Recombinant DNA Technology L2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
what is it
- taking a piece of DNA and combining it with another strand of DNA
- •Amplification, maintenance and manipulation of specific DNA
Applications of Recombinant DNA Technology
•Genome organisation and gene expression
•Production of recombinant proteins (vaccines, therapeutics, enzymes)
•Transgenic organisms
•Gene Therapy
molecular cloning process
•1. Extraction of relevant nucleic acids
•2. Determine base sequence of required piece of DNA
•3. Create many copies of required piece of DNA using PCR
•4. Clone amplified DNA fragments into a cloning vector to construct recombinant DNA molecules
•5. Transform recombinant DNA molecules into competent E.coli cells
•6. Identify recombinant DNA molecules (plasmids) containing correct DNA sequence
•Molecular cloning starts with amplifying a specific gene by PCR.
•The source of DNA can be either
Nucleic acid extracted from human cells
•
- a DNA library (gDNA or cDNA)
genomic DNA libary gDNA
•Break up entire genome into small fragments
- Restriction endonuclease
- Mechanical shearing
•Insert all DNA fragments into plasmid vector
•Recombinant plasmids transformed into competent E.coli cells
Applications of a genomic library: 4
•Determine complete genome sequence of an organism
•Source of genomic sequence for generation of transgenic animals through genetic engineering
•Study of function of regulatory sequences in vitro
•Study of genetic mutations in cancer tissues
cDNA Library
•cDNA inserted into vector
•Entire collection of clones from one mRNA preparation
•Collection of actively transcribed genes!
Applications of a cDNA library: 4
•Discovery of novel genes
•Cloning of full-length cDNA molecules for in vitro study of gene function
•Study of the repertoire of mRNAs expressed in different cells or tissues
•Study of alternative splicing in different cells or tissues
- contains uninterrupted coding sequence of gene unlike gDNA
•Which nucleic acid is required?
•DNA -
•Prokaryotes
•Some lower eukaryotes
•
•mRNA -
•Higher eukaryotes
Extraction of Relevant Nucleic Acids
- •Cell disruption or cell lysis to expose the NA.
- Remove membrane lipids by adding a detergent - ethanol precipitation
- 2.Phenol-chloroform extraction
- 3.Minicolumn purification
ethanol precipitation
Precipitation improved by increasing of ionic strength
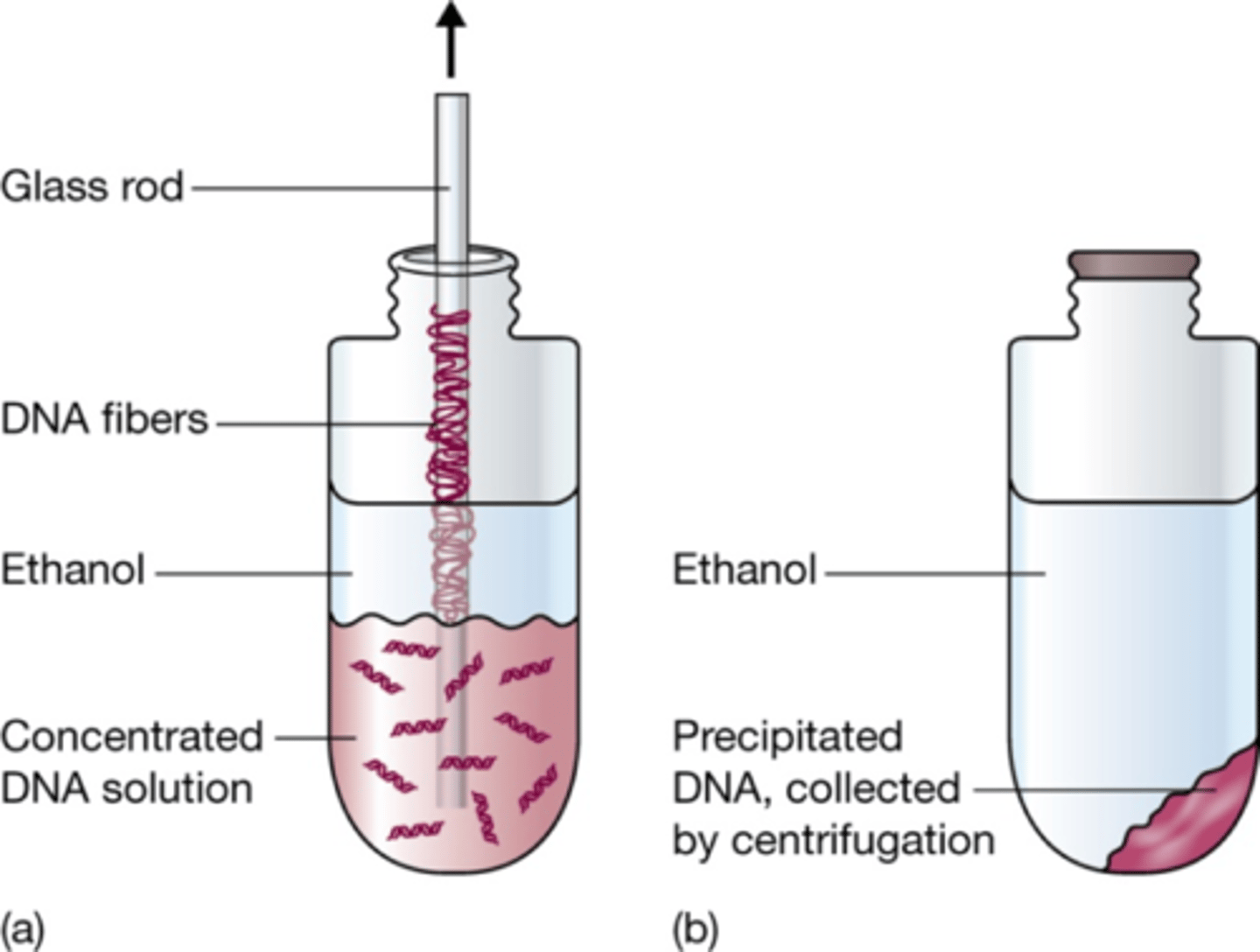
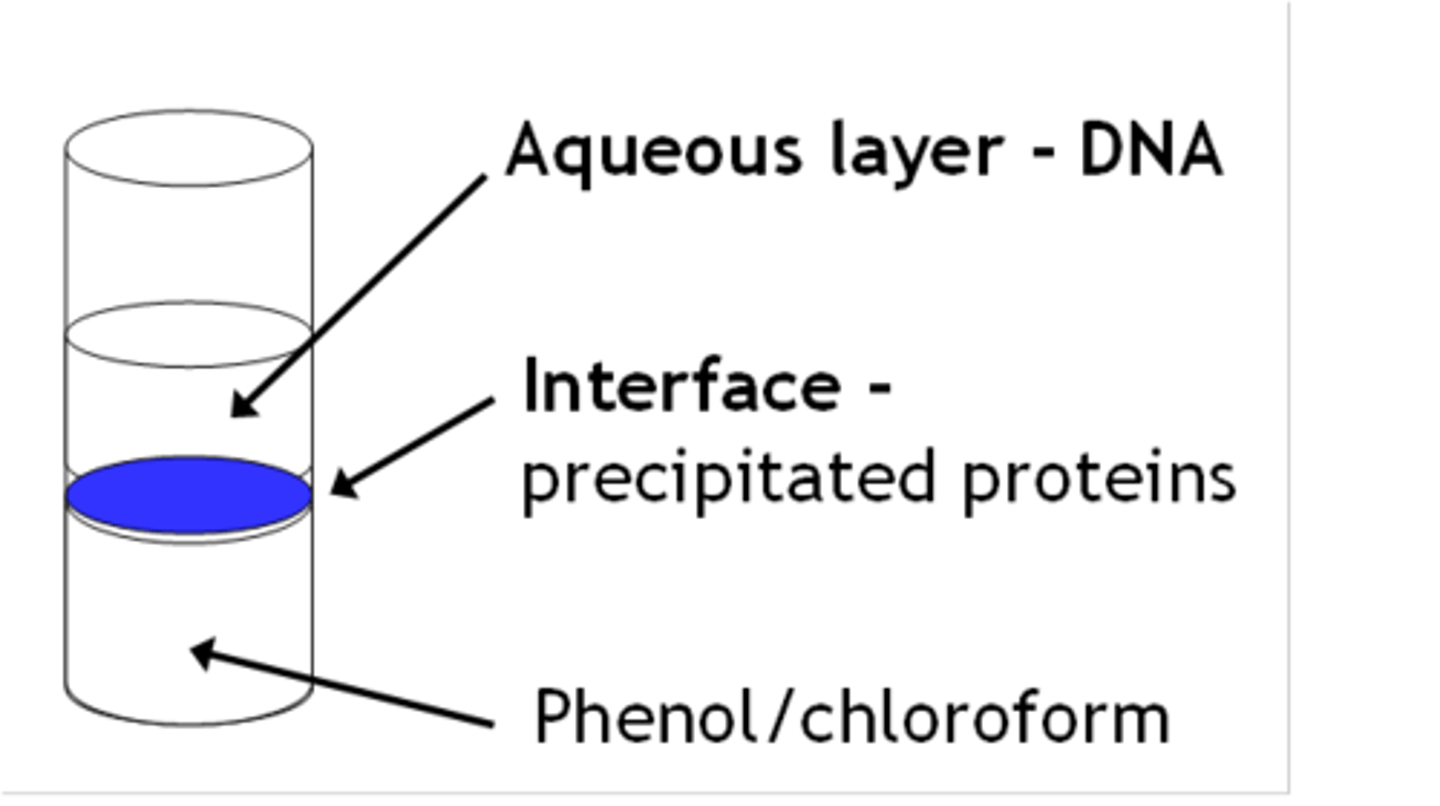
2.Phenol-chloroform extraction
•Phenol denatures proteins - stay in organic phase
•Aqueous phase containing nucleic acid mixed with the chloroform
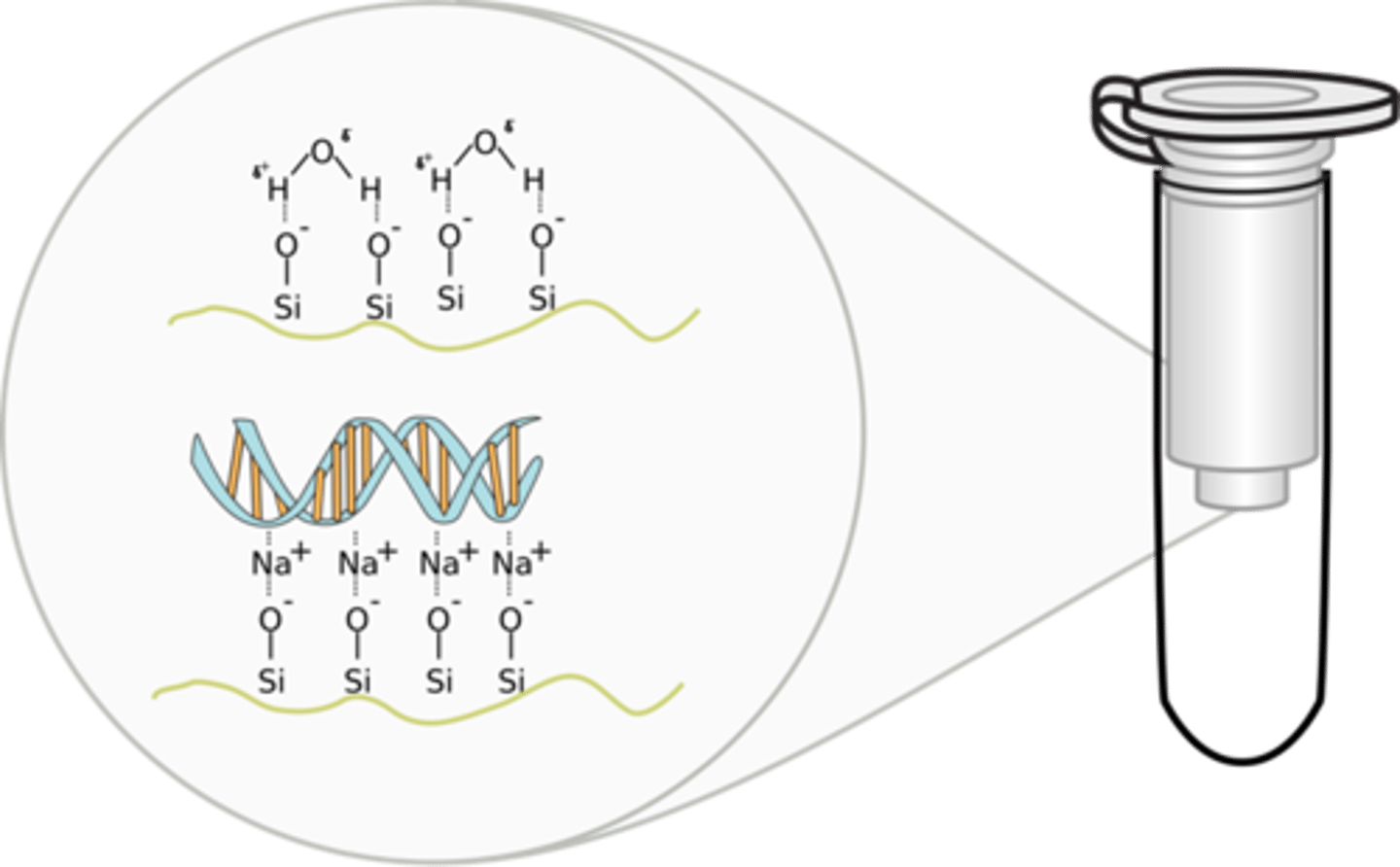
3.Minicolumn purification
•Nucleic acid binds to solid phase (silica or other)
bind due to lower pH and salt concn of the binding solution
Methods to analyse DNA or RNA
- UV Absorbance (DNA)
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (BOTH)
- Fluorescent Dye-Based Quantification (RNA)
UV absorbance
•Abs260nm used to measure the amount of NA
•Abs280 to measure the amount of protein
•Abs230 to measure the amount of sugars
Fluorescent Dye-Based Quantification
•NA sample and series of standards incubated with the fluorescent dye.
Dye binds to NA causing a conformational change - increased fluorescence
creating Many Copies of DNA using PCR
•Template DNA containing the sequence to be amplified
•
•Pair of primers that flank the sequence
•Most commonly used - plasmid vector
•Small, circular molecules of dsDNA
from bacteria
•
•Easily separated and purified from
gDNA
restriction enzymes
act as "molecular scissors."
-come from various types of bacteria
-allow scientists to study and manipulate genes more easily
-cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence called a restriction site
some restriction enzymes cut straight across and leave
blunt ends
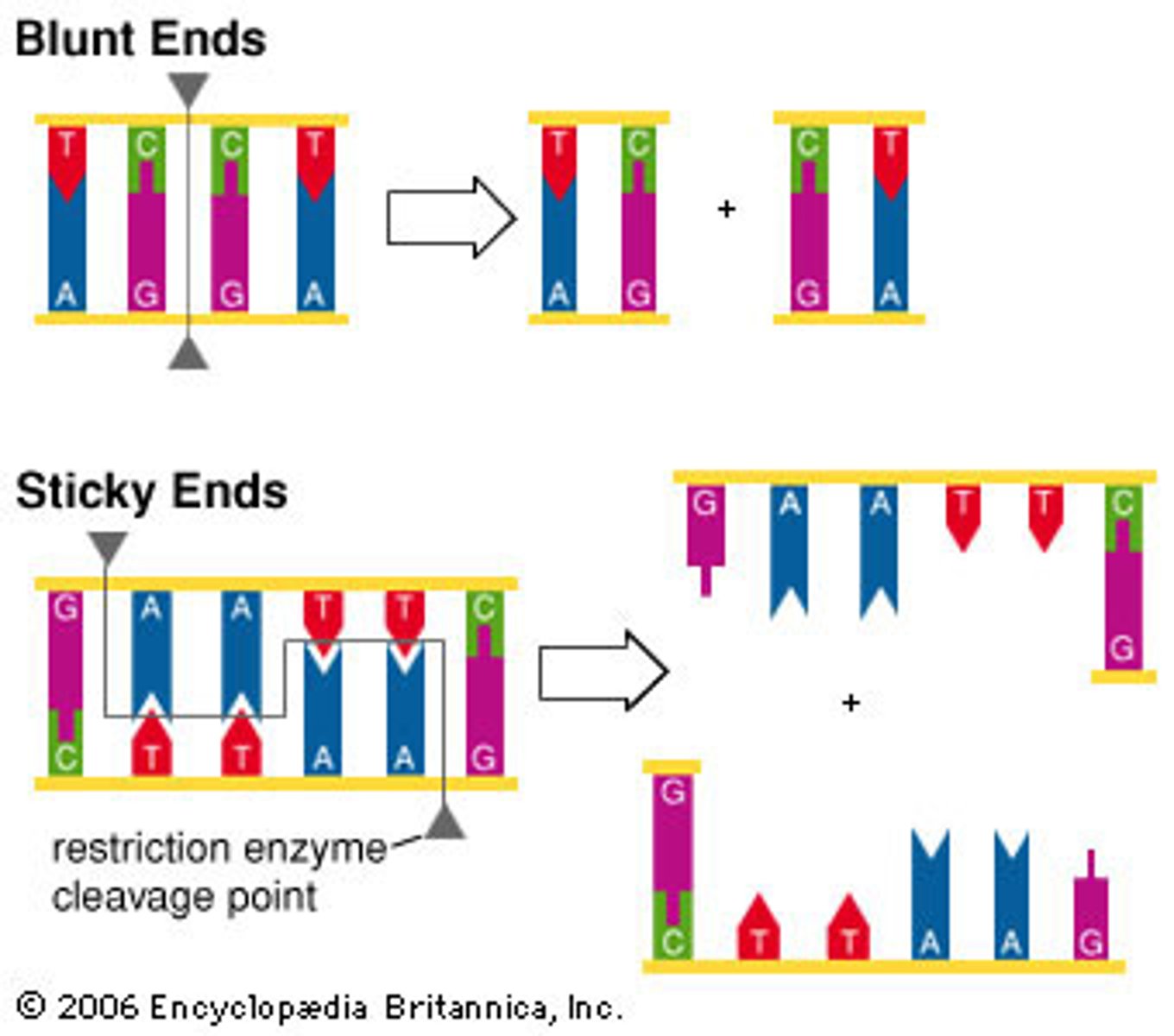
some restriction enzymes make staggered cuts and leave
sticky ends
Gel electrophoresis is used to
•separate DNA fragments by size.
-A DNA sample is cut with restriction enzymes.
-Electrical current pulls DNA fragments through a gel.
how does Gel electrophoresis work
Smaller fragments move faster and travel farther than larger fragments
- Fragments of different sizes appear as bands on the gel
A restriction map shows
the lengths of DNA fragments between restriction sites.
- only indicate size, not DNA sequence
useful in genetic engineering
used to study mutations
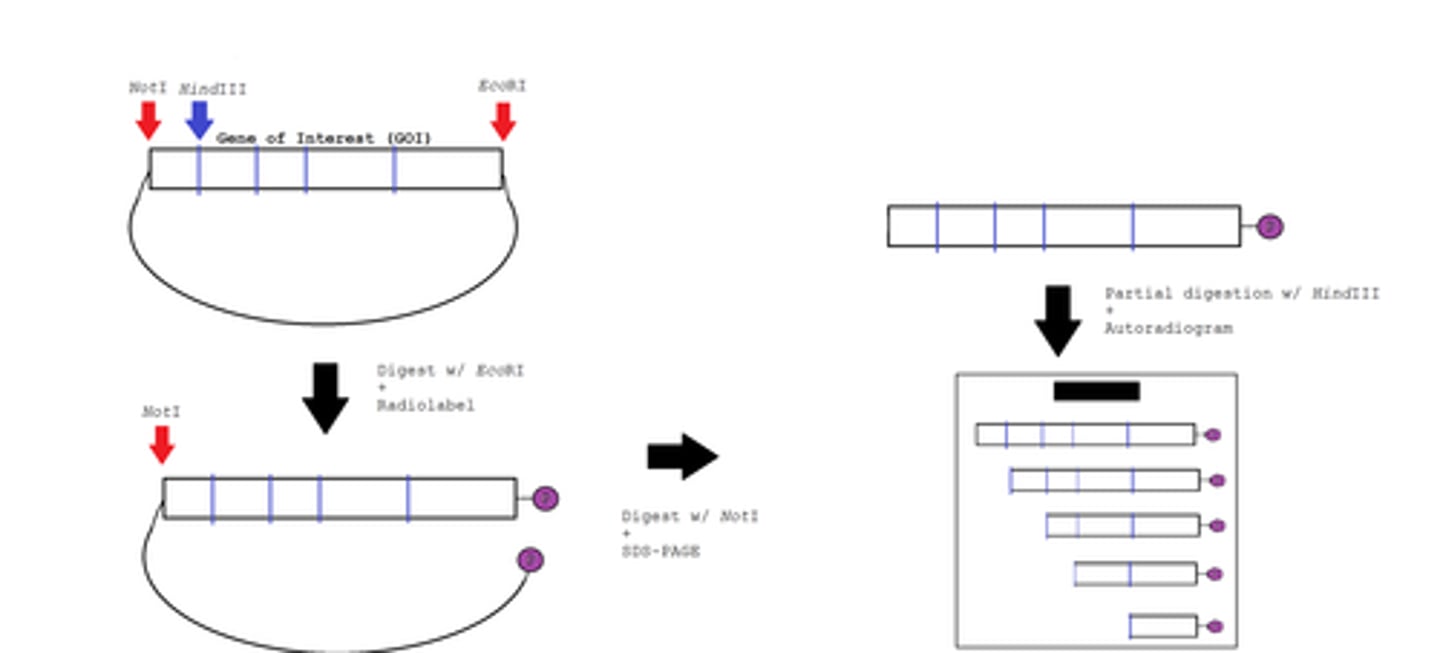
Clone the gene into cloning vector using the restriction enzyme
•NcoI (5'-end)
- •NcoI cuts at CCATGG sequence
•Forward primer - add restriction nuclease site
•Aim: Create recombinant molecules with single piece of donor source (insert) combined with single cloning vector.
Problem: Variety of recombinant molecules produced!
• E coli chemically treated with divalent cations i.e. Ca2+ or electrical shock
•Open pores in membrane - take up exogenous DNA
after transformation
- allowed a recovery period
- put onto grwoth media that selects for a selectable marker gene
- only bacteria with vector DNA will survive
•Methods to verify if gene of interest was successfully cloned 4
1.Blue - White Screen
2.Diagnostic Restriction Digest
3.Colony PCR
4.Sequencing
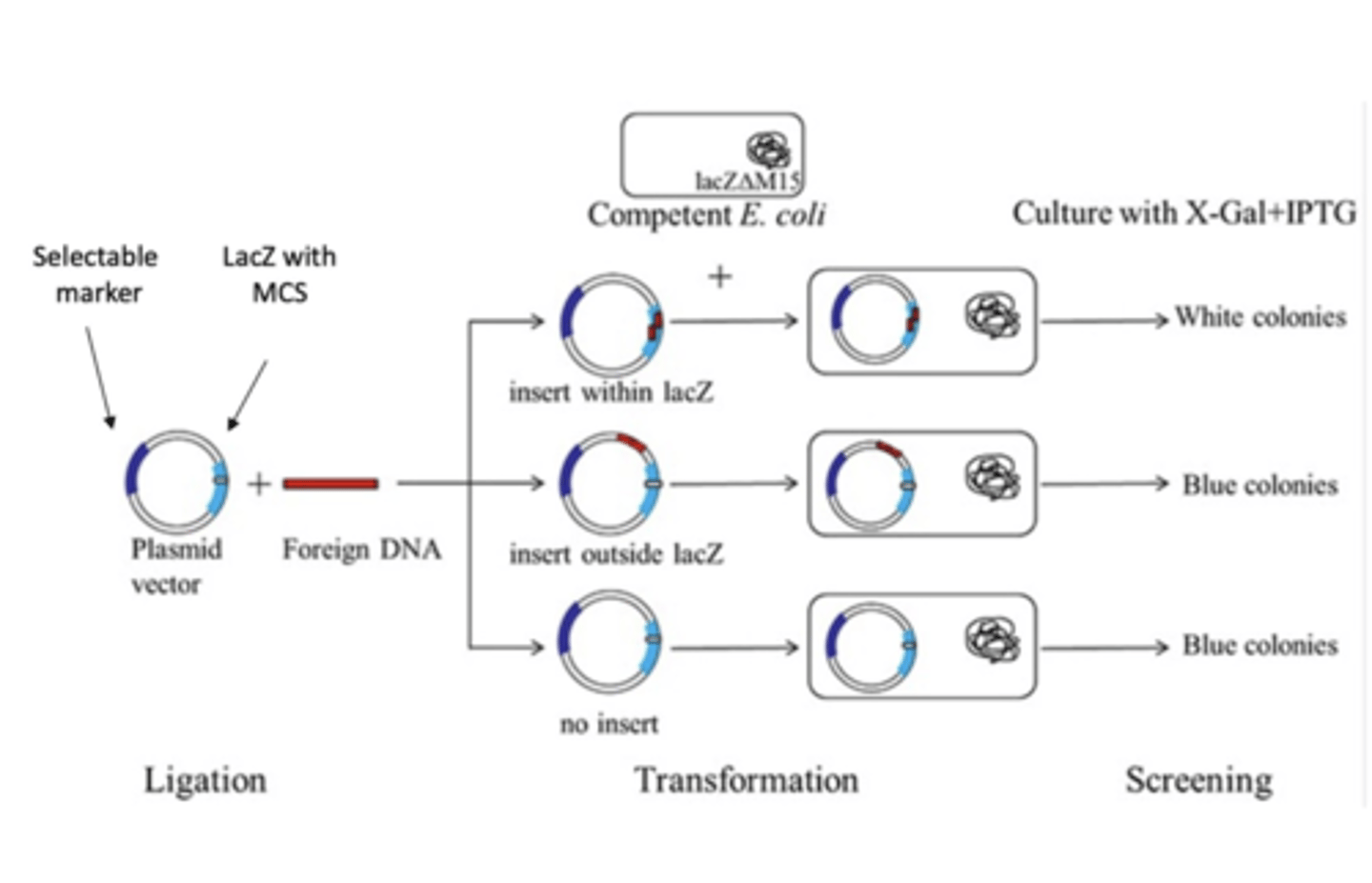
blue - white screen
Blue colonies: cells transformed with cloning vectors not containing inserts(b-galactosidase is active)
White colonies: cells transformed with recombinants. b-Galactosidase gene disrupted by insert
- Method to identify successful gene insertion in plasmids based on color change
2.Diagnostic Restriction Digest
•Choose restriction enzymes to determine if the plasmid contains an insert.
Run the digested plasmid on agarose gel to verify the vector backbone and insert are expected sizes
3.Colony PCR
•DNA insert determined by screening bacterial colonies by PCR.
•Primers may be insert-specific or vector-specific.
•Suitable for inserts shorter than 3 kb.
- can also use gel electrophoresis
4.Sequencing
•Most accurate way to verify recombinant colonies.
•Plasmid DNA isolated from bacterial culture.
•Insert identified by sequencing using sequencing primers appropriate for the vectors.
•Sequence across entire insert - verify exact sequence of insert.
Human recombinant proteins produced by microbes examples
•Insulin - diabetes
•Growth hormone - dwarfism
•Interleukin 2 (IL-2) - cancer
•Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF) - cancer
Today approx. 60% recombinant proteins are produced by mammalian cells- why not bacteria cells
•has post transcription modifications unlike bacteria cells
further applications
•In revealing details of various infections, diseases
•Finding out the complete nucleotide sequence of genome of an organism and identification of genes.
•Preventing various genetic disorders
•Understand a molecular event in a biological processes
Possible Negative effect
•: extensive erosion and genetic
- destruction of plant Germplasm; - ecological imbalance;
- production of dangerous toxic chemicals,
- production of highly lethal microbes and their use in microbiological warfare to kill humans, animals and plants.