Antivirals MedChem
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is a diagram showing different viral families? (COVERED ELSEWHERE)
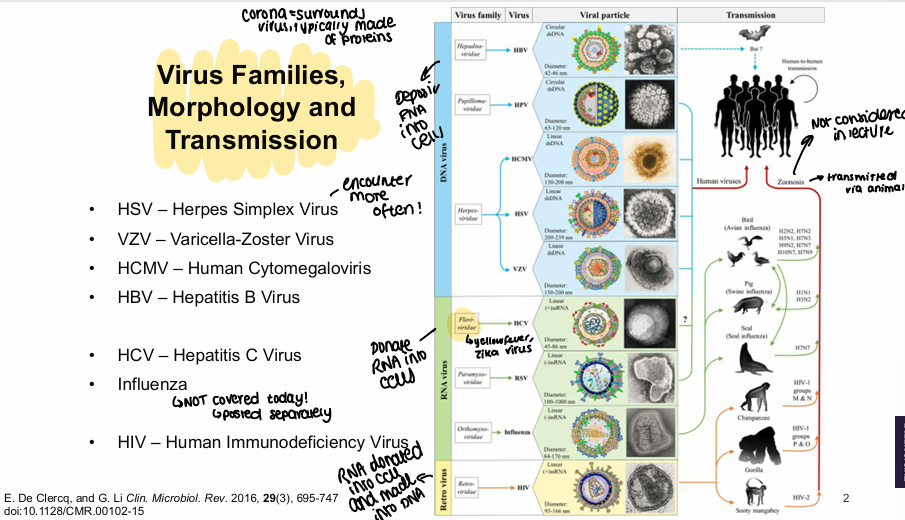
What is an overview for how viruses replicate?
Adhere to cell surface or entry into cell via penetration of cell wall, release DNA/RNA when inside and enters the nucleus, incorporates their DNA into genome and encapsulates into a protein before being released again
What are examples of NRTIs?
Deoxyguanosine, aciclovir, zidovudine, deoxythymidine
What does NRTI stand for?
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor
What class are most antivirals part of?
NRTIs
What properties do most NRTIs have?
Can be phosphorylated - usually triphosphorylated, synthetic analogues of nucleosides
How do NRTIs work?
Selectively inhibit viral reverse transcriptase, when triphosphorylated are incorporated into viral DNA and doesn’t encode for DNA repair proteins - leads to chain termination
What functional groups does zidovudine contain?
Lipophilic azide
What NRTI is zidovudine an analogue of?
Deoxythymidine
What are examples of deoxyguanosine analogue antivirals?
Aciclovir, valaciclovir, penciclovir, famciclovir
What amino acid residue does valaciclovir have?
Valine residue
What happens to the valine residue when valaciclovir is metabolised?
Cleaved off and leaves the hydroxyl group to be phosphorylated
What is a potential advantage of using penciclovir instead of aciclovir?
Retained in cell longer
What antiviral is a prodrug of penciclovir?
Famciclovir
What part of famciclovir needs to be cleaved to become active?
Ester groups
Why are prodrugs of deoxyguanosine favourable?
Aids absorption
What antivirals are used against human cytomegalovirus?
Ganciclovir, valganiciclovir, letermovir, cidofovir
What antivirals are commonly used for herpes simplex/zoster infections?
Deoxyguanosine analogues
What is the structural difference between ganciclovir and aciclovir?
Ganciclovir has an additional primary alcohol group
What type of antiviral is letermovir?
Non nucleoside inhibitor of DNA-terminase complex
What is cidofovir a derivative of?
Cytidine
What is a benefit of cidofovir?
Already phosphorylated
How does letermovir work?
Prevents processing of long, repeating viral DNA into individual mature viral genomes and prevents release of new virions
What antivirals are used against Hep B?
Entecavir, lamivudine, adefovir
What functional group is present in lamivudine that makes it very active for HIV?
Oxygen and Sulphur inside a carbocycle
What nucleotide base is entecavir a derivative of?
Guanosine
What nucleotide base is lamivudine a derivative of?
Cytosine
What nucleotide base is adefovir a derivative of?
Adenosine
Why is entecavir not used to treat hepatitis B in HIV patients?
Risk of selecting for resistance to lamivudine
What can tenofovir be formulated as?
Fumarate salt of tenofovir alafenamide or tenofovir disoproxil
How does tenofovir work?
Inhibits viral DNA polymerase by causing chain termination
What is tenofovir an analogue of?
Acyclic nucleotide analogue of AMP
What are the characteristics of tenofovir alafenamide?
Isopropyl ester, alanine residue and phenol increase uptake of the cell
What antivirals are used to treat Covid-19?
Nirmatrelvir, remdesivir, molnupiravir
What is combined with nirmatrelvir to increase its bioavailability?
Ritonavir
What does nirmatrelvir inhibit?
Inhibits viral 3C-like protease found in coronaviruses
How do remdesivir and molnupiravir act?
Both inhibit viral RNA-dependant RNA polymerase
What properties does remdesivir have?
Alanine based moeity, furan ring and nitrile in position 1
What is the only change in molnupiravir from a nucleotide?
N-OH group on the N containing ring
What is remdesavir an analogue of?
Adenosine monophosphate analogue, prodrug
How does the hepatitis C virus replicate?
Virus entry into the cell
Fusion and uncoating, sRNA released
Translation into single polypeptide
Cleave of polyprotein by NS3 protease, gives 3 structural and 7 non=structural proteins
Forms membrane-bound complex of viral and host proteins
Replication/transcription dependant on RNA-dependant RNA polymerase
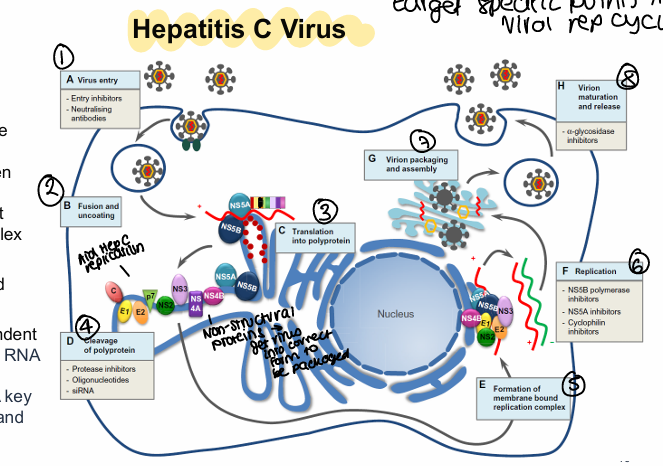
What is the key to viral replication and assembly in Hep C?
NS5A
What indicates the therapeutic regime for Hep C?
Genotype of infection
What are examples of NS3/4A inhibitors for Hep C?
Voxilaprevir, paritaprevir
What are examples of NS5A inhibitors for Hep C?
Velpatavir, ombisavir
What NS5A inhibitor can be used for all genotypes of Hep C?
Pibrentasvir
What are examples of NS5B inhibitors for Hep C?
Sofosvucir, dasabuvir
What is an example of an auxillary treatment for Hep C?
Ritonavir
What are the characteristics of rivavirin?
1,2,4 triazole which is triphosphorylated and incorporated into DNA
What is ribavirin?
Nucleoside analogue that acts in same way as other nucleoside DNA polymerase/reverse transcriptase inhibitors
What are the characteristics of paritaprevir?
Sulfonamide region binds into active site, rest of molecule positions into the active site
Where is NS4A found in Hep C?
ER membrane and associates with NS3 protease
What is used to increase paritaprevirs bioavailability?
Ritonavir
What should inhibit protein cleavage in Hep C?
Peptide/peptidomimetic in NS3 active site - peptide that wouldn’t be cleaved!
What is glecaprevir used in combination with to be active against all phenotypes of Hep C?
Pibrentasvir - includes strains resistant to 1st gen NS3 inhibitors
What are examples of me too NS3/4A inhibitors?
Grazoprevir, voxilaprevir, glecaprevir
What does NS5A exist as?
Homodimer - crucial for replication of HCV
What was the first discovered NS5A inhibitor?
Daclatasvir
What key functional groups did daclatasvir contain?
Imidazole and prolene regions
How was daclatasvir discovered?
Serendipity in SAR studies
What is a summary for discovery of daclatasvir?
Initial screening contained imidazole-proline moeity
SAR study done showed oxygen to methylene has a large difference in activity
Compound 8 decomposed in common solvent of DMSO, unstable in media
Symmetrical analogues then investigated
What part of ombitasvir has potential for activity?
Methylester
Why is pibrentasvir hard to formulate?
Large size - poor solubility
What are some examples of non-symmetrical NS5A inhibitors?
Elbasvir, ledipasvir, velpatasvir
What is the issue with the non-symmetrical NS5A inhibitors?
Difficult to synthesise
What are NS5B inhibitors always used as?
Combination!
What are examples of NS5B inhibitors?
Sofosbuvir, dasabuvir
What are sofosbuvir and dasabuvir derivatives of?
Uridine
What is sofosvbuvir a prodrug of?
NRTI - converted to triphosphate in the liver
What is dasabuvir?
NNRTI that binds to an allosteric site in palm domain of HCV NS5B