C2 - Neural Signalling
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Dendrites
Short, branched nerve fibres, used to transmit impulses in brain and spinal cord
Axons
Elongated nerve fibres, transmit nerve impulses from extremities to spinal cord
Nerve Impulses as Action Potentials
A type of electrical signal due to the movement of positively charged ions. The brief reversal of normal polarization (resting potential). Due to facilitated diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions. Creates a change in voltage called the action potential
Depolarization (Nerve impulses 1)
Sodium channels in the membrane open
Na+ diffuses into the neuron
Entry of Na+ reverses the charge imbalance so the inside becomes positive
Potential: -70 mV → +40 mV
Repolarization (Nerve impulses 2)
Happens immediately after depolarization and is the closing of the sodium channels and opening of potassium channels.
Potassium ions leave the neuron making it become negative relative to outside
Channels remain open until membrane potential falls to -70
Rebuilding Gradients (Nerve Impulses 3)
Sodium-potassium pump re-establishes Na+ and K+ concentration gradient.
Resting Potential
Typically -70 mV. The number of ions pumped in and out is unequal, 3 Na+ ions and only 3 K+ ions, causing a charge imbalance.
Na+ and K+ ions diffuse back through the membrane, leakage of K+ is faster
Negatively charged proteins inside the neurons which add to the imbalance
Synapses
Junctions between two cells in the nervous system. Signals can only be passed in one direction across a synapse. The transmitting neuron brings the action potential with a presynaptic membrane.
The receiving neuron carries the signal away with a postsynaptic membrane.
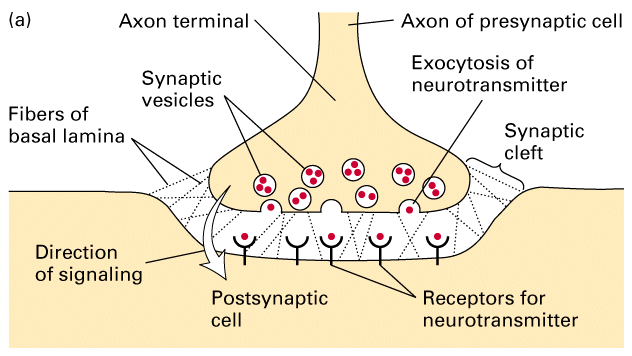
Neurotransmitter
Chemical substance that transfers a signal across the synaptic gap. Contained in vesicles released by the influx of Ca+ after depolarization.
Myelination
Modification that increases the speed of nerve impulses. Myelin are non-continuous layers of phospholipid bilayer. The nerve impulses jump between gaps (nodes of Ranvier) causing faster transmission.
Correlation Coefficient, R
Measure of how strongly associated two variables are. Between -1 and +1.
Coefficient of Determination, R²
Measures the proportion of variation in the DV that can be attributed to the IV
Range of the Correlation Coefficient and The Coefficient of Determination

Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
A change in potential that is large enough to stimulate an action potential
Acetylcholine
A widely sued neurotransmitter at synapses. Used in neurons and muscle fibres. Bonds to receptors that act as Na+ channels. Is rapidly broken down in the synaptic gap by acetylcholinesterase.