Orgo Chem - Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Amines and Amides
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
aldehyde
the carbonyl group is attached at the end of the parent chain
ketone
the carbonyl group is bound to a carbon which is bound to 2 carbon atoms in the carbon chain. For this reason, the simplest ketone is propanone.
carbonyl
a carbon double bonded to an oxygen; C=O
Naming Aldehydes
Lowest address (number) to carbonyl carbon
Base name will end in -al or -dial – we do not need to include a number because we know it is found at the end of the chain
Follow the same naming rules as before for substituent chains in alphabetical order
naming Ketones
Lowest address (number) to carbonyl carbon
Base name will end in –one, -dione, -trione, etc. – address necessary since the carbonyl carbon can be anywhere in the chain
Follow the same naming rules as before for substituent chains in alphabetical order
Carboxylic Acids
Organic family characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group –COOH
Naming Carboxylic Acids
Count the carbon atoms and pick the longest chain that contains the carboxyl group
Number the main chain such that the carboxyl group falls on carbon number one.
Branches are named as before. • Name the main chain like it was an alkane but drop the ‘e' and add –oic acid
Like alcohols and ketones, keep the ‘e’ if there is more than one.
Carboxylic acids will never need a number as the COOH group will always be found on the end of the chain. HIGHEST PRIORITY!! You simply count the number of carbons like you would an alcohol and add -oic acid or -dioic acid to the end of the name.
Properties of Carboxylic Acids
weak acids found in many foods
Polar molecule
capable of hydrogen bonding
Similar solubility to alcohols
General form of an ester
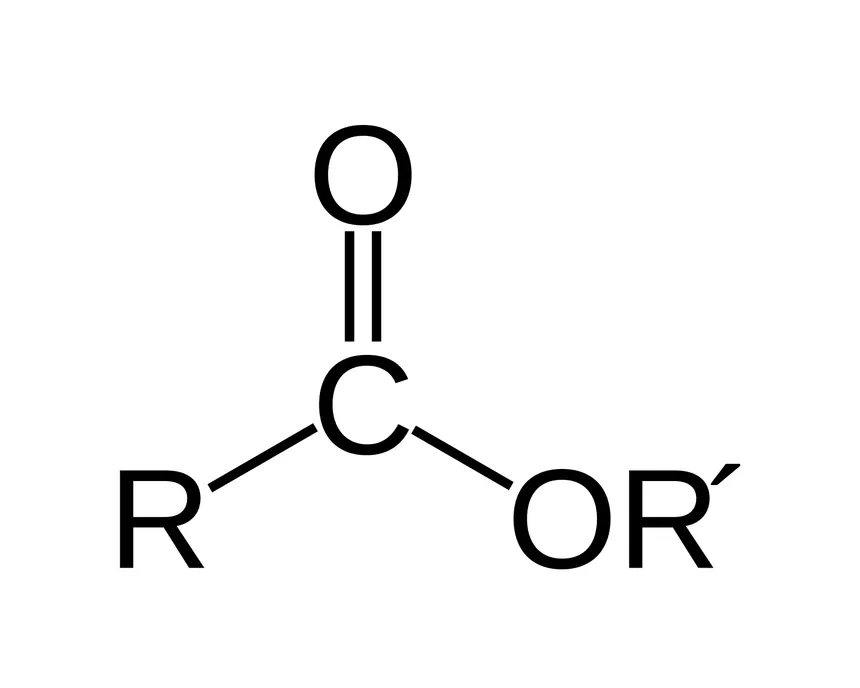
Esters form from
the reaction of an acid and an alcohol
Naming Esters
Identify the alkyl groups on either side of the functional group (note: the carbon in the C=O bond must be included in the alkyl group)
Write the name of the alkyl group attached to the oxygen first, and the alkyl group attached to the carbonyl (C=O) second
The first group named gets the –yl ending, the second group named drops the ‘e’ and gets the ending -oate
Branches are named as before
Properties of Esters
less polar than carboxylic acids because they do not contain the hydroxyl group
Do not form hydrogen bonds
Less soluble than carboxylic acids
Smaller esters are gases at room temp, where larger ones can be waxy solids
amines
an organic fam made up of an ammonia (NH3) molecule that has one or more hydrogens replaces by alkyl (methyl, butyl, etc) or aromatic groups
properties of amines
higher melting pts than similar sized hydrocarbons
polar molecules w hydrogen bonding
three types of amines
primary - one alkyl group
secondary - 2 alkyl groups
tertiary - 3 alkyl groups
naming amines
iden the longest alkyl group attached to the N which will be used for the ending and everything else will be considered a branch
other groups attached to the N are named by the same branch prefix but their location would be “N” and not a number since numbering is only for carbons
for the ending → use the alkane group but drop the e and replace w the location for the N and “amine”
however the “e” is left alone if there are multiple amine groups
benzene on amines
if they are the main chain, they are called aniline
if there are MORE THAN ONE BENZENE, they are referred to as phenyl
and if they are not the main branch they are also referred to as phenyl
amides
an orgo fam of compounds with a carbonyl functional group bonded to a NH3 atom
properties of amides
polar molecules
made from carboxylic acids bonding to ammonia or amine groups
naming amides
iden the alkyl chain that contains the carbonyl group → would be the parent alkane
name the other chains attached to the N like branch chains
location is denoted with N for such branches
for the ending, drop the e and replace w amide
unless there are amide groups on both sides (“diamide”) so keep the e
Prefix for a carbonyl carbon is “ ____ if it is not the priority in the chain
oxo”