lab 6 nervous tissue
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
neuron develop at rate of?
250,000 per minute
how many nerve cells we got by adulthood
100 billion
how many do we really use?
4%
what are our biggest cells?
neurons
messages transmit at speed of?
180
main function of nervous tissue?
senses
transmitting and processing information
producing resposne
major compnent of nervous system
cns
pns
cns is?
central nervous system - brain and spinal cord
pns is?
peripheral nervous system - nerves away from cns and ganglia
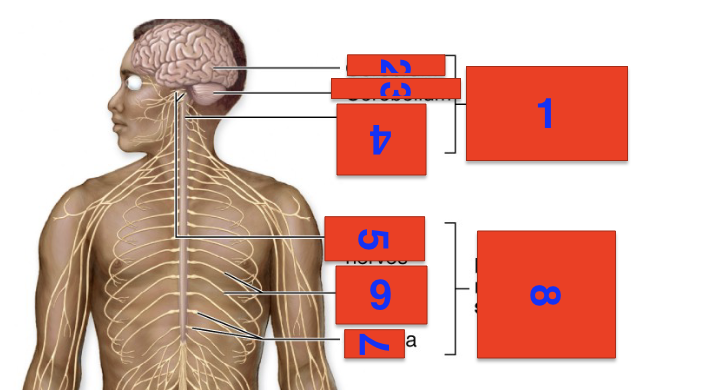
1?
cns
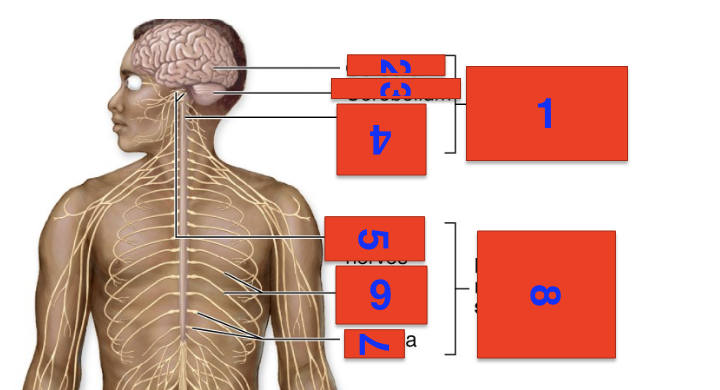
2?
cerebrum
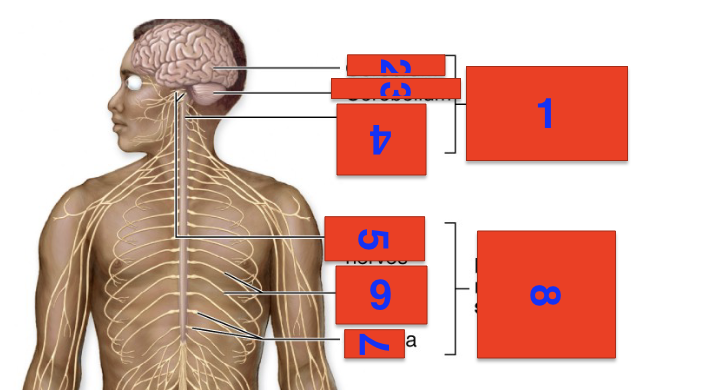
3?
cerebellium
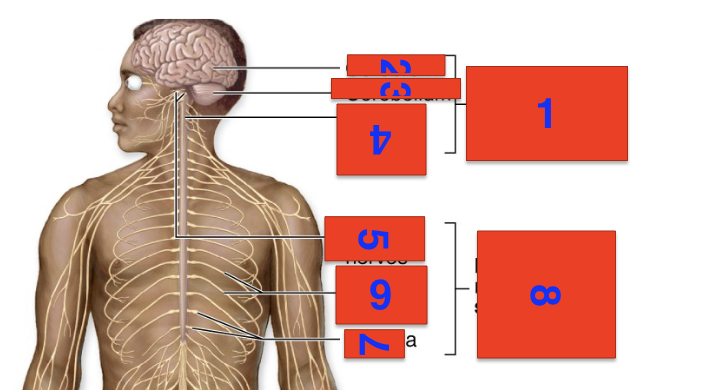
4?
spinal cord
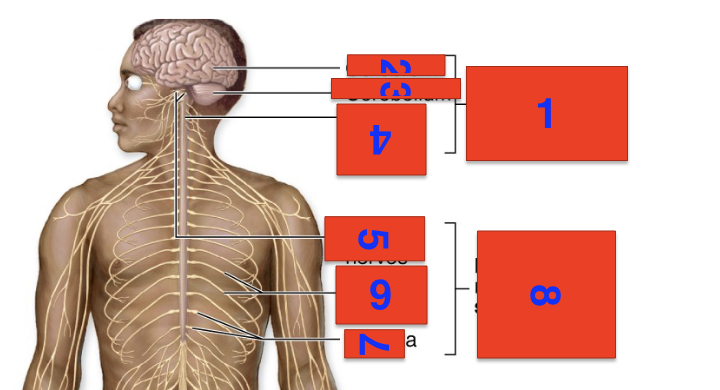
5?
cranial nerves
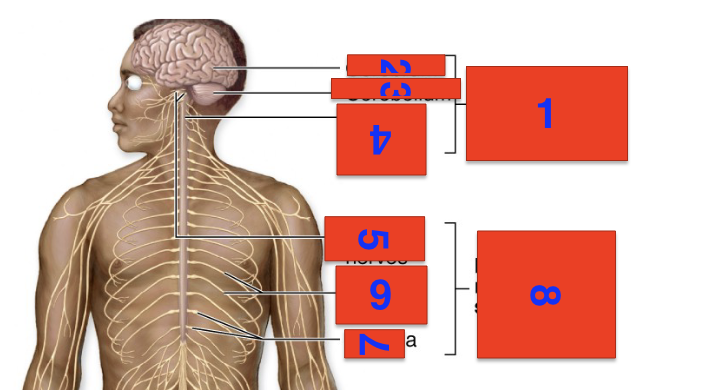
6?
spinal nerves
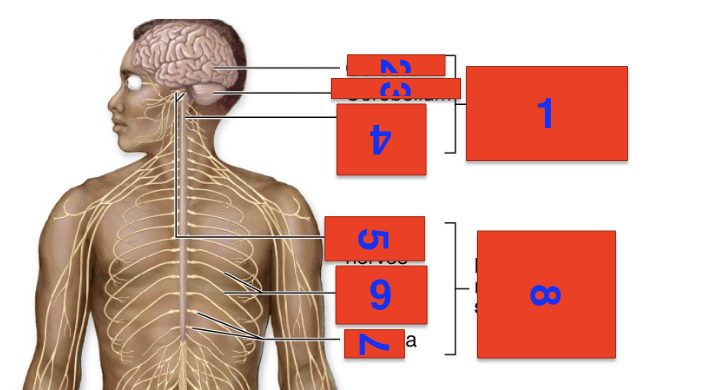
7?
ganglia
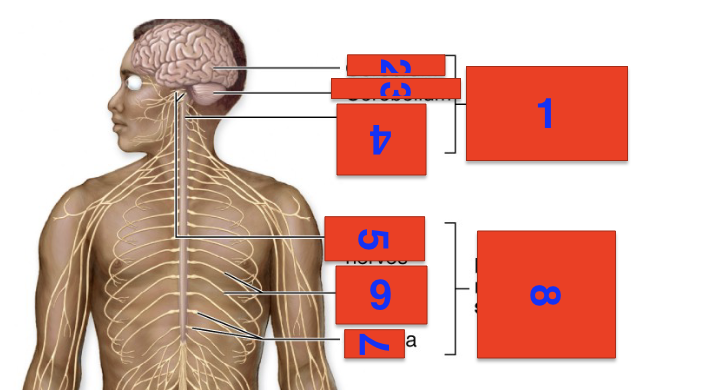
8?
pns
two main cells in nerve tissue?
neurons
glialcells
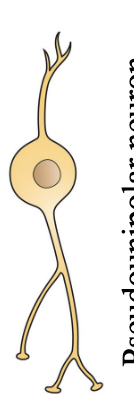
?
bipolar nueron
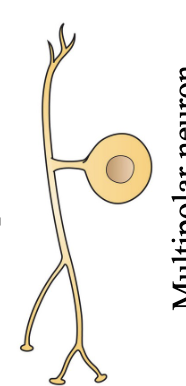
?
pseudounipolar neuron
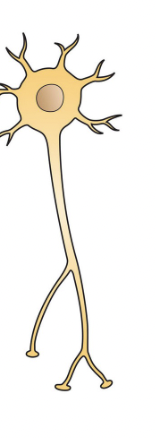
?
multipolar nueron
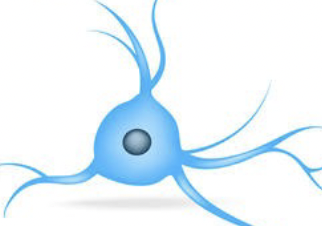
?
glial cell
neuron structure
cell body
nucelus
dendrite
axon temrina;
node of ranvier
myelin sheath
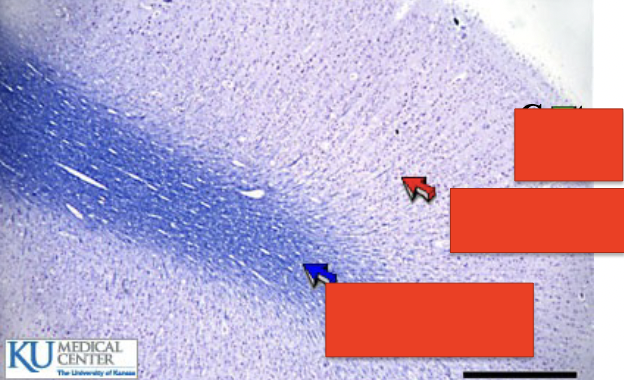
what is this?
cerebrum
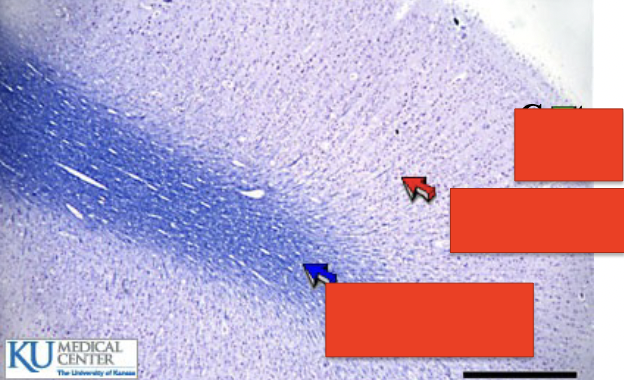
top?
cortex layer
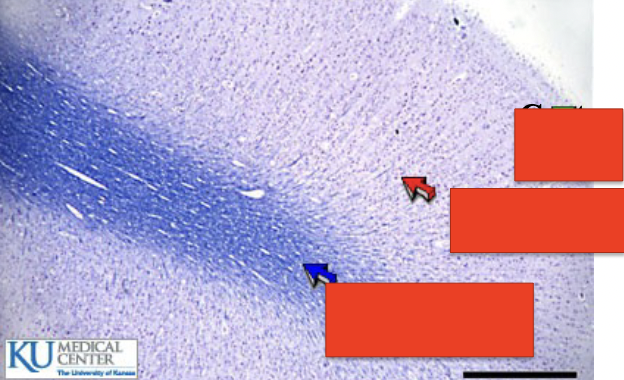
middle
gray matter
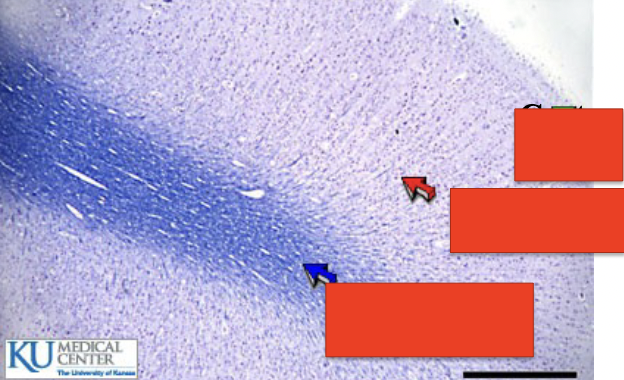
bottom
white matter
cns has
organs
spinal cord
regions
grey and white matter
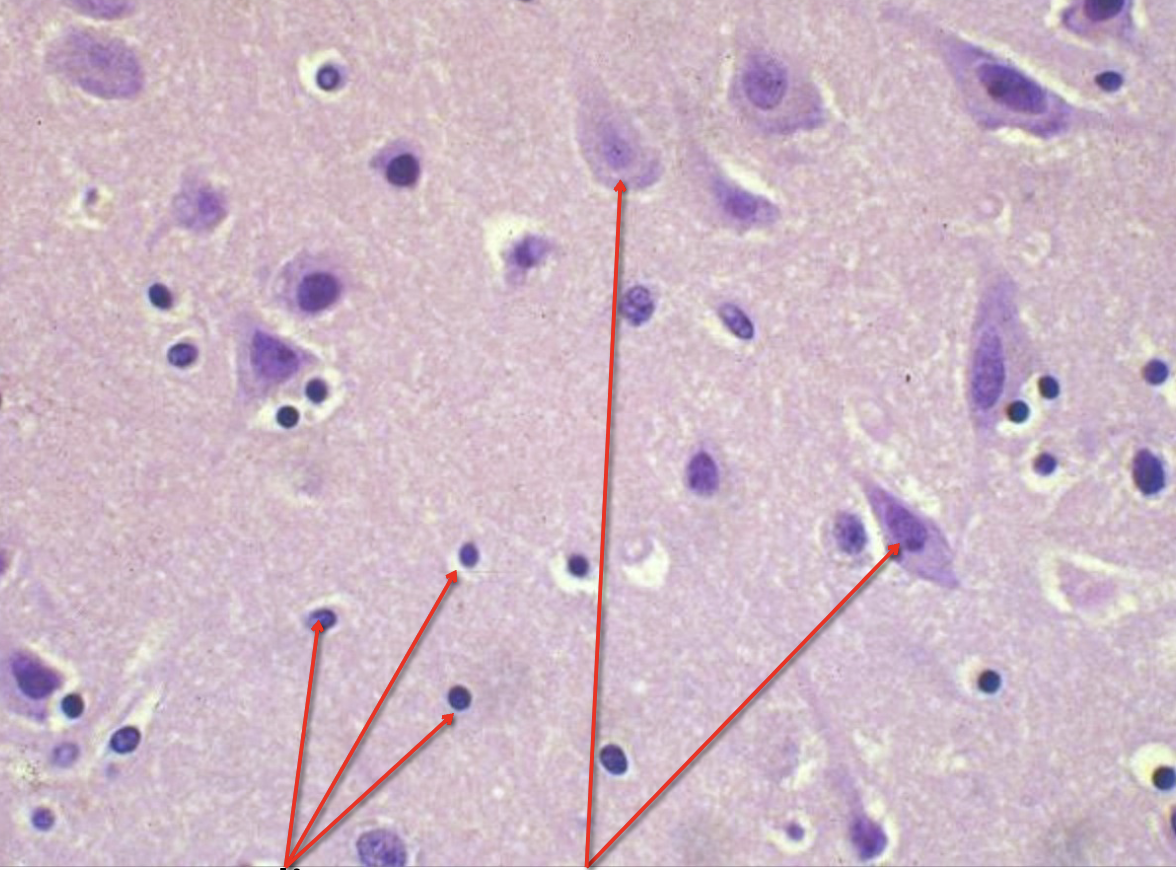
left arrow
glia
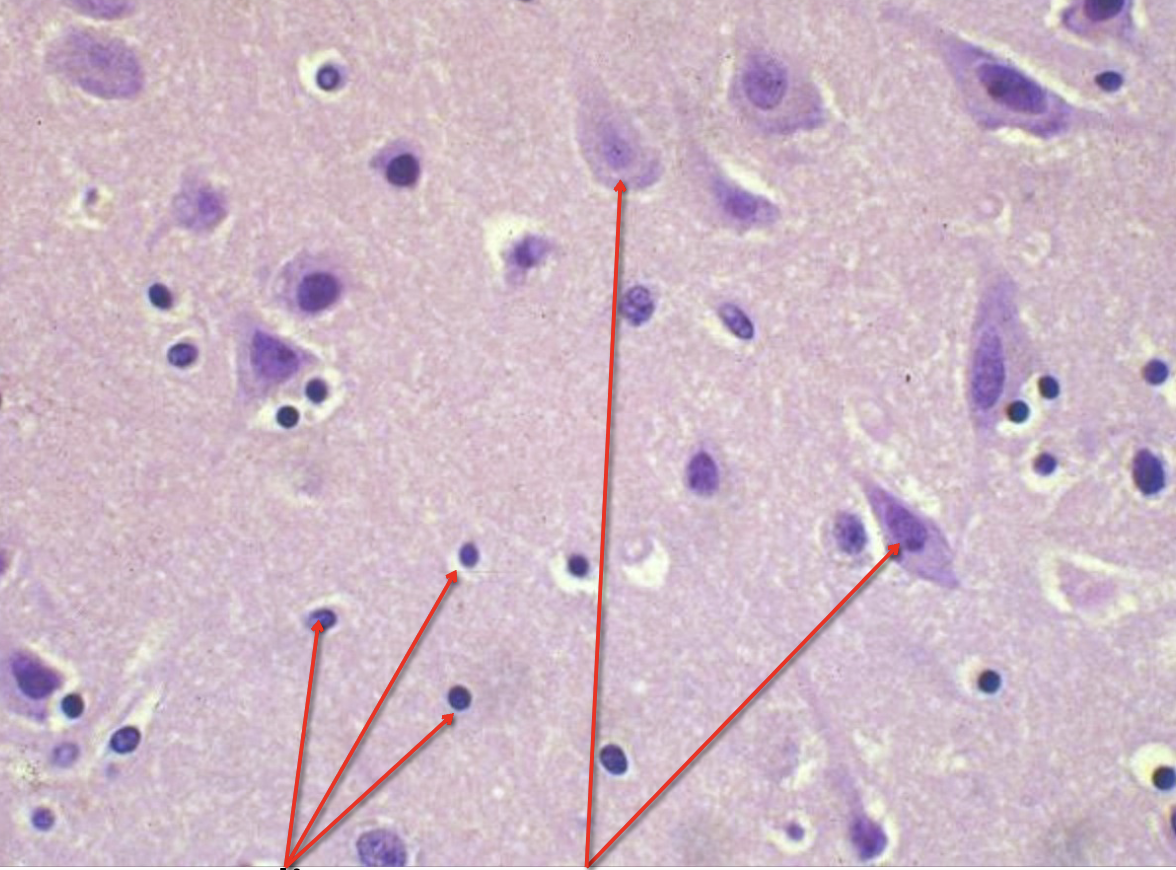
right arrow?
neurons
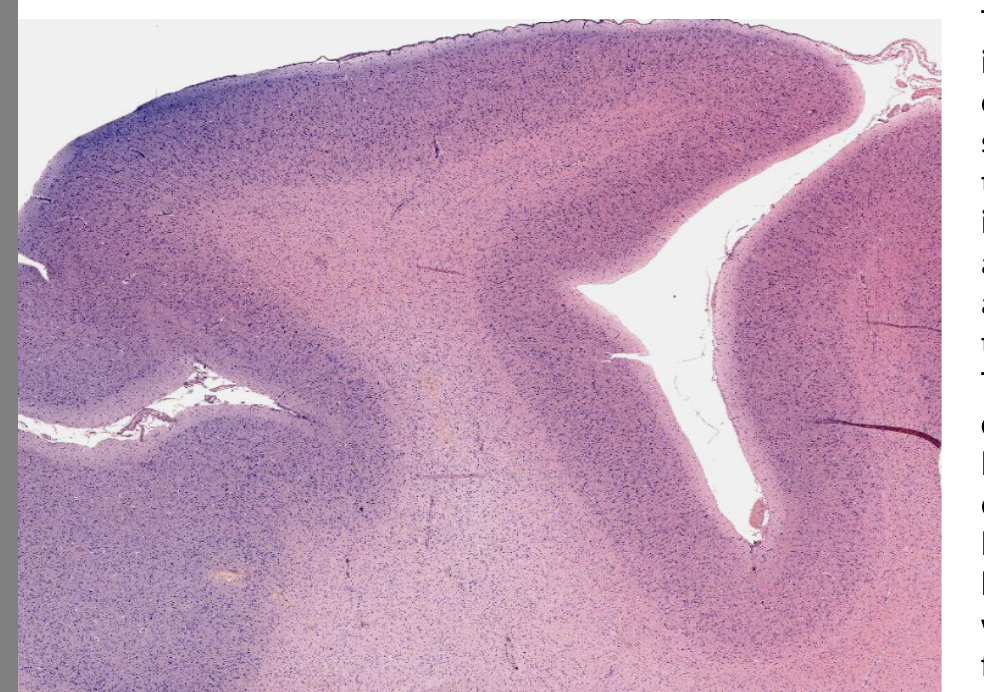
where is this?
cerebrum
what is the deep grove called
logitudianl fissure
right half of cerebrum corntrols
left side of body
cerebrum is the
largest part of human brain
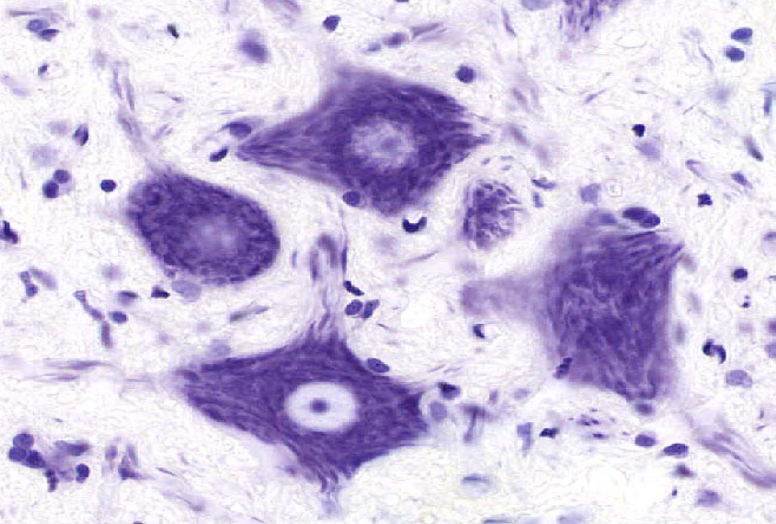
what is this?
multipolar nueron
single axon
many dendrites
mulitpolar neuron located?
cns
multipolar neuron fucntion?
convey impulses
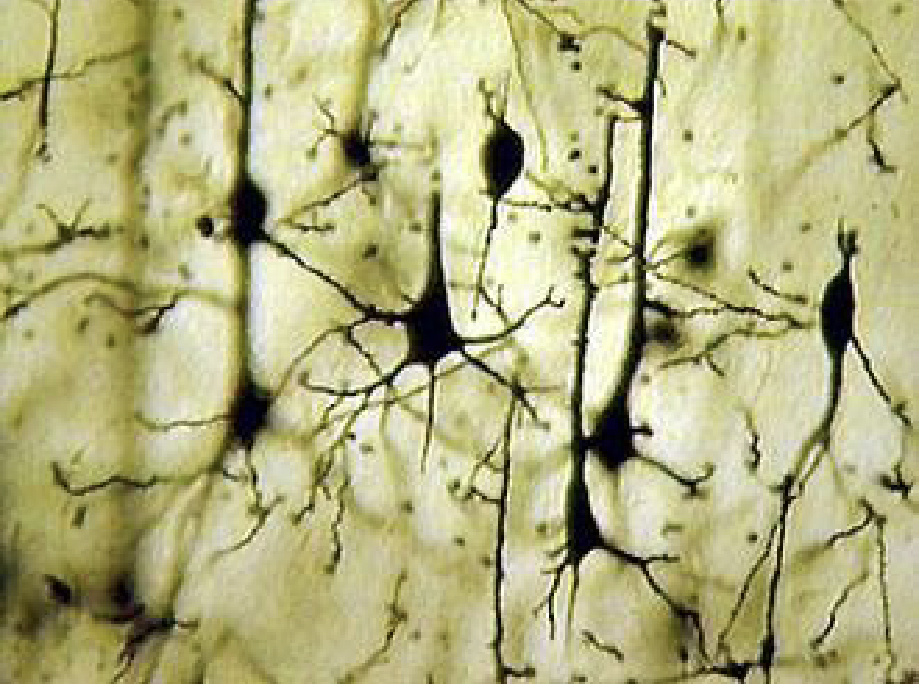
what this are?
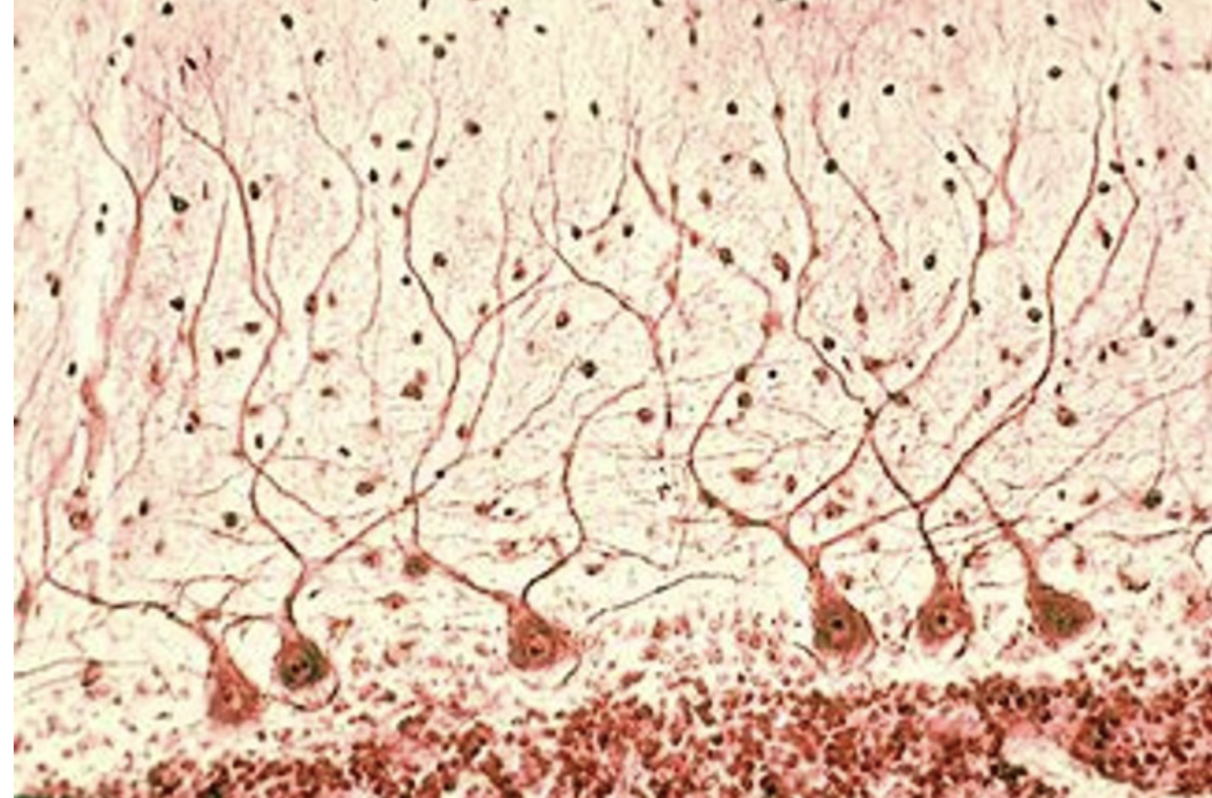
pyrimidial cells
pyrimidail cell also a
multipolar neuron
pyrimidial cell found in?
brain like cerebral cortex
fucniton of pyrimidial nueron
excitaroy cell trype
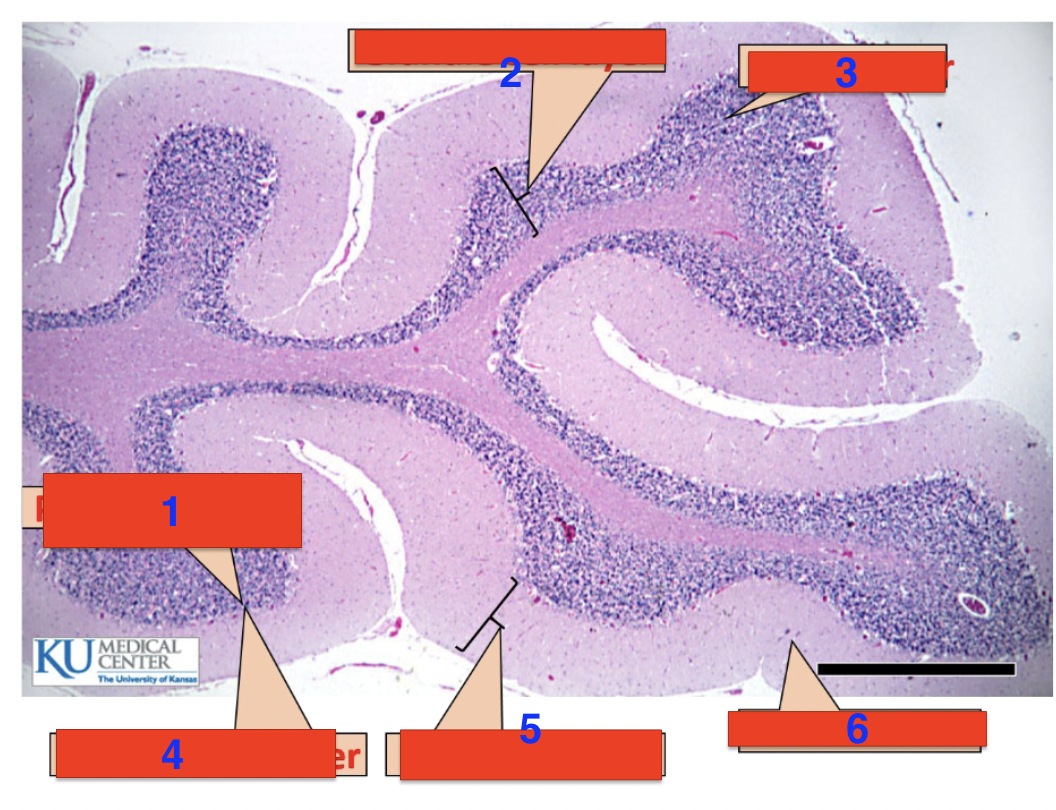
what is the cerebellum composed of folds called?
folia
these folds have what?
cortical gray matter, medullary white matter
white matter is where?
inside
what are the three layers of gray matter
molecular layer, purkinje layer, granular layer
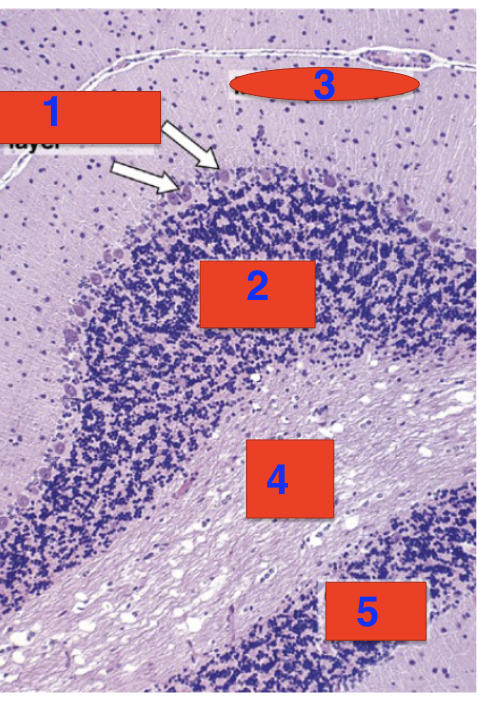
1?
purkinje layer
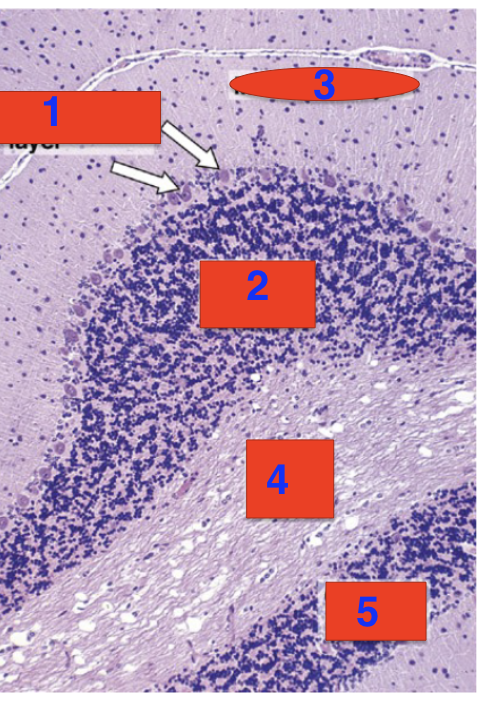
2?
granular layer
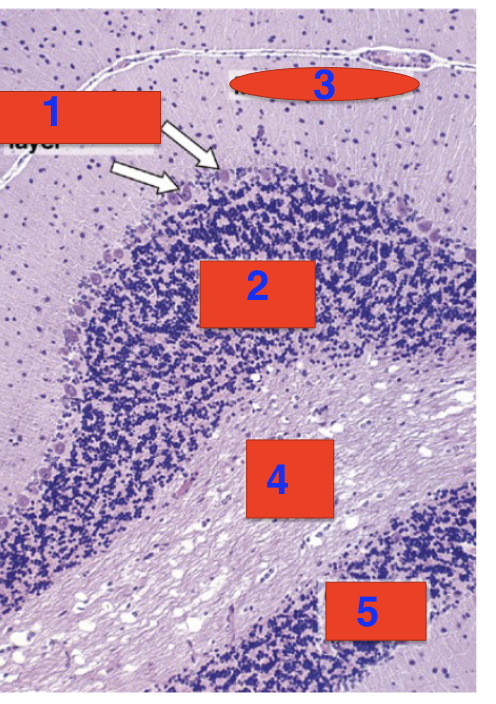
3?
molecular layer
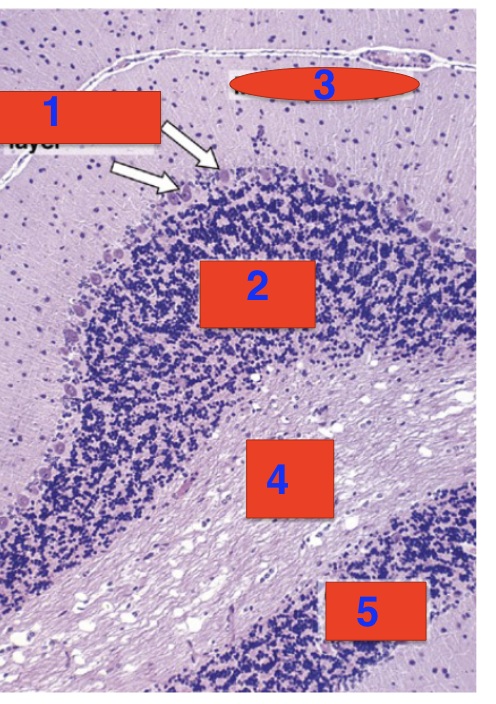
4?
white matter
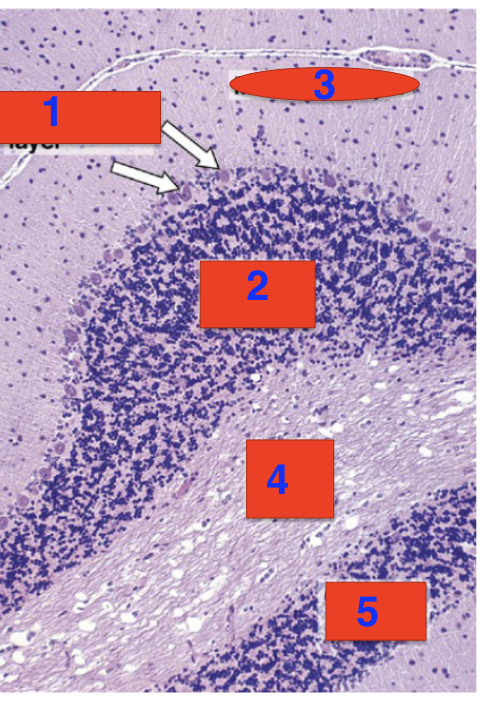
5?
granular layer
location?
cerebellum
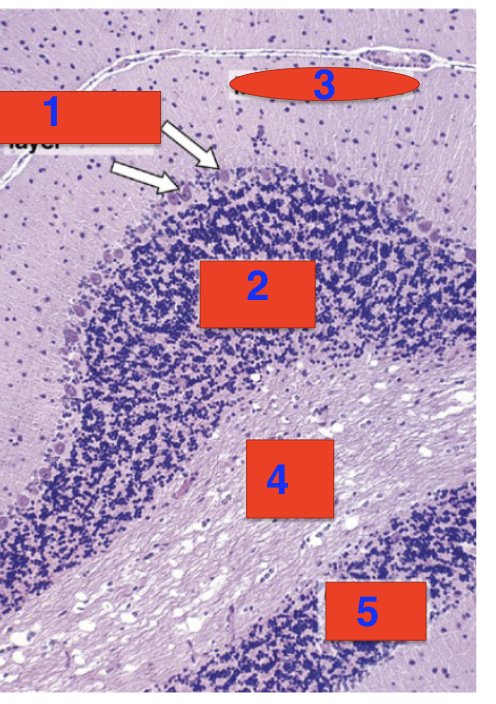
1?
purkinje cells
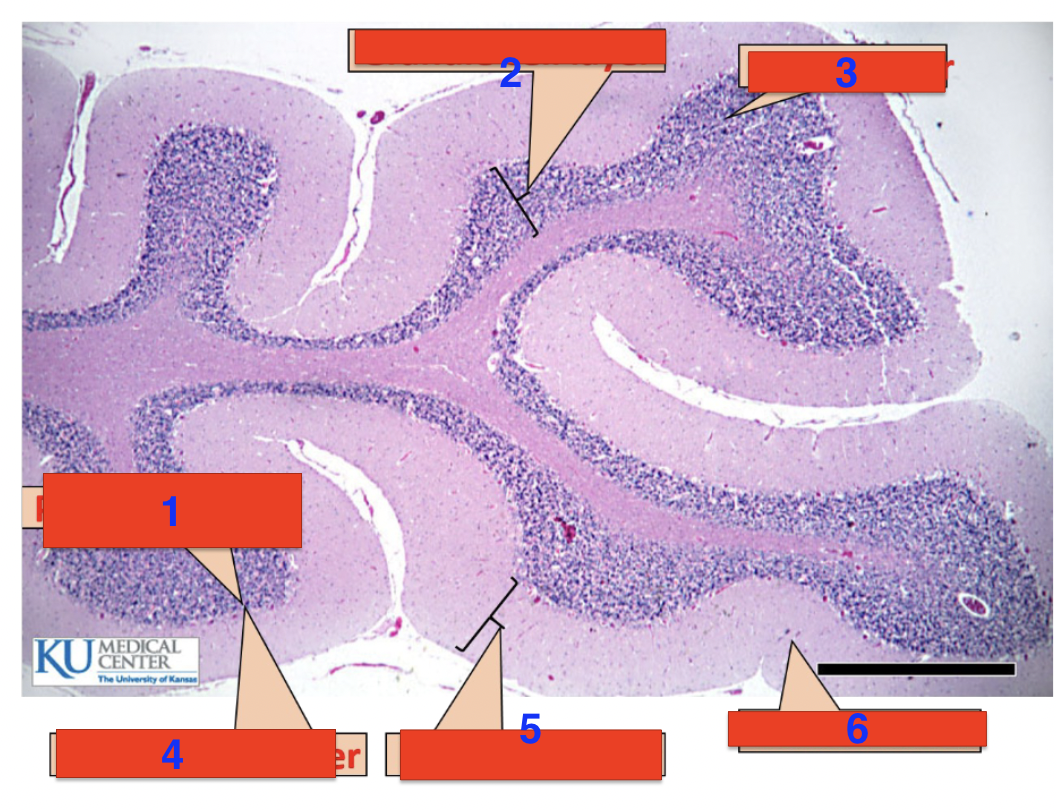
2?
granule cell layer
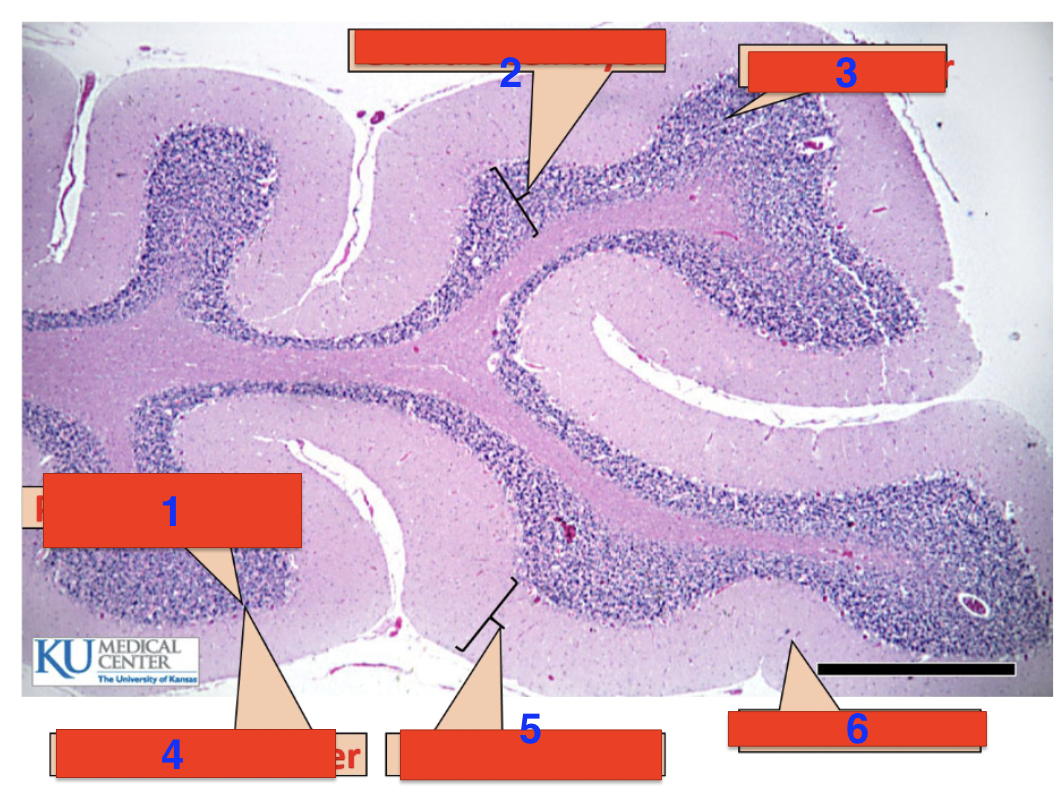
3?
grey matter
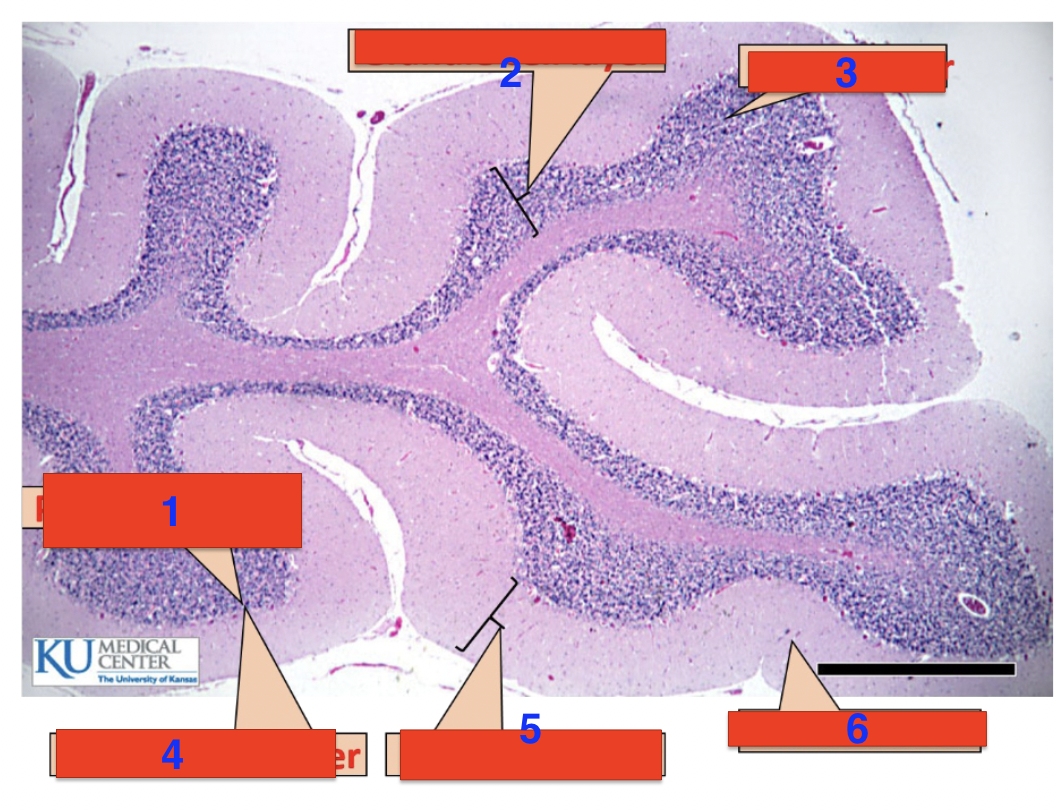
4?
purkinje cell layer
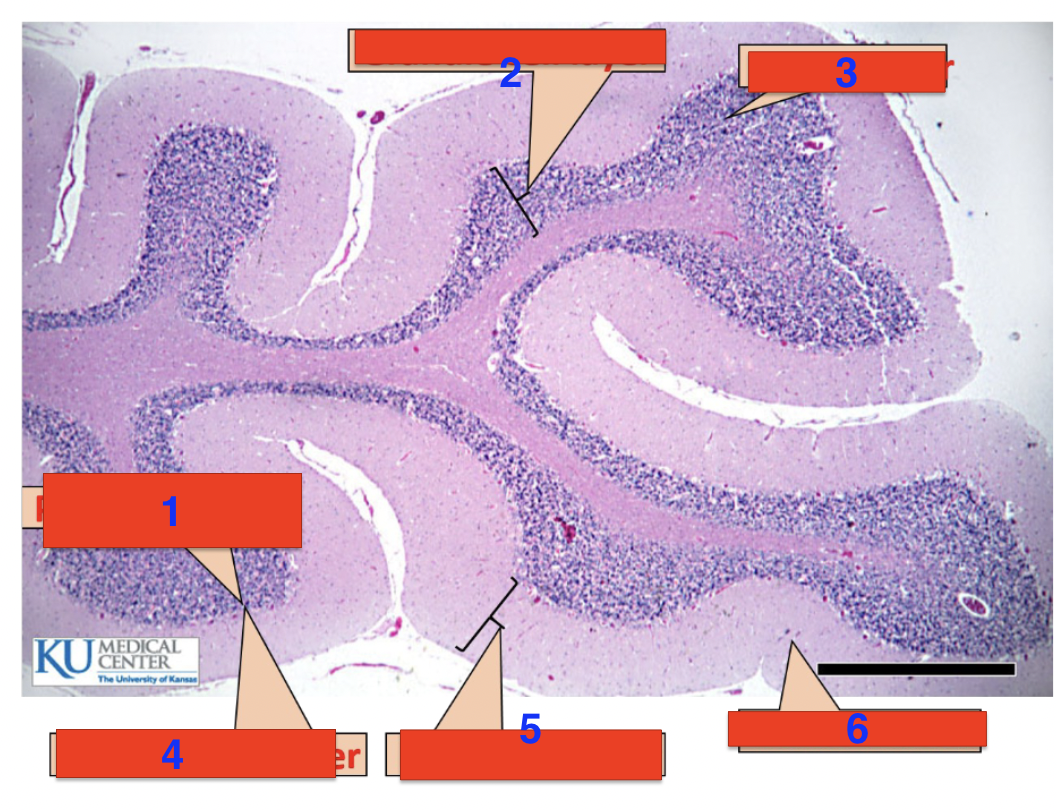
5?
molecular layer
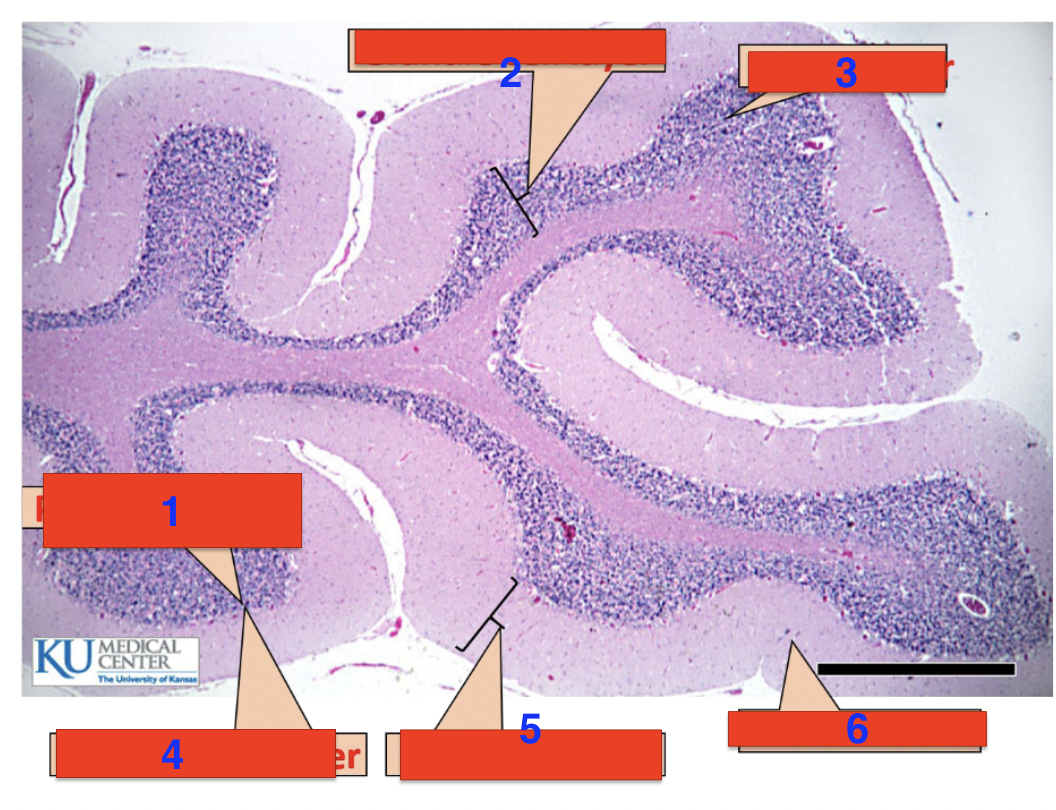
6?
white matter
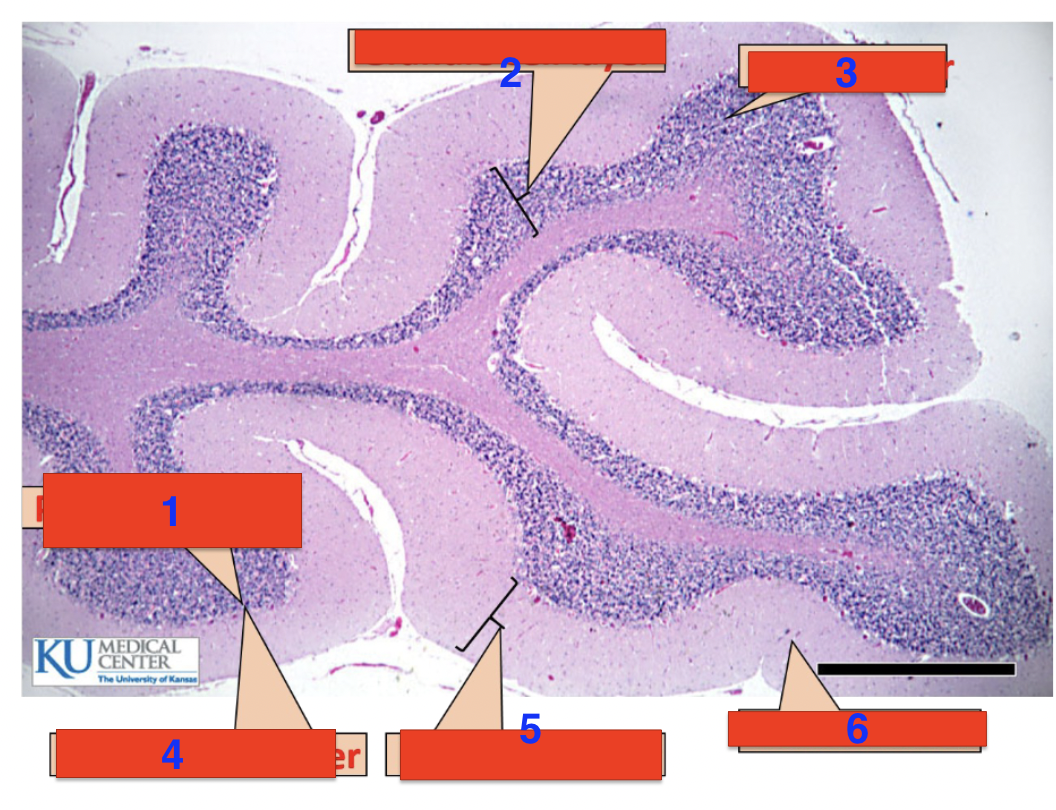
location
cerebellum
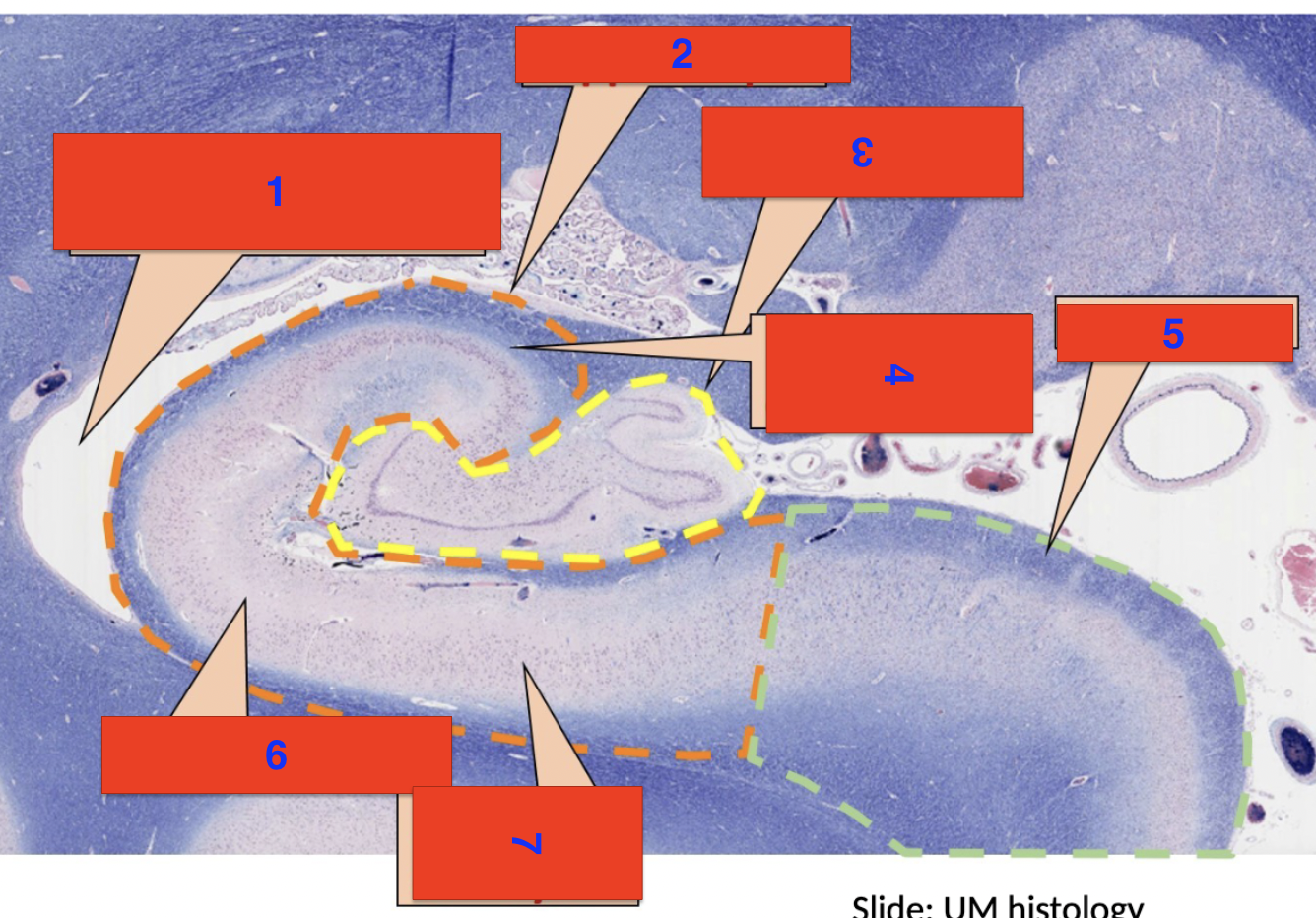
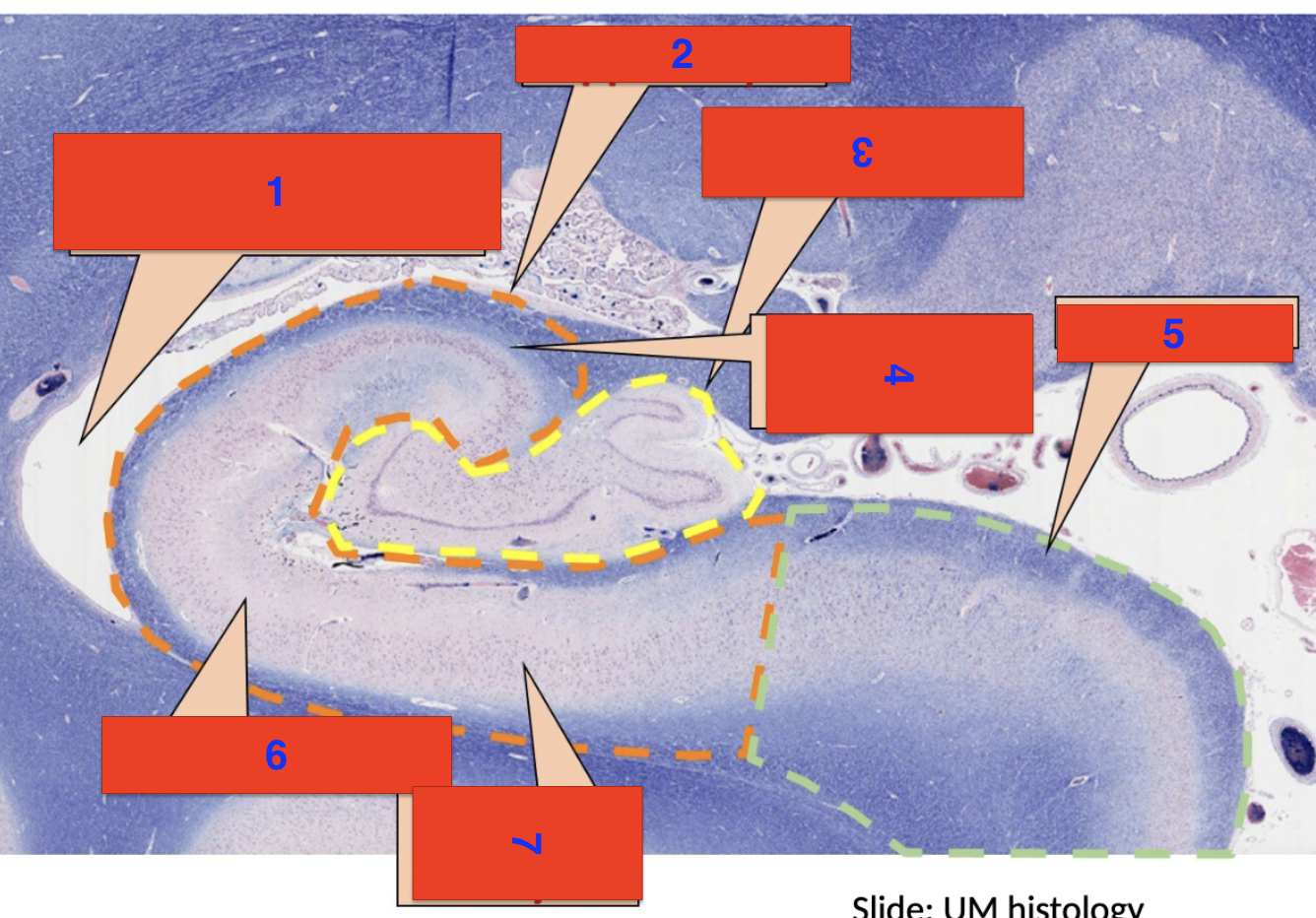
1?
inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
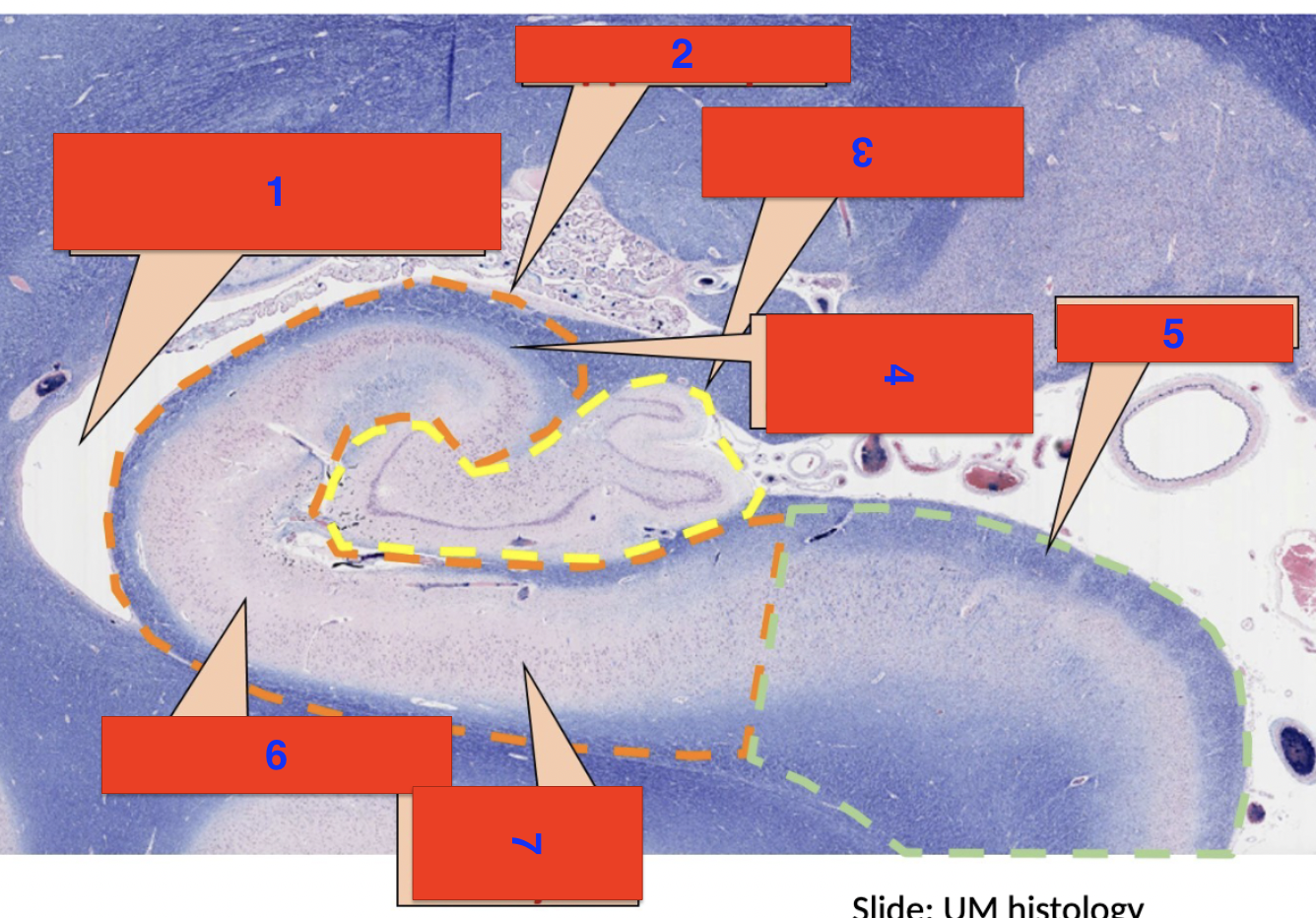
2?
hippocampus
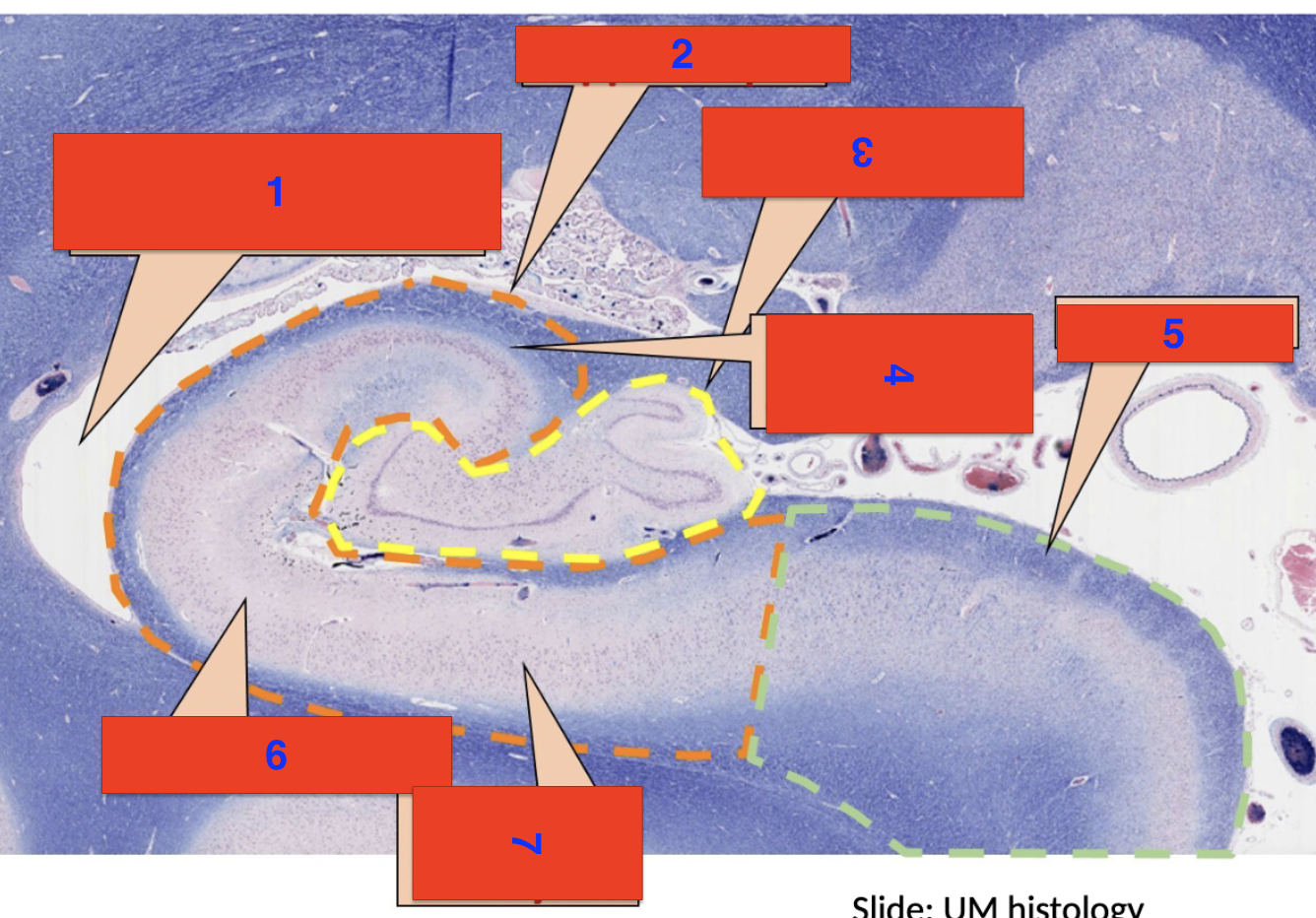
3?
dentate gyrus
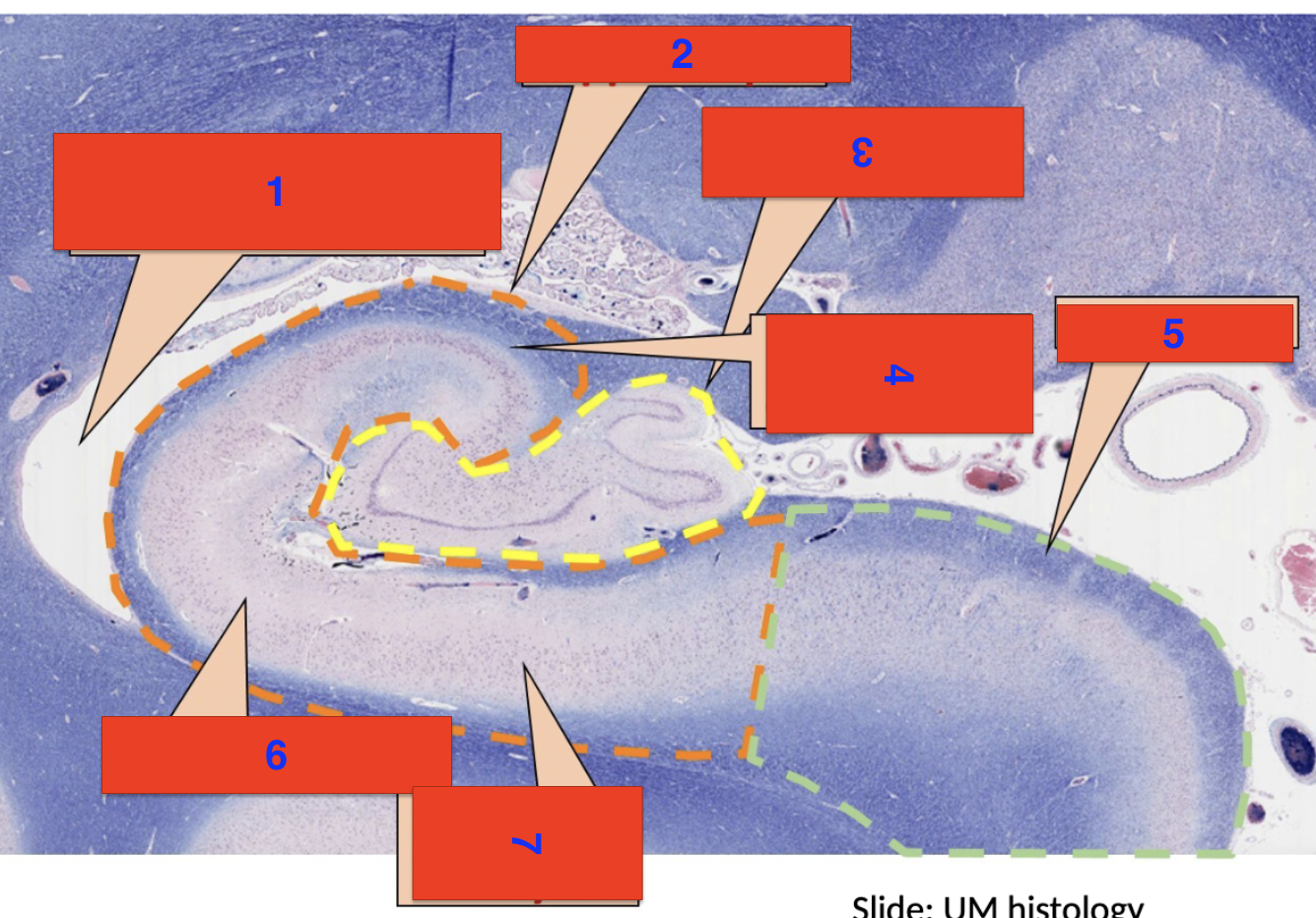
4?
polymorphic cell layer
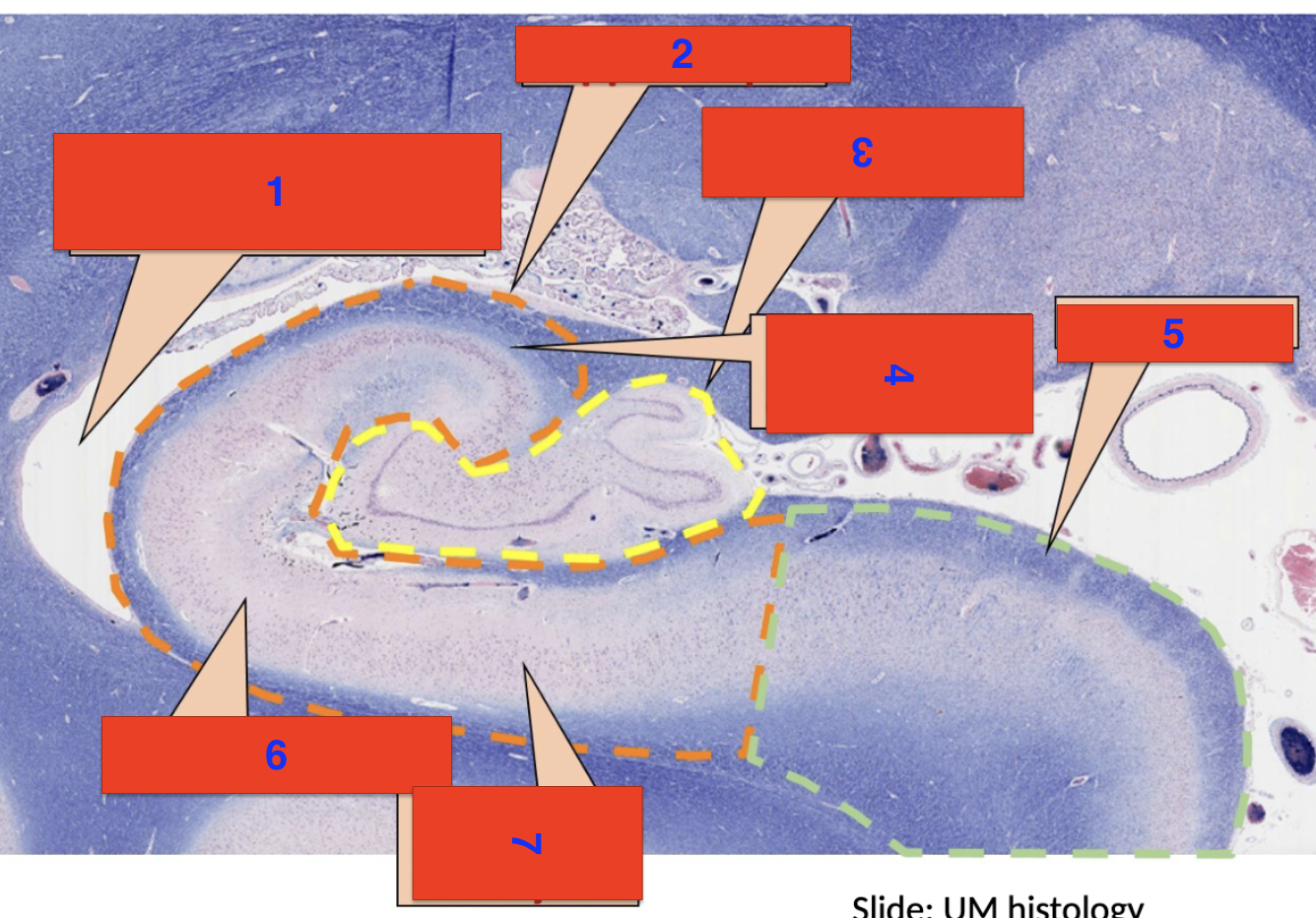
5?
subiculum
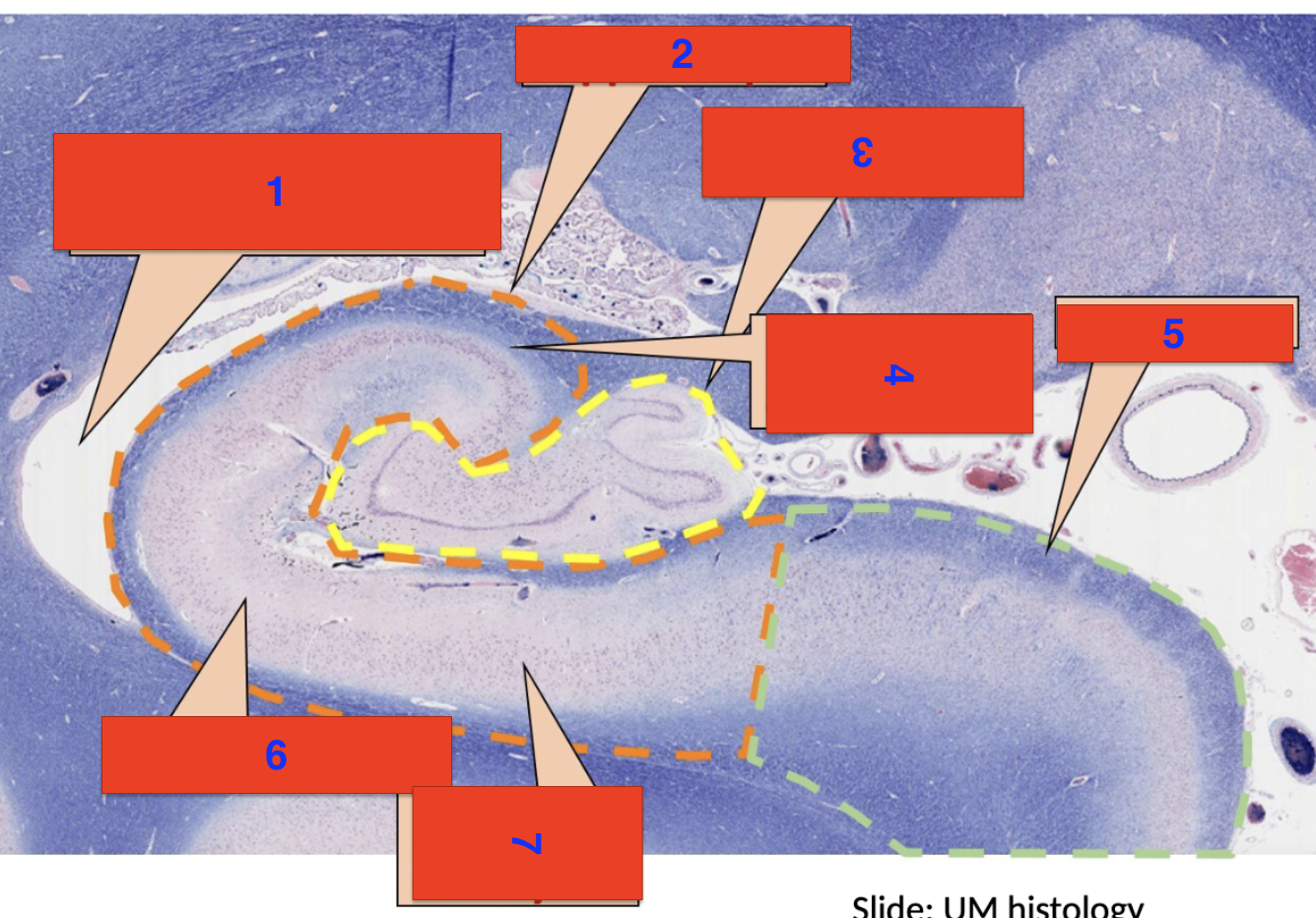
6?
molecular layer
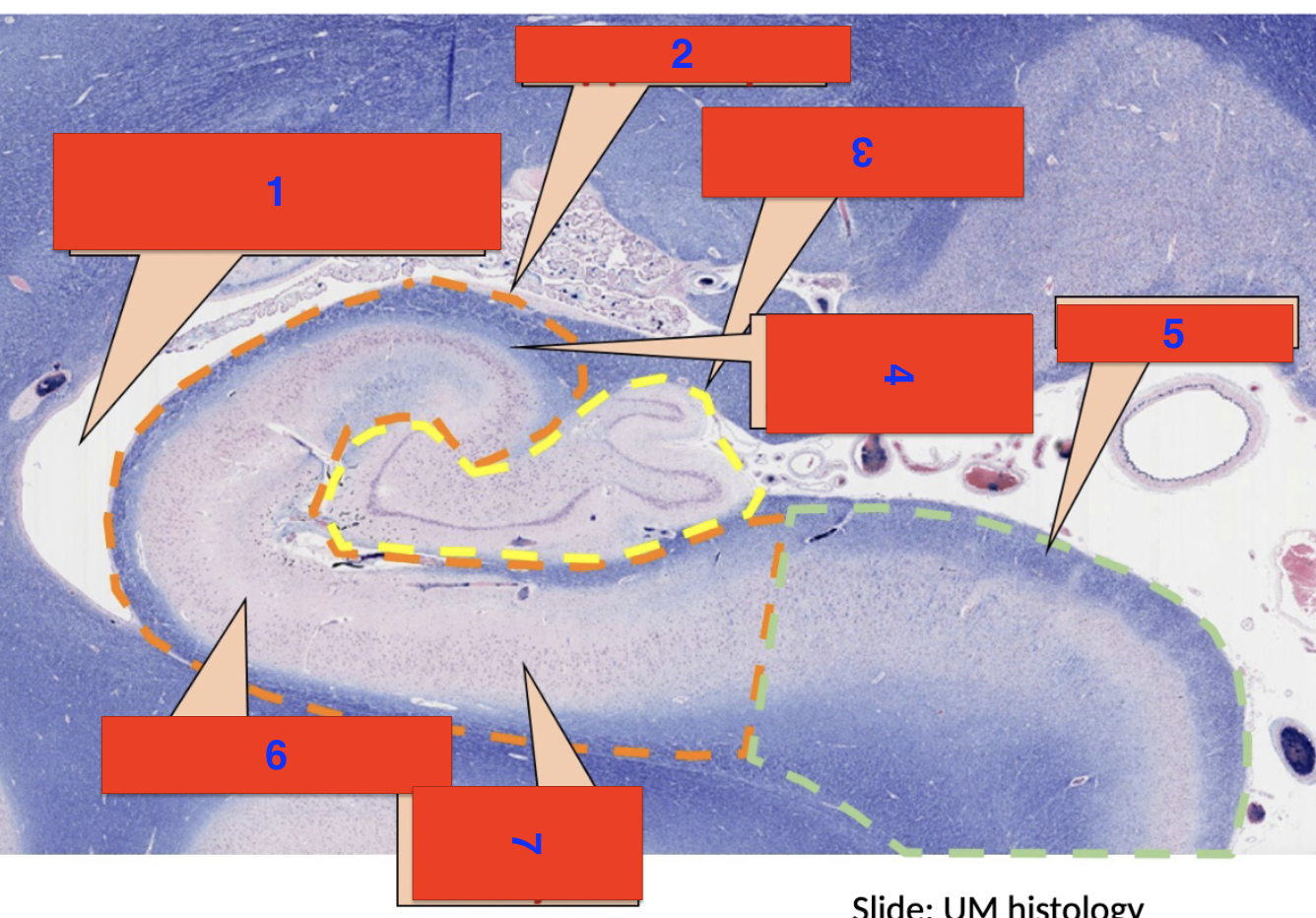
7?
pyrimidial cell layer
location
cerebrum
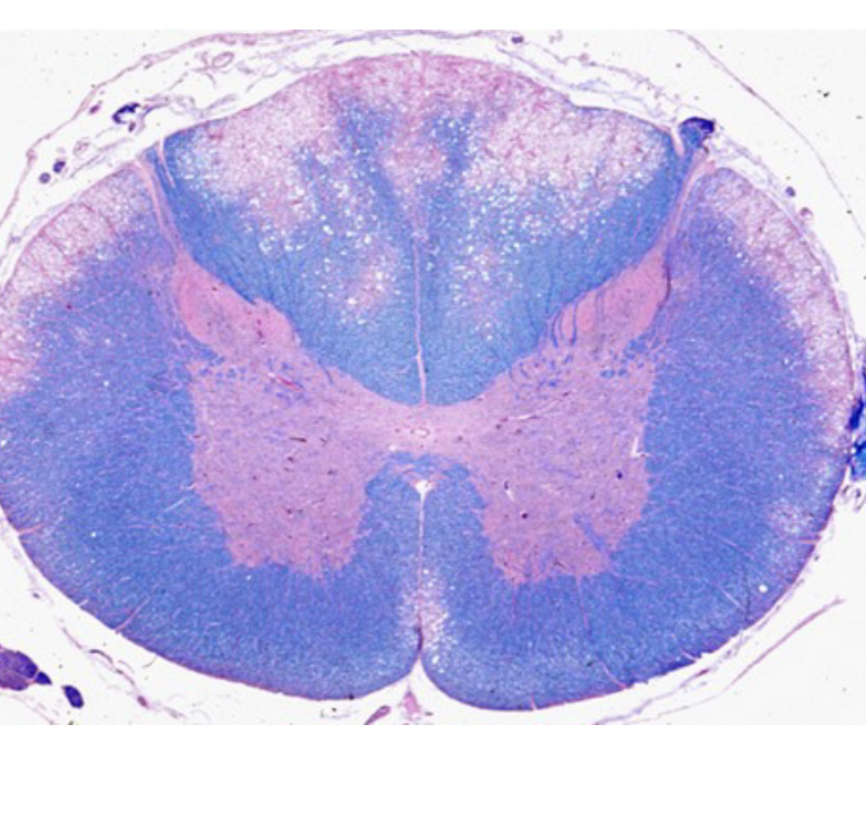
locations
spinal cord
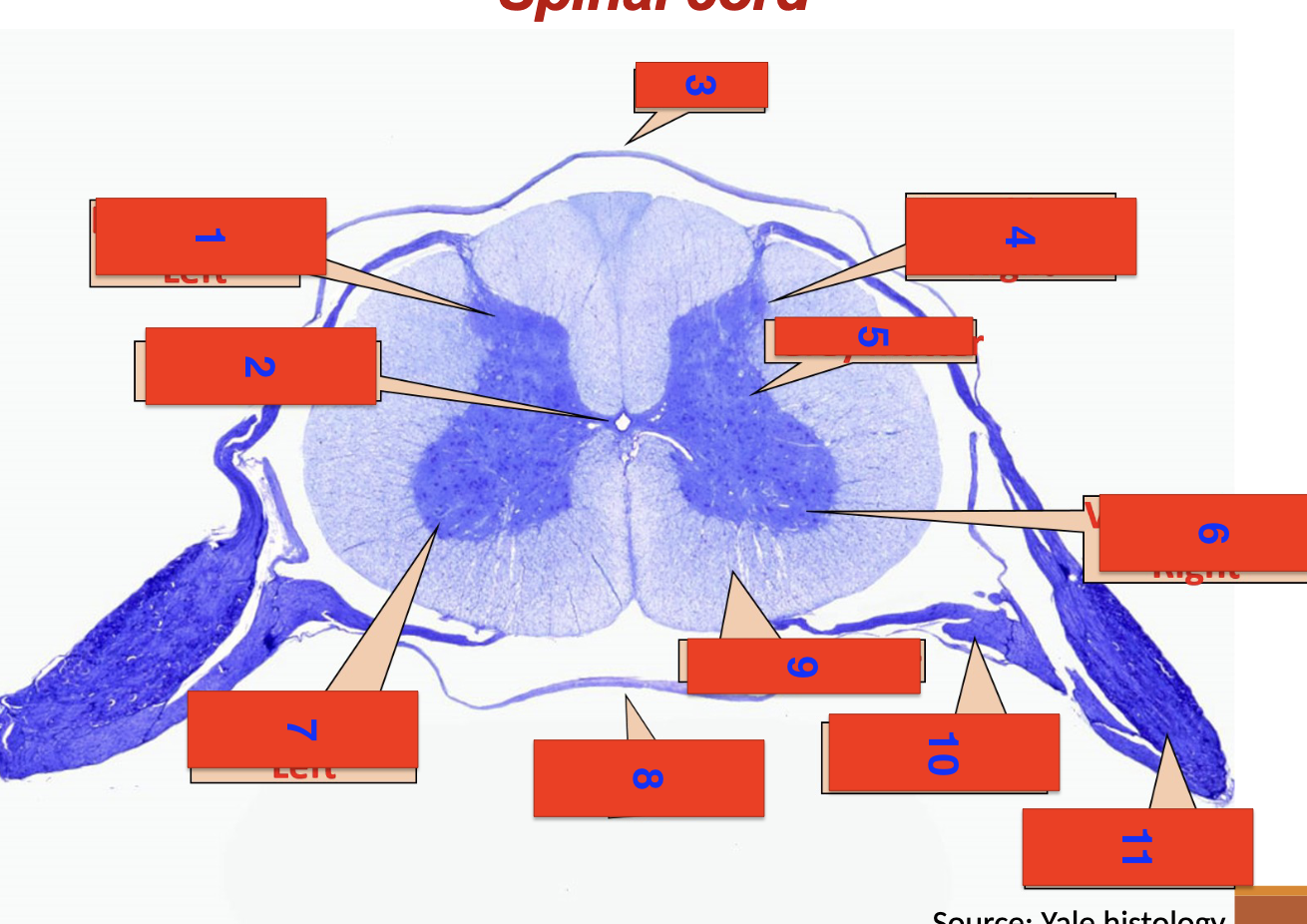
1?
dorsal horn left
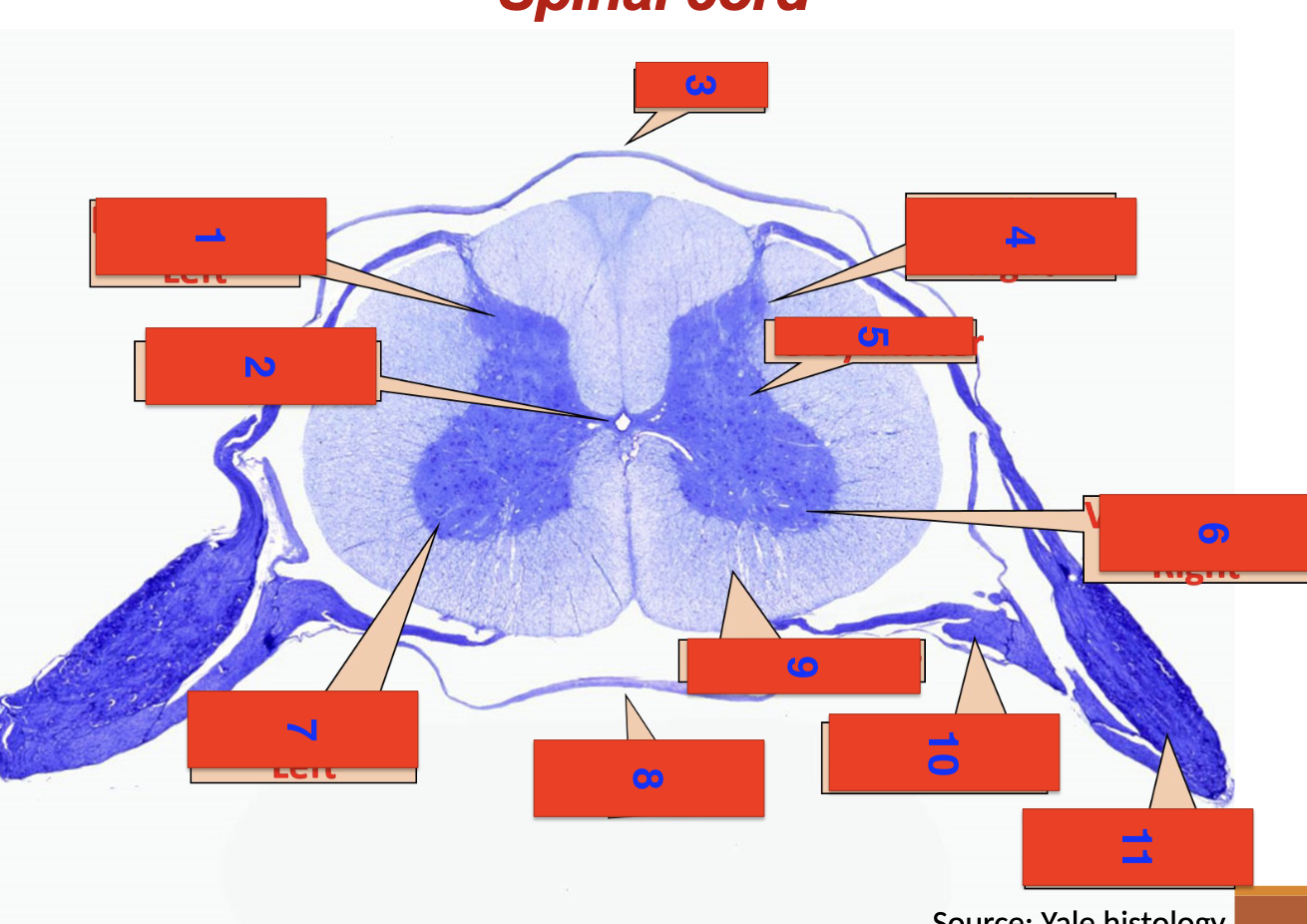
2?
central canal
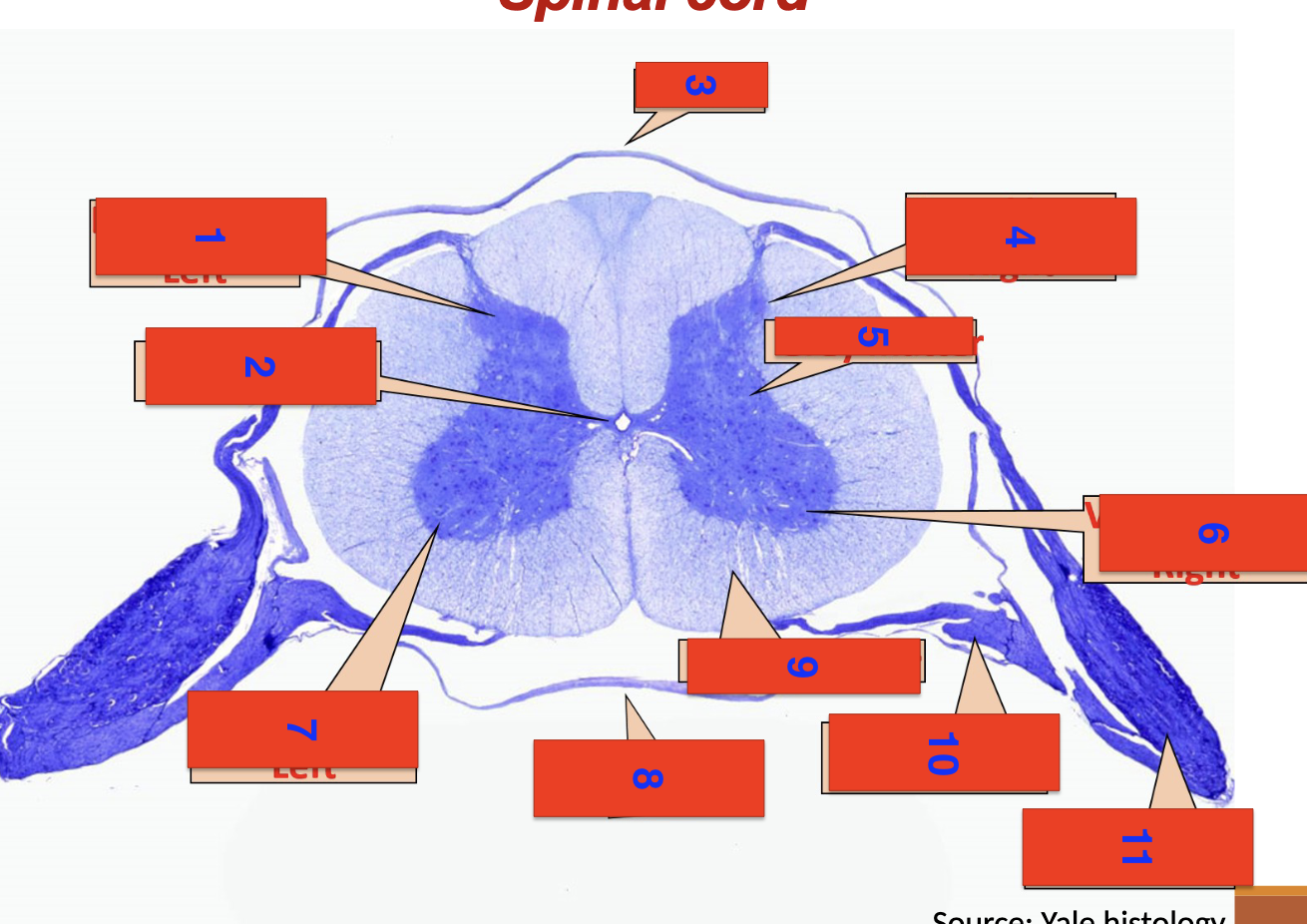
3?
dorsal
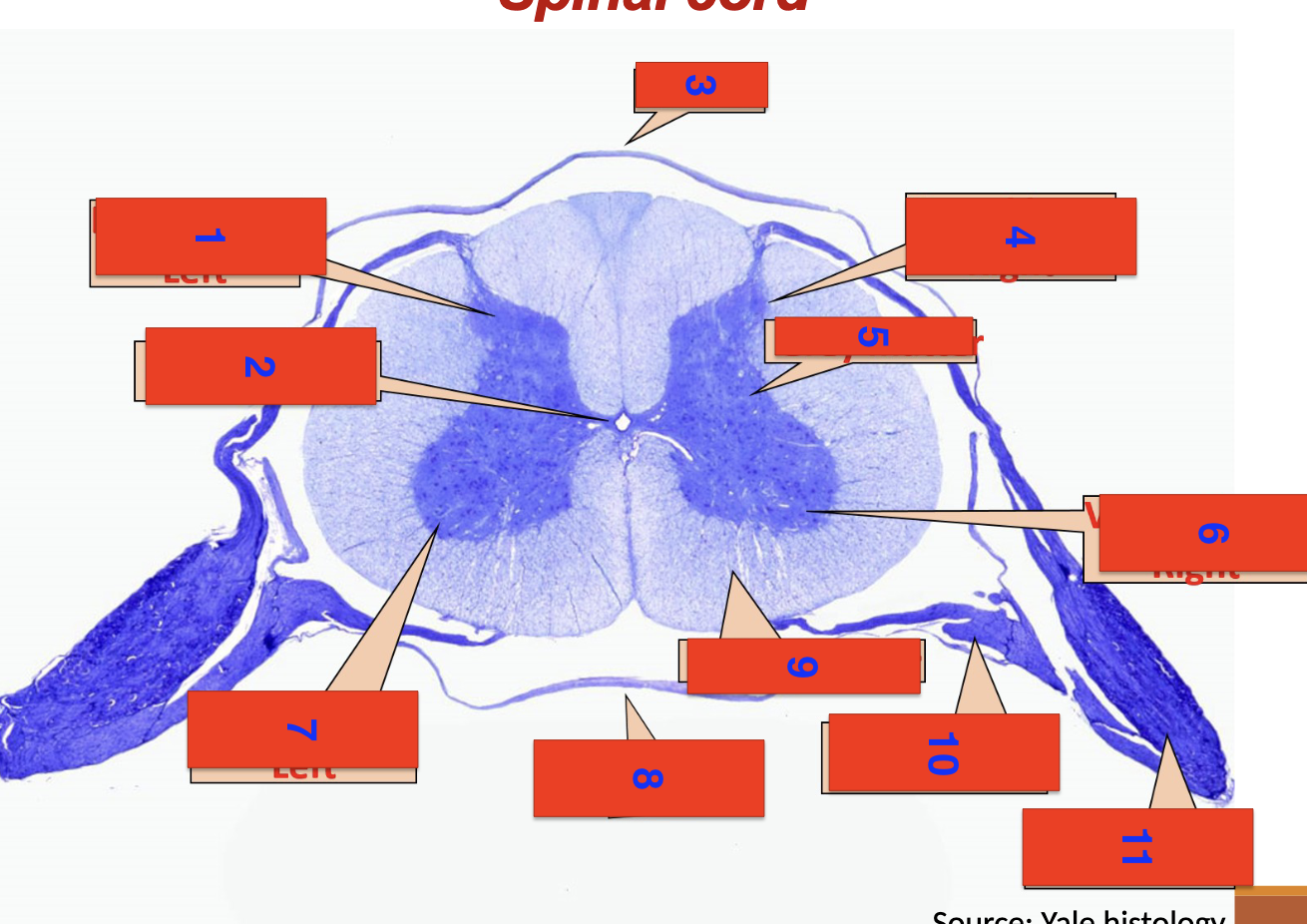
4?
dorsal horn right
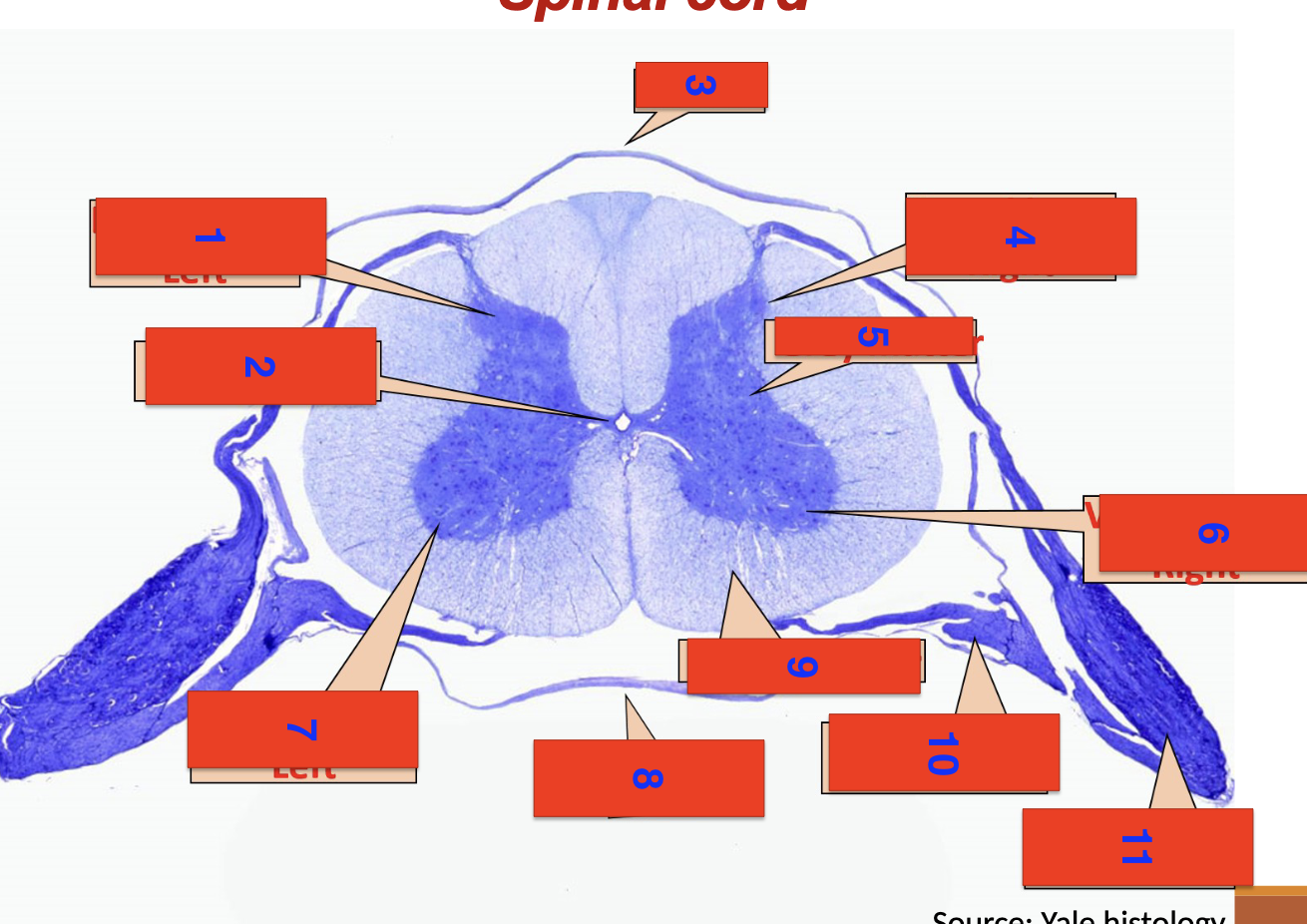
5
grey matter
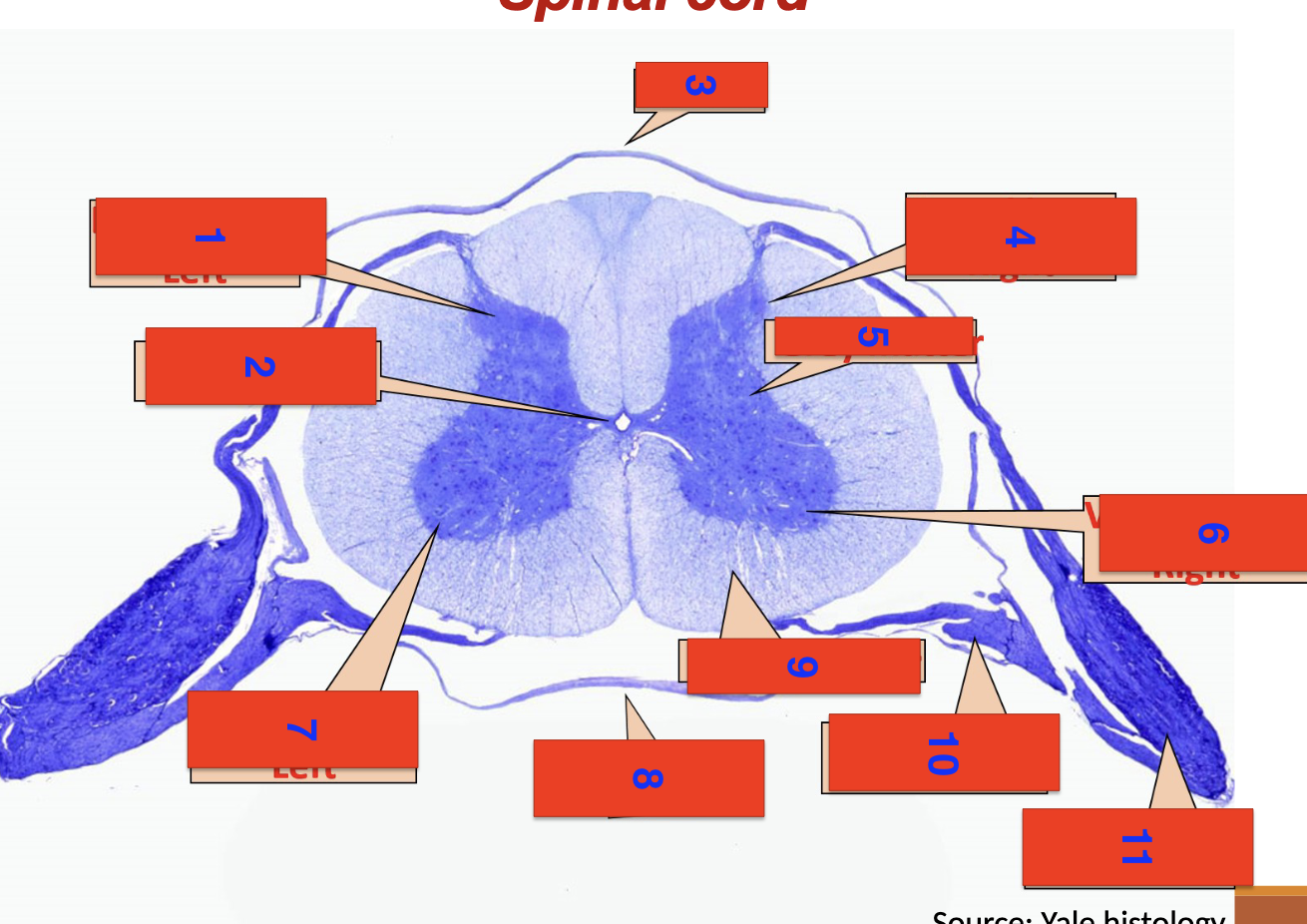
6
ventral horn right
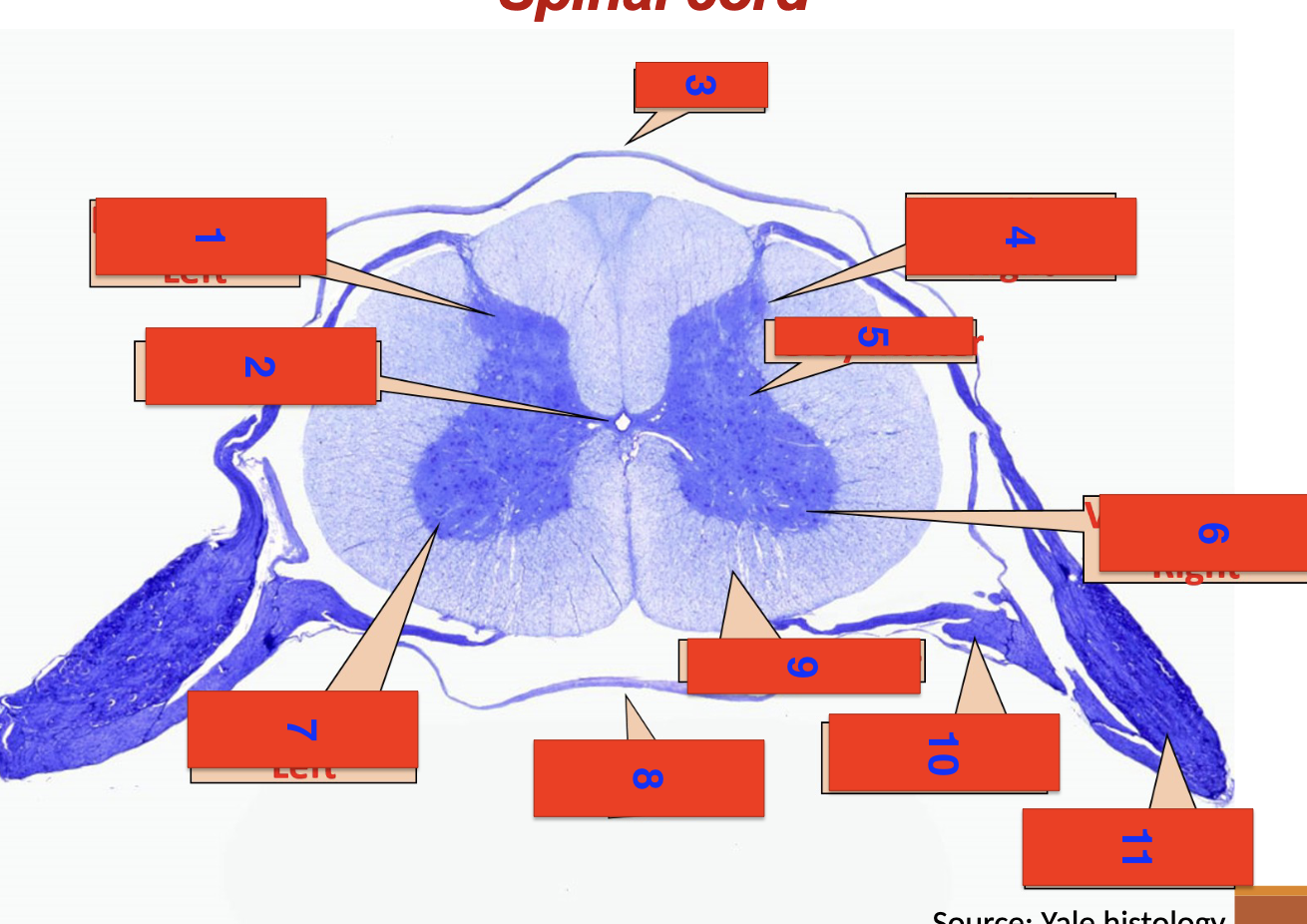
7
ventral horn left
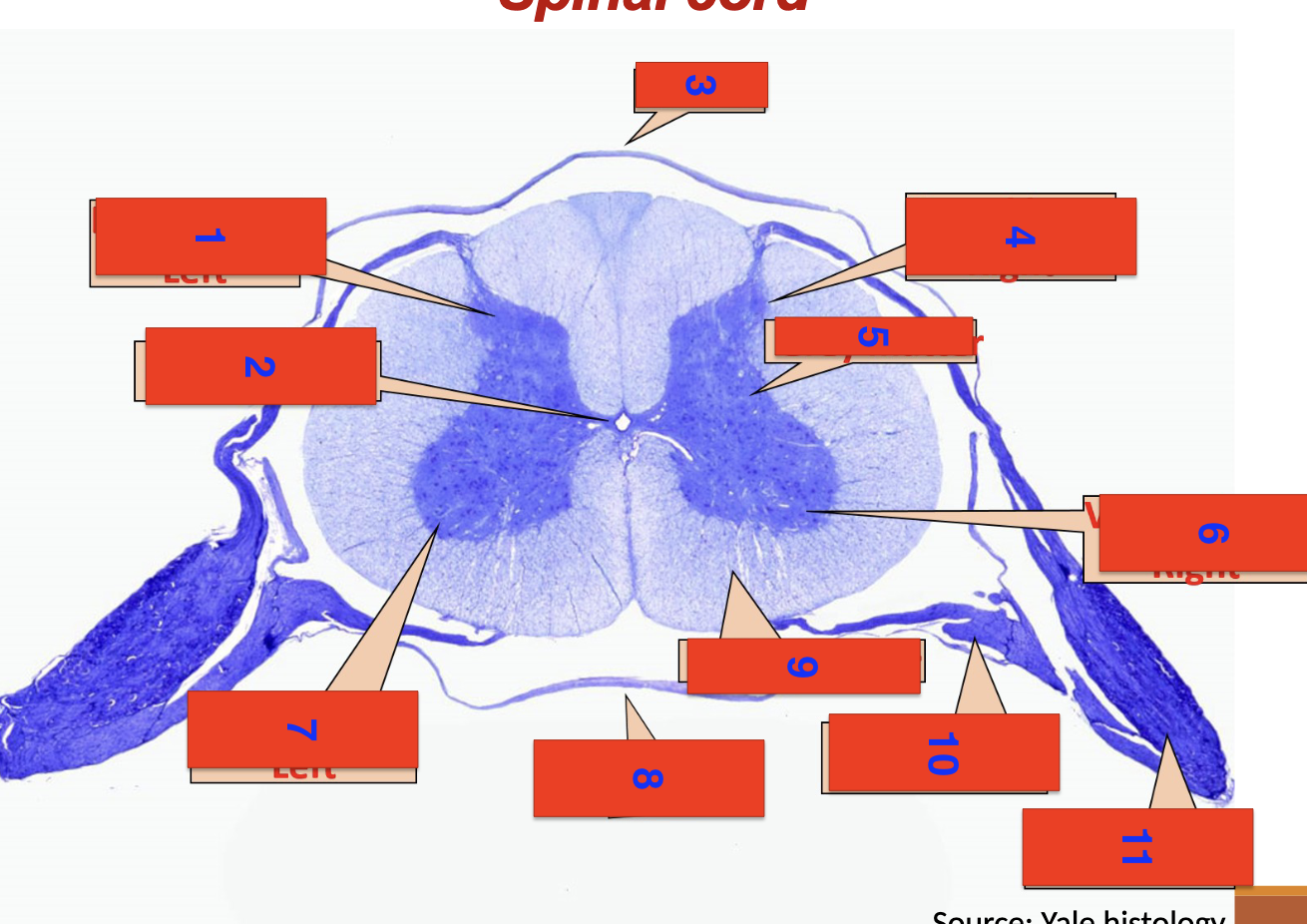
8
ventral
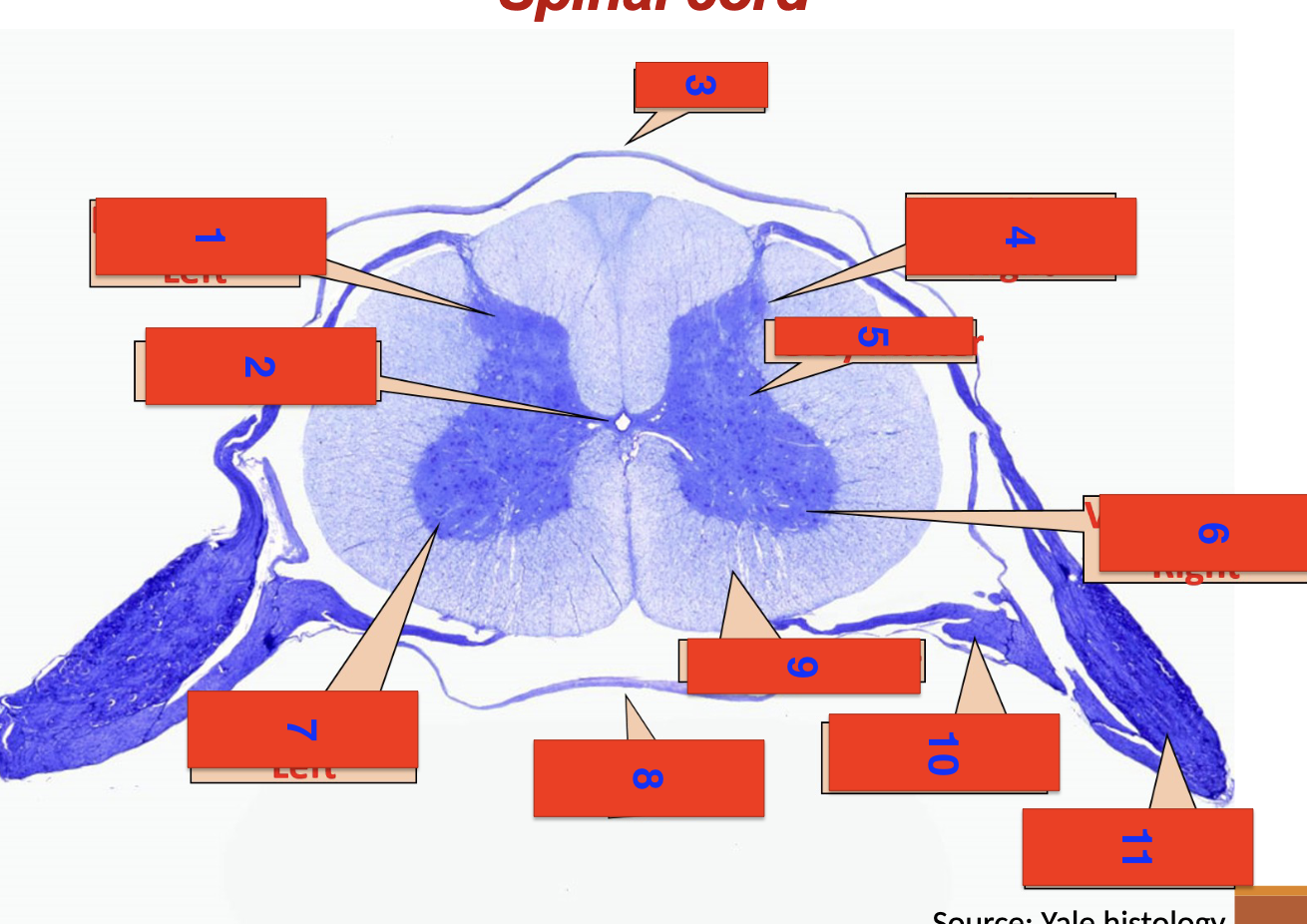
9
white matter
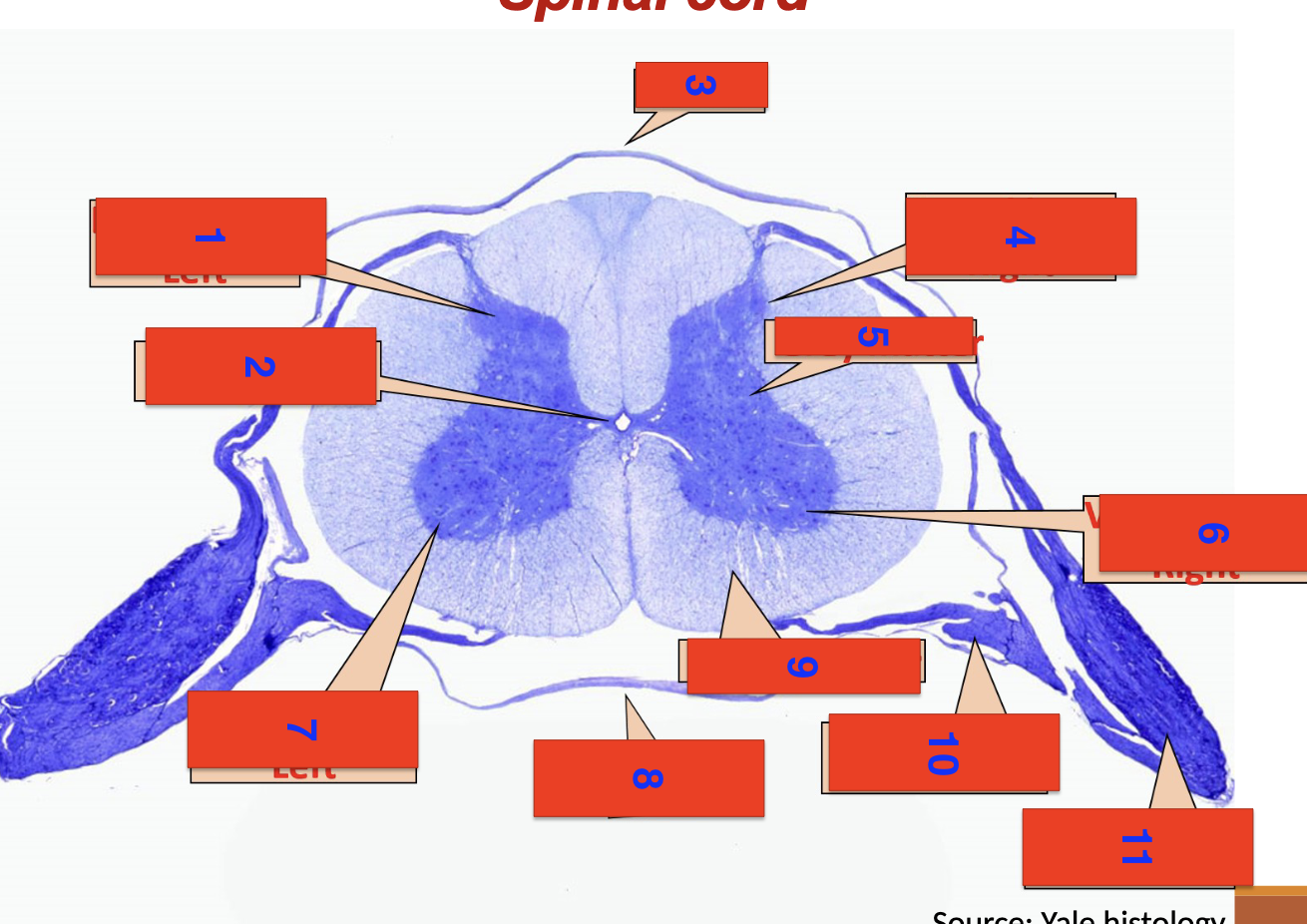
10
ventral root
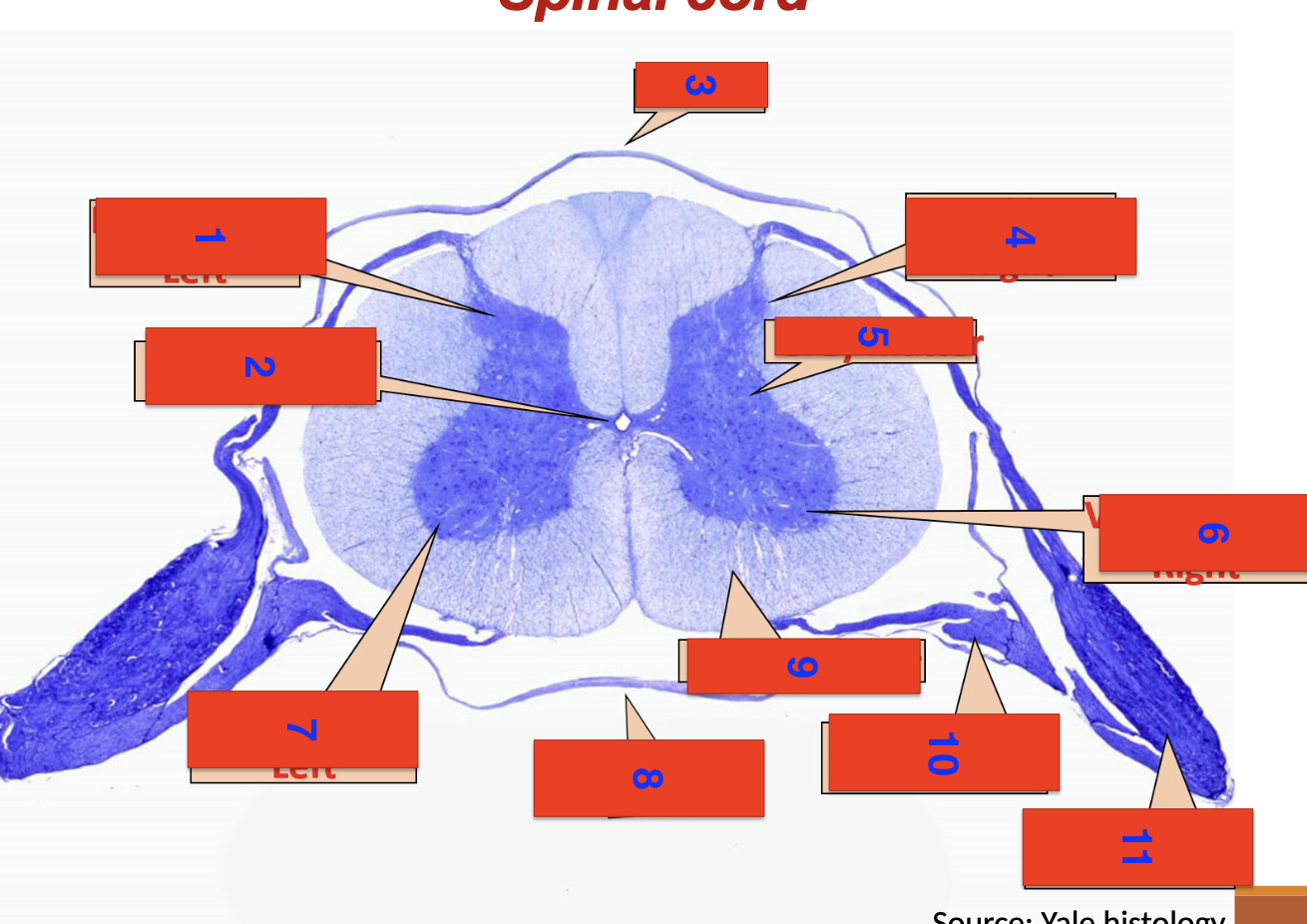
11
dorsal root
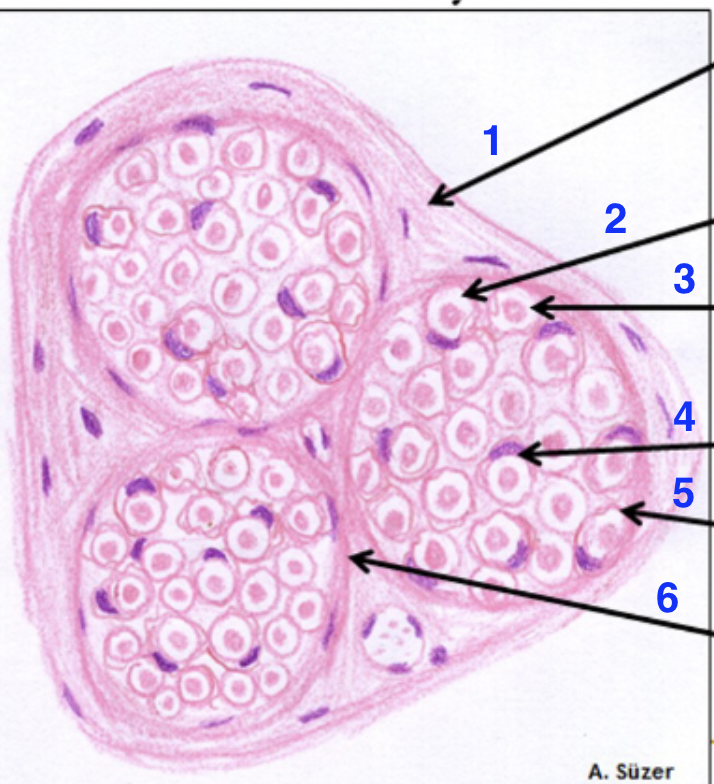
1?
epinerium
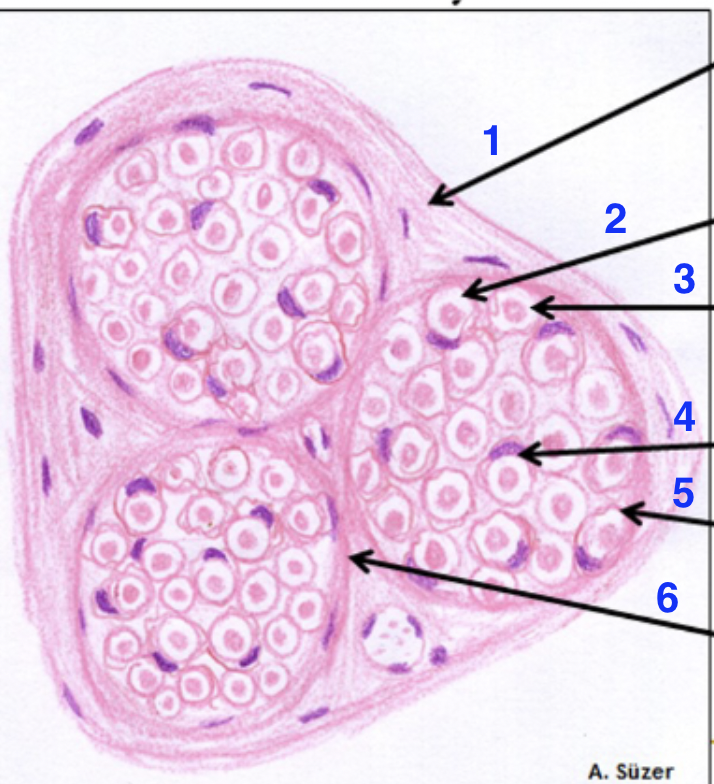
2?
dissolved myelin sheath
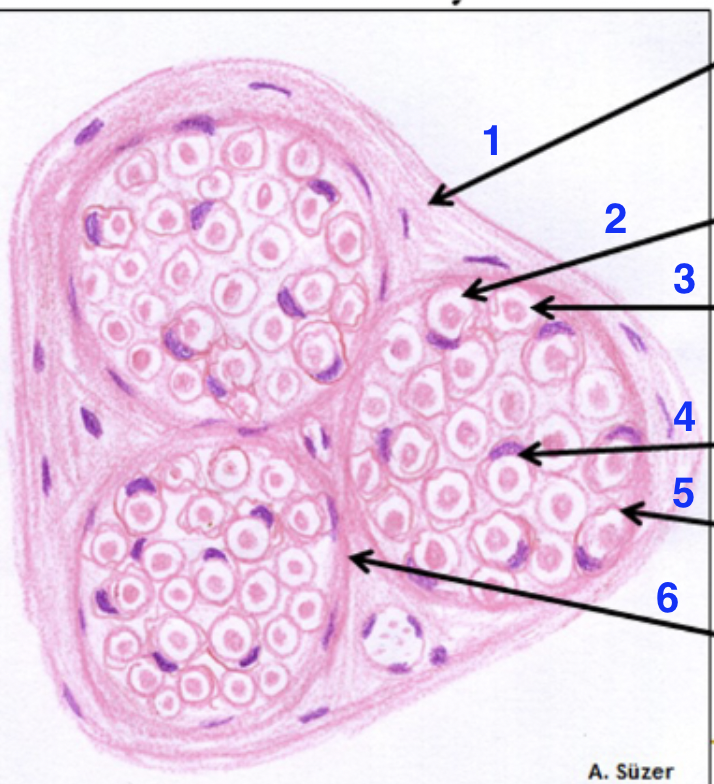
3?
axon
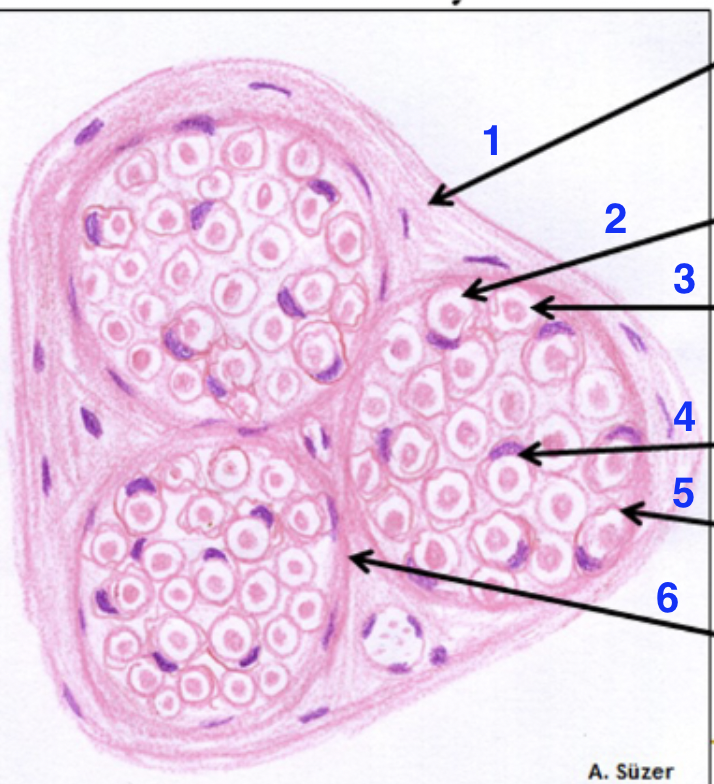
4?
schwann cell nucleus
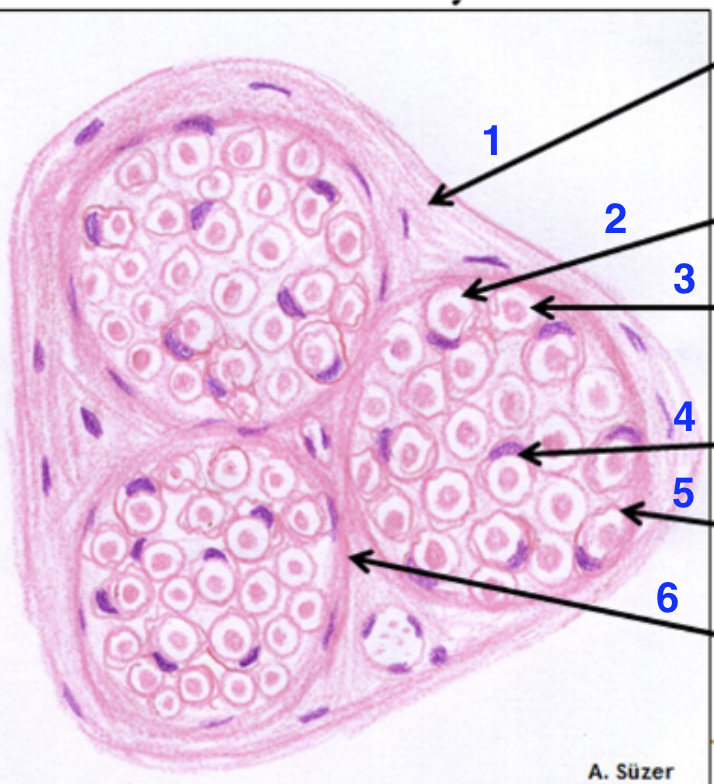
5?
endonerium
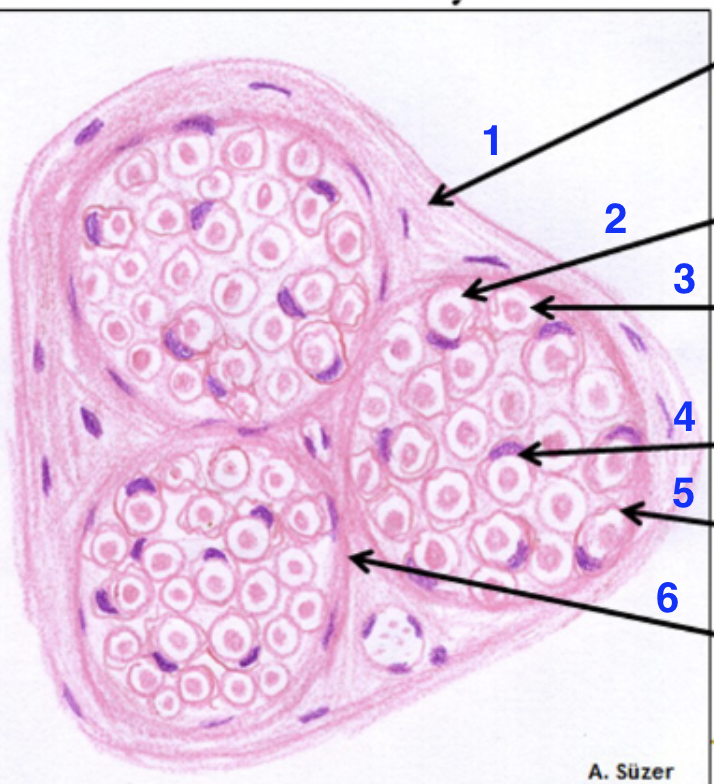
6?
perineurium
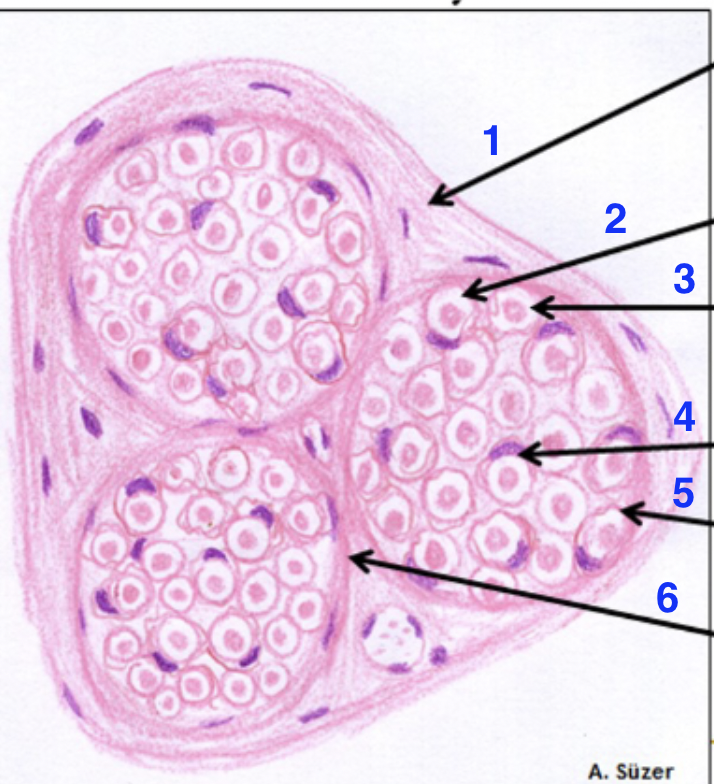
what is this
peripheral nerve
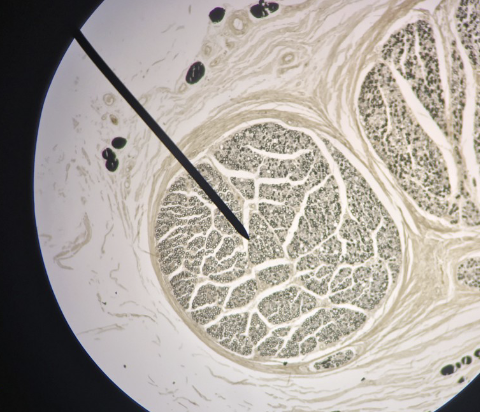
what is this?
peripheral nerve
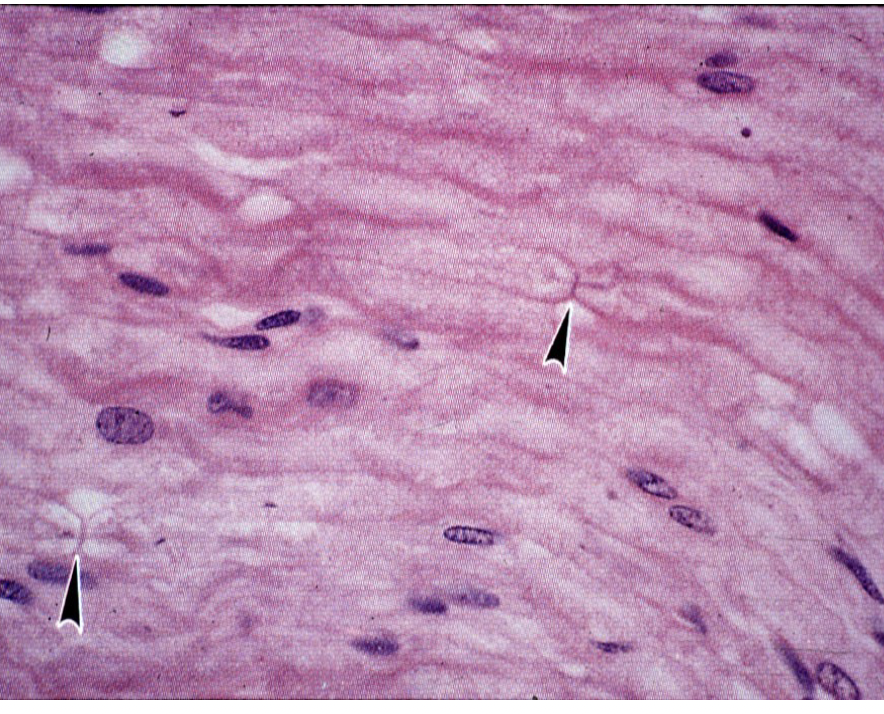
?
node of ranvier
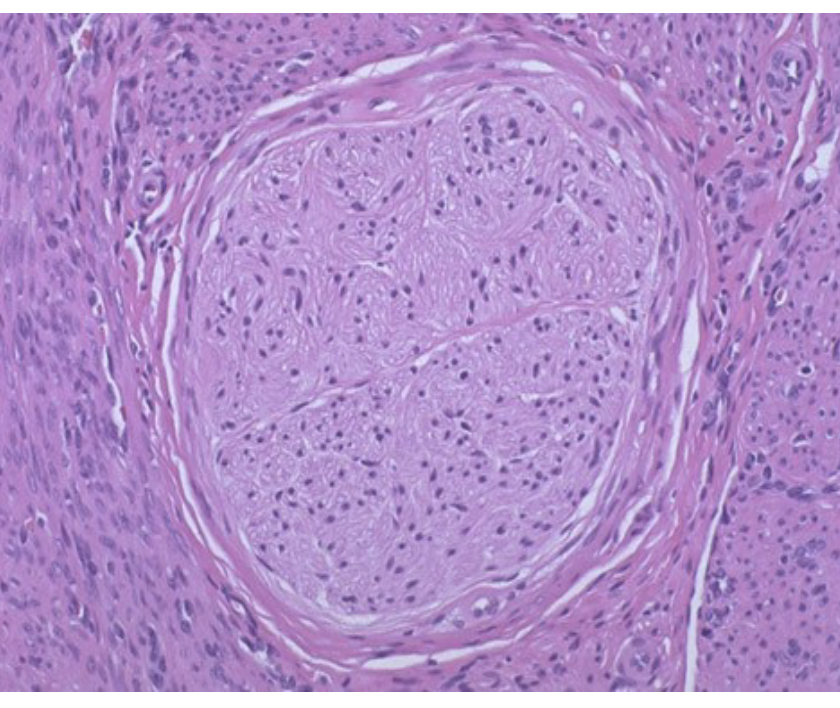
?
peripheral nerve (cross section)
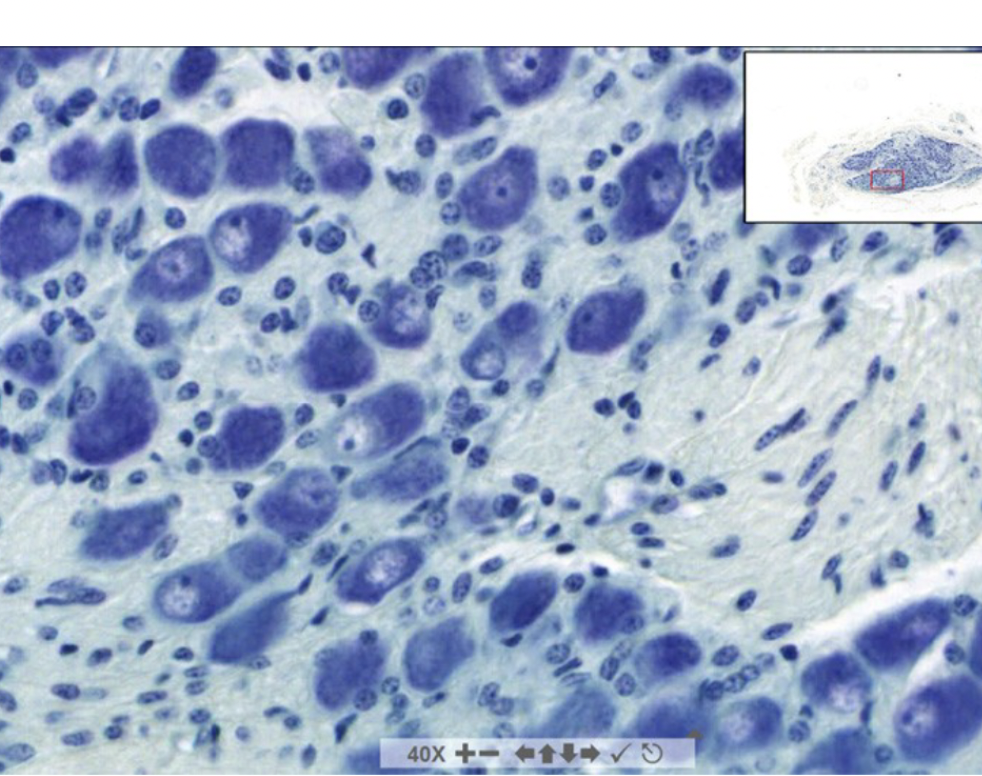
?
sympathetic ganglion cells
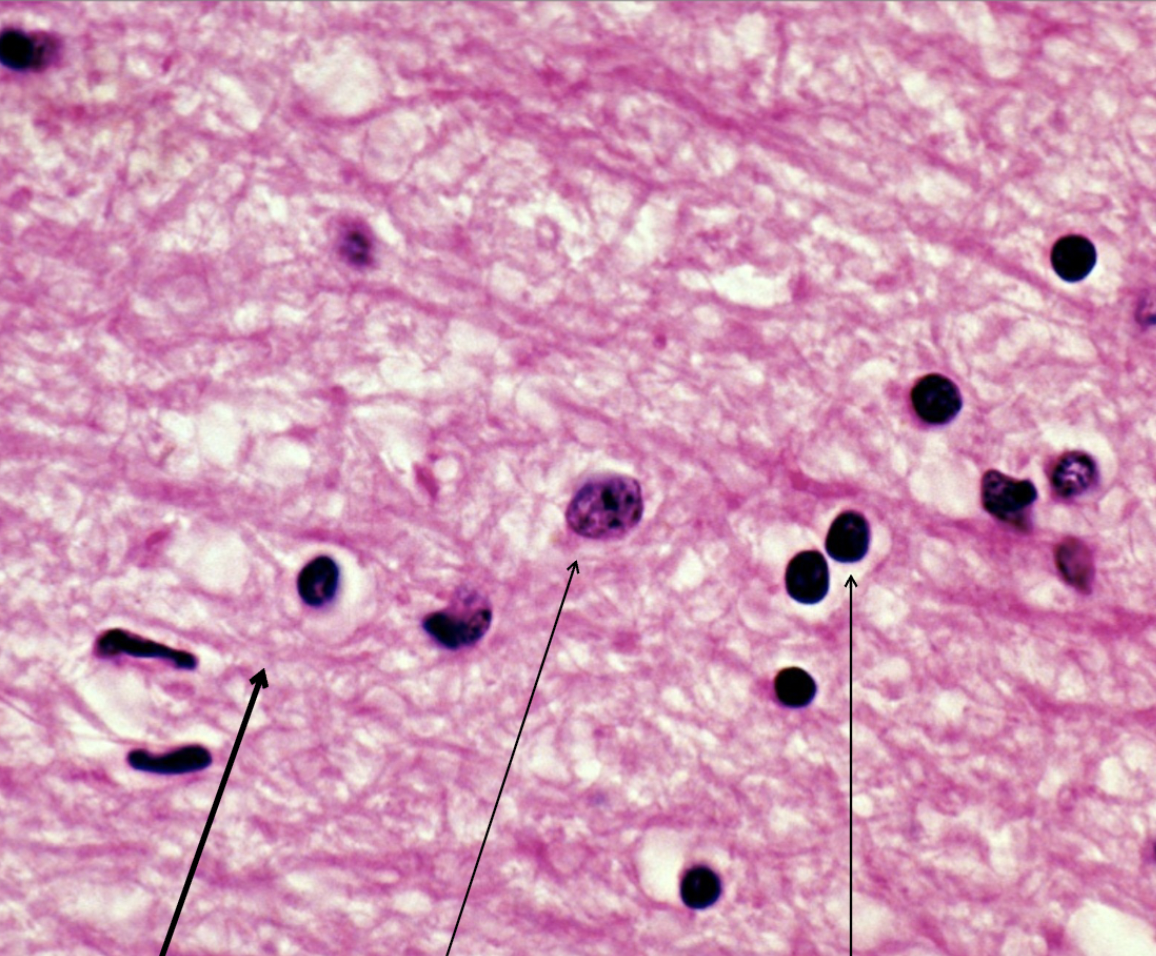
left
neurophil
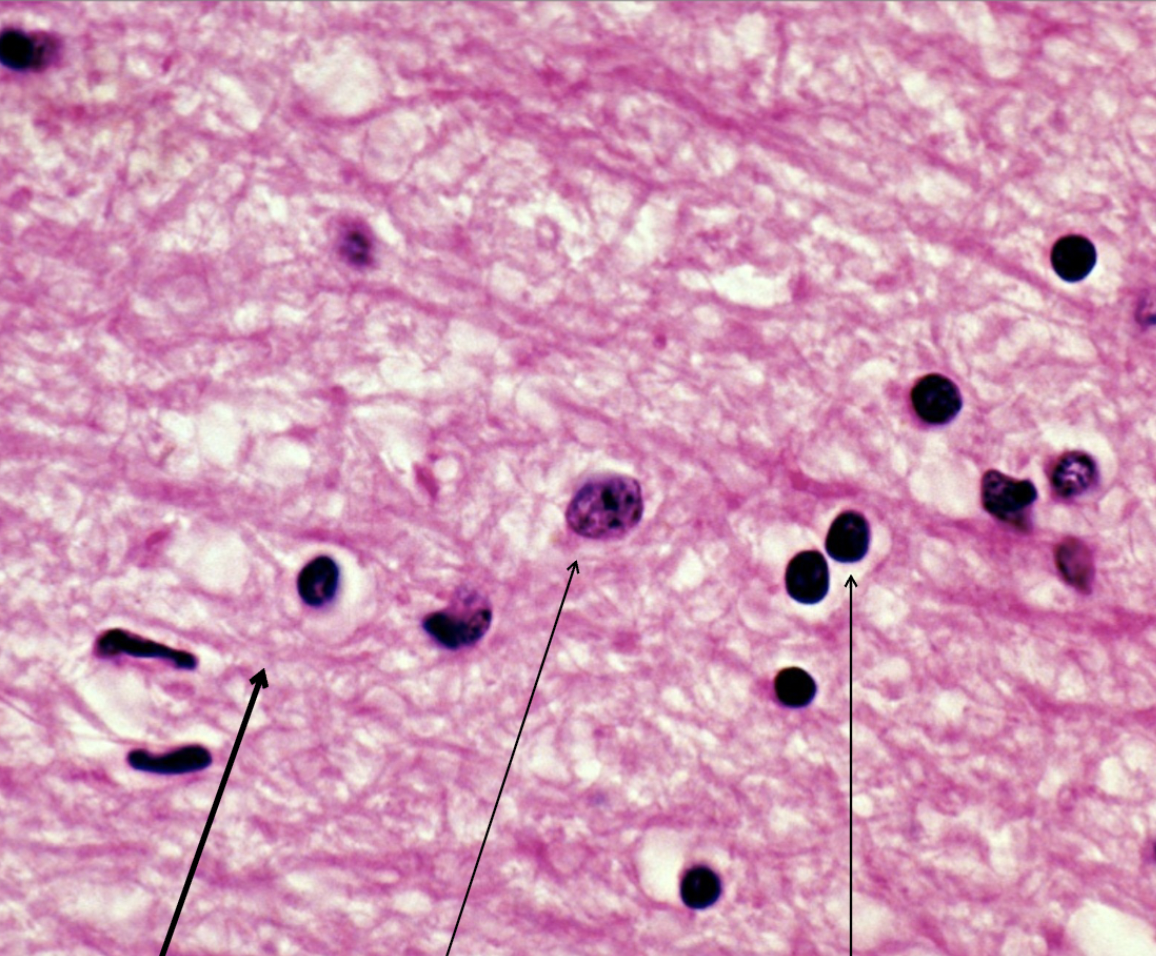
middle
astrocyte
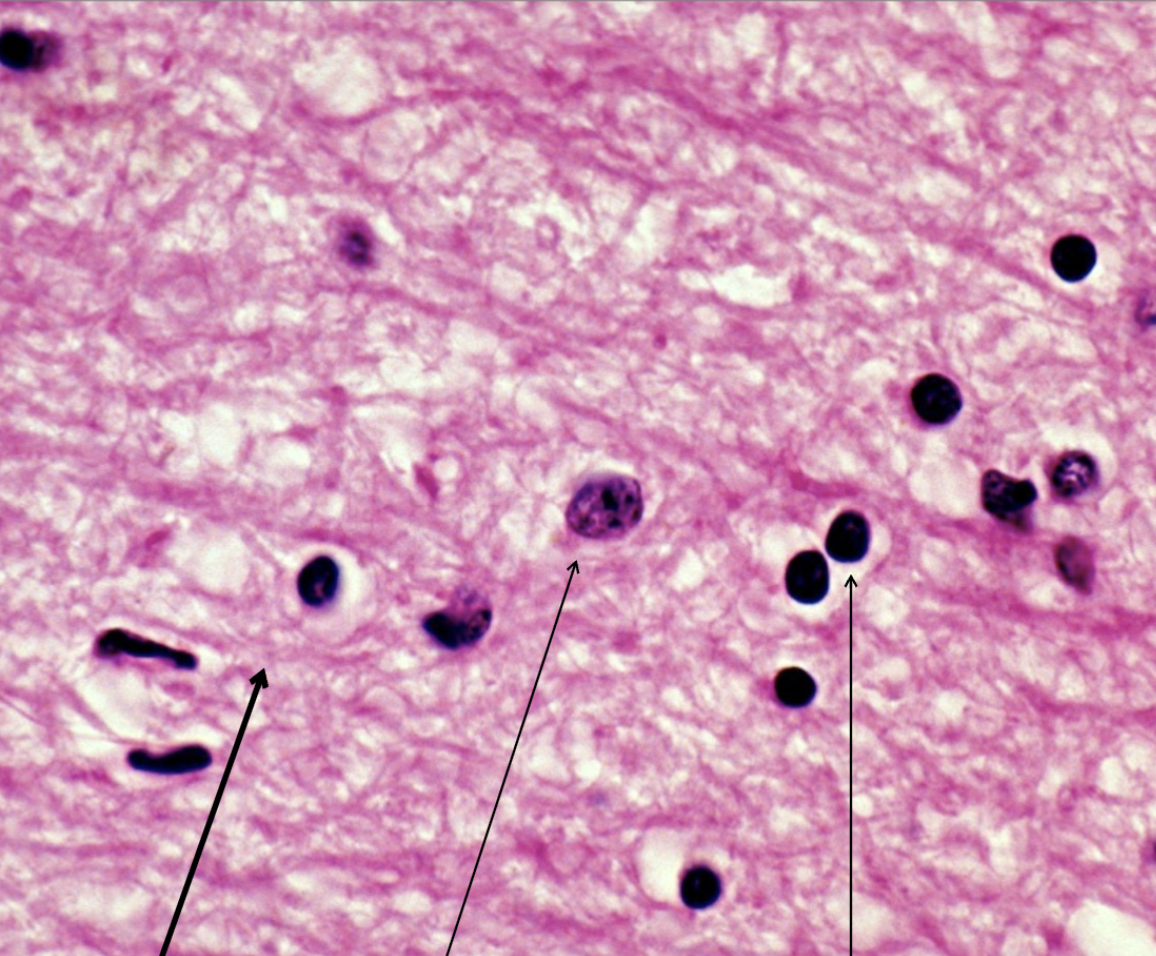
right
astrocytes oligodendrocytes
what is thei?
purkinje cells
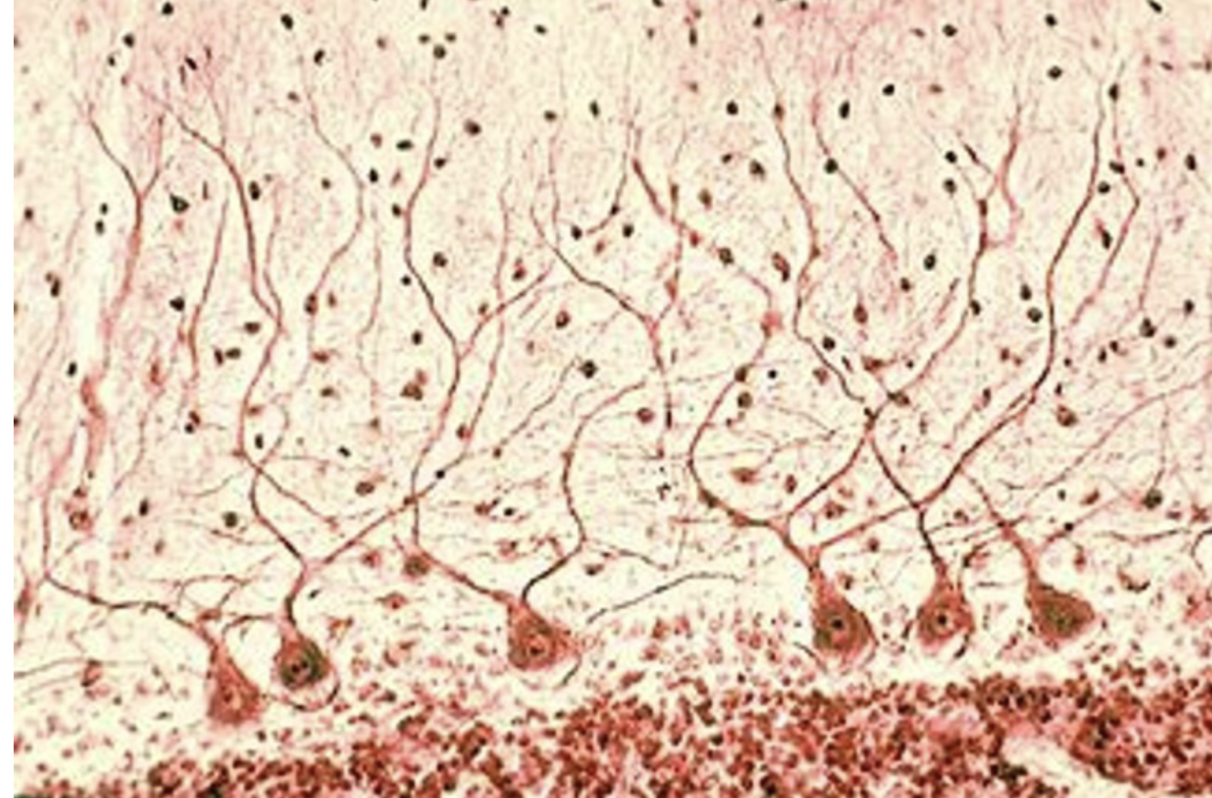
where?
cerebellum
astrocyte location
CNS
oligodendrocyte location
CNS
schwann cell locarion
PNS
ependymal cell location
CNS
microglila cell location>?
CNS
oligendorcyte and schwann cell function
makes myelin and insulates axons