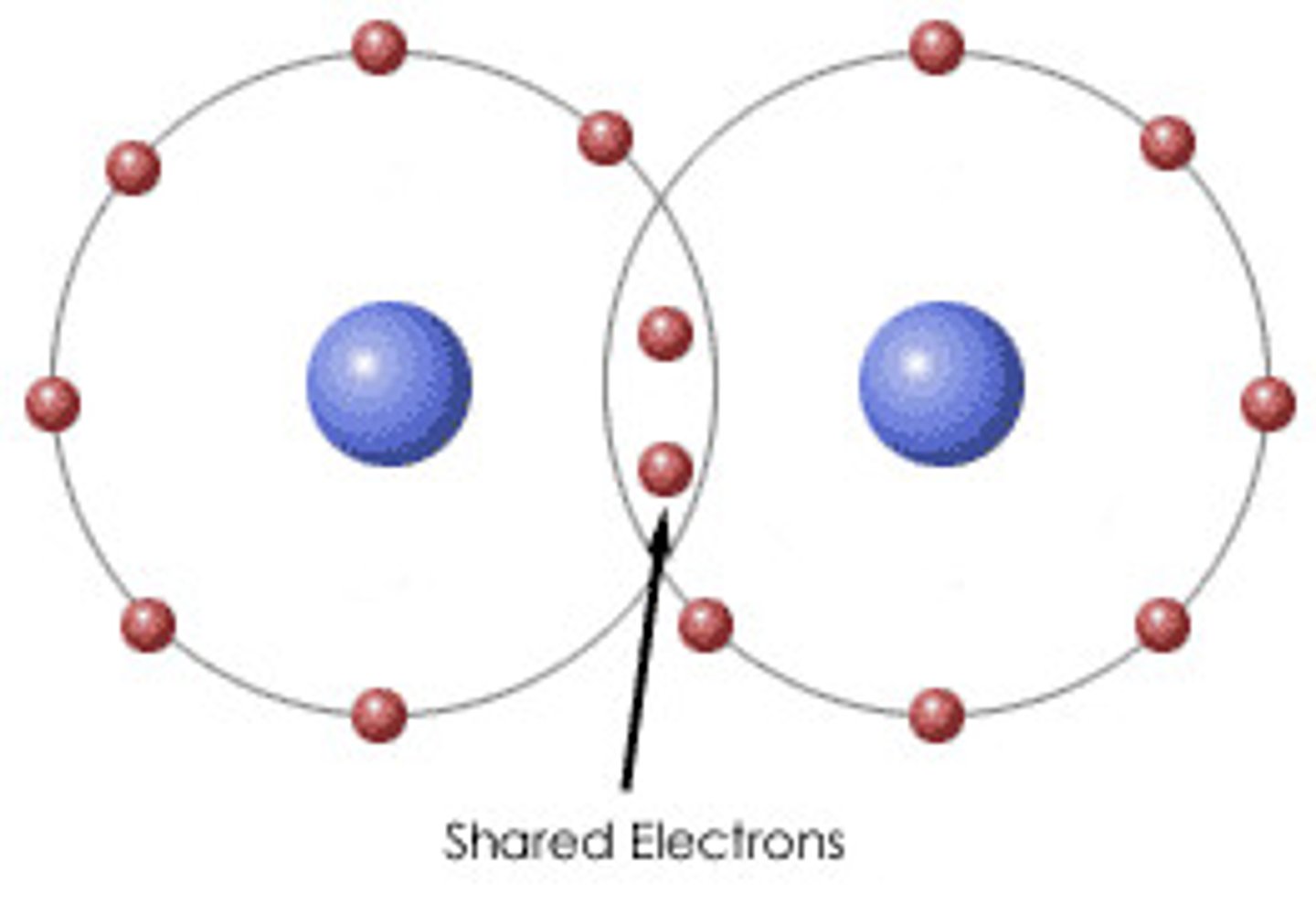
What is a covalent bonding?
when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
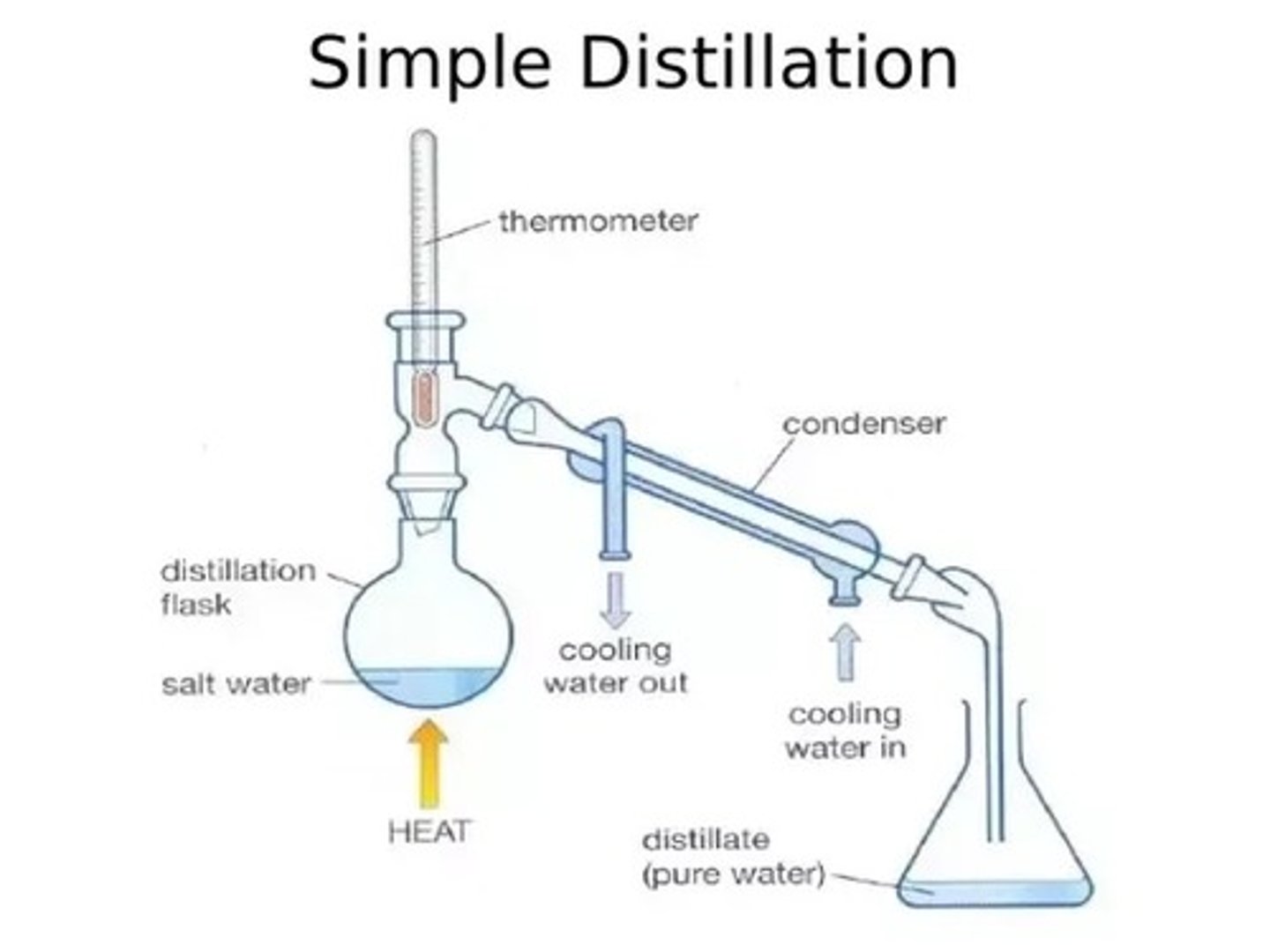
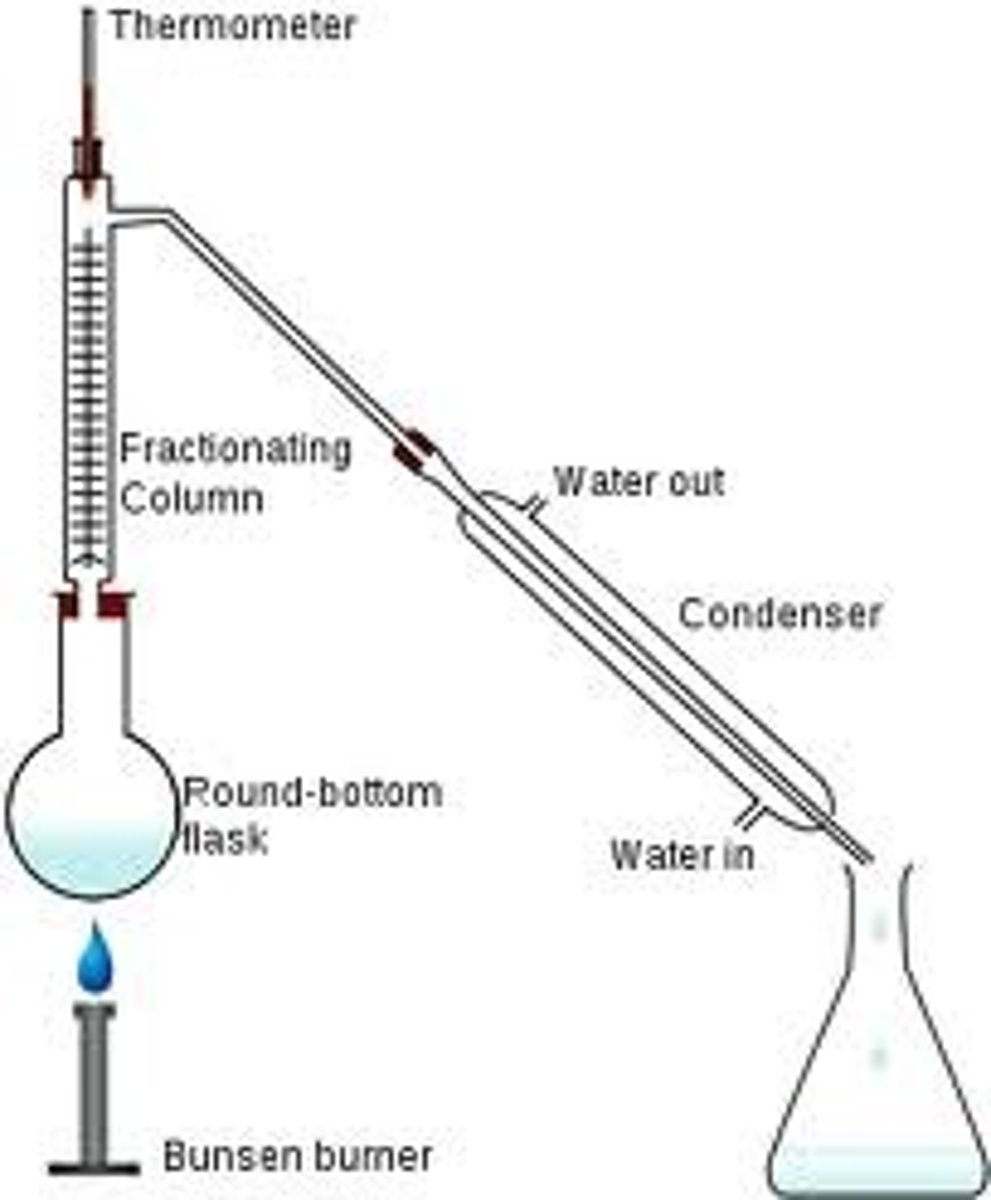
What is simple distillation?
Used for separating a liquid from a solution
What is fractional distillation?
A technique for separation of a mixture of liquids that have different boiling points
What does miscible mean?
Two liquids which can mix together
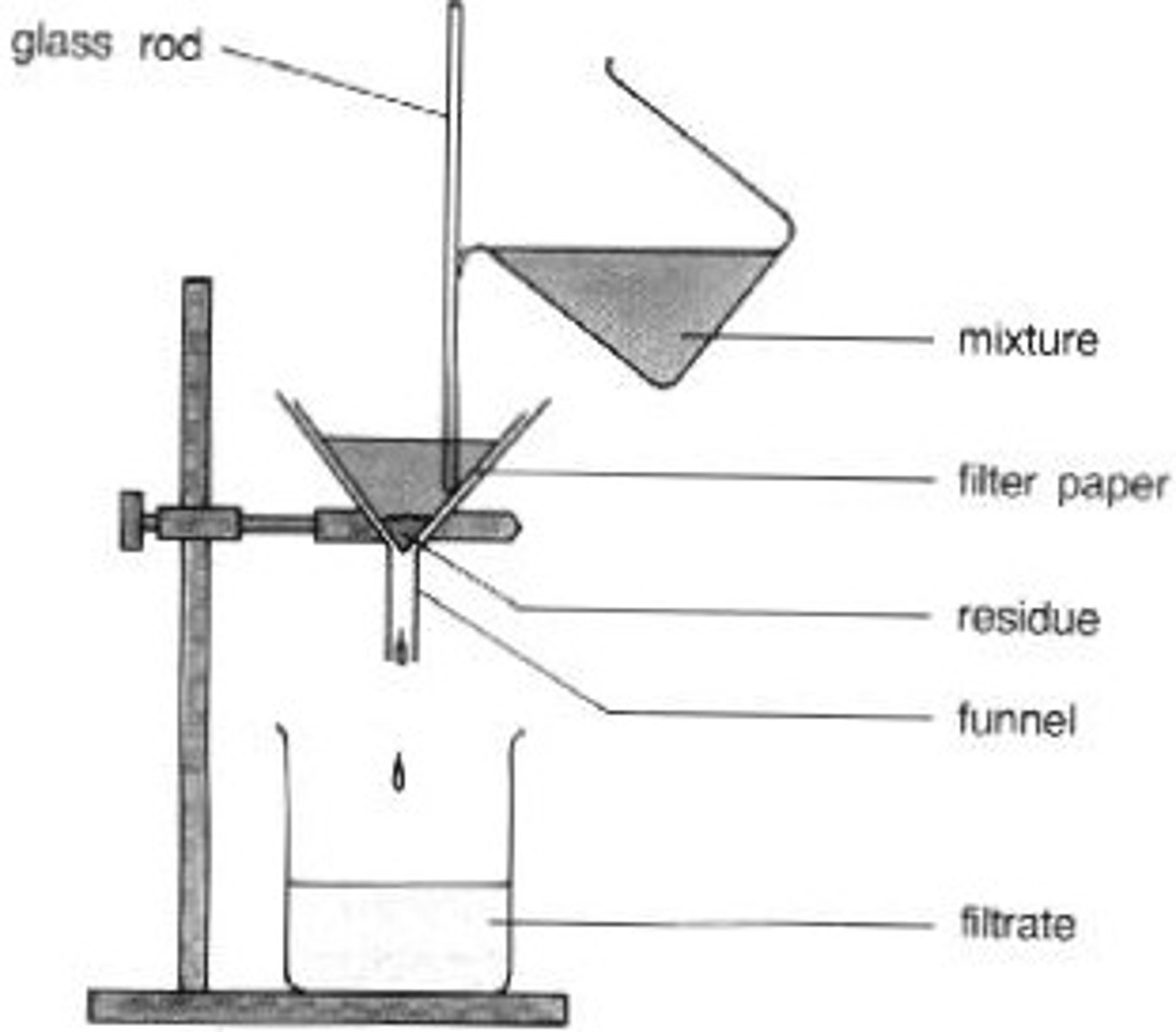
What is filtration?
Used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid
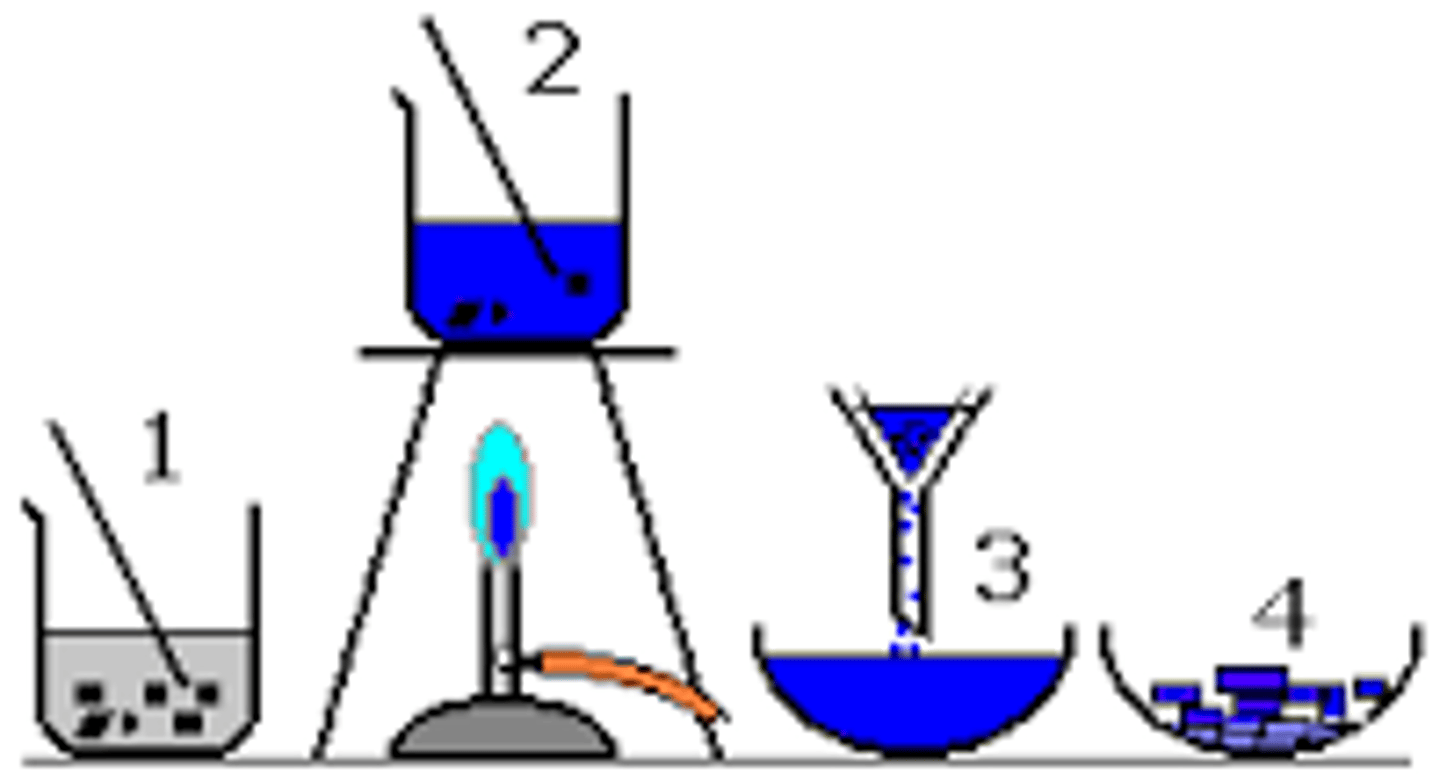
What is crystallisation?
Separates a soluble solid in a solvent from a solvent
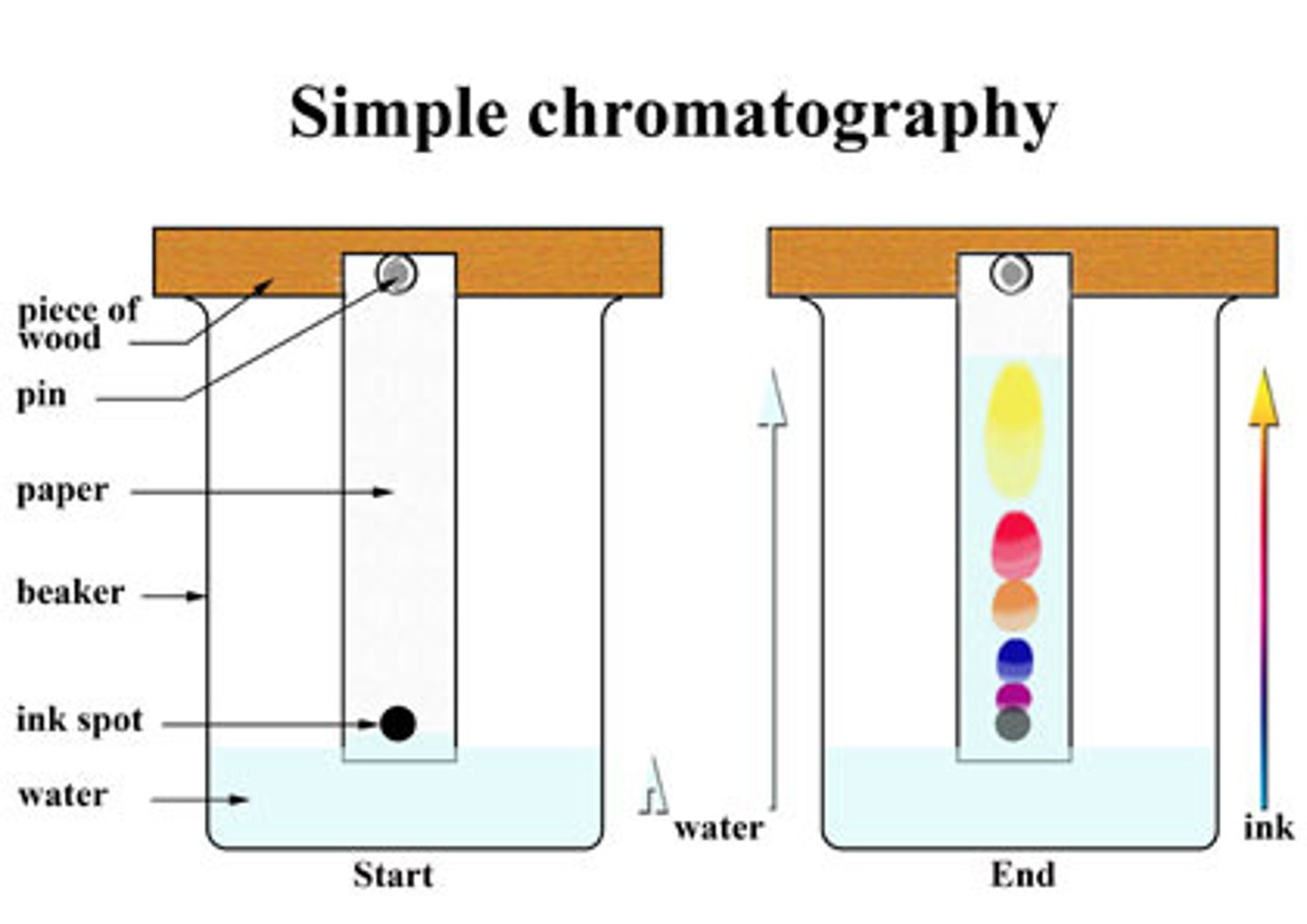
What is chromatography?
Used to separate a mixture of substances dissolved in a solvent
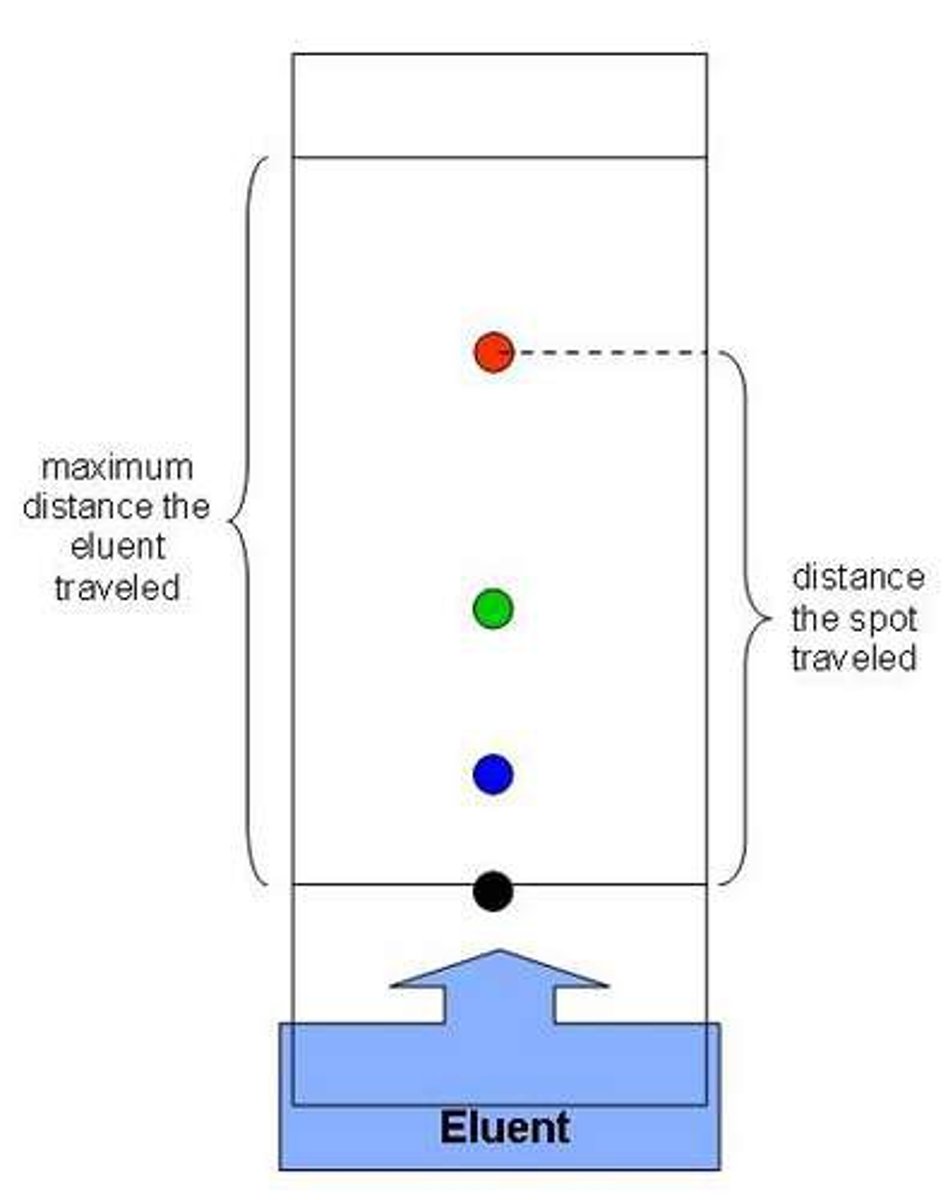
Why is the line drawn in pencil in chromatography?
Pencil is insoluble and will not dissolve in the solvent

Why are group 1 metals so reactive?
Because they only have one electron in their outer shell
What are group 1 atoms known as?
The alkali metals
What are group 7 atoms known as?
The halogens
Why does bonding occur?
To make atoms stable
What is an element?
A substance that contains only one type of atom
What is a compound?
2 or more elements chemically combined
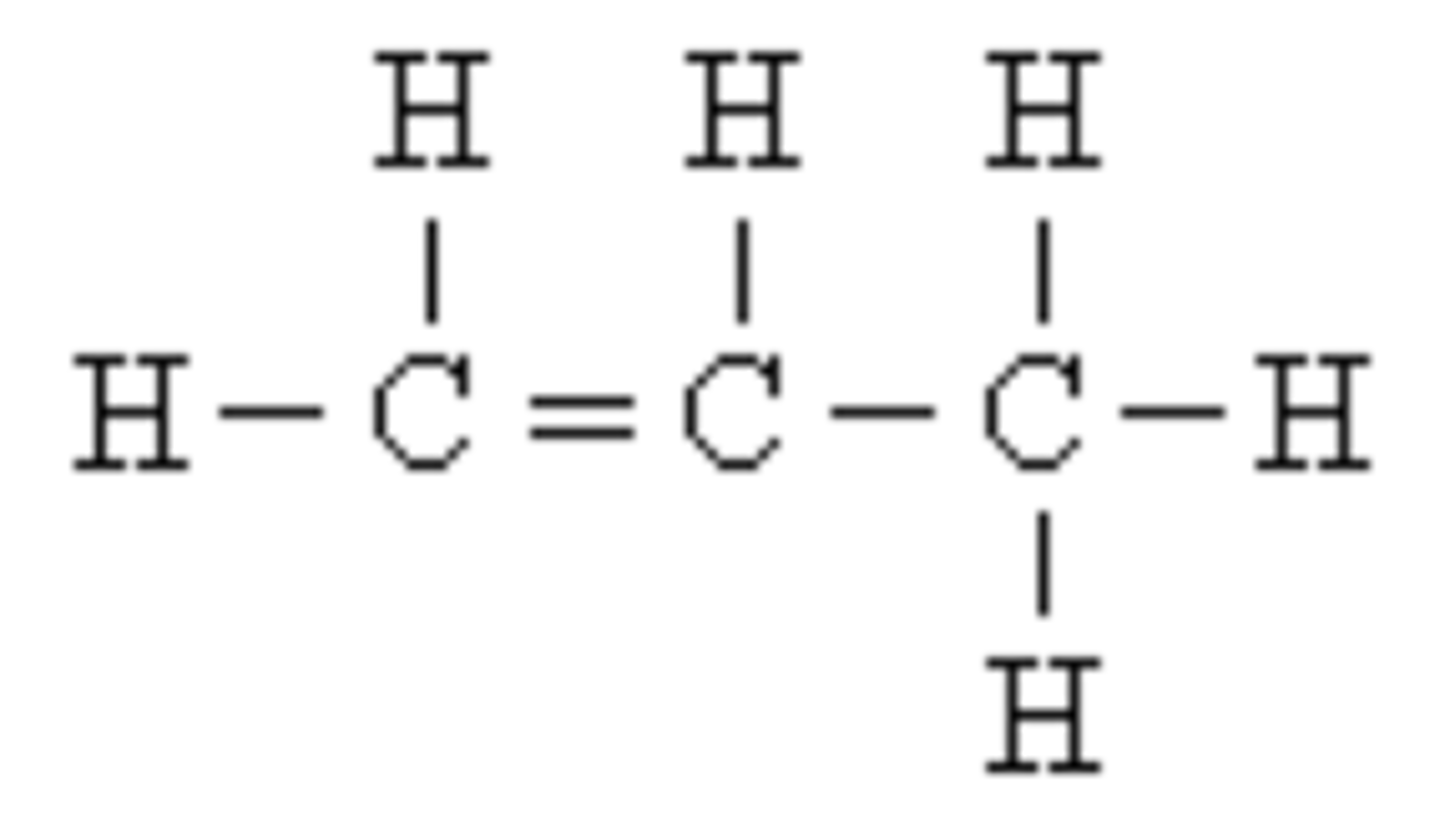
What is a mixture?
Two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together

What is a molecule?
2 or more atoms bonded together
What does the amount of energy needed to change state from solid to liquid or liquid to gas depend on?
The strength of the forces between the particles of the substance
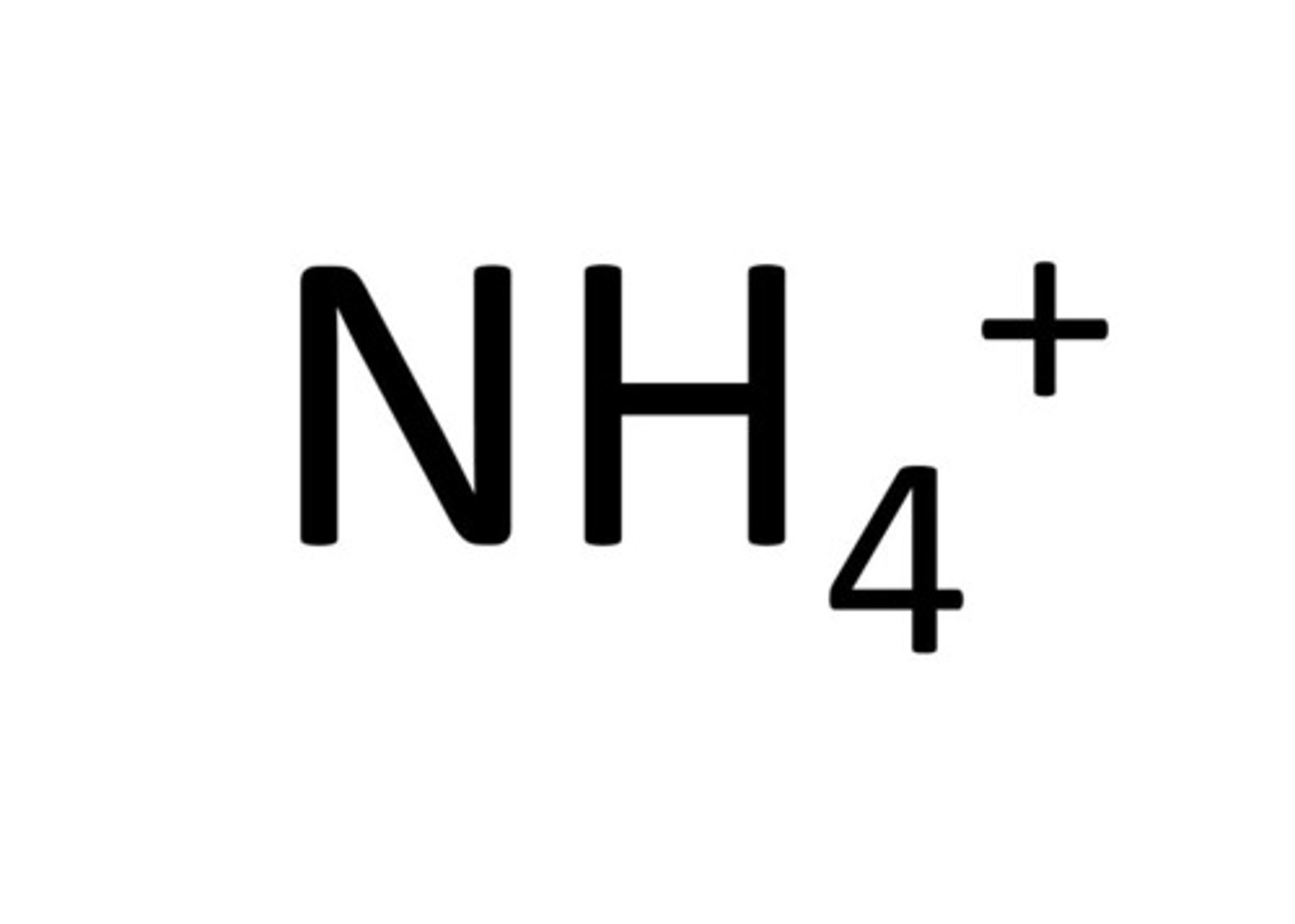
Ammonium
NH₄⁺
Hydroxide
OH⁻
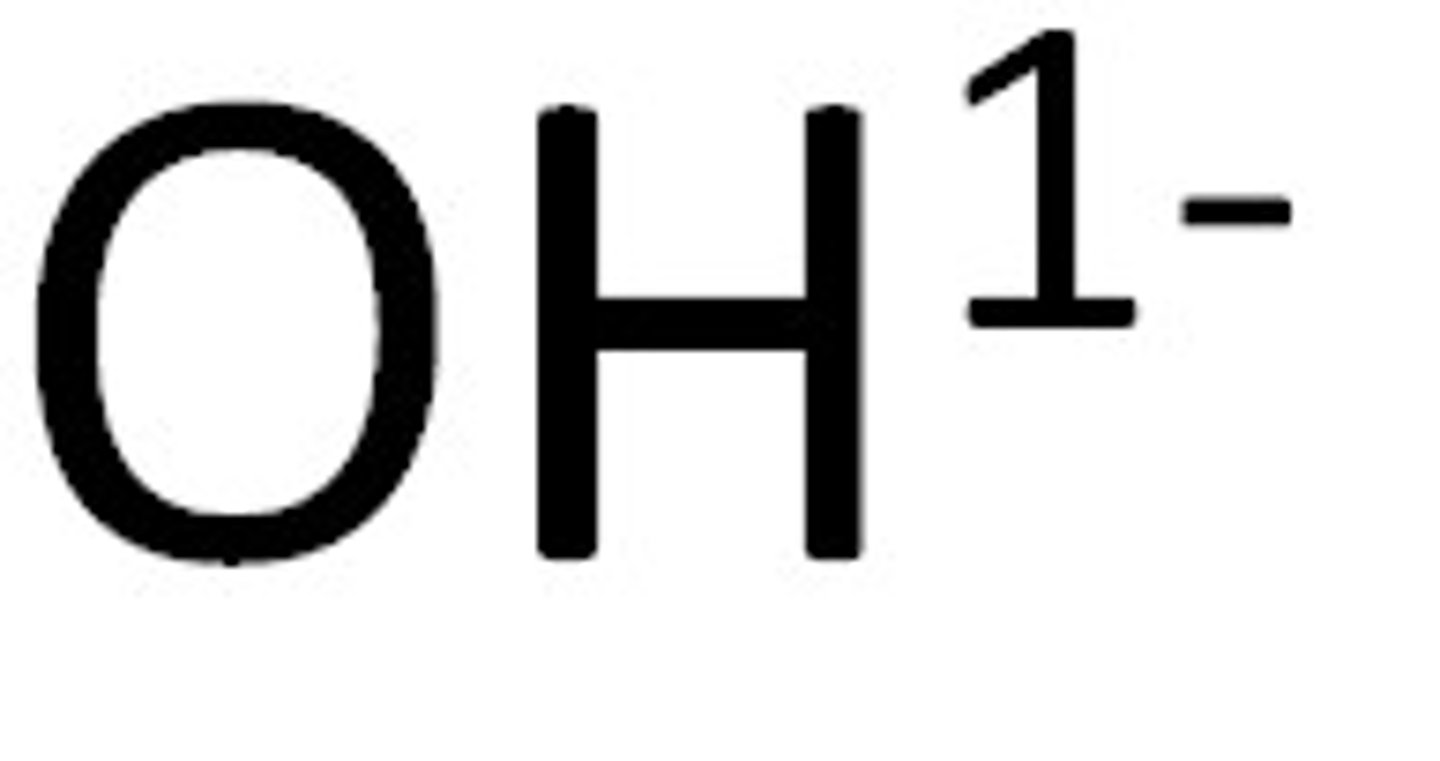
Carbonate
CO₃²⁻
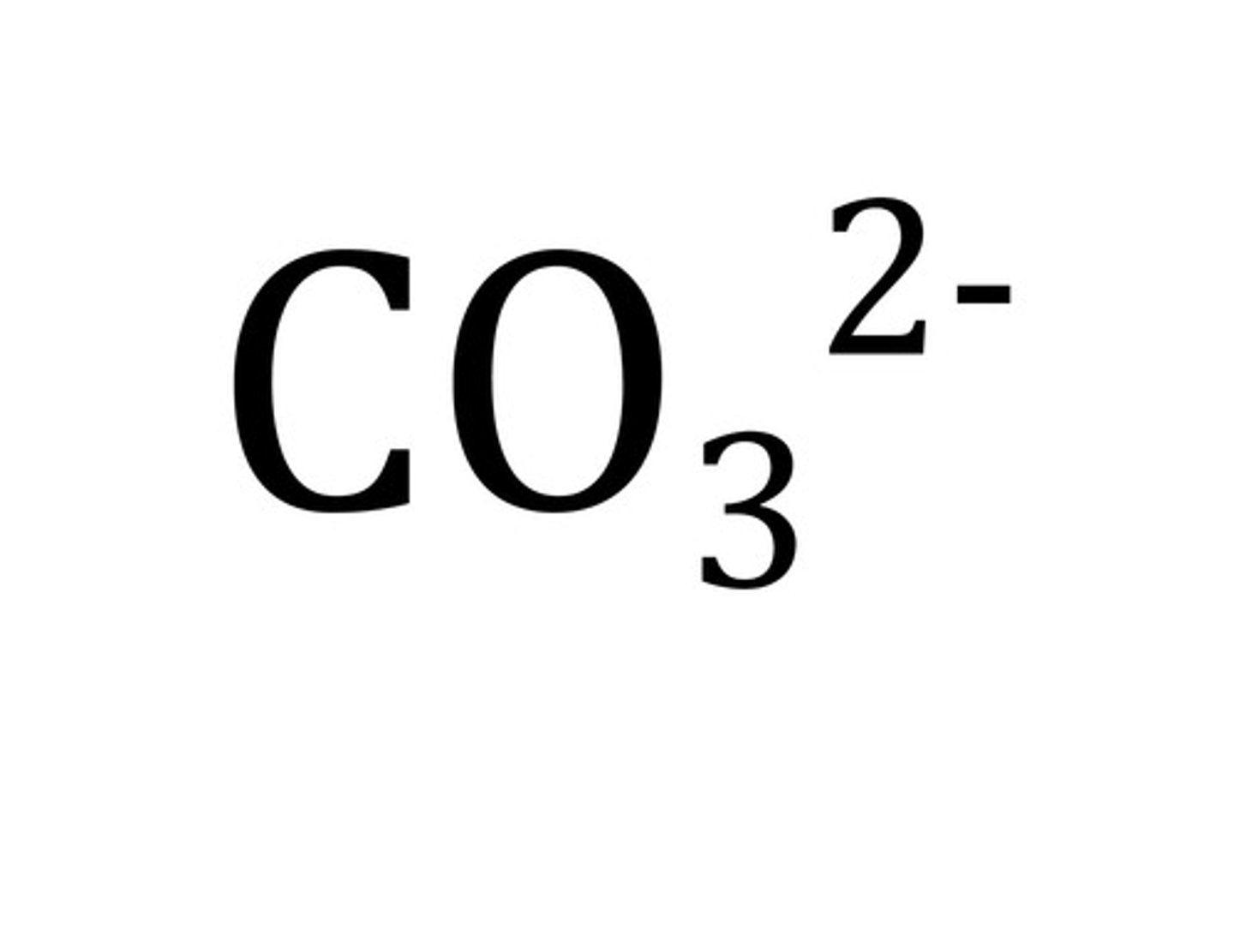
Nitrate
NO₃⁻
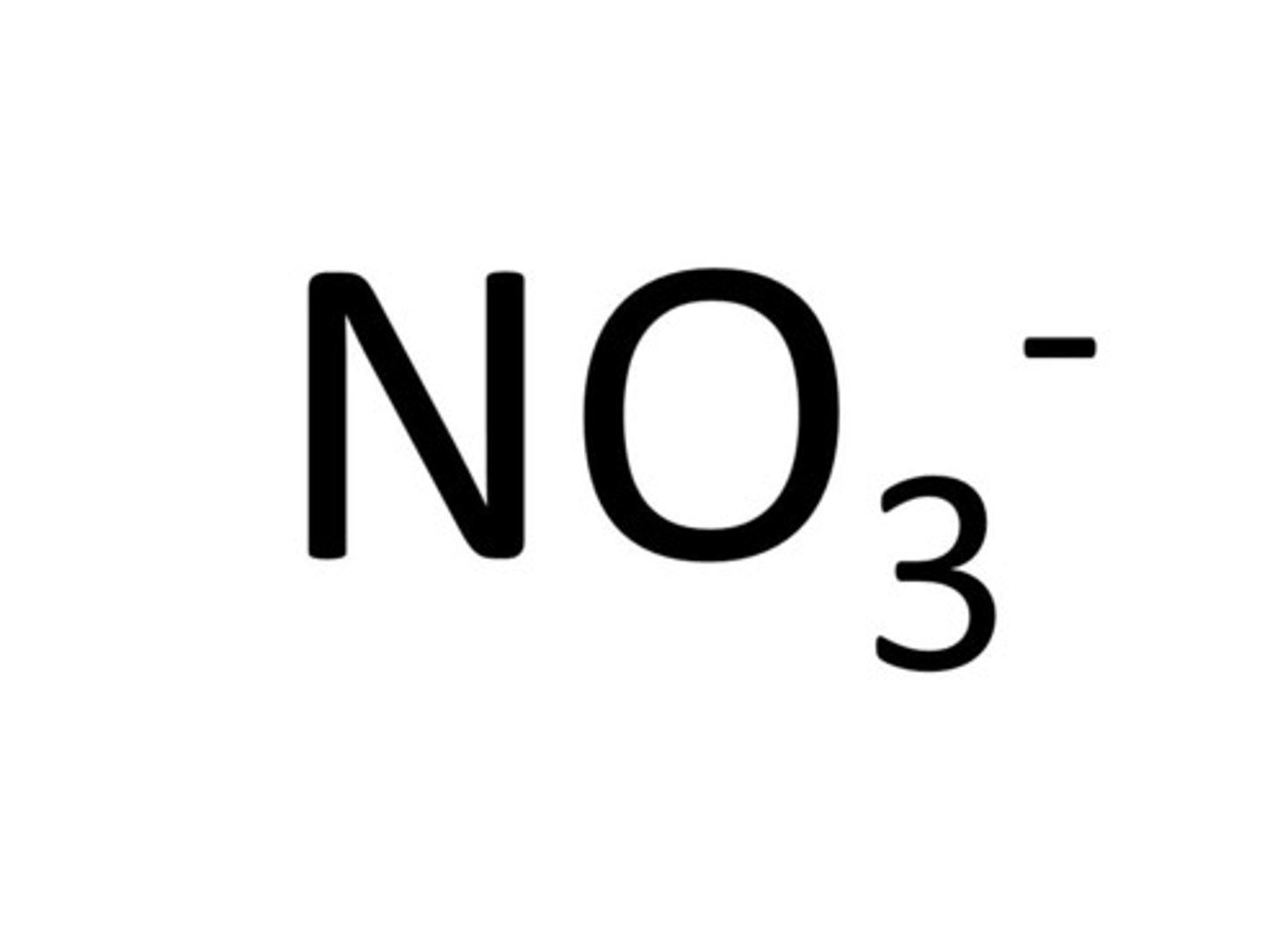
Sulfate
SO₄²⁻
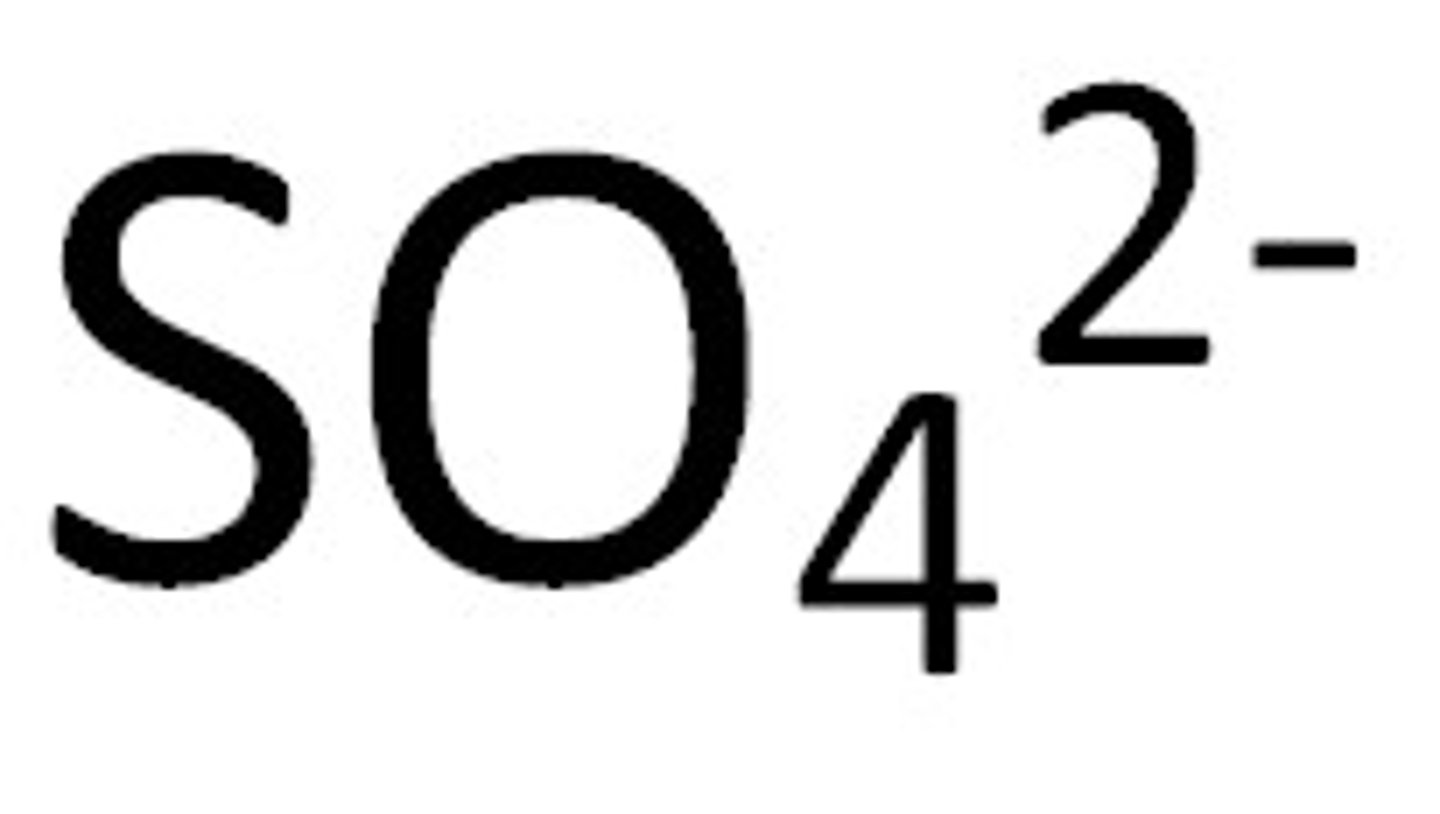
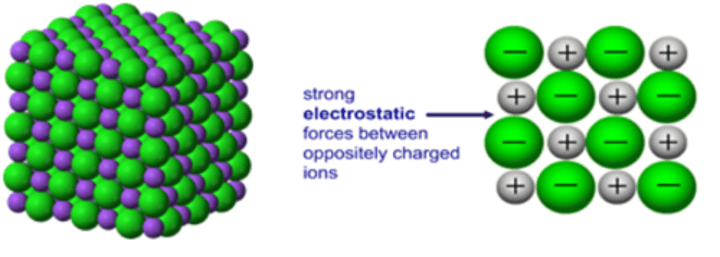
What is the structure of an ionic compound?
Giant ionic lattice
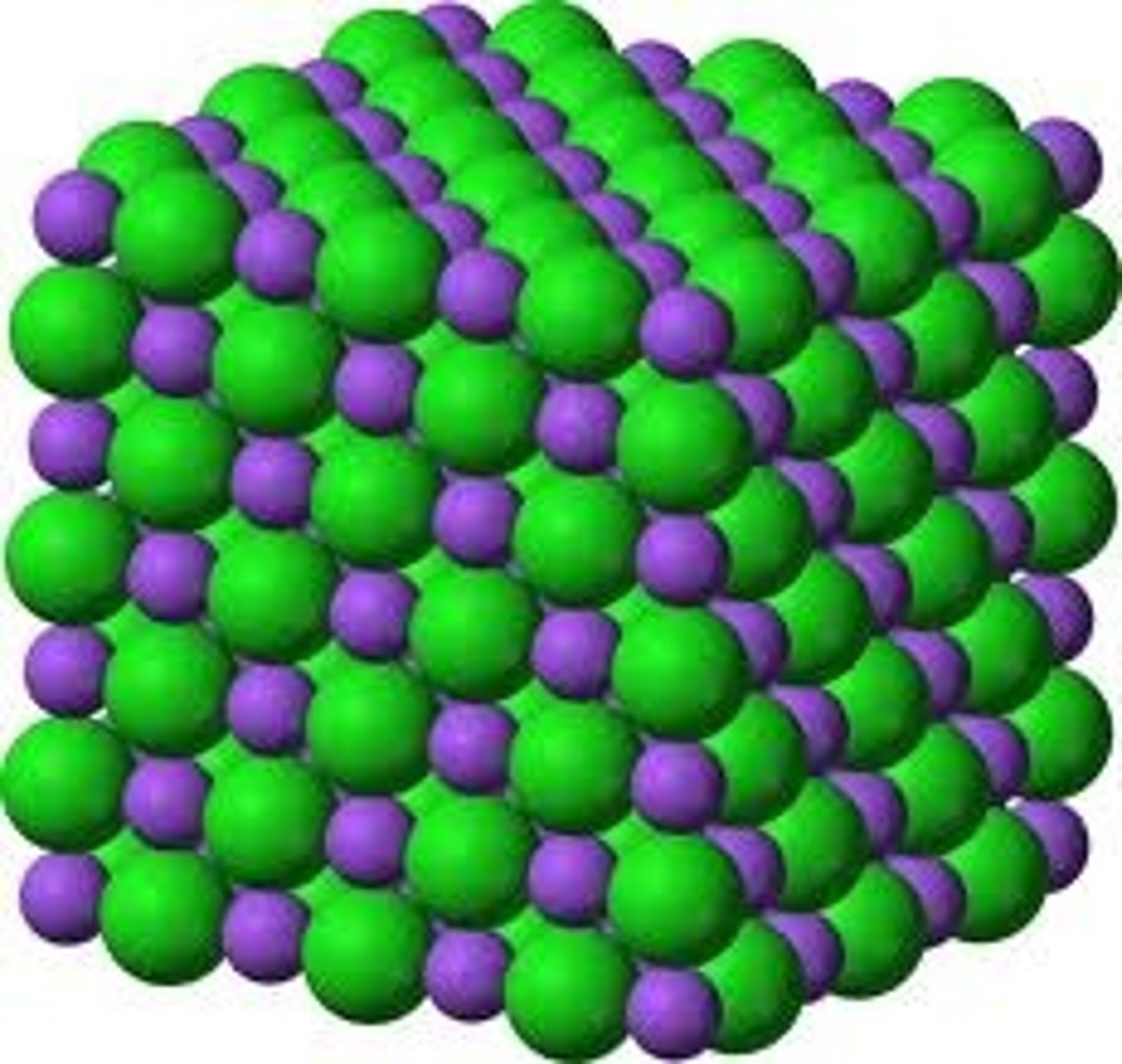
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
Due to the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
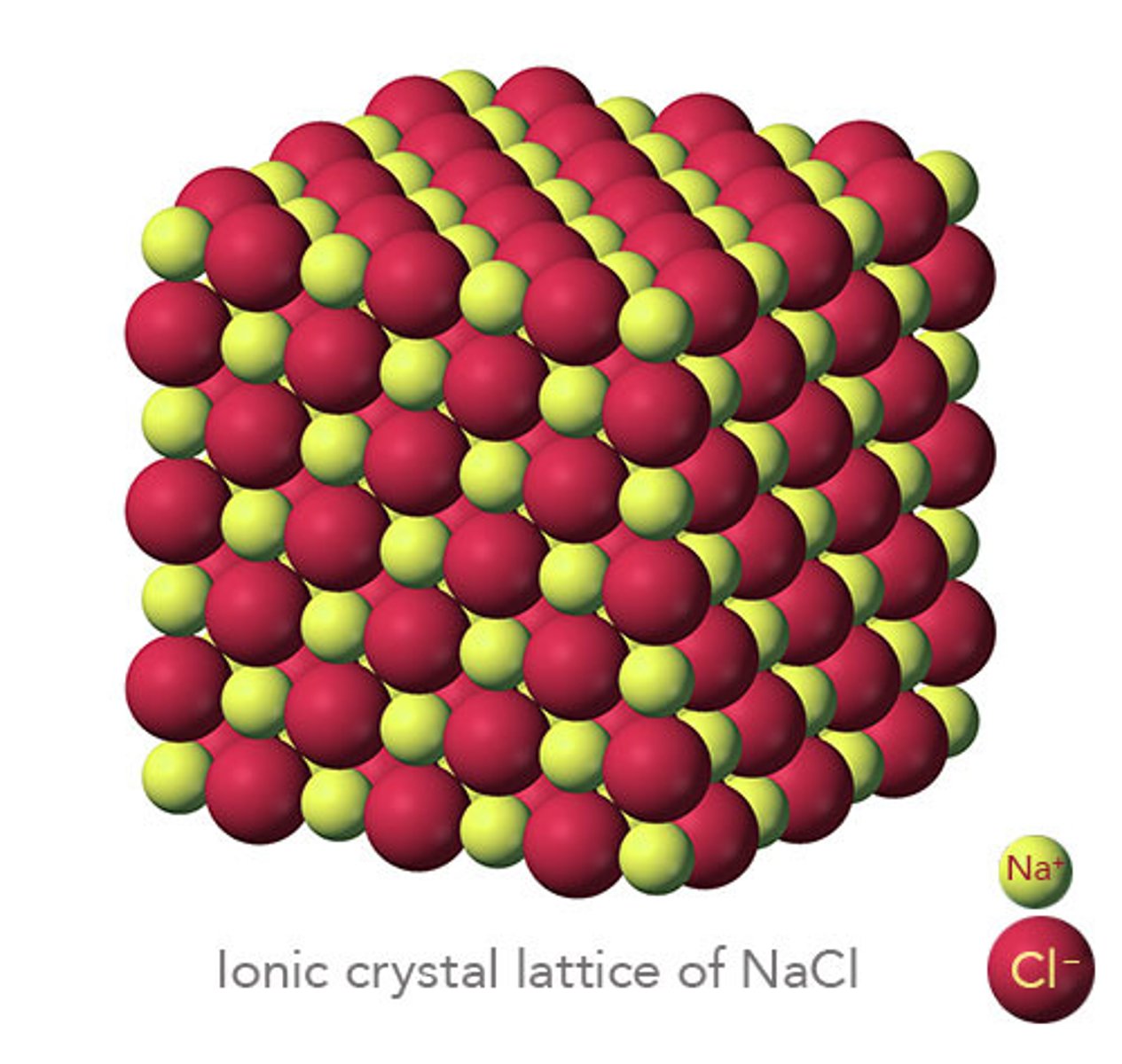
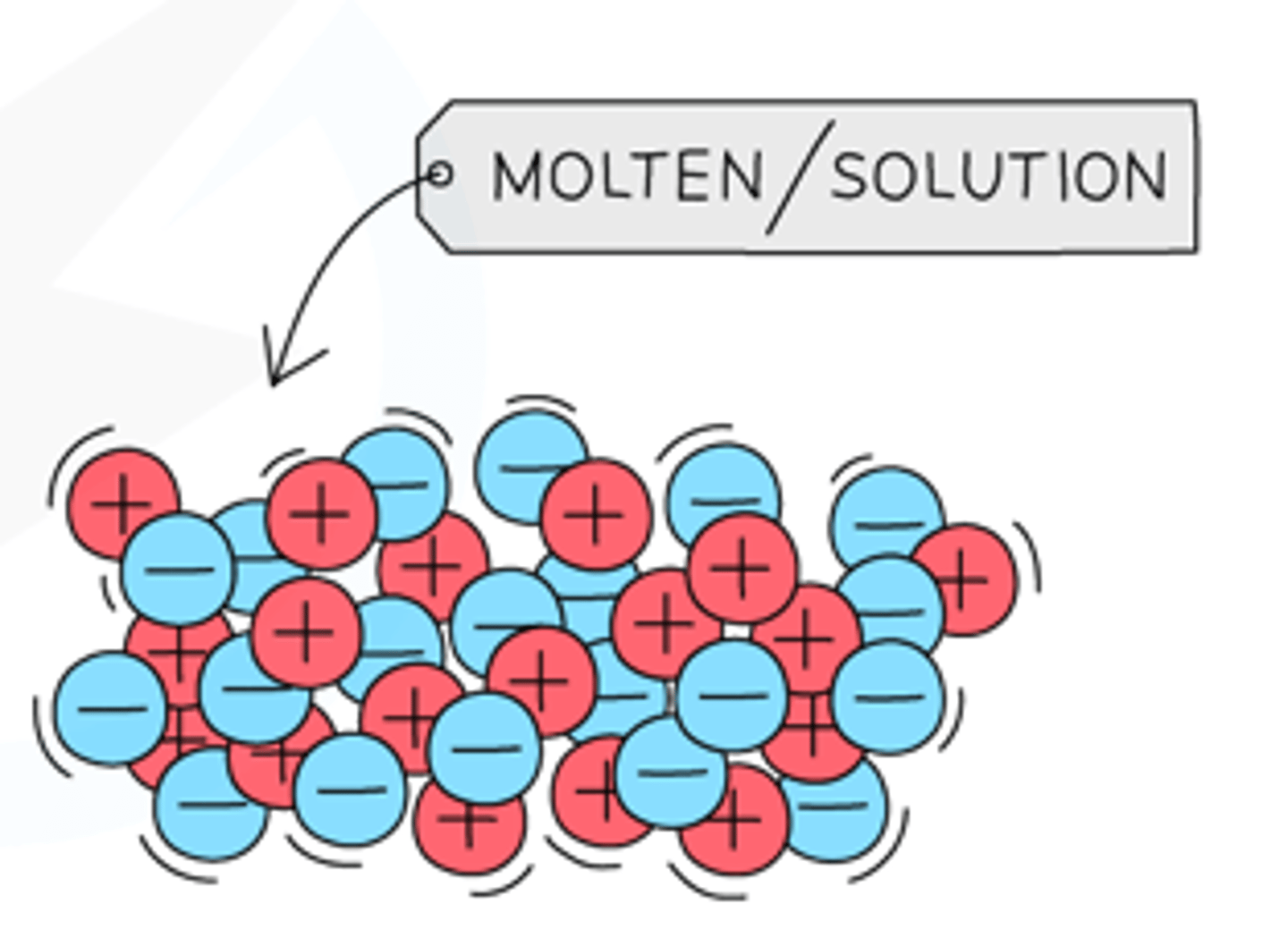
In what state do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Liquid state
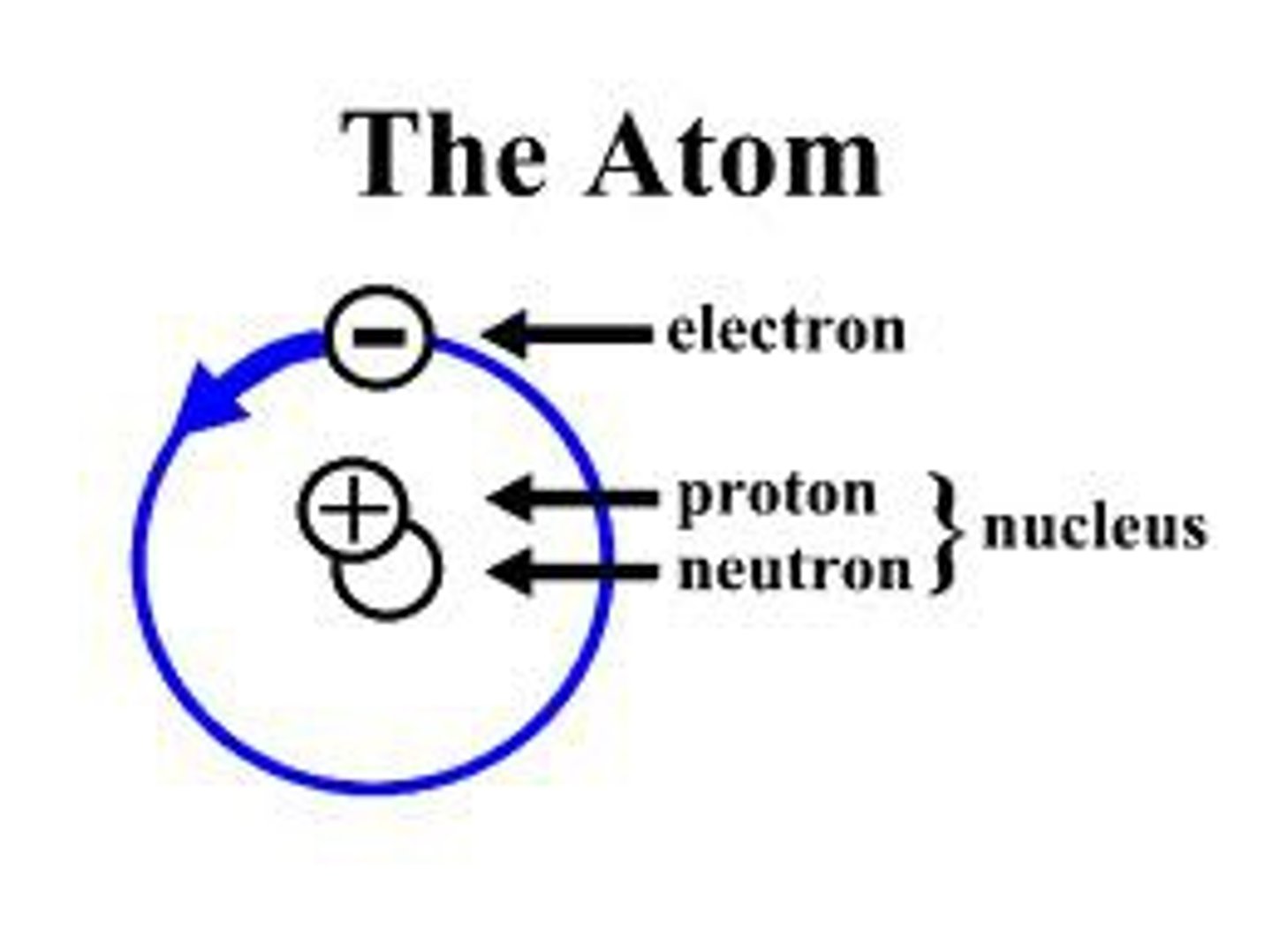
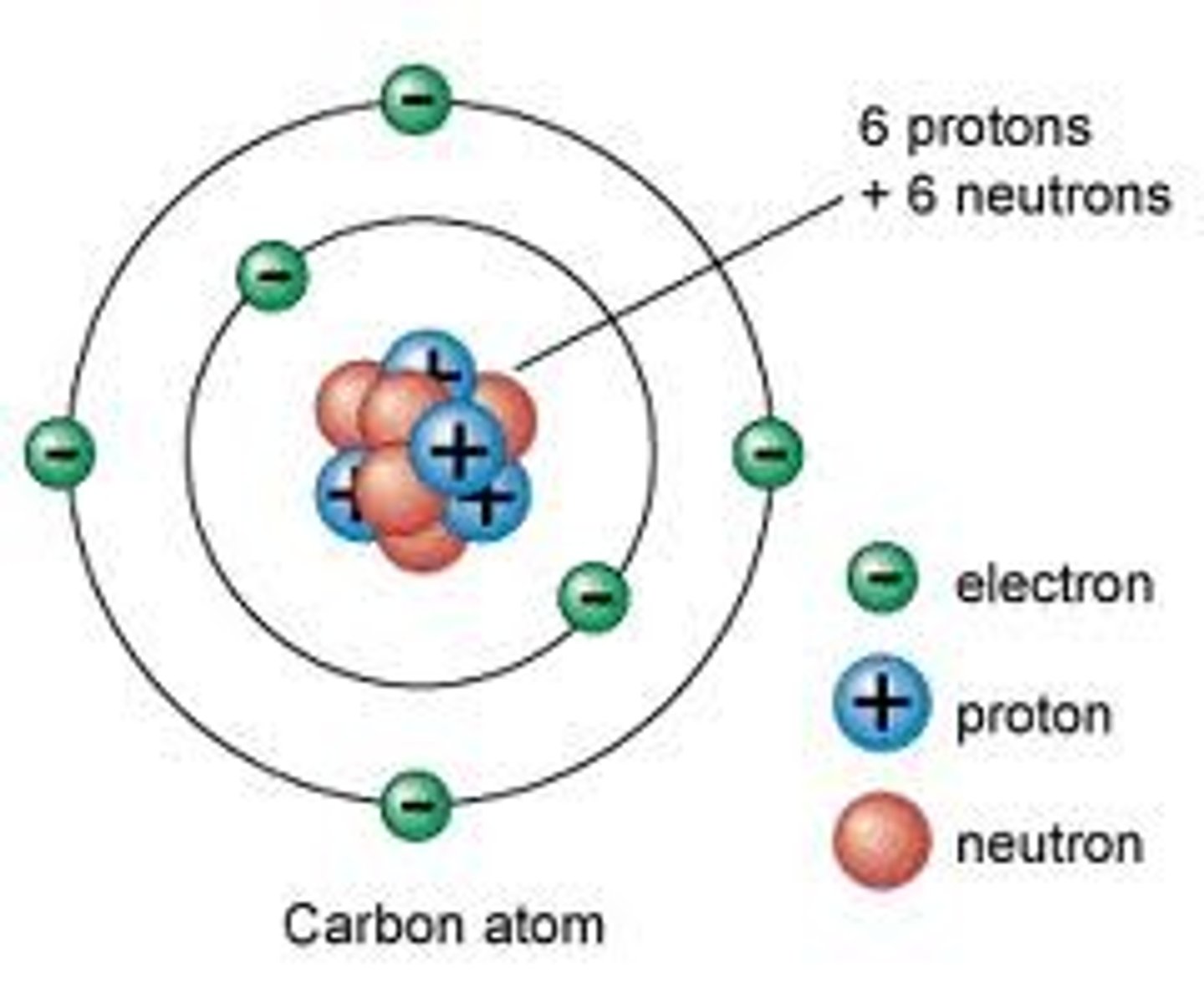
What is an atom?
Ana atom is the smallest unit of matter
What is an RF value?
The ratio of the solute's distance travelled to the solvent's distance travelled

What is relative atomic mass?
Average of the mass numbers of the different isotopes
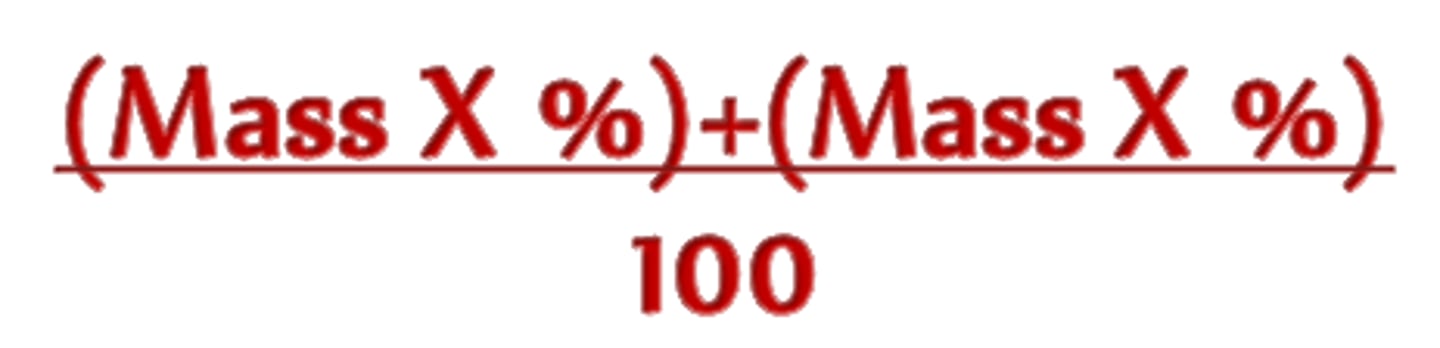
What is abundance?
Relative amount of each isotope
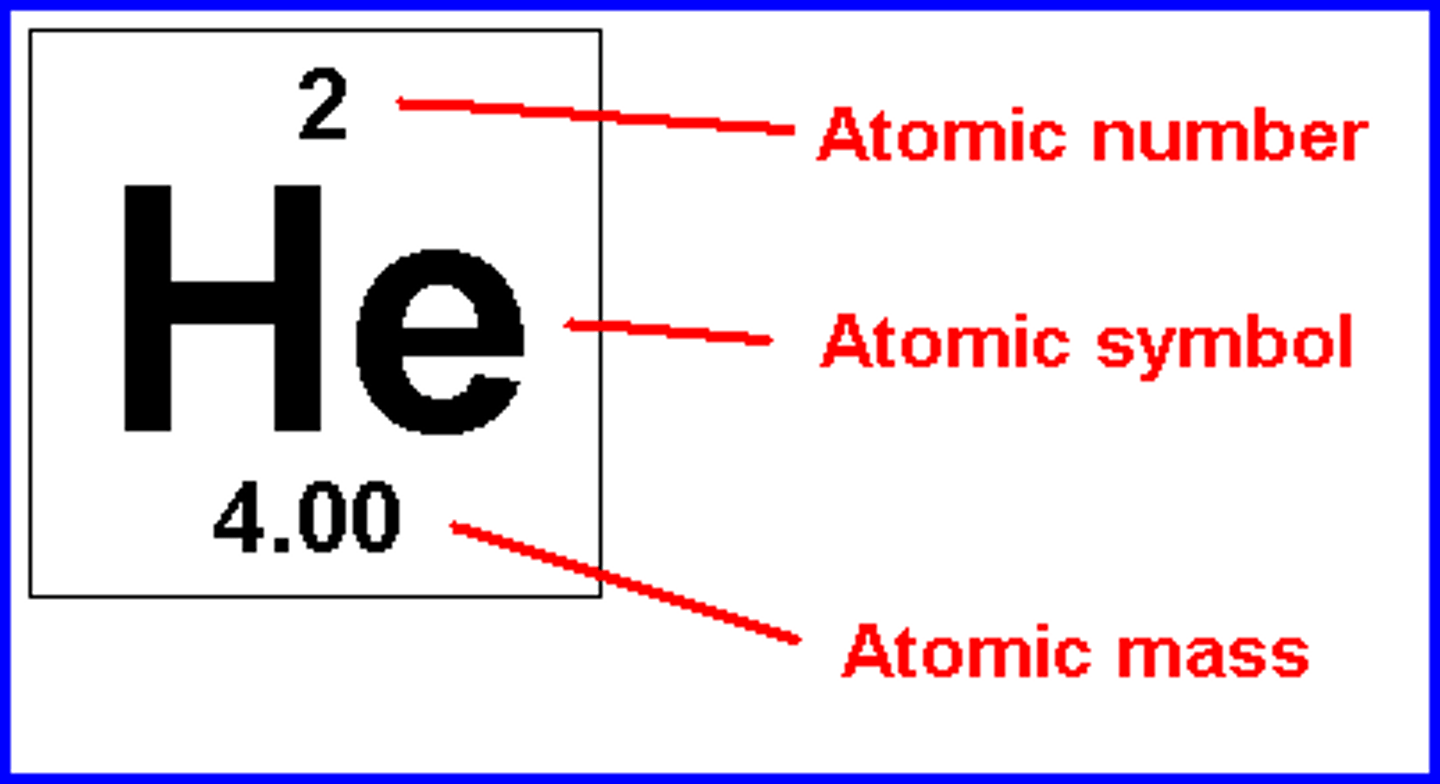
What is the mass number?
Number of protons and neutrons
What is an electron?
A negatively charged subatomic particle
What is the difference between boiling and evaporation?
Boiling affects the whole liquid while evaporation only affects the surface
What is solubility?
A measurement of how much a substance will dissolve in a given volume of a liquid
What is an ion?
An atom that is charged because it has lost or gained and electron
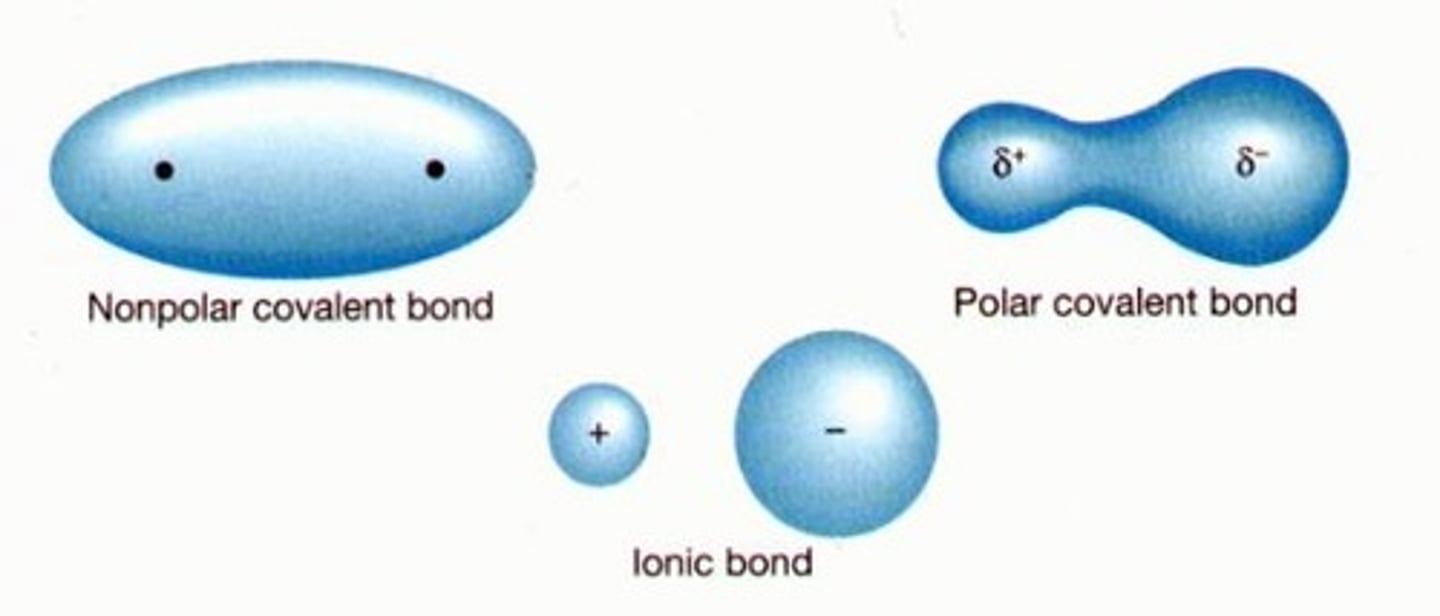
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding?
Covalent bonding refers to the sharing of electrons while ionic bonding is the complete transfer of electrons
What is matter?
Anything that has mass and takes up space
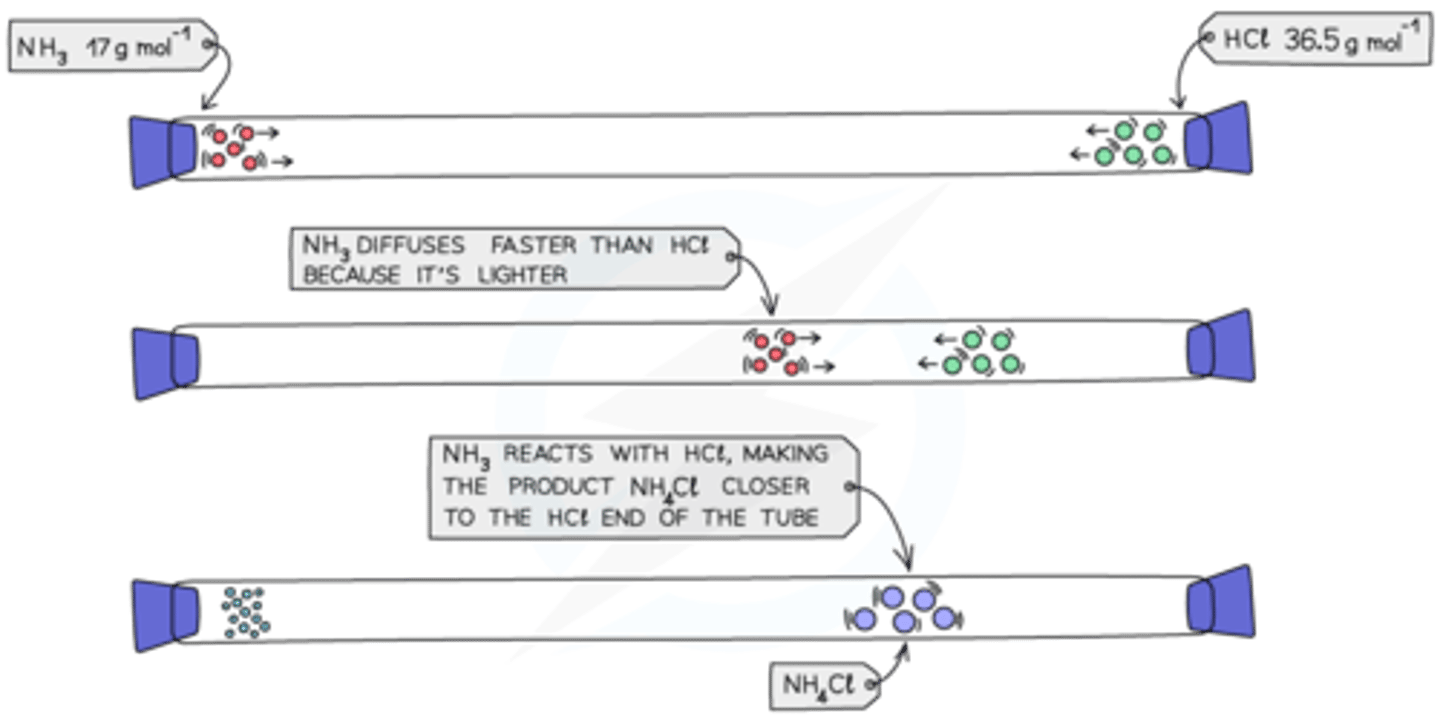
How does molecular mass affect the rate of diffusion?
Heavier molecules move more slowly; therefore, they diffuse more slowly
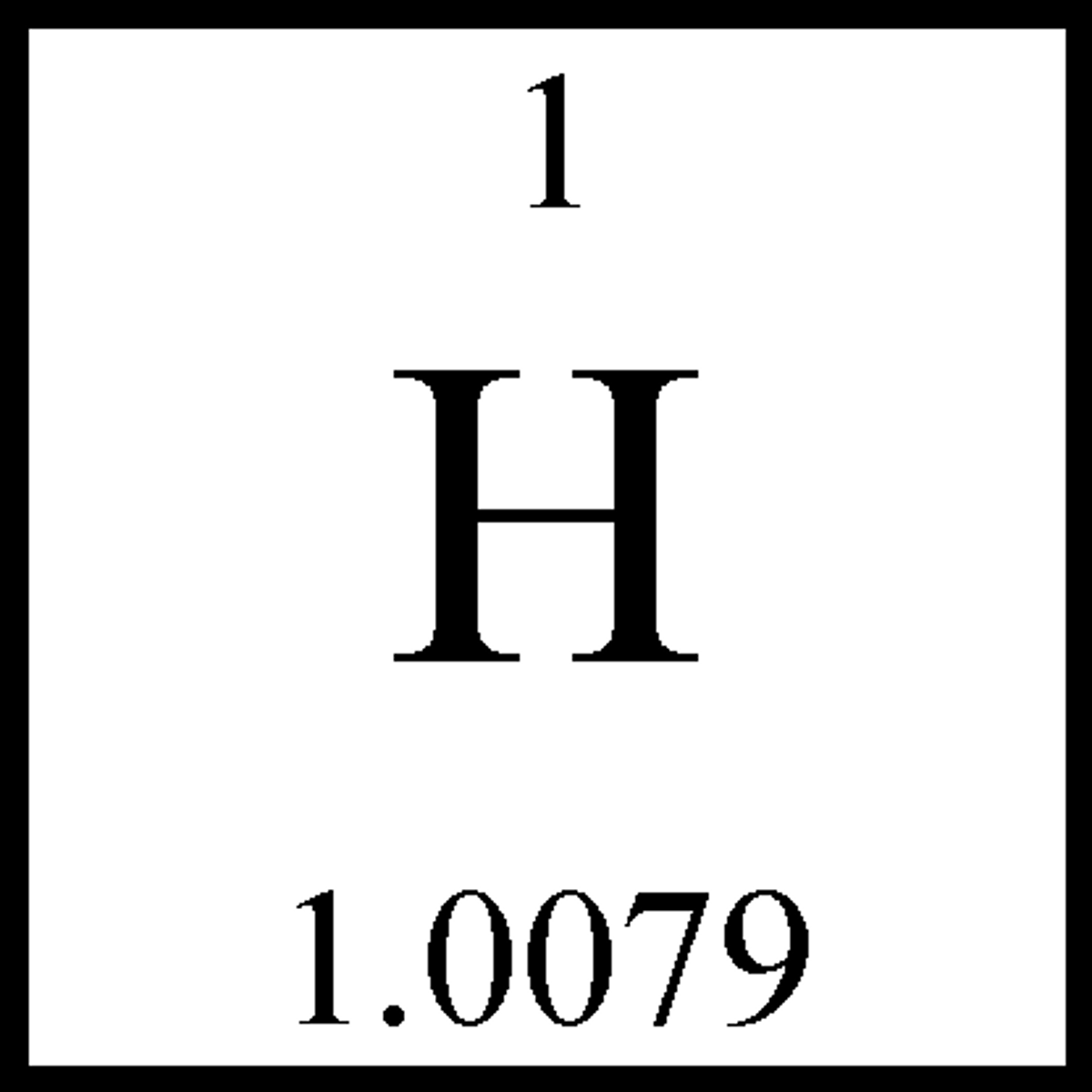
Hydrogen
H⁺
What is a diatomic molecule?
A molecule consisting of two atoms

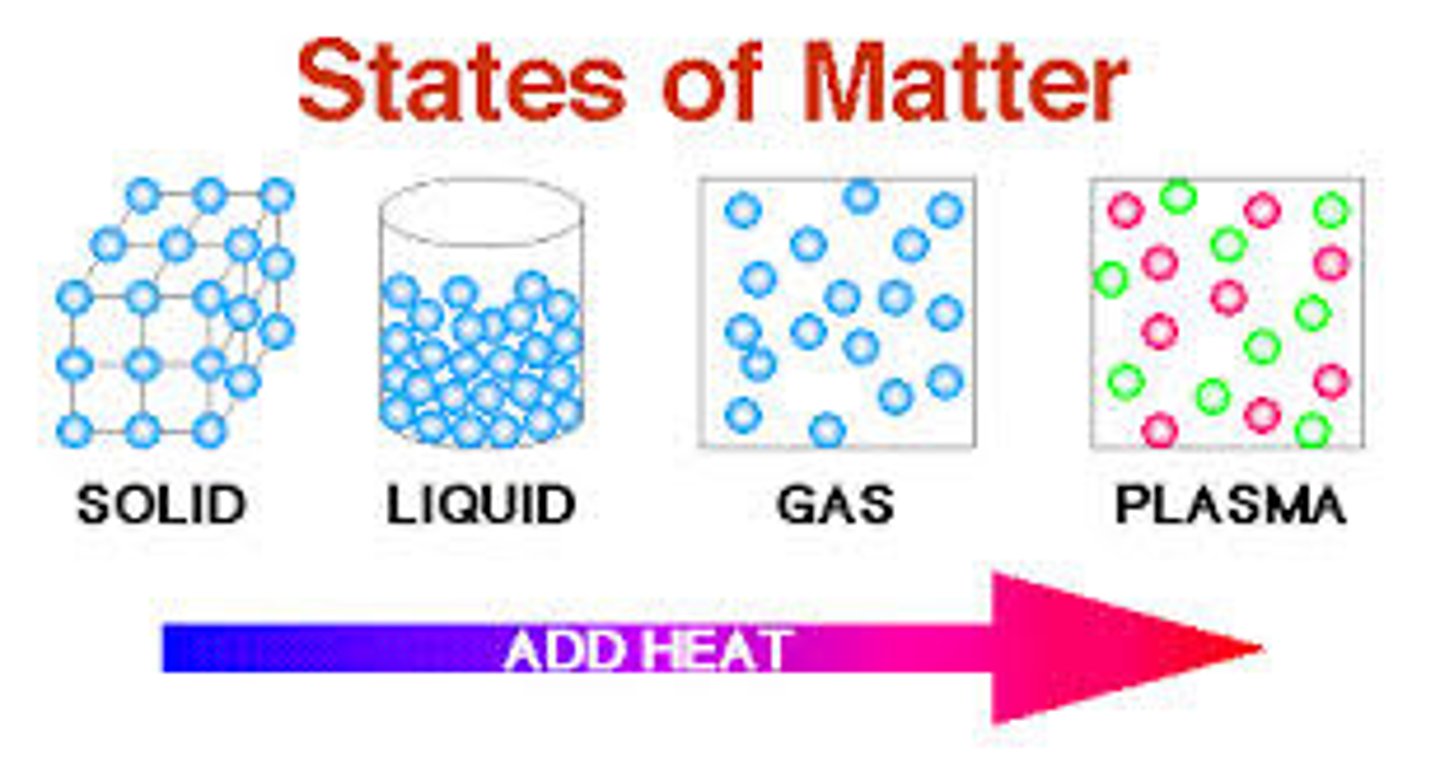
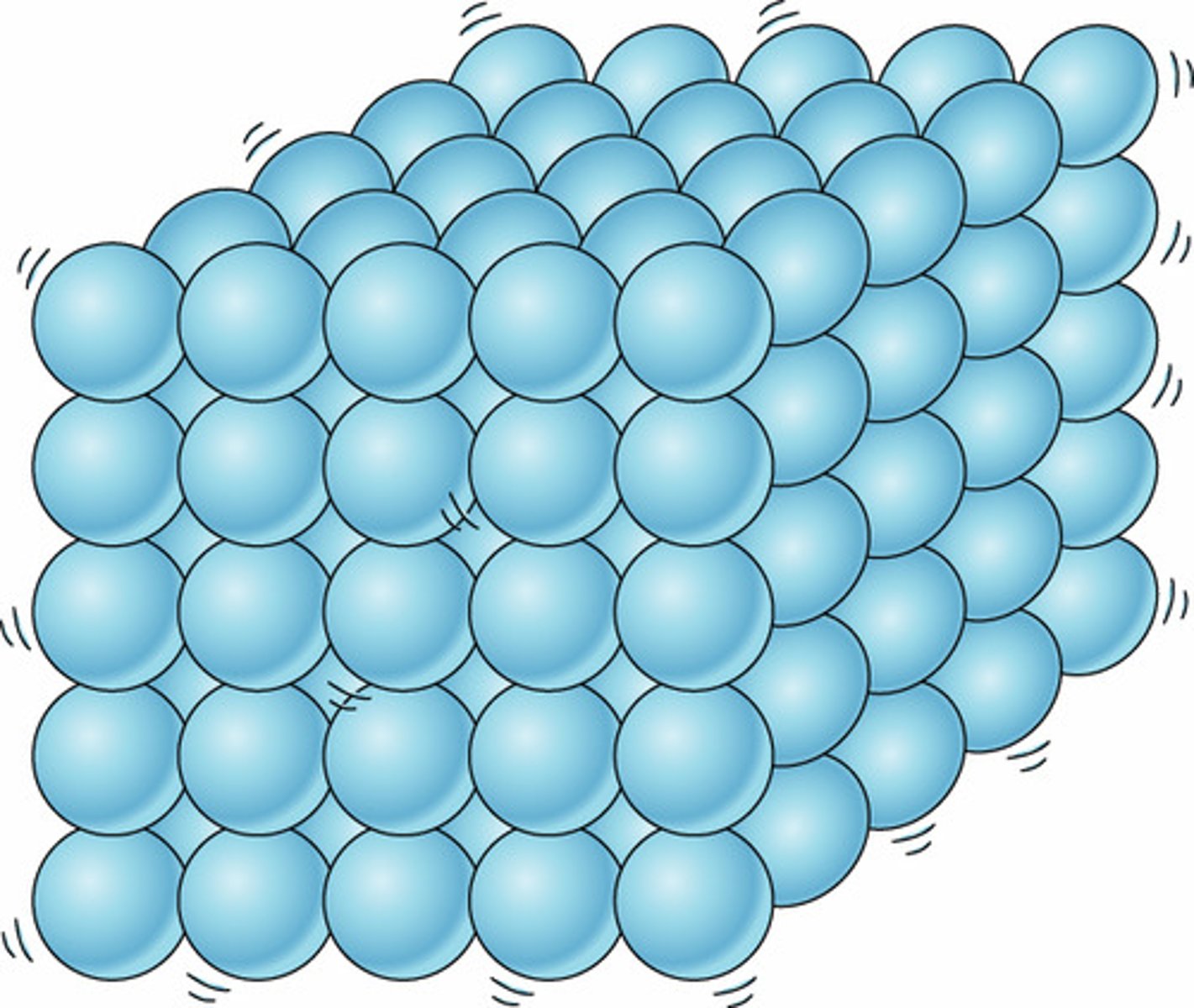
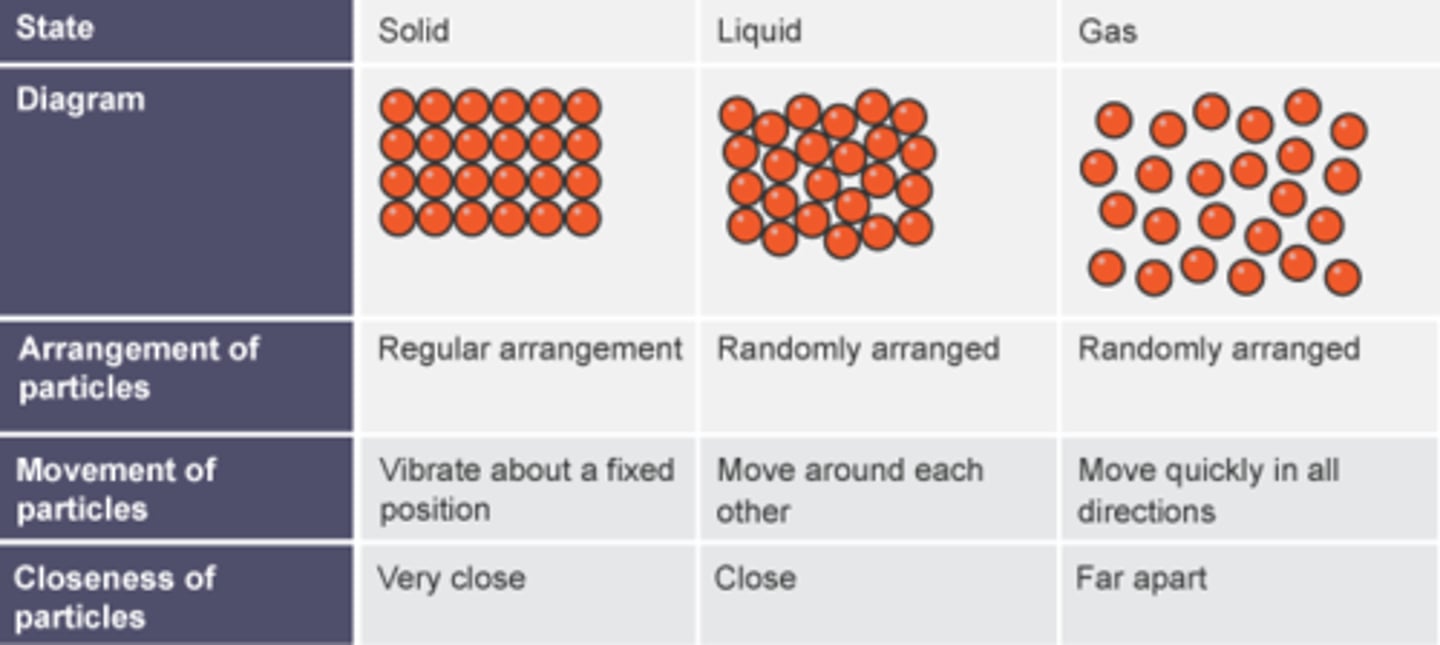
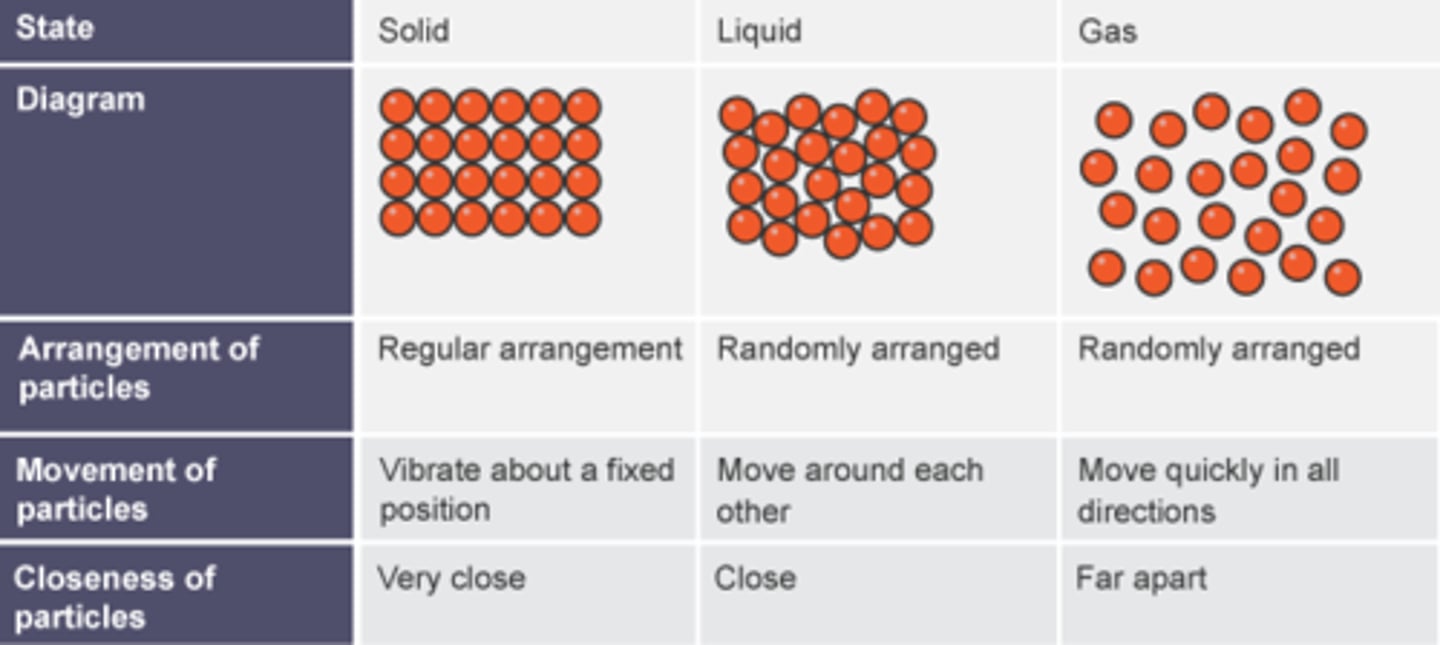
What is the arrangement of particles in a solid?
They are close together in a regular pattern
What is the arrangement of particles in a liquid?
They are close together in a random pattern
What is the arrangement of particles in a gas?
They are far apart and in a random pattern
What is the movement of particles in a solid?
Vibrate around a fixed position
What is the movement of particles in a liquid?
Flow past each other
What is the movement of particles in a gas?
Move quickly in all directions
Describe the energy of particles in a solid
Low energy
Describe the energy of particles in a liquid
Medium
Describe the energy of particles in a gas
High
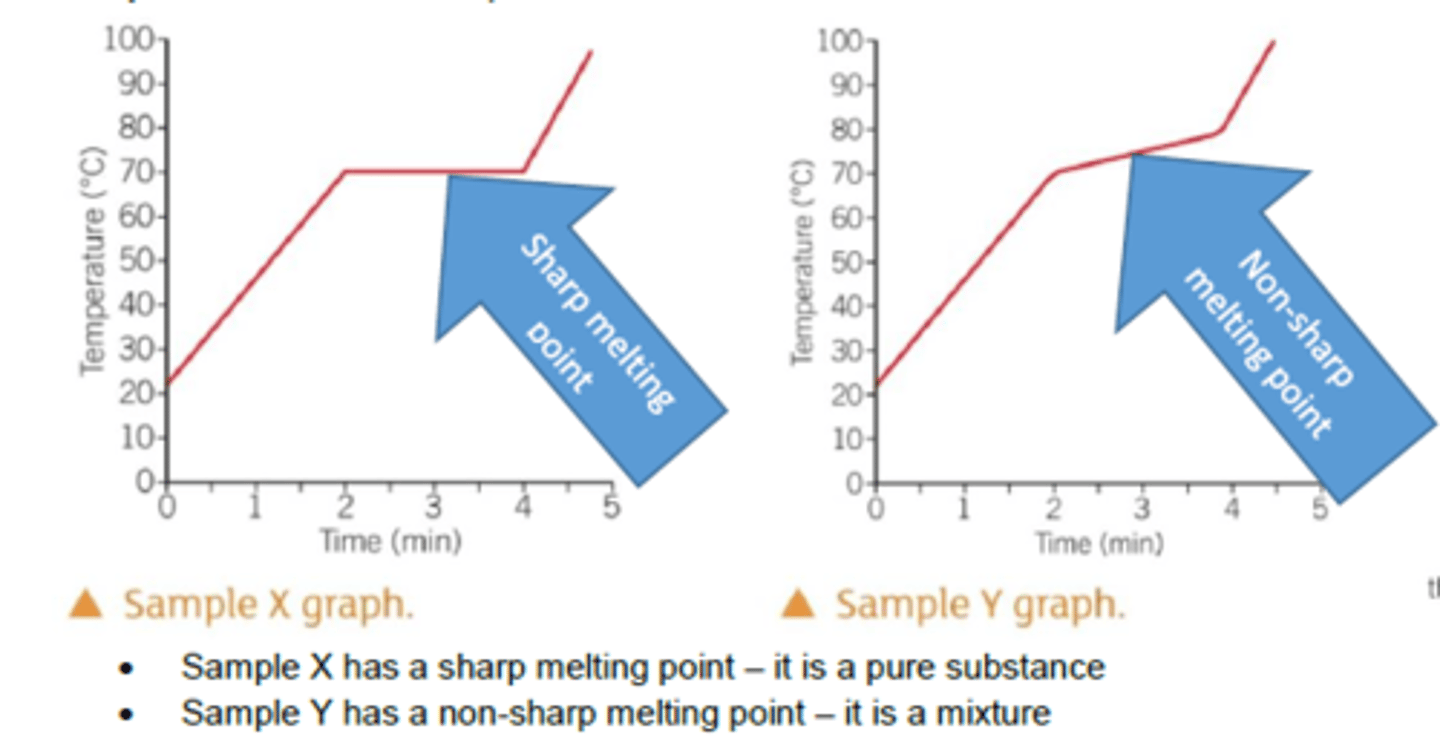
How do can you distinguish purity in substances?
Pure substances melt and boil at specific and sharp temperatures e.g. pure water has a boiling point of 100 °C and a melting point of 0 °C
Why do mixtures have a range of melting and boiling points?
They consist of different substances that tend to lower the melting point and broaden the melting point range
What is the stationary phase?
Where the molecules can't move. It is a solid or a really thick liquid
What is the mobile phase?
Where the molecules can move. This is always a liquid or a gas
What are ions?
An atom or molecule with an overall positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of an electron
What are cations?
Positively charged ions (lose electrons)

What are anions?
Negatively charged ions (gain electrons)

What is electrostatic attraction?
Attraction between opposite charges
What is an ionic lattice?
A giant structure of ions that held together by ionic bonds that have a regular, repeating arrangement
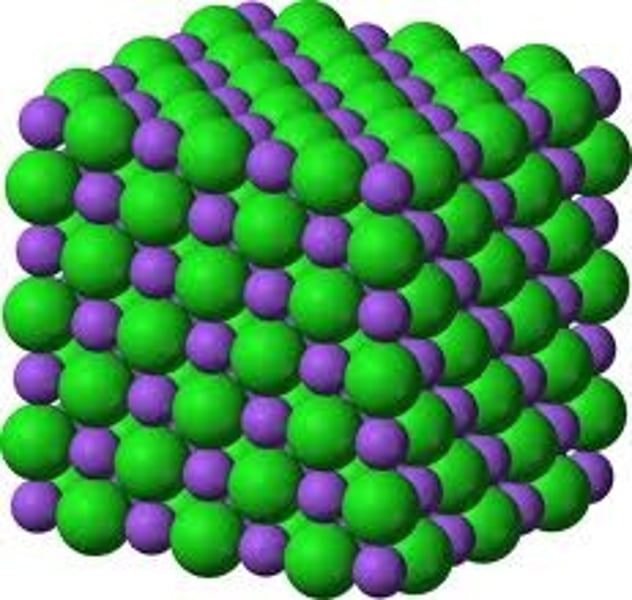
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
They have strong ionic bonds so it takes large amounts if energy to overcome forces
Why don't ionic compounds conduct electricity when solid?
The ions in solids are not free to move as they are held together by strong forces
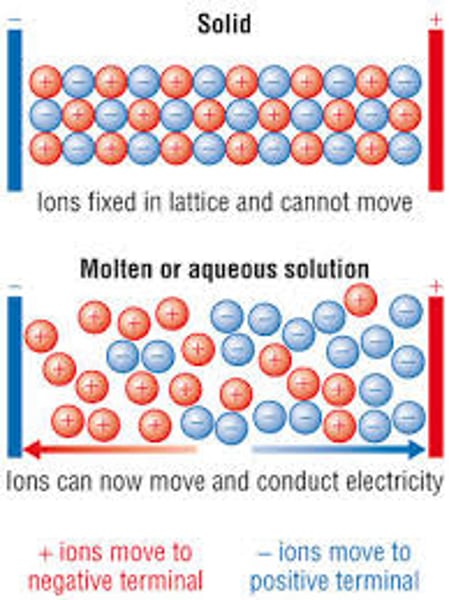
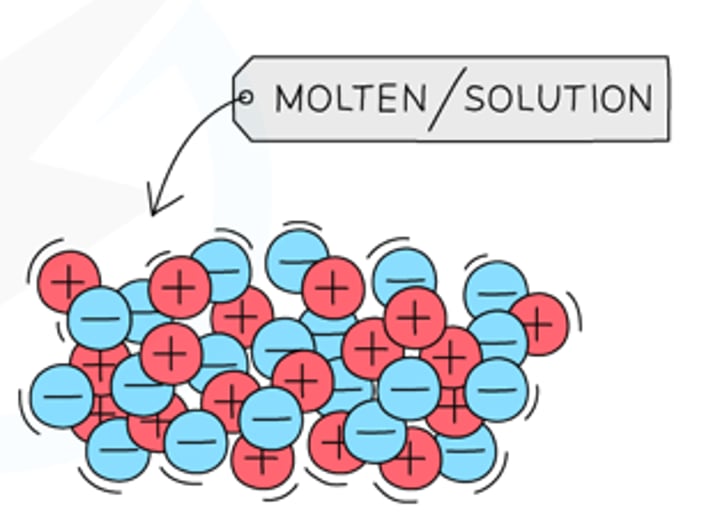
In what state do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Molten or aqueous state
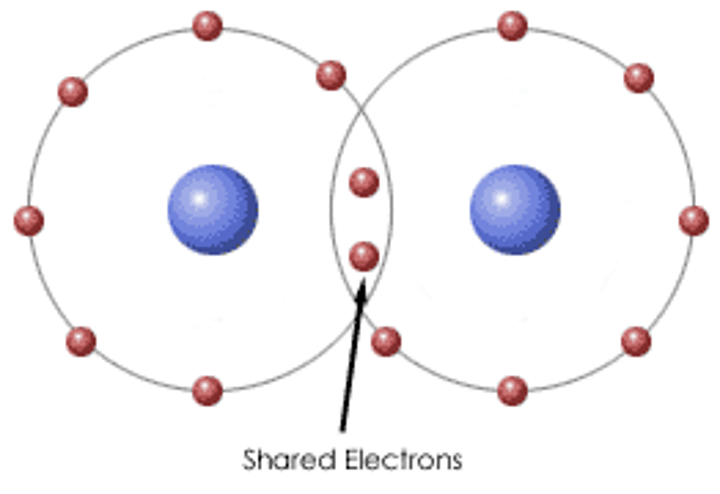
What is covalent bonding?
The strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms
What are simple molecular structures?
When a substance consists of molecules with inter molecular forces of attraction
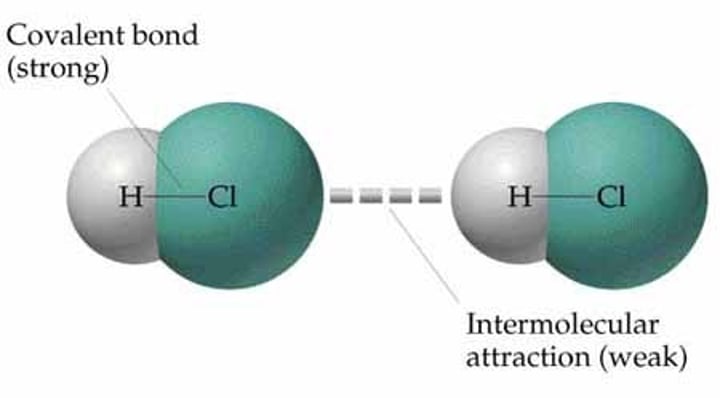
Why do simple molecular substances have low melting and boiling points?
There are weak intermolecular forces although the covalent bonds or intramolecular forces are not broken
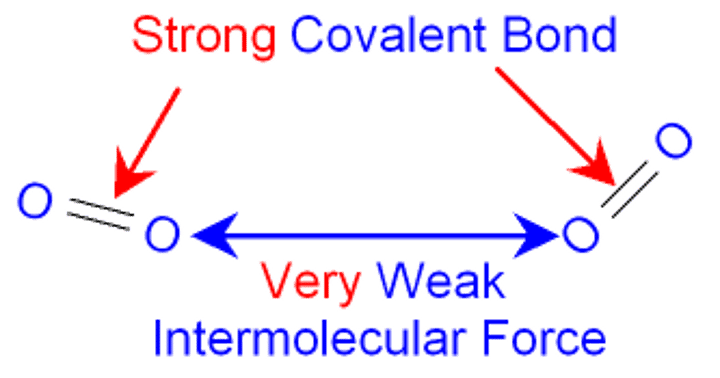
Why does relative molecular mass increase the melting point and boiling point?
There are more inter molecular forces that need to be broken

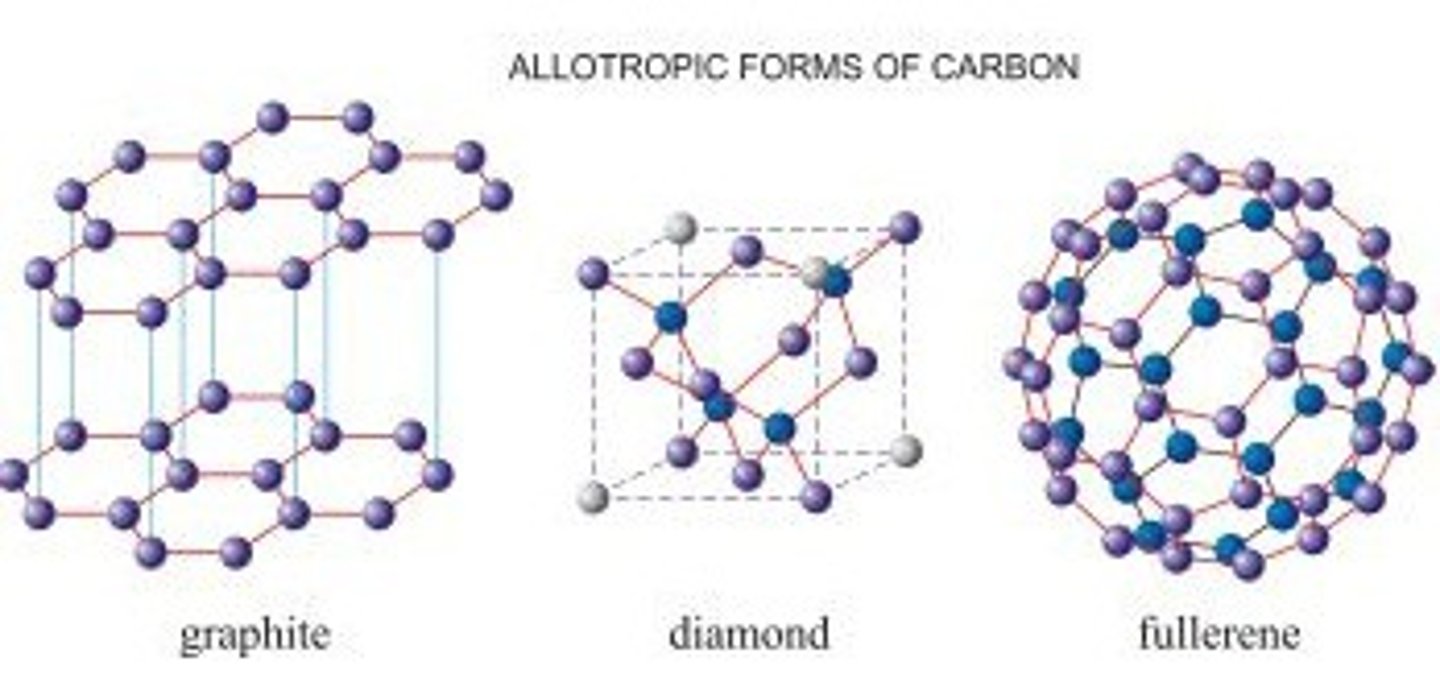
What is a giant covalent structure?
A huge 3D network of covalently bonded atoms
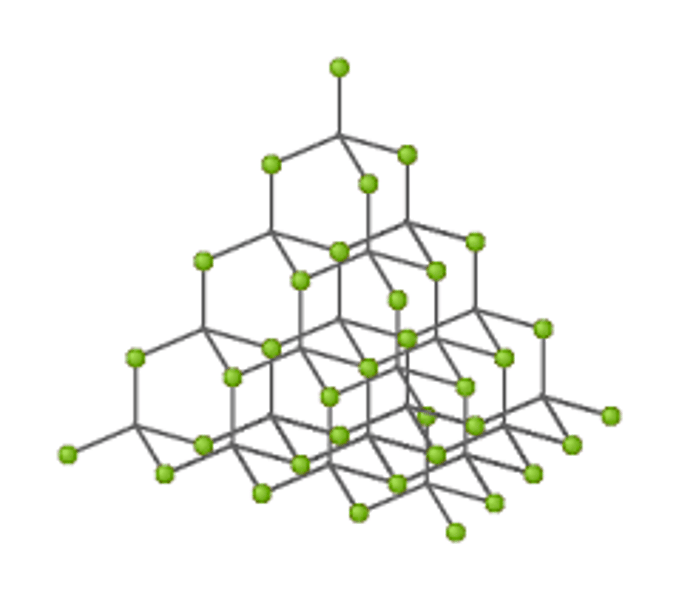
Why do giant covalent structures have high melting and boiling points?
Large amounts of energy are needed to overcome strong covalent bonds
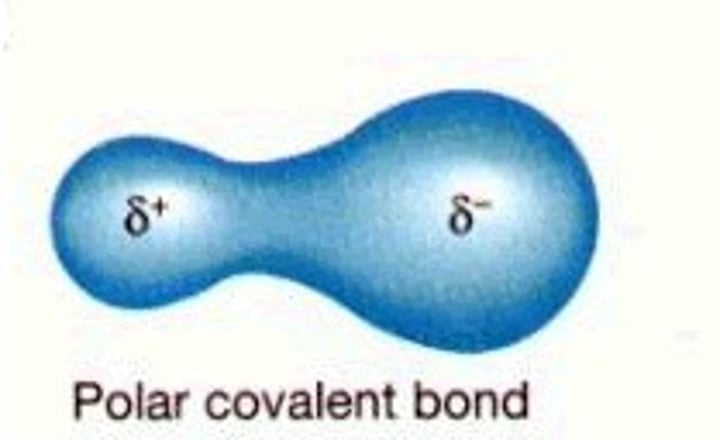
What is a polar covalent bond?
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
Why do atoms bond?
Because they want to be stable by gaining a full valence shell
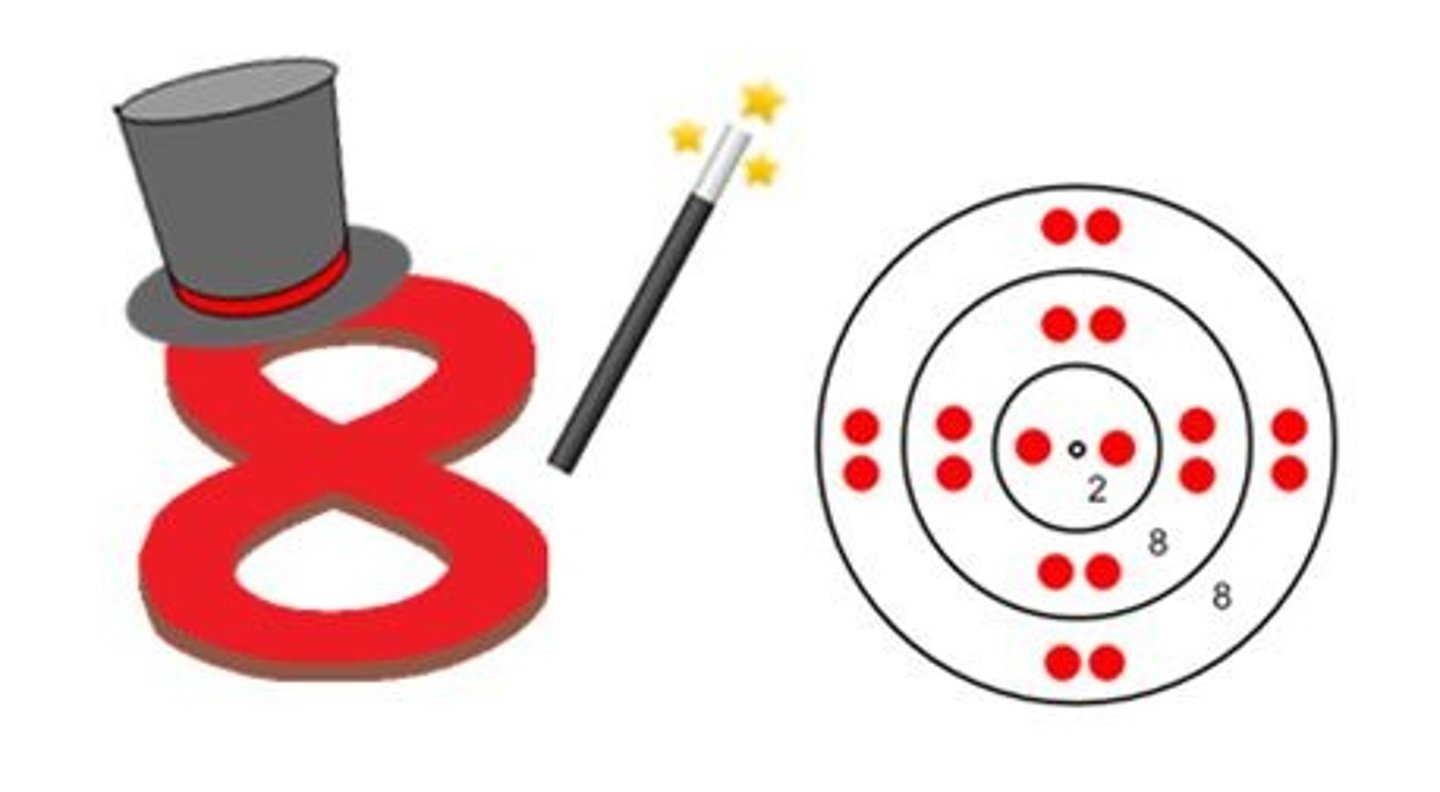
What is a molecule?
A group of atoms bonded together
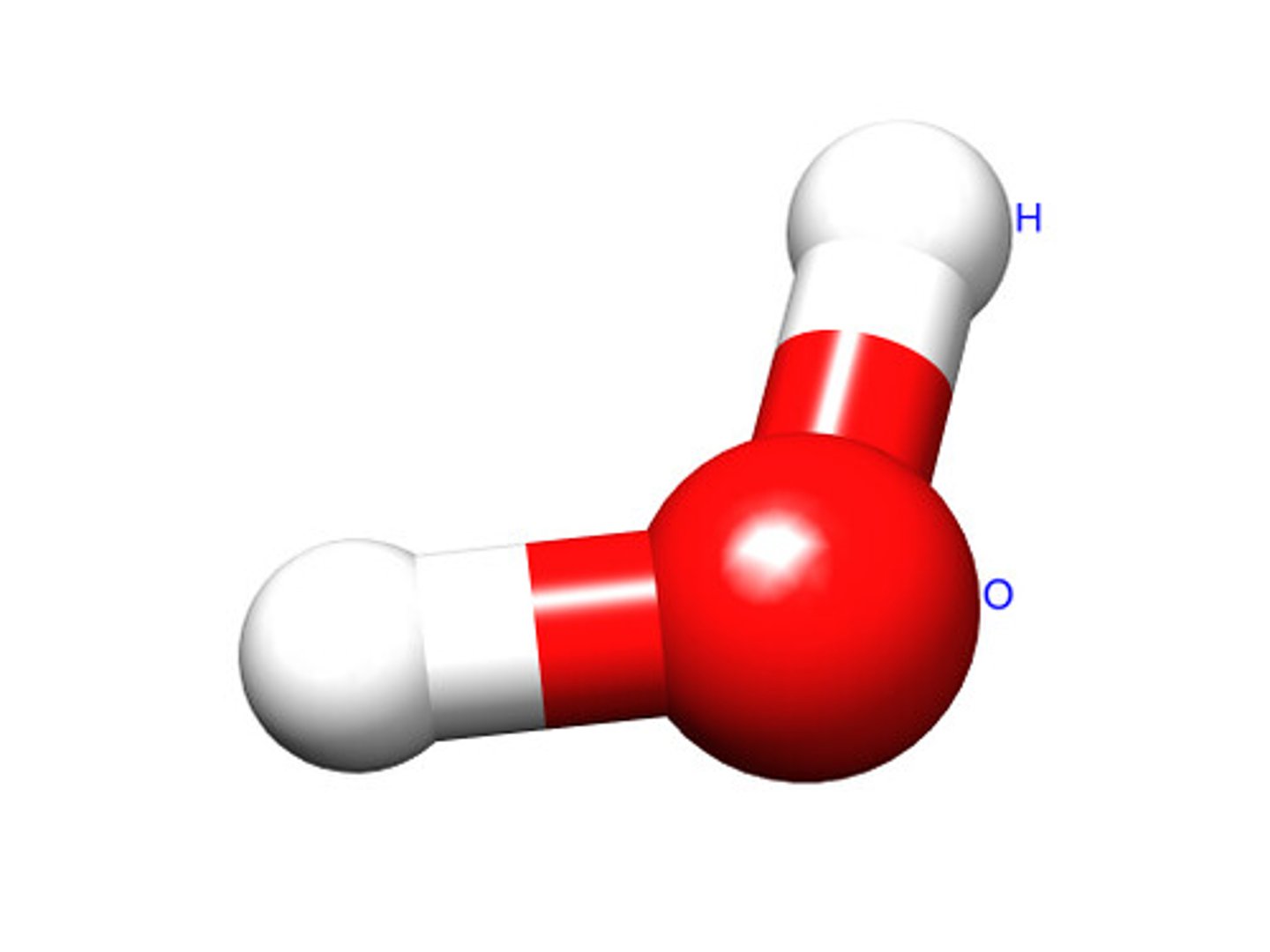
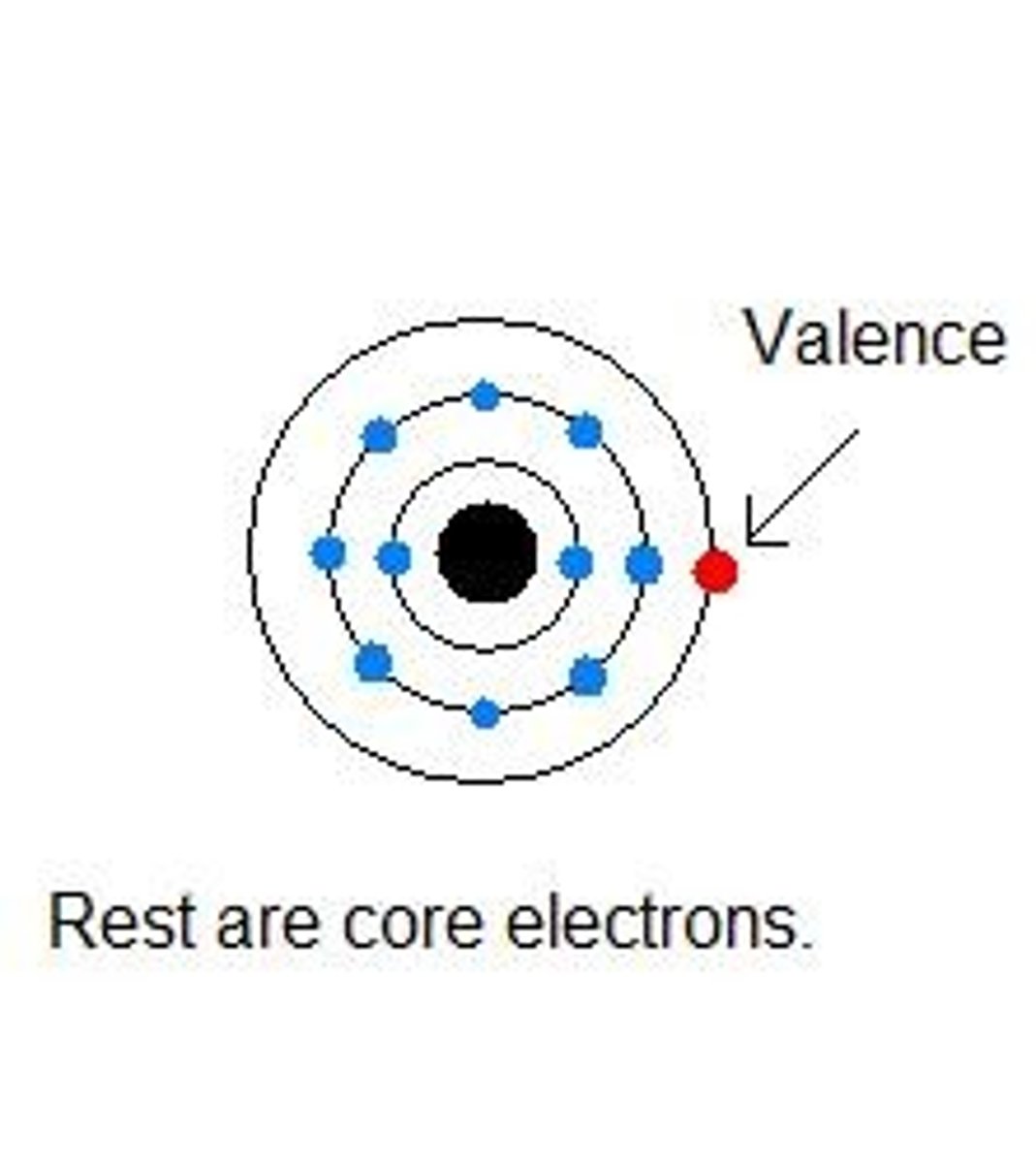
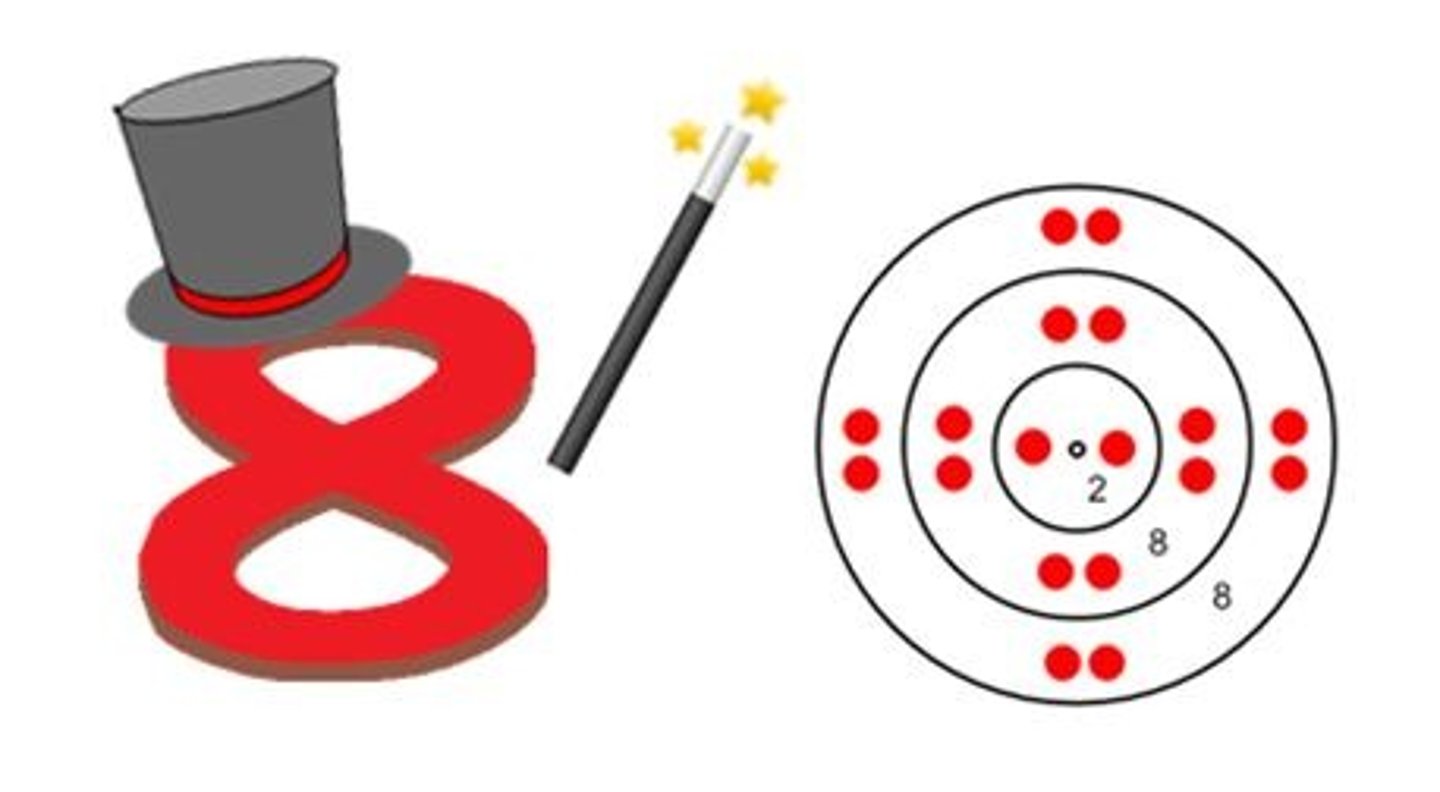
What is an octet?
8 valence electrons
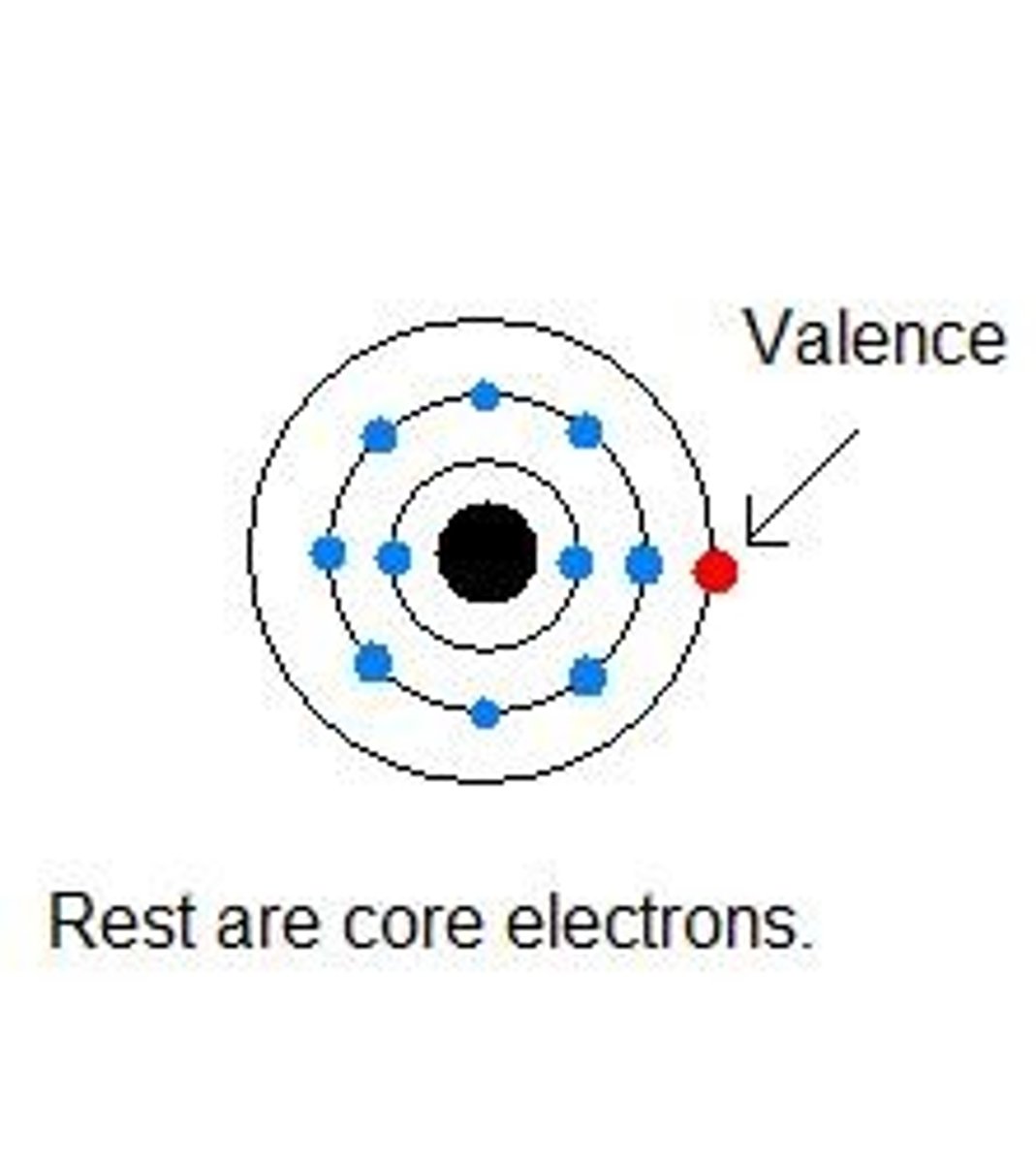
What is valence?
The outershell
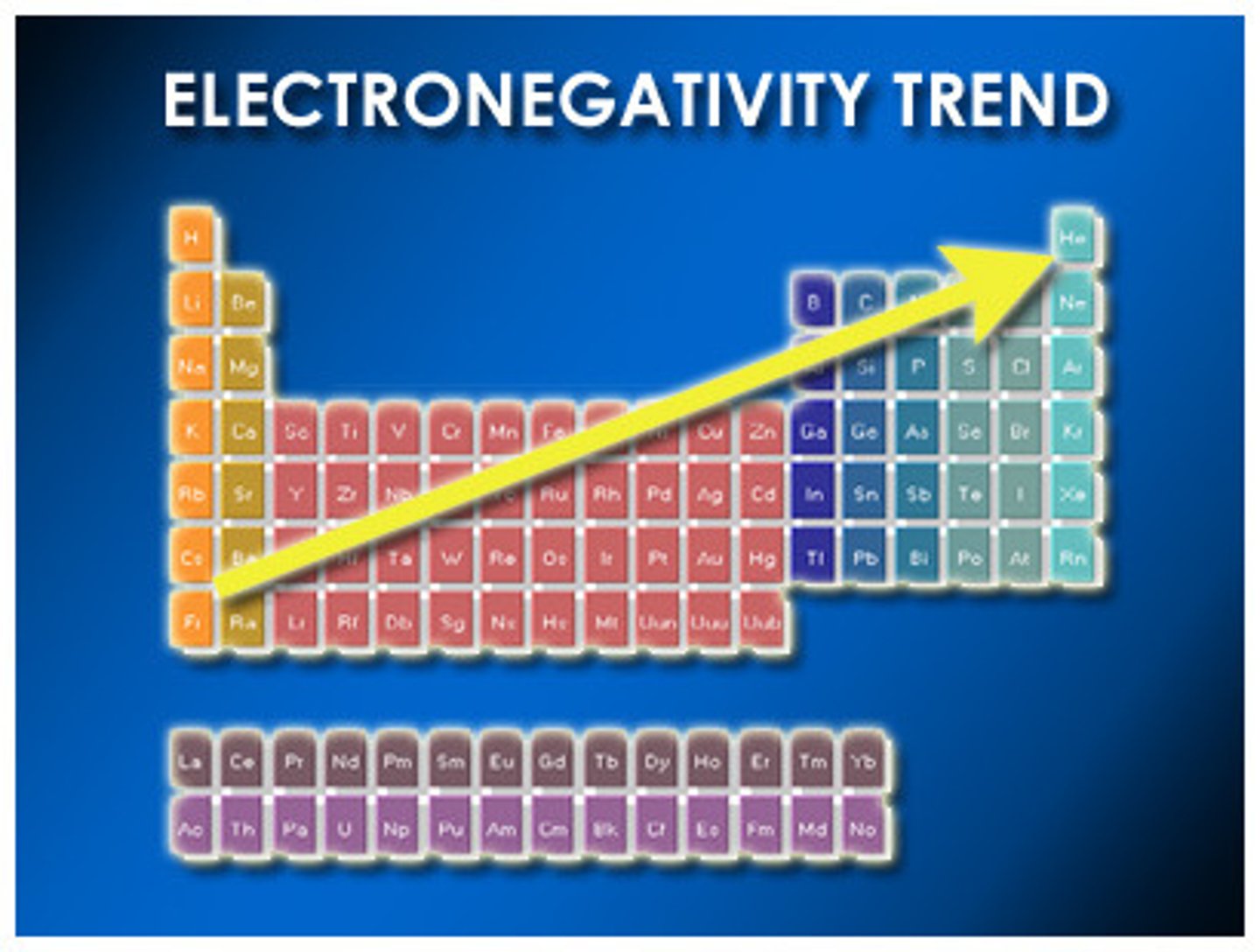
What is electronegativity?
Ability to attract electrons
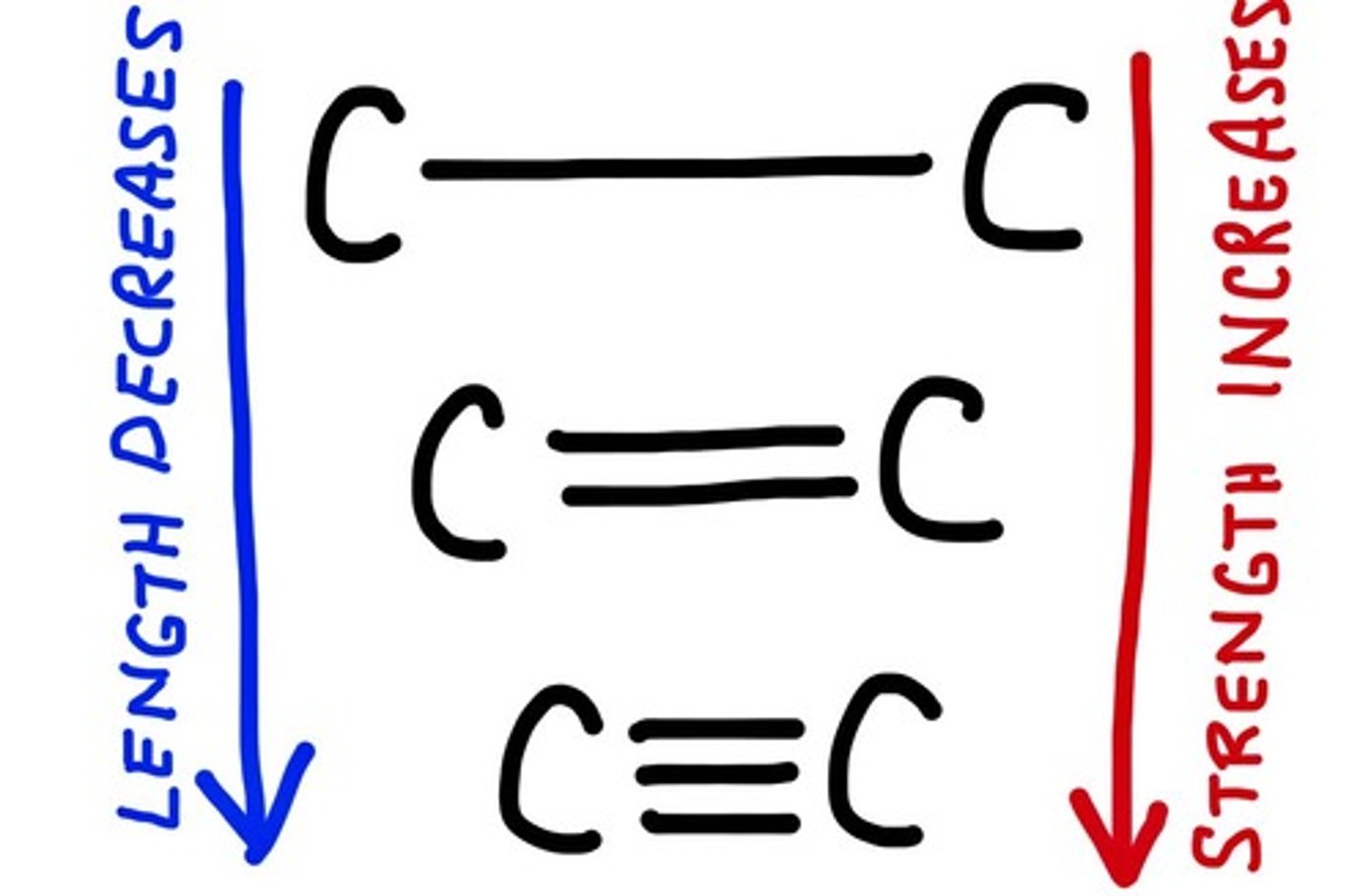
What is bond length?
The distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
What are allotropes?
Different forms of the same element