ecological heterogeneity
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
what variations in biotic and abiotic components can occur in an ecosystem
differences or changes in environmental characteristics (rainfall, sunlight, nutrients, wind)
\
relative concentration or distribution of organisms
\
relative concentration or distribution of organisms
2
New cards
define structural heterogeneity
the complexity and variability of a property of an ecosystem in three-dimensional space and over time
3
New cards
define spacial heterogeneity
different values of an ecosystem component in different places within an ecosystem; “patchy” distribution (e.g. plant cover, soil N values)
4
New cards
define temporal heterogeneity
change in values of an ecosystem component time (e.g. seasonal variation in precipitation, migratory species)
5
New cards
boundaries are a form of spatial heterogeneity, what is a type of boundary that can occur? and give examples of how they can be created
sharp boundaries
\
created by fires, strong storms (hurricanes/tornados) and human impacts (clear-cutting) or changes from one ecotype to another (aquatic to the terrestrial boundary - like body of water)
\
created by fires, strong storms (hurricanes/tornados) and human impacts (clear-cutting) or changes from one ecotype to another (aquatic to the terrestrial boundary - like body of water)
6
New cards
what results in terms of the landscape after a forest fire
fire kills/damages trees in patches
\
resulting in patches with differences in vegetation & soil properties (moisture, nutrients, pH, etc.)
\
sharp boundaries between then affected and unaffected areas
\
exchange across the boundaries affects the ecological structure and function of the patches
\
resulting in patches with differences in vegetation & soil properties (moisture, nutrients, pH, etc.)
\
sharp boundaries between then affected and unaffected areas
\
exchange across the boundaries affects the ecological structure and function of the patches
7
New cards
can a highway be considered spatial heterogeneity
yes
8
New cards
what conditions can differ across a boundary
light, moisture, wind, aerosols, nutrient availability, biota etc.
9
New cards
is this considered an example of the boundaries created through spatial heterogeneity:
\
in deserts, abiotic and biotic conditions (organic matter content of soils, nutrients, moisture, wind, temperature, predation, etc.) can differ under plants vs in exposed areas
\
in deserts, abiotic and biotic conditions (organic matter content of soils, nutrients, moisture, wind, temperature, predation, etc.) can differ under plants vs in exposed areas
yes, it is still different values of an ecosystem in different places with patchy boundaries
\
some species can live in the patches, some can live between the patches
\
some species can live in the patches, some can live between the patches
10
New cards
what is an example of a natural cause of heterogeneity
forest fire mosaics
pit and mound microtopography
pit and mound microtopography
11
New cards
true or false: due to advancements in technology, wild fires are more easily controllable therefore the acres burned from these fires has drastically increased
FALSE: the acres burned has increased a lot while the number of fires per year has remained constant
12
New cards
define pit and mound microtopography
large tree falls due to wind, snow or the inexorable forces of time
after 5-10 years, a mound forms as the root mass decays
where the roots get ripped up, creates a pit
earthworms move in
create microenvironment
after 5-10 years, a mound forms as the root mass decays
where the roots get ripped up, creates a pit
earthworms move in
create microenvironment
13
New cards
define ecological extinction
when a species is still present, but in such a small population that they don’t have any ecological significance or an impact on other species
14
New cards
with smaller fragmented areas, would that mean a more likely cause for extinction or proliferation of the species
more likely to have extinction
species richness is low
species richness is low
15
New cards
what are edges?
they are where different adjacent plant communities intersect
16
New cards
define brood parasitism. what bird is more likely to suffer from this and why?
when birds put their eggs into other birds nests
passerine birds suffer from this since they are nesting in edge zones and cowbirds are likely to do this
passerine birds suffer from this since they are nesting in edge zones and cowbirds are likely to do this
17
New cards
true or false: birds typically like to nest deep in the forrest not the edges, since theres less wind, its less exposed and more hidden from predators so theyre less likely to be eaten
TRUE
18
New cards
where is the bacteria reservoir of lyme disease
a. deer
b. birds
c. white footed mice
d. tics
a. deer
b. birds
c. white footed mice
d. tics
c
19
New cards
where do white footed mice thrive
in small forest fragments and on the edge habitats
20
New cards
where are you most likely to find white footed mice
a. rural areas
b. urban areas
c. suburban areas
a. rural areas
b. urban areas
c. suburban areas
a
21
New cards
define gradients in spatial heterogeneity
give an example
give an example
continuous variation in ecological factors
ex. mountain slopes, coastal environments, rivers
\
think of river system and varying degrees of nutrients (stream orders)!
ex. mountain slopes, coastal environments, rivers
\
think of river system and varying degrees of nutrients (stream orders)!
22
New cards
define fragmentation
a reduction in the area covered by a habitat type
\
a change in the habitat configuration with the remaining habitat apportioned into smaller more isolated patches
\
a change in the habitat configuration with the remaining habitat apportioned into smaller more isolated patches
23
New cards
what are the four types of landscapes
intact
variegated
fragmented
relict
variegated
fragmented
relict
24
New cards
define intact landscapes
most of the original vegetations with little or no loss
\
>90% remain from original
\
>90% remain from original
25
New cards
define variegated landscapes
mostly dominated by the original vegetation
26
New cards
define fragmented landscapes
fragments are minor components of the landscape dominated by other land uses
27
New cards
define relict landscapes
urban or intense agriculture
28
New cards
which of these has the highest degree of connectivity
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
a
29
New cards
which of these landscapes has loss of original landscpae, but can still allow for movement of organisms between patches smoothly
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
b
30
New cards
which of these has abrupt boundaries
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
b
31
New cards
which of these has a high degree of space between the patches (low connectivity)
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
c
32
New cards
which of these has no connectivity
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
a. intact landscape
b. variegated landscape
c. fragmented landscape
d. relict landscape
d
33
New cards
what type(s) of species are usually the first lost during habitat loss
rare species
endemic species
endemic species
34
New cards
define crowding effect
when a territory is isolated, the influx of migrants from displaced areas will increase population densities
35
New cards
would temperate and tropical species be more susceptible to fragmentation and insuralization?
no! they are more endemic and rare species so they will not deal with disturbacnes from humans well and will therefore be lost due to the changes caused to the habitat
36
New cards
with greater species richness in areas this means…
the ecosystem is more resistant to disturbance and can be more productive
37
New cards
what is a diel cycle
occurs over a 24 hr period
\
tracks photosynthesis/ respiration (sunlight and temp)
tracks migration/movement (zooplankton, nocturnal/diurnal animals)
\
tracks photosynthesis/ respiration (sunlight and temp)
tracks migration/movement (zooplankton, nocturnal/diurnal animals)
38
New cards
with annual variability measurements, what types of things are being measured
flood pulse
temp
precipitation
ice presence
net ecosystem respiration of carbon
GPP
ecosystem respiration
(all in different biomes over a year)
temp
precipitation
ice presence
net ecosystem respiration of carbon
GPP
ecosystem respiration
(all in different biomes over a year)
39
New cards
what does a disruption in ecosystems consist of
a disruption in ecosystems consists of disturbance and response
characterized by their temporal patterns
characterized by their temporal patterns
40
New cards
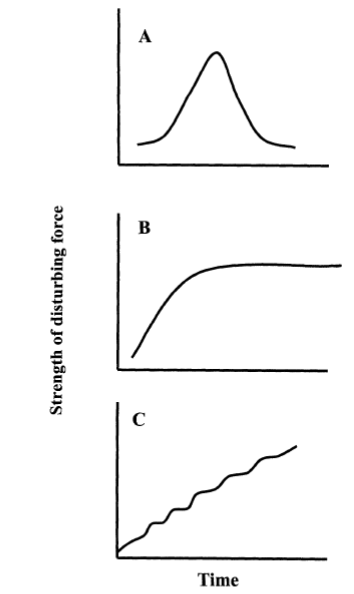
what are the types of disturnaces, give an example of each
pulse: sudden onset, short-lived, ends fast (ex. windstorm, seasonal disturbance, seasonal flooding etc.)
\
press: once instigates remain in place a long time (ex. climate shift to a new regime)
\
ramp: steady increase over time without an endpoint (ex. acid rain, eutrophication, drought)
\
press: once instigates remain in place a long time (ex. climate shift to a new regime)
\
ramp: steady increase over time without an endpoint (ex. acid rain, eutrophication, drought)
41
New cards
what are the responses that can occur due to disturbances
resistance = a measure of the capacity of a system to withstand a disturbance
\
resilience = a measure of the capacity of the system to recover from disturbance
\
resilience = a measure of the capacity of the system to recover from disturbance
42
New cards
define succession
the gradual change in biological communities in an area following a disturbance or the creation of a new geological substrate
43
New cards
what are the two types of succession
primary = occurs on newly exposed geological substrate
\
secondary = occurs after a disturbance destroys the biological community but does not destroy the soil
\
secondary = occurs after a disturbance destroys the biological community but does not destroy the soil
44
New cards
would it be easier for the ecosystem to bounce back from secondary or primary succession
secondary since the soil is still intact
\
primary rips up everything, and you start from scratch
\
primary rips up everything, and you start from scratch
45
New cards
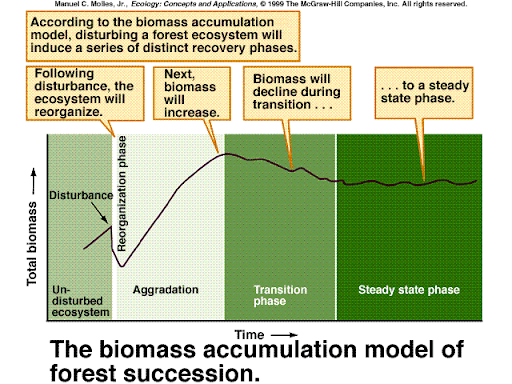
briefly describe the process of secondary succession
theres an **undisturbed ecosystem**
\
\*\*\*disturbance\*\*\*
\
causes sharp decline
\
following the disturbance, the ecosystem **reorganizes** (0-20 years… forest loses biomass, water, and nutrients)
\
**aggradation** occurs (100+ years) biomass starts to accumulate (water and nutrients are strongly retained - LOTS)
\
transition phase occurs, biomass declines from peak(loss of nutrients and increase in water)
\
steady state phase - biomass is between a steady fluctuation of a mean value
\
\*\*\*disturbance\*\*\*
\
causes sharp decline
\
following the disturbance, the ecosystem **reorganizes** (0-20 years… forest loses biomass, water, and nutrients)
\
**aggradation** occurs (100+ years) biomass starts to accumulate (water and nutrients are strongly retained - LOTS)
\
transition phase occurs, biomass declines from peak(loss of nutrients and increase in water)
\
steady state phase - biomass is between a steady fluctuation of a mean value
46
New cards
what is the transition phase of the secondary succession model considered
a. press response
b. ramp response
c. pulse response
a. press response
b. ramp response
c. pulse response
b
47
New cards
what is the steady state phase of the secondary succession model considered
a. press response
b. ramp response
c. pulse response
a. press response
b. ramp response
c. pulse response
a
48
New cards
what is the reorganization phase of the secondary successtion model considered
a. press response
b. ramp response
c. pulse response
a. press response
b. ramp response
c. pulse response
c