republican town planning and pompeii
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
gauls
Tribes from France
Invaded Rome in early 4th century BCE
titus livy
Roman historian
early rome town planning
Hilly terrain, so urban planning was not systemic
Street layout was irregular
town planning in the mediterranean
Orthogonal city plans
right angled
Grid systems
This was happening before the foundation of Rome, during the Republic
roman republic town planning
Starts out organic and unplanned
Later on they began using systemic, grid based planning
Etruscan
Earlier
Reflected in the layout of Rome and temples like the temple of Jupiter
They used fortification walls for defence and civic structure
Greek
Orthogonal grid system
It reflects symmetry, proportion, rationality
Infrastructure
They added pavements and sidewalks
Insured water supply and drainage systems
ostia
Rectangular city
1st roman colony
castrum inspired layout
Military camps
2 main street
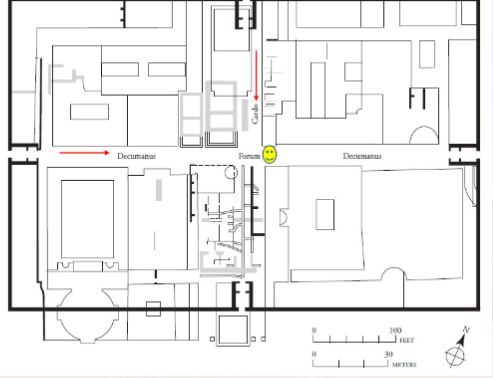
cardo
N to S
decumanus
E to W
forum
The intersection of the cardo and decumanus
Central public space of the city
contains important places
Map is from the 4th century BCE
timgad
followed ostia's layout
Also rectangular
Forum at the centre
monumental gates at the ends of the cardo and decumanus
city is divided into square blocks
Insulae
The city symbolized unity and the centralized power of the Roman Empire
as the city expanded there is irregular planning Due to a more organic development
no longer in the square form
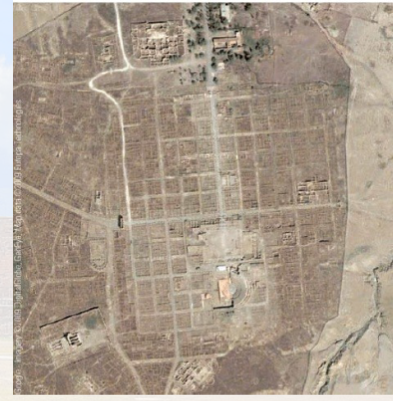
pompeii
in southern italy
not originally a roman city
first group of people living in the area are oscans and then samnites
after romans came into power pompeii absorbed Both groups
After the social war in 80 BCE
mount vesuvius
79 CE
erupted and city covered in ash
caused great preservation of everyday life
stone steps
pompeii tend to get flooded
Not the typical castrum plan
not rectangular
blocks were more trapezoidal
streets bend
We know that this is not due to organic development because the newer sections which is on the east and the older areas surrounding the forum both show this type of irregularity
public spaces
bakeries
Thermapolla
Hot food vendors
Brothels
Contain mural paintings
Residential areas
Included homes and shops
Included aqueducts and drainage systems
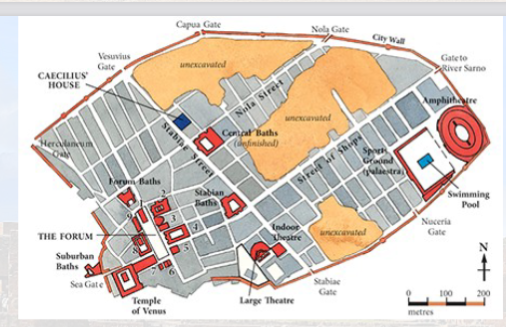
pompeii’s capitolium
aka Temple of Jupiter
converted by romans
etruscan influence and roman culture
narrow staircase
structure attracts viewers to look inside

temple of apollo
etruscan
high podium
narrow staircase
greek
inside
corinthian columns
outside
doric and ionic
apollo statue
etruscan
energetic movement
Hellenistic architecture
used local and imperial influences

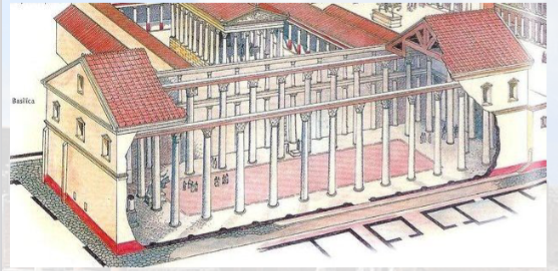
basilica
long and narrow
like the forum itself
has a central nave and flanking aisles divided by two-story columns
corinthian and ionic
in the SW corner of the forum
oldest and most well preserved basilica
built in late 2nd cent
some think 80 bce
for businesses and housed a law court
forum baths
separate for women and men
but shared yard for exercise and
unique engg. system
central furnace
warms up air which flows under the raised floor
hypocaust system
3 section
cold room
frigidarium
warm room
tepidarium
hot room
caldarium
stones + plaster (stucco)
curved ceiling
rectangular windows
Hot water tub
circular window on top
controls steam, light, and air
Photo
Men's caldarium
Pompeii
80 to 70 BCE

theater
function
speeches
plays
Performances
semi-circular
Focuses into One Direction
stage (orchestra) + seating (cavea)
In Pompeii
80 to 70 BCE
Inspired by Greek theatres
Has a portico
Shelter for spectators
Was renovated in the 1st century BCE
Added second seating level and vaulted entrances
odeum theatre
had a roof at that time made of concrete
used for concerts and meeting

amphitheater
function
hunting animals
gladiator combat
Public spectacles
looks like combining 2 theaters together
circular or oval shaped
tiered seating on all sides
in pompeii
80 - 70 bce
Earliest ever built
roman ones larger and with more seating than the greek ones
20,000 spectators
more than pop.
Seating arranged by rank
Concrete vaults
made of velarium for weather protection
After 59 CE riot, closed for 10 years

pompeii’s necropolis
Burials were outside the walls
For memorialization and to attract tourists
made of characterized homes
most had reflection benches outside of them for visitors
evidence
Historical texts
Comparative studies
Archaeological findings
Limitations
Not all Roman towns have the same level of excavation which can change our understanding of urban planning
Some of the written sources are mythological or have bias