Chapter 2: Chemistry
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Matter
Life is made up of matter, which occupies space and has mass.
Elements
Substances that cannot be broken down or changed chemically into other substances; composed of atoms.
Each element has a chemical symbol and possesses unique properties.
Atom
The smallest unit of an element that retains the properties of that element.
Electrically neutral (number of protons = number of electrons)
Protons
Positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutrons
Neutral particles found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electrons
Negatively charged particles found in the space around the nucleus of an atom.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
Ion
An atom with a charge due to the loss or gain of electrons.
This occurs in atoms that have very different electronegativities.
Periodic Table
A table that provides information about the properties of elements and their electron organization.
Atomic Mass
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom, which defines the element.
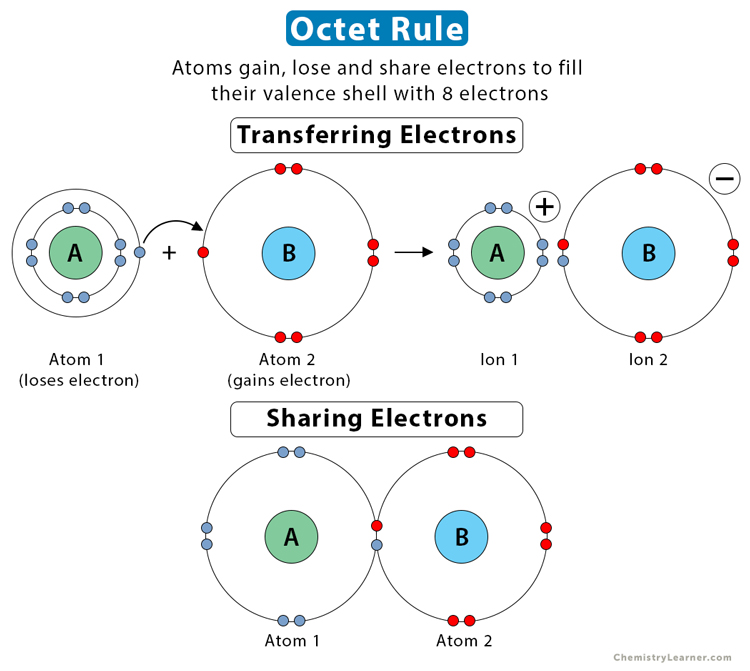
Octet Rule
A rule predicting how atoms form chemical bonds to achieve eight electrons in their outer shell.
Hydrogen is an exception to this rule since it only needs two valence electrons to have a full outer shell.
Covalent Bond
A bond formed when atoms share electrons.
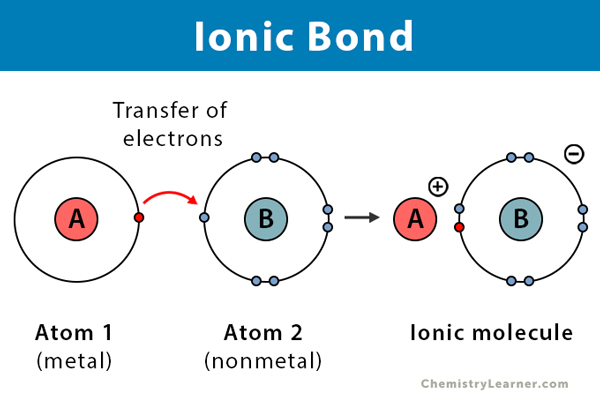
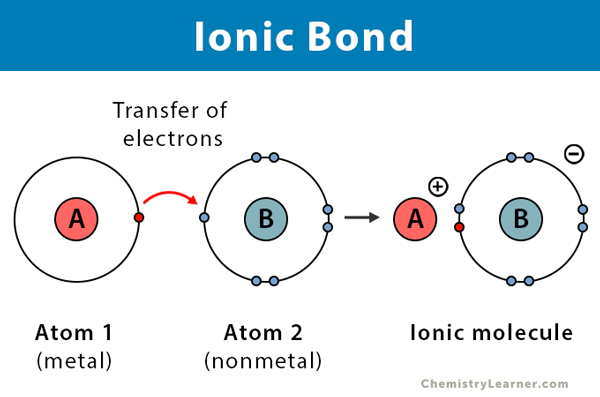
Ionic Compound
A compound formed when a metal transfers electrons to a non-metal.
They do not share valence electrons, but transfer them
Chemical bonds
The interactions between atoms
Electronegativity
The degree to which an atom attracts and holds onto electrons.
If two atoms come together and have similar electronegativities, they will share an electron between the two of them.
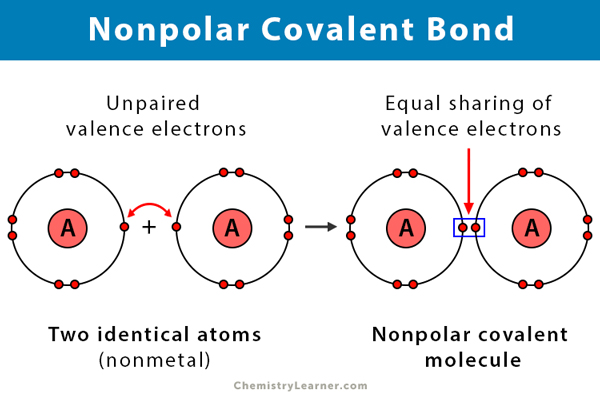
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
A bond formed when atoms with the same electronegativity share electrons equally.
Polar Covalent Bond
A bond formed when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unequally.
Electrons will spend more time next to the atom with a higher electronegativity.
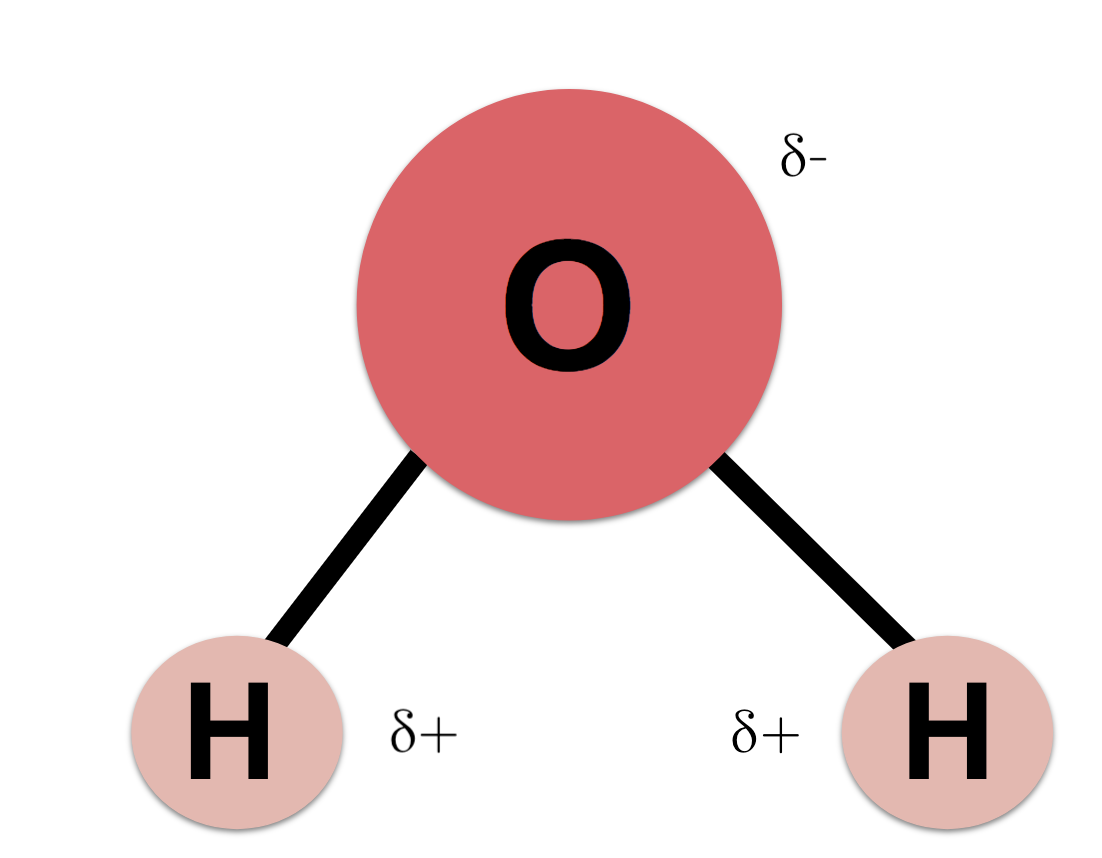
Example: In water, oxygen has stronger electronegativity than hydrogen, causing oxygen to hog more electrons than hydrogen. This leads to oxygen to have a partial negative charge, and hydrogen to have a partial positive charge.
Cation
A positively charged ion formed when an atom loses electrons.
Anion
A negatively charged ion formed when an atom gains electrons.
Ionic Bond
A bond formed through the electrostatic attraction between cations and anions.
Weaker than most covalent bonds
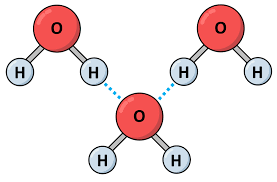
Hydrogen bond
The next weaker bond after ionic bonds.
There are hydrogen bonds that hold different water molecules together, which makes water so cohesive.
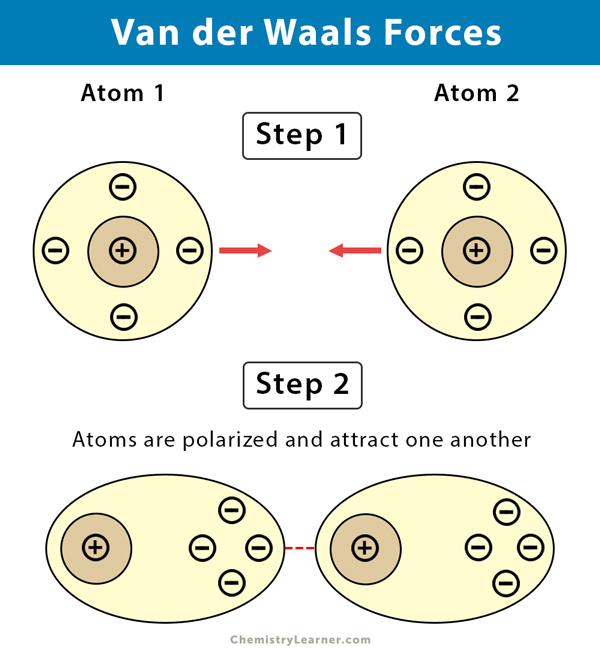
Van Der Waals Interactions
Weak attractions between molecules due to temporary partial charges.
Occur between polar, covalently bound, atoms in different molecules.
Properties of Water
Polar - hydrogen and oxygen for polar covalent bonds
Stabilizes temperature - hydrogen absorbs and releases heat energy slowly
Excellent Solvent - ionic compounds and polar molecules can readily dissolve in it
Cohesive and adhesive - water molecules are attracted to each other and other molecules
pH Level
A measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, indicating acidity or basicity.
As positive hydrogen ions increases, pH goes down and becomes more acidic.
As positive hydrogen ions decreases, pH goes up and becomes more basic.
Acids
Substances that release hydrogen ions in solution, increasing acidity.
How strong an acid is depends on how many hydrogen ions are produced.
Bases
Substances that increase the concentration of hydroxide ions in solution, decreasing acidity.
They can be strong or weak depending on how well they break apart.
Salts
Compounds formed from the reaction of an acid and a base, dissociating into ions in solution.
Salts break apart or dissociate in water to form positive and negative ions, important for body functions.
Carbohydrates
Organic molecules that provide energy, consisting of simple sugars and polysaccharides.
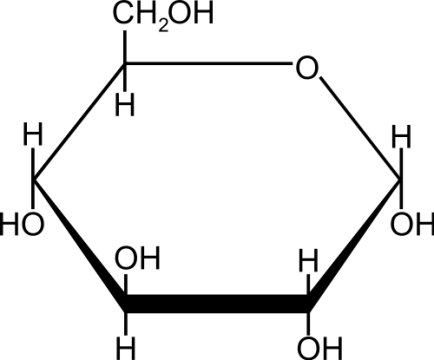
Monosaccharide
The simplest form of carbohydrates, a single sugar unit.
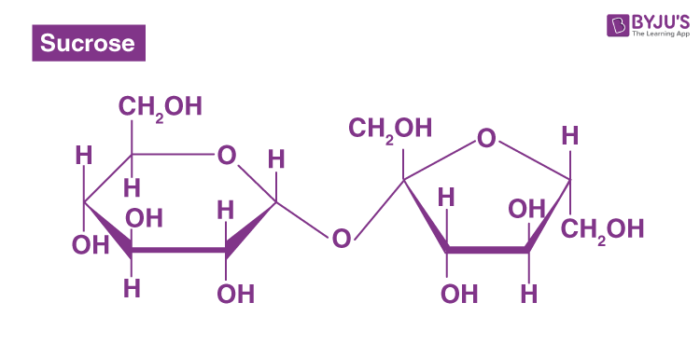
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate formed from two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond.
A dehydration synthesis reaction must occur (an H2O molecule is lost)
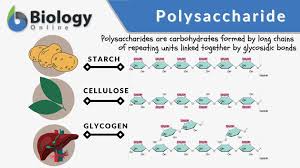
Polysaccharide
A long chain of monosaccharides linked by covalent bonds, such as starch and cellulose.
Proteins
Essential compounds made of amino acids that perform various functions in the body, such as hormones and enzymes in the body.
Amino Acid
The basic unit of proteins, linked by peptide bonds.
Denaturation
The process by which proteins lose their structure due to external factors like temperature or pH.
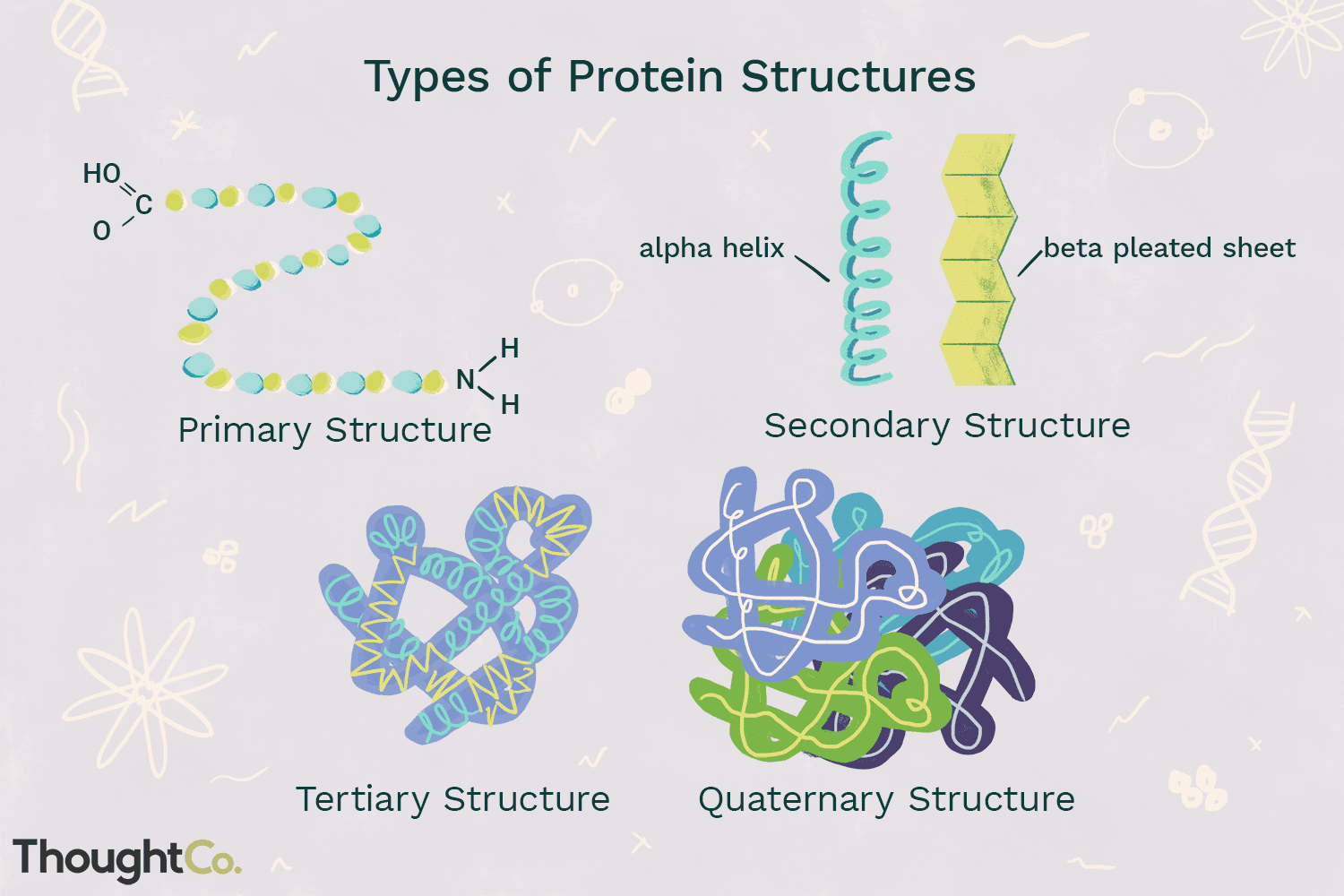
Protein Structure
Primary - The unique sequence and number of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Secondary - Two main types, alpha helix and beta pleated sheets; Hydrogen bonding of the peptide backbone causes the amino acids to fold into a repeating pattern.
Tertiary- Three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide; caused by chemical interactions between various amino acids and regions of the polypeptide.
Quaternary - consists of more than one amino acid chain
Lipids
Hydrophobic organic molecules, including fats, oils, and steroids, that store energy.
Building blocks of many hormones and make up the plasma membrane
Triglyceride
A fat molecule made of glycerol and three fatty acid tails.
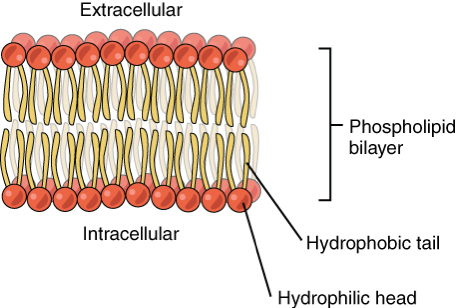
Phospholipid
A lipid molecule with two fatty acid tails, a glycerol, and a phosphate group, forming cell membranes.
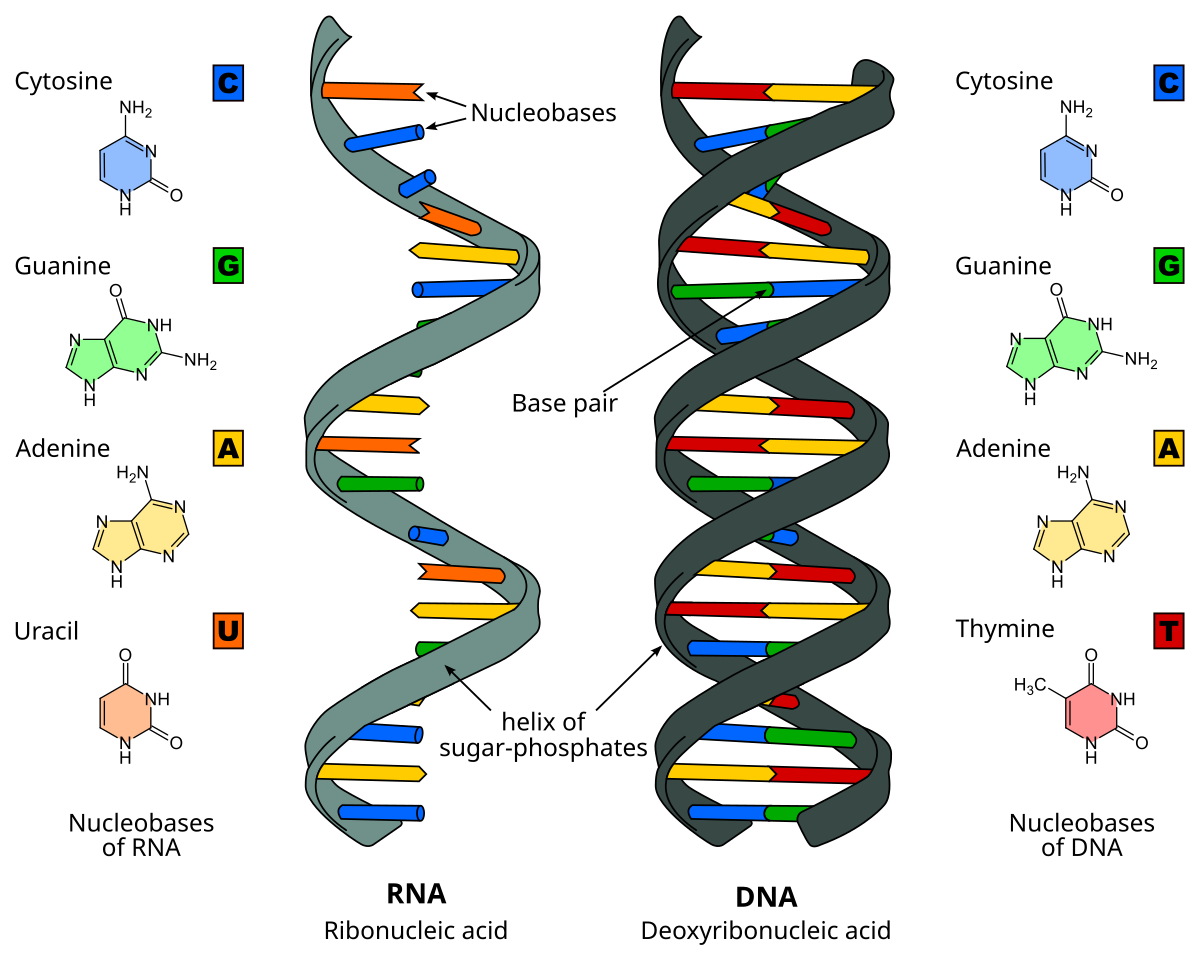
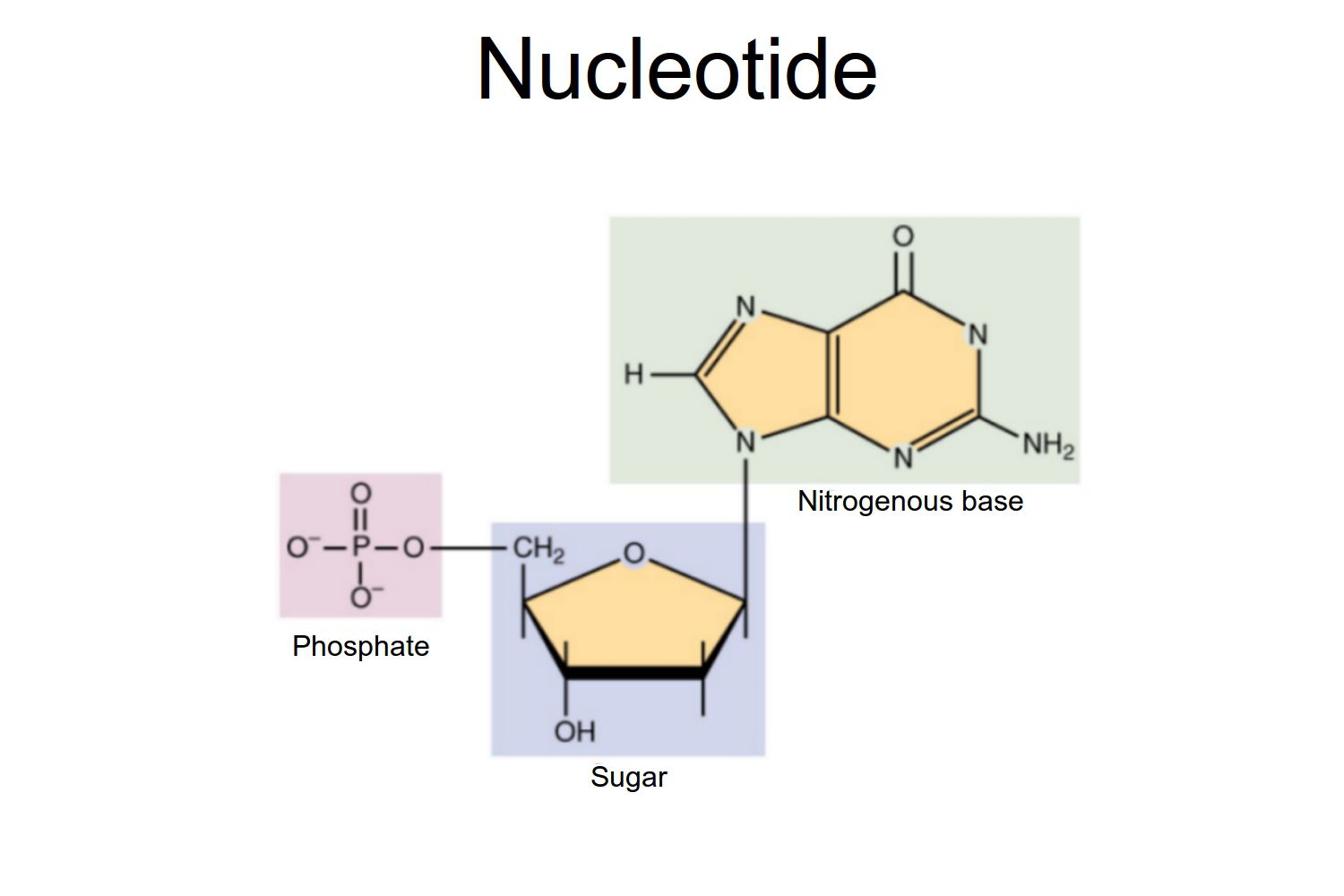
Nucleic Acids
Molecules that contain genetic information, including DNA and RNA.
Consist of a 5’ carbon sugar, a nitrogen base and a phosphate.
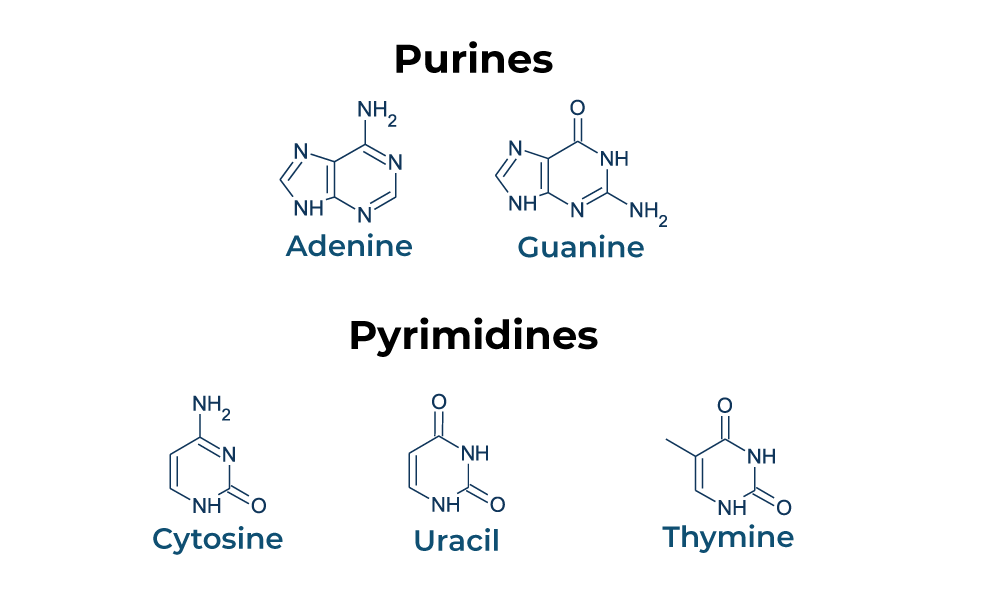
Two Types of Nitrogen Bases
Purines - Adenine and guanine; consist of two carbon-nitrogen rings
Pyrimindines - Cytosine, thymine, and uracil; consist of one carbon-nitrogen ring
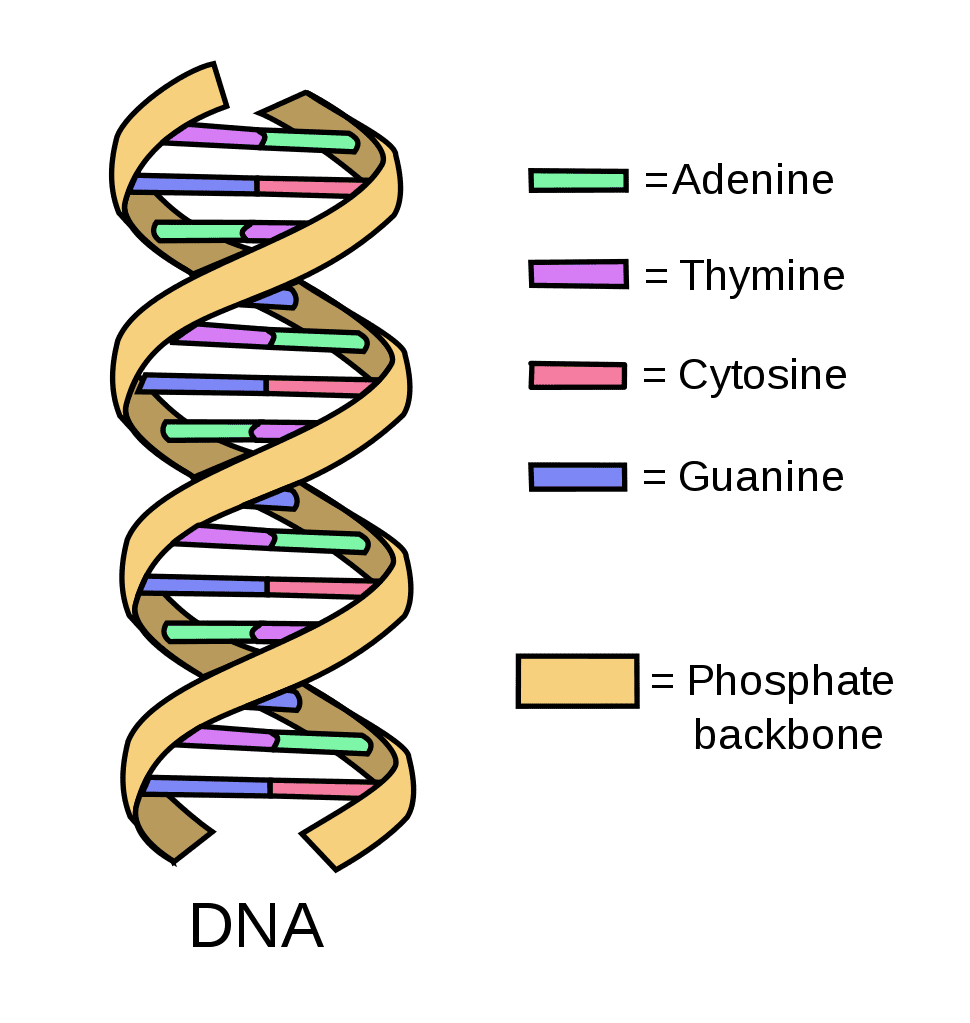
DNA
A double helix structure that contains genetic material, with a sugar-phosphate backbone.
Bases: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and cytosine (C)
RNA
A single-stranded molecule that codes for proteins, containing ribose sugar.
Bases: Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G)
Uracil replaces Thymine