A&P CH 16: The Endocrine System
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Thyro-
Relating to the thyroid gland
Para-
beside, near, alongside
Adreno-
Relating to the adrenal gland
Gluco-
sugar/glucose
Tropi-
to turn on
The group of hormones made by the adrenal cortex that regulate sugar metabolism are called
Glucocorticoids
Follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone turn on the gonads and are called
Gonadotropins
The glands located alongside the thyroid gland are called
Parathyroid glands
A chemical signal that targets the adrenal cortex is called
Adrenocorticotropic
The main hormone produced by the thyroid gland is called
Thyroxine
The amplification of the signal from a water-soluble hormone is achieved through an increase in
cAMP in cytoplasm
Water-soluble hormones affect target cells by binding to
plasma membrane receptors
How do endocrine hormones reach their target cells?
Hormones are transported through the blood stream to target cells
What is the role of activated protein kinases?
phosphorylate proteins
Cyclic AMP is degraded by
phosphodiesterase
Which of the following is not one of the functions of the endocrine system?
Promotes growth
Regulates metabolic reactions
Maintains fluid balance
Controls memory and learning
Controls memory and learning
Compared to the effects of the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system
Last longer, can require seconds, several hours, or even days to elicit effects
Which of the following is a primary endocrine organ?
Heart
Pineal gland
Testes
Thyroid gland
Thyroid gland
The anterior pituitary hormone that controls the release of glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex is
ACTH
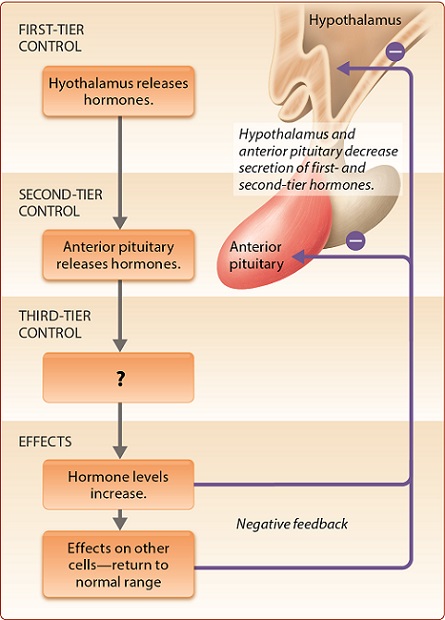
Which of the following best belongs in the box with the question mark?
Thyroid gland
Pancreas
Posterior pituitary
Adrenal medulla
Thyroid Gland; TSH from the anterior pituitary stimulate the thyroid gland
Which of the following hormones is secreted by the posterior pituitary?
ADH
Prolactin
Somatostatin
TSH
ADH
Hormones that control hormone secretion from other glands are known as:
Tropic hormones
Where is antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, made?
Hypothalamus produces it and posterior pituitary stores and releases it
What is the primary effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH, or vasopressin)?
Water retention by the kidneys
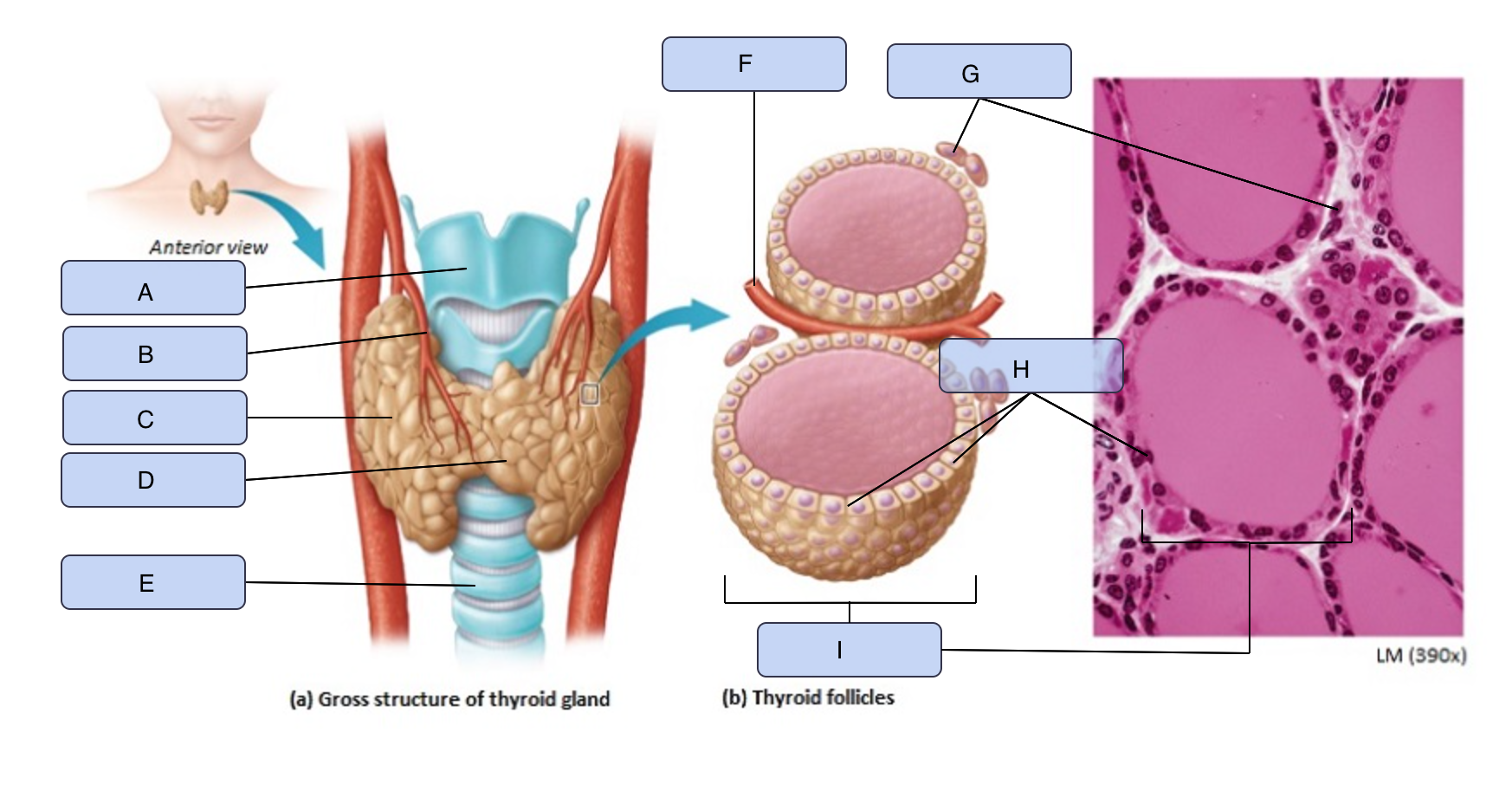
What is A
Larynx
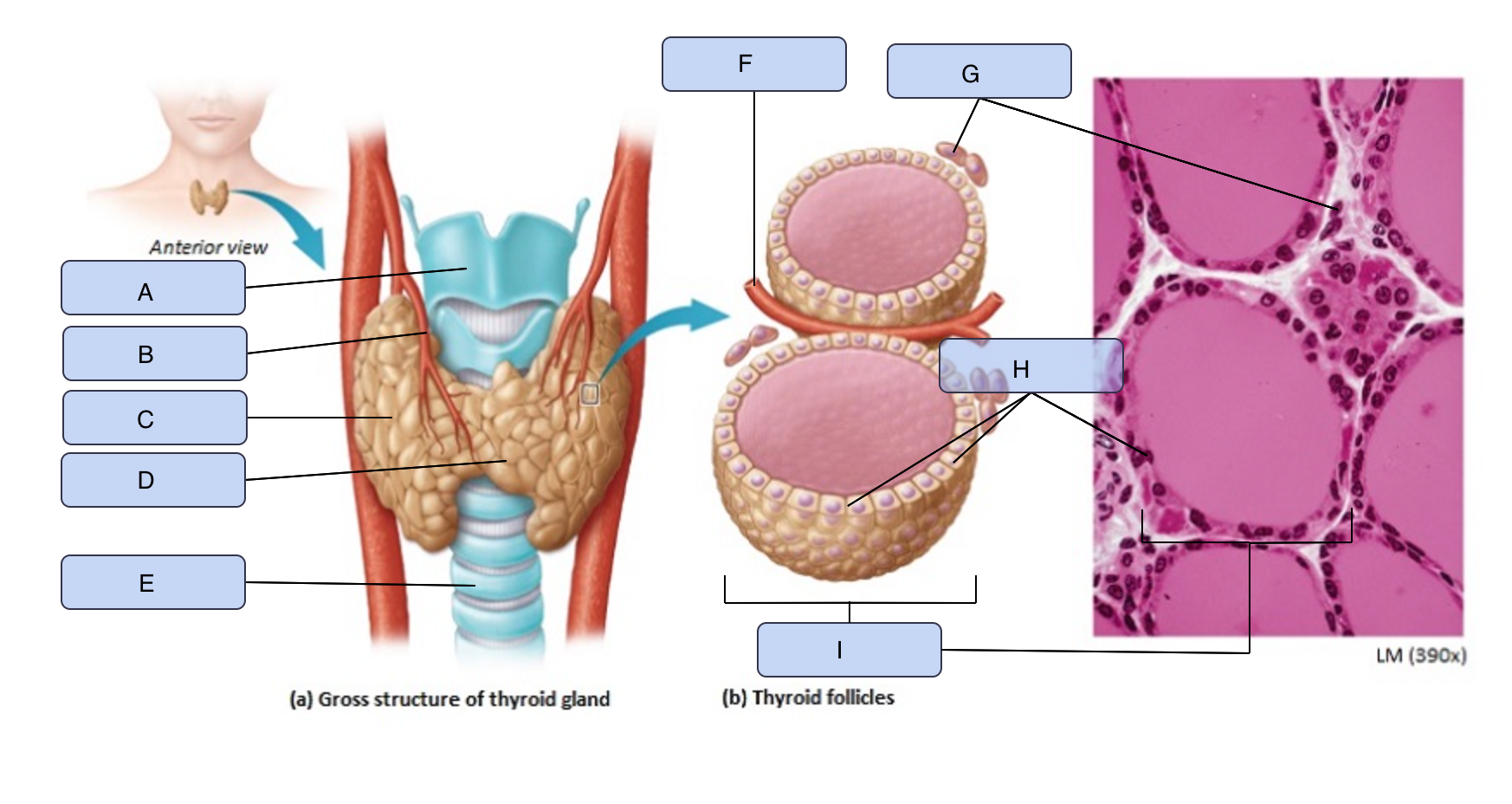
What is B
Superior thyroid artery
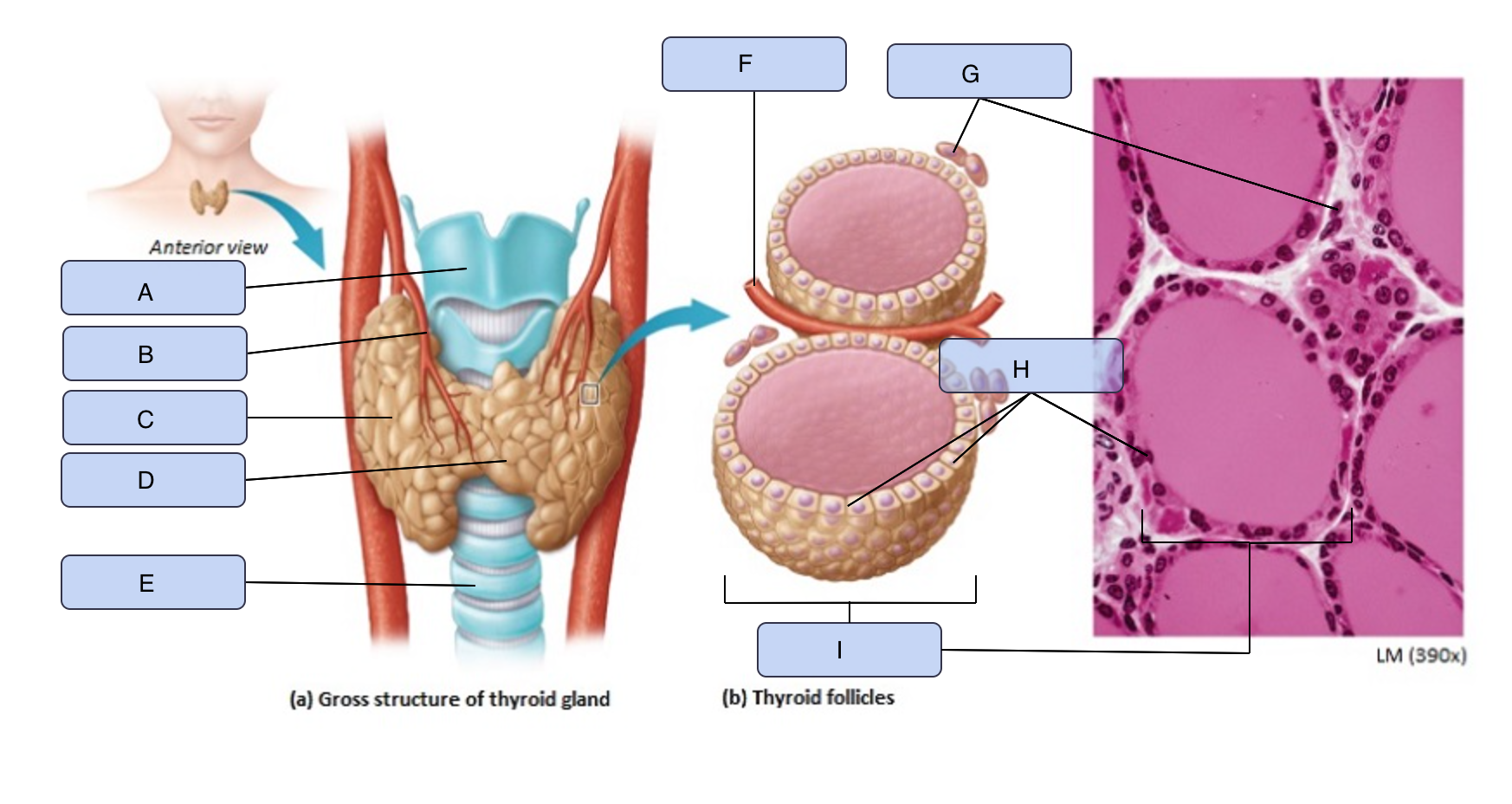
What is C
Thyroid gland (right lobe)
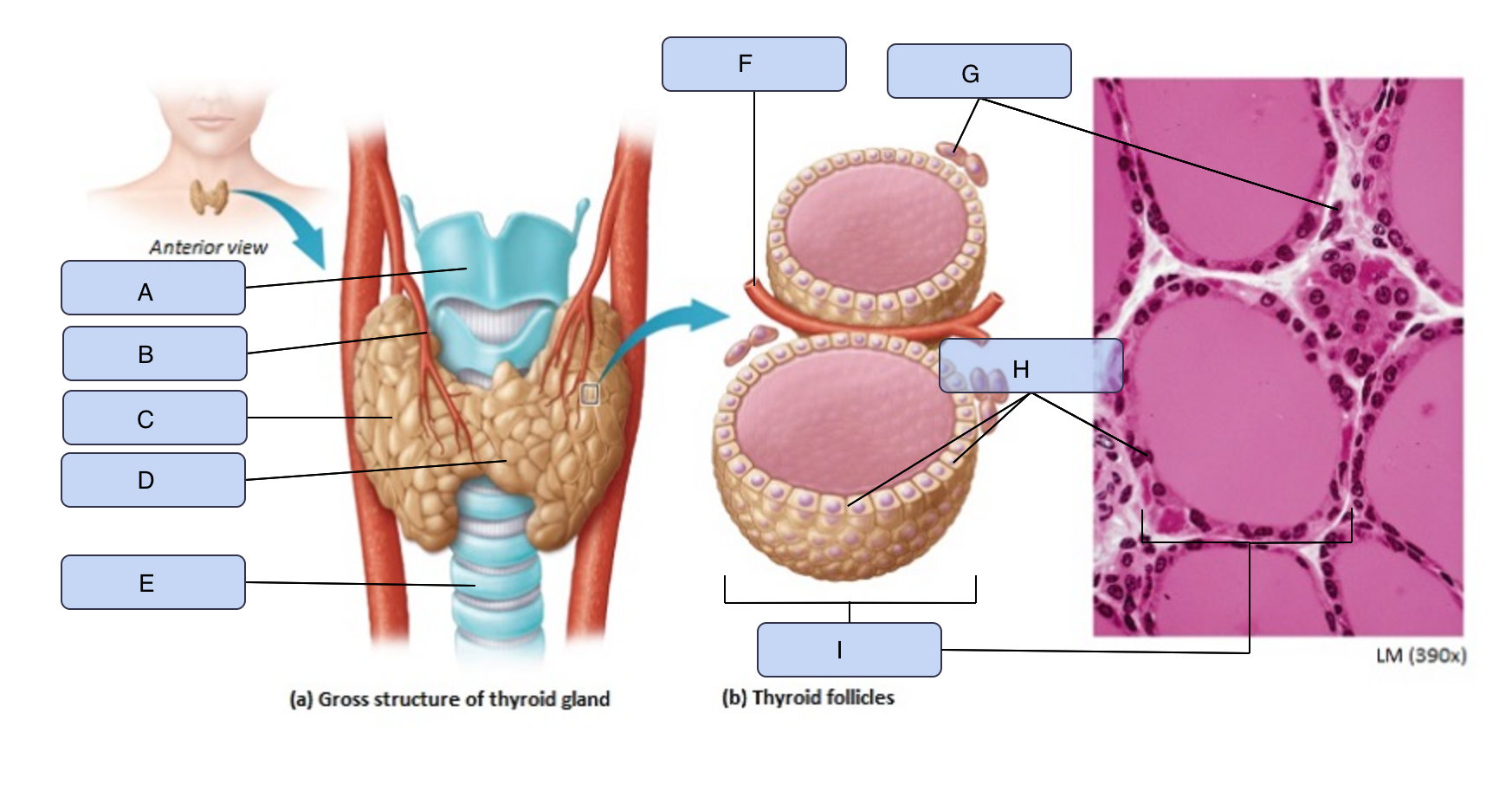
What is D
Isthmus
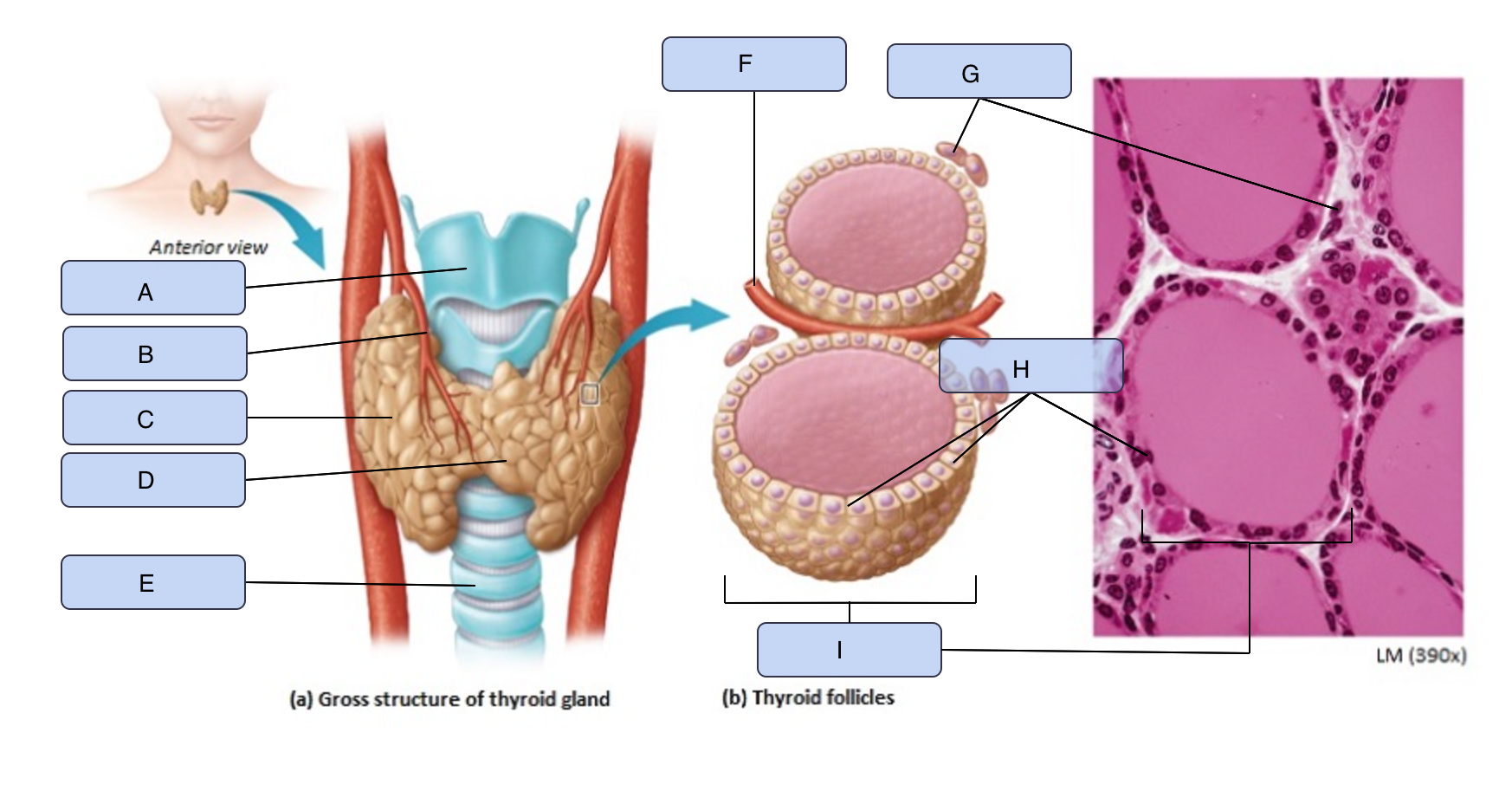
What is E
Trachea
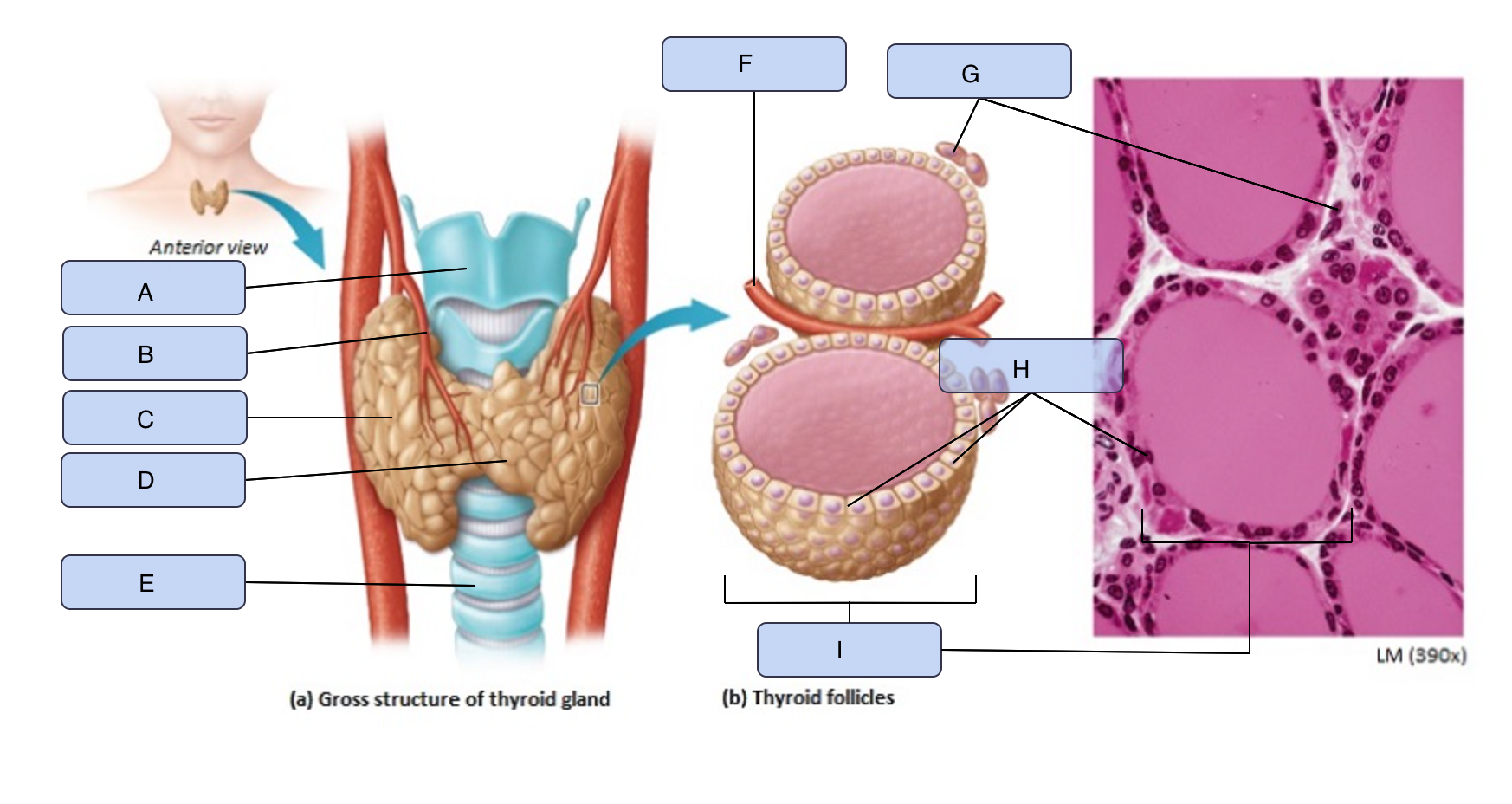
What is F
Blood vessel
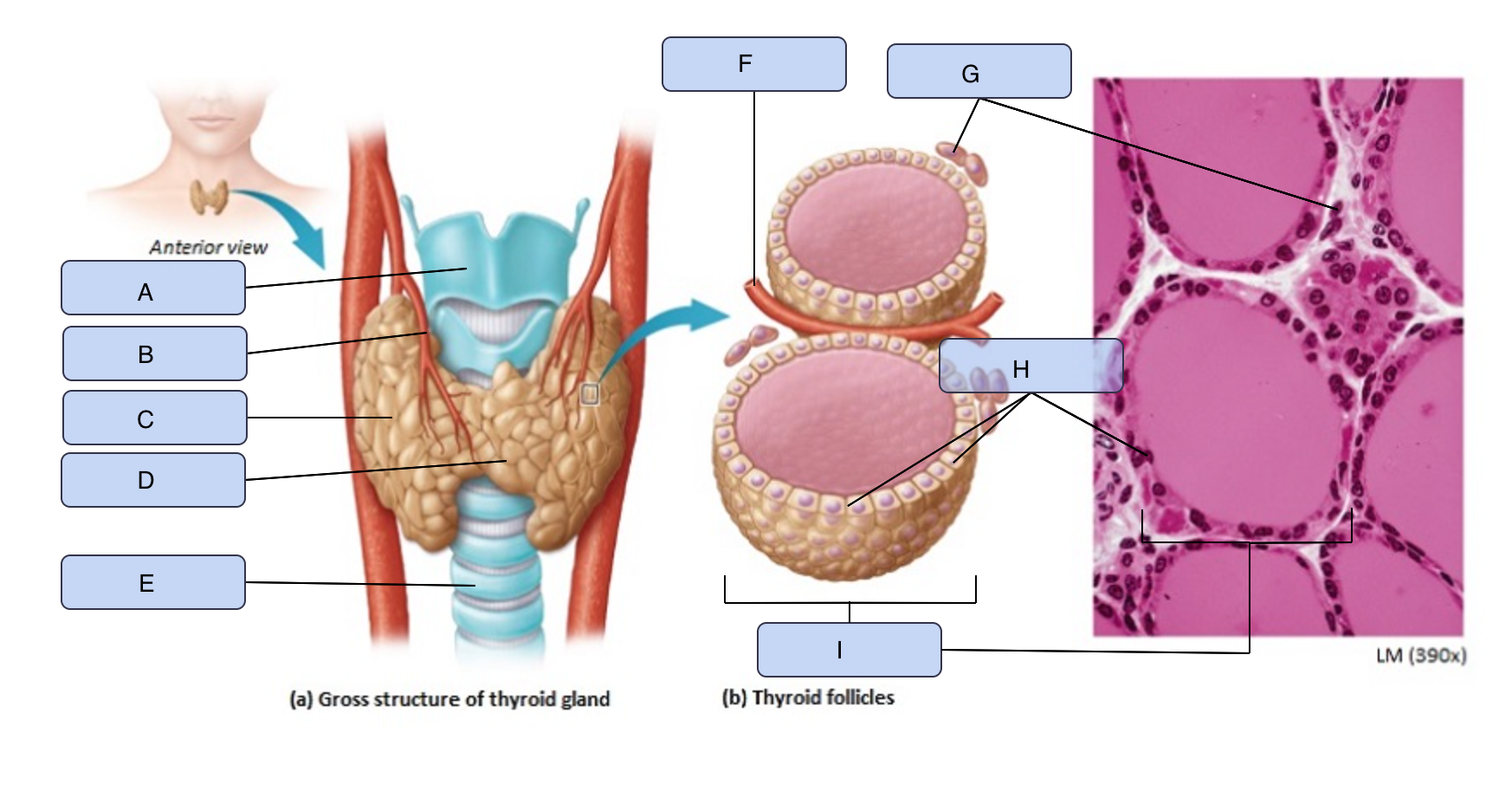
What is G
Parafollicular cells
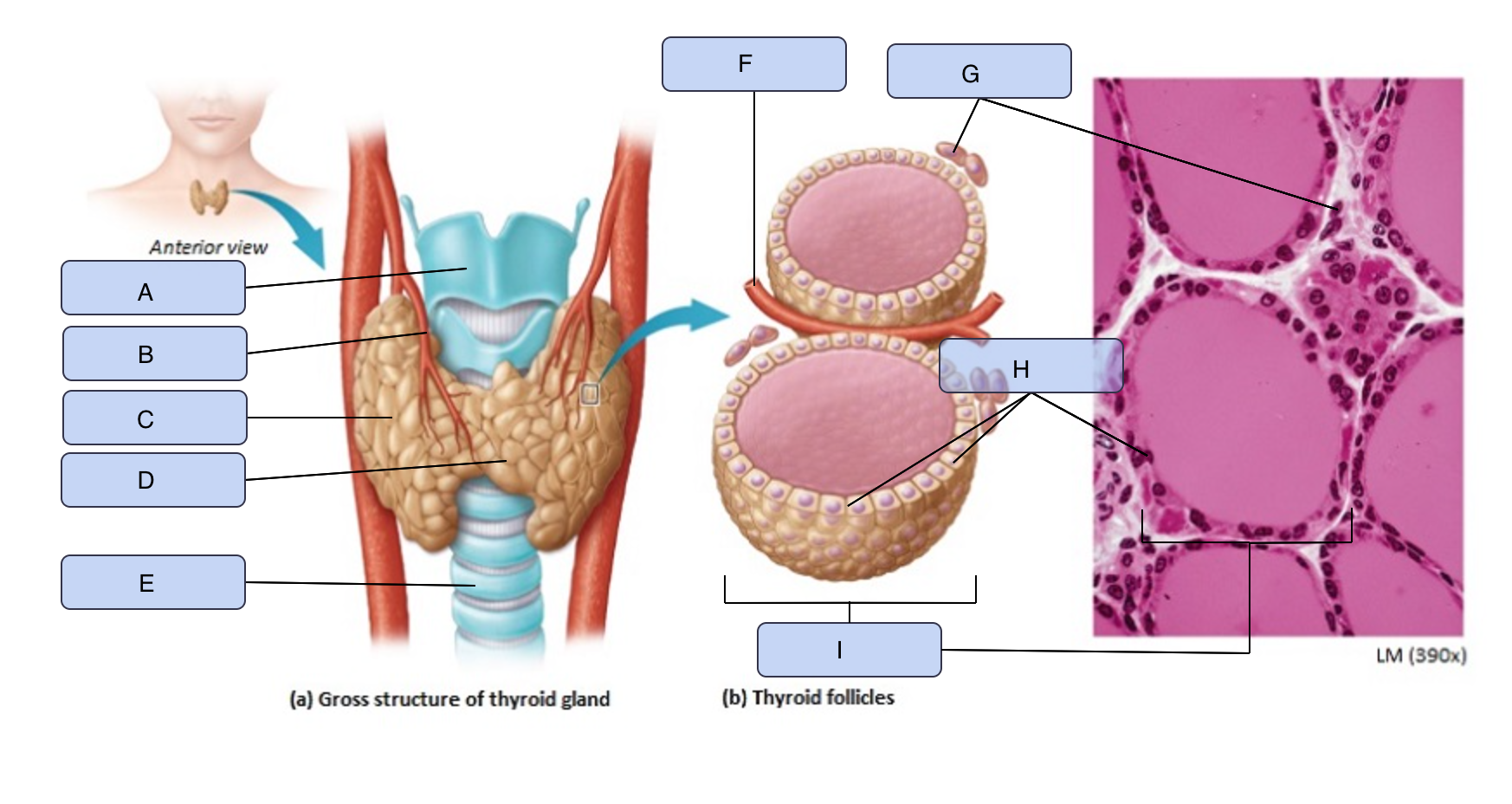
What is H
Follicle cells
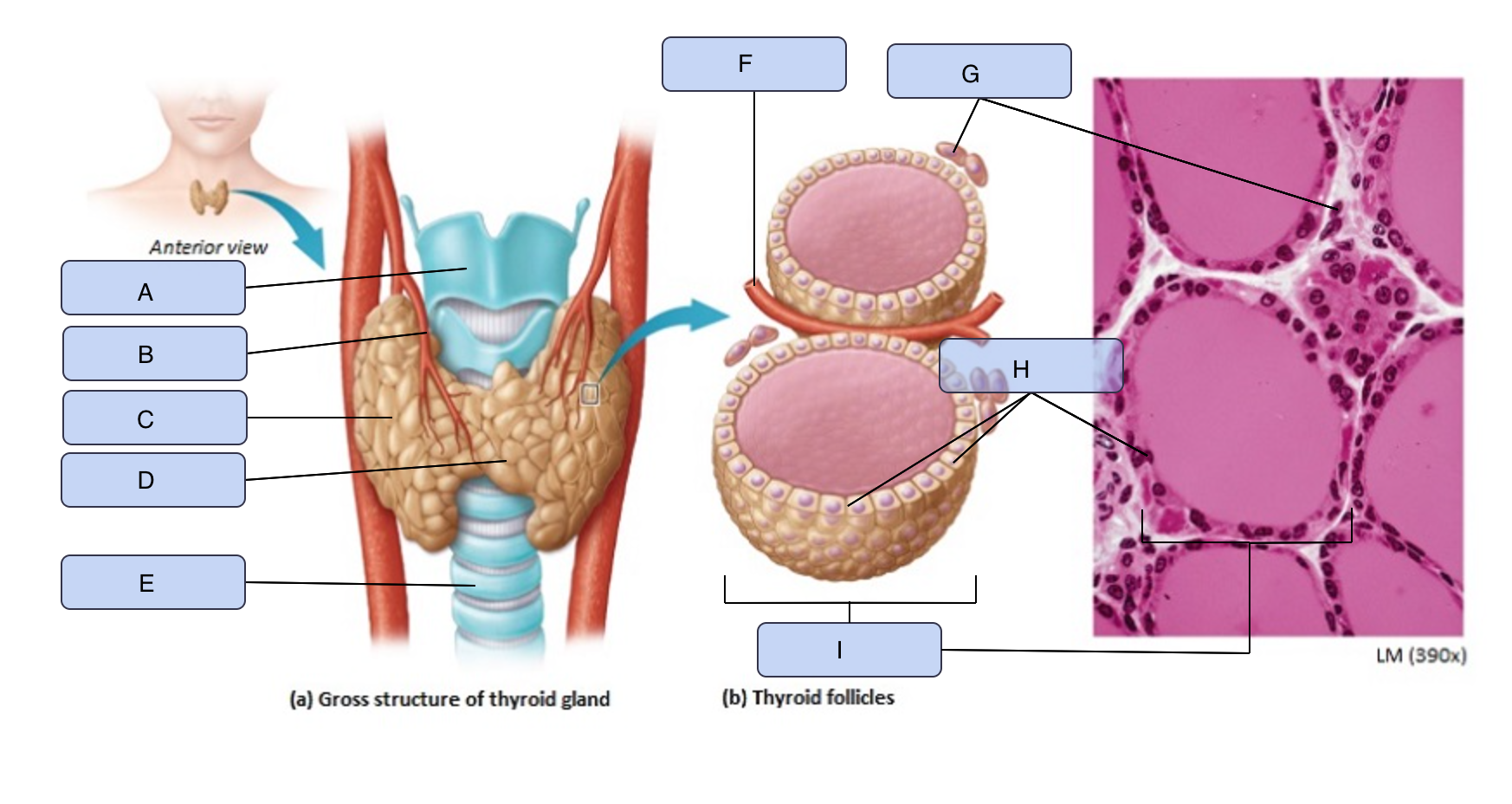
What is I
Thyroid follicle containing colloid
The hormone calcitonin is produced by the __________ cells of the thyroid.
Parafollicular
What element is necessary for the production of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)?
Iodine
Place the following hormones in the correct order of their control, from first tier to third tier:
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
Production of T3 and T4
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), production of T3 and T4
What stimulates the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Hypocalcemia
What is NOT an effect of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Increased release of calcium ions from bone
Increased absorption of calcium ions by the small intestine
Increased osteoblast activity
Increased reabsorption of calcium ions from fluid in the kidneys
Increased osteoblast activity
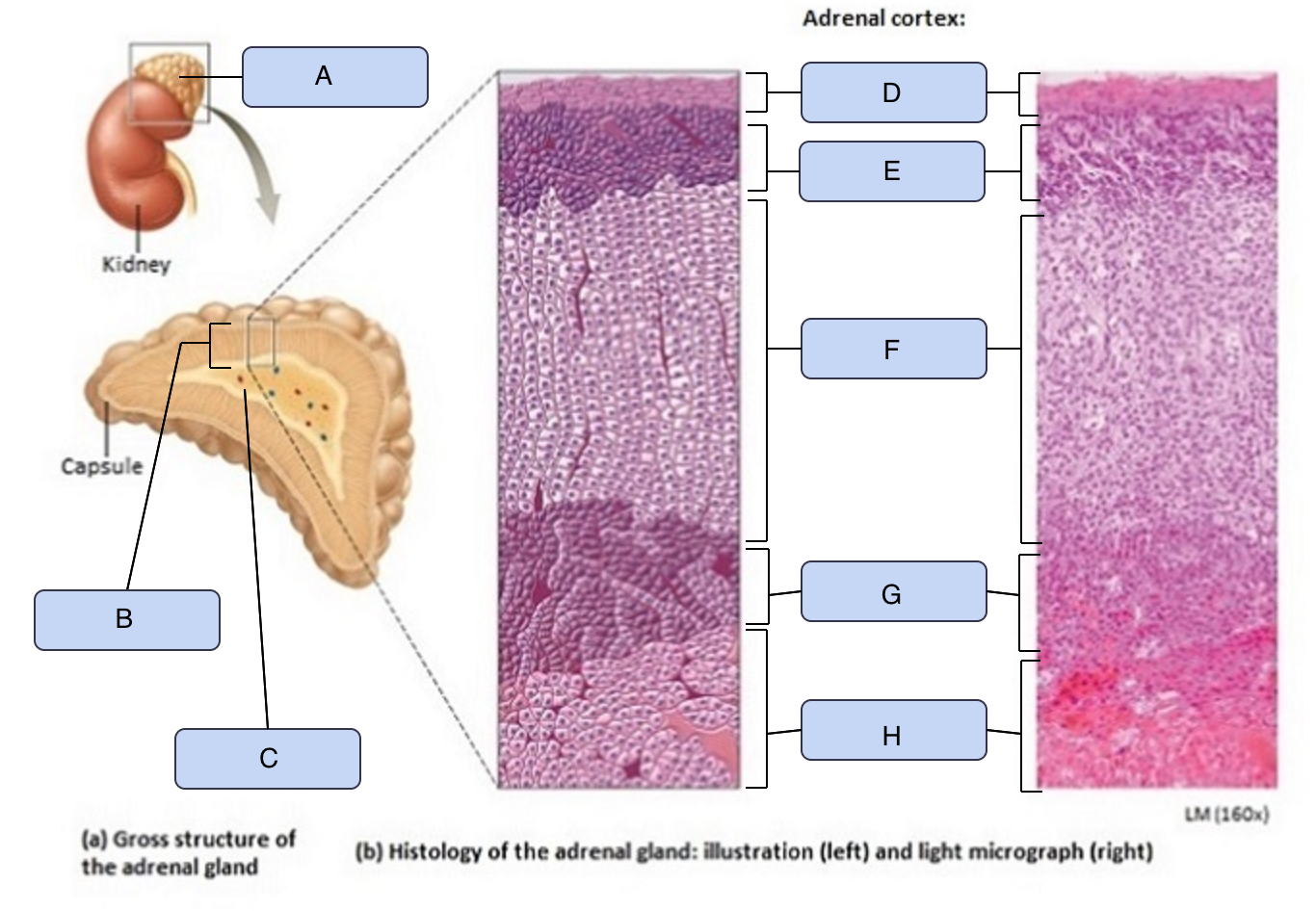
What is A
Adrenal gland
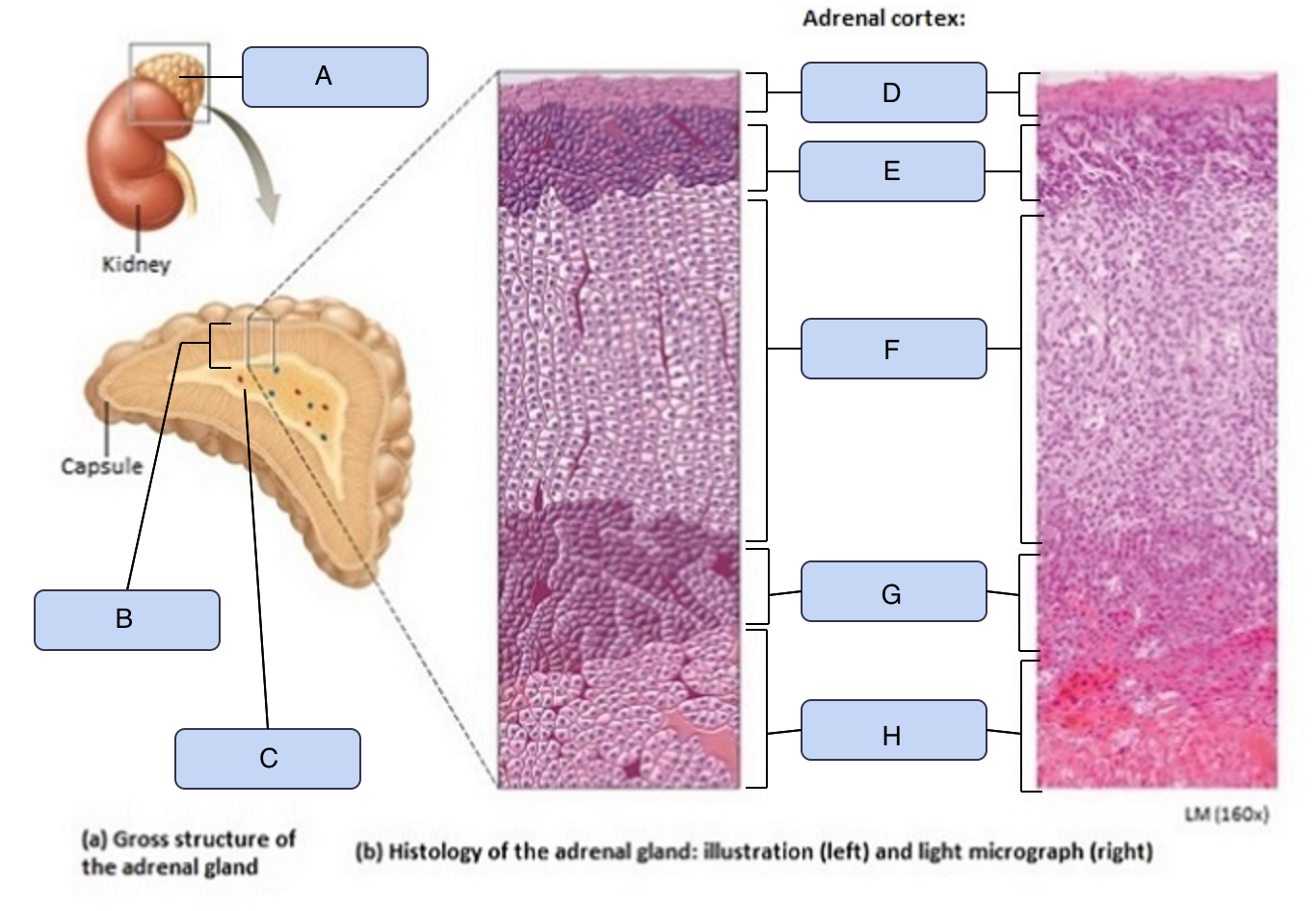
What is B
Adrenal cortex
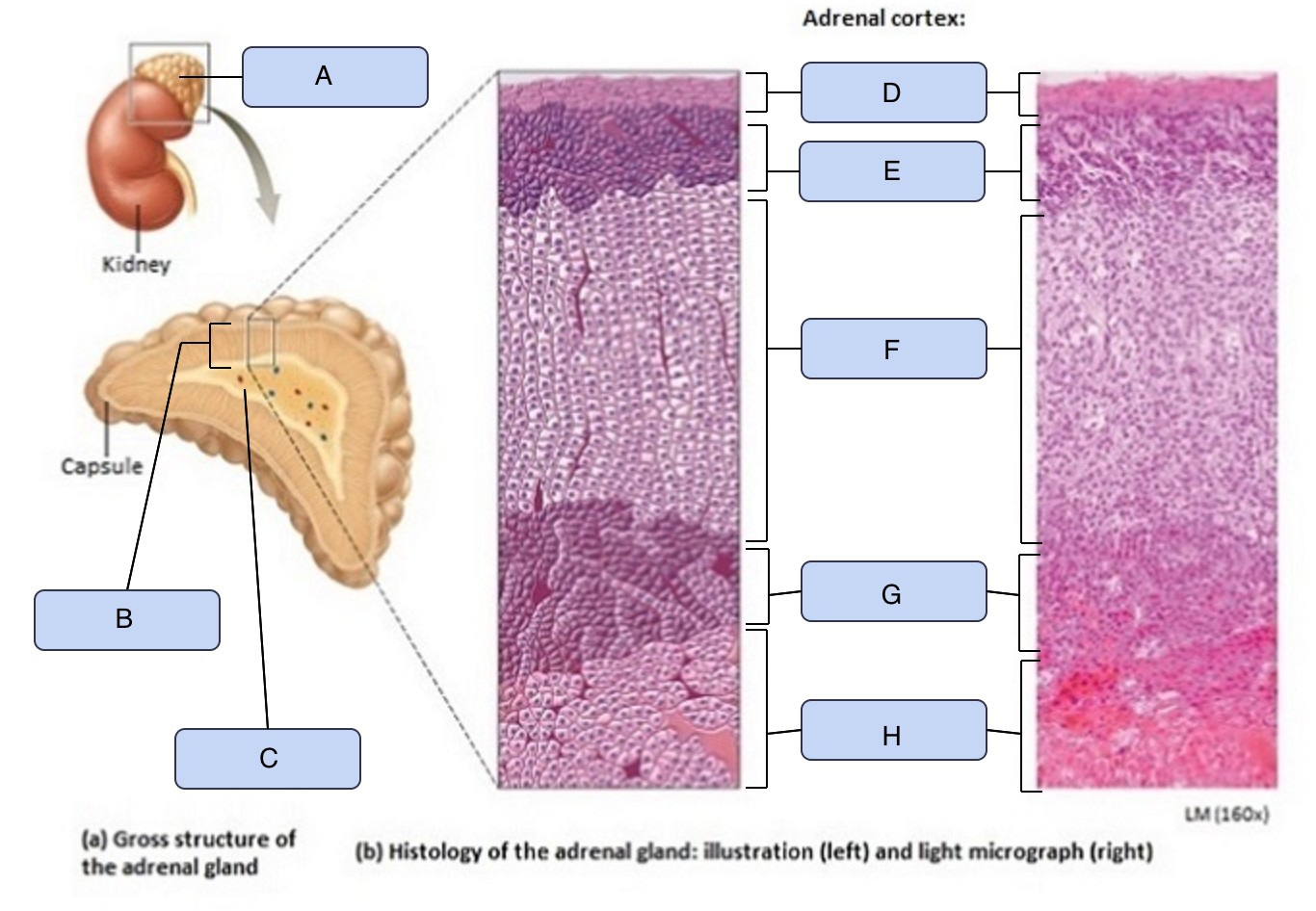
What is C
Adrenal medulla
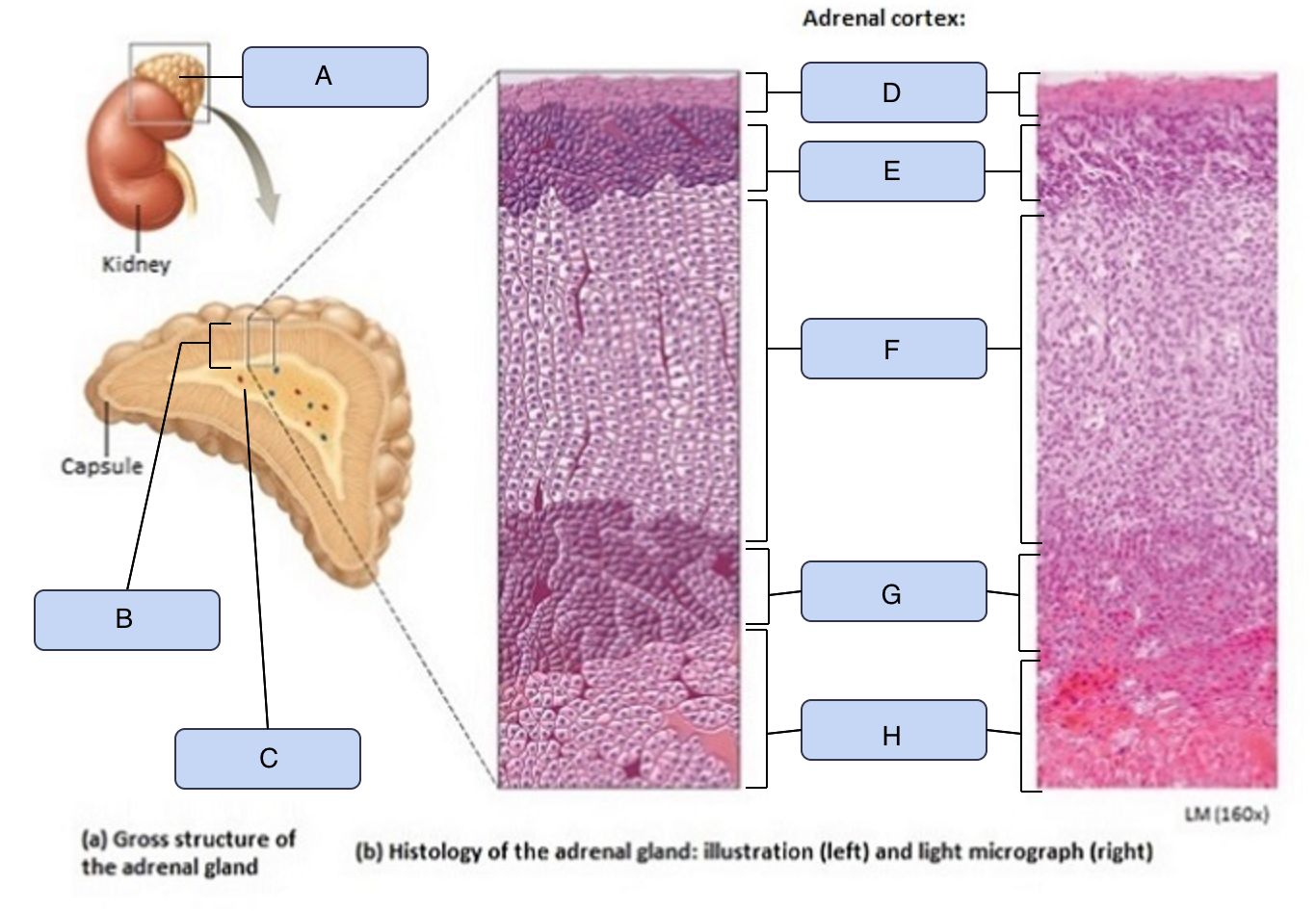
What is D
Capsule
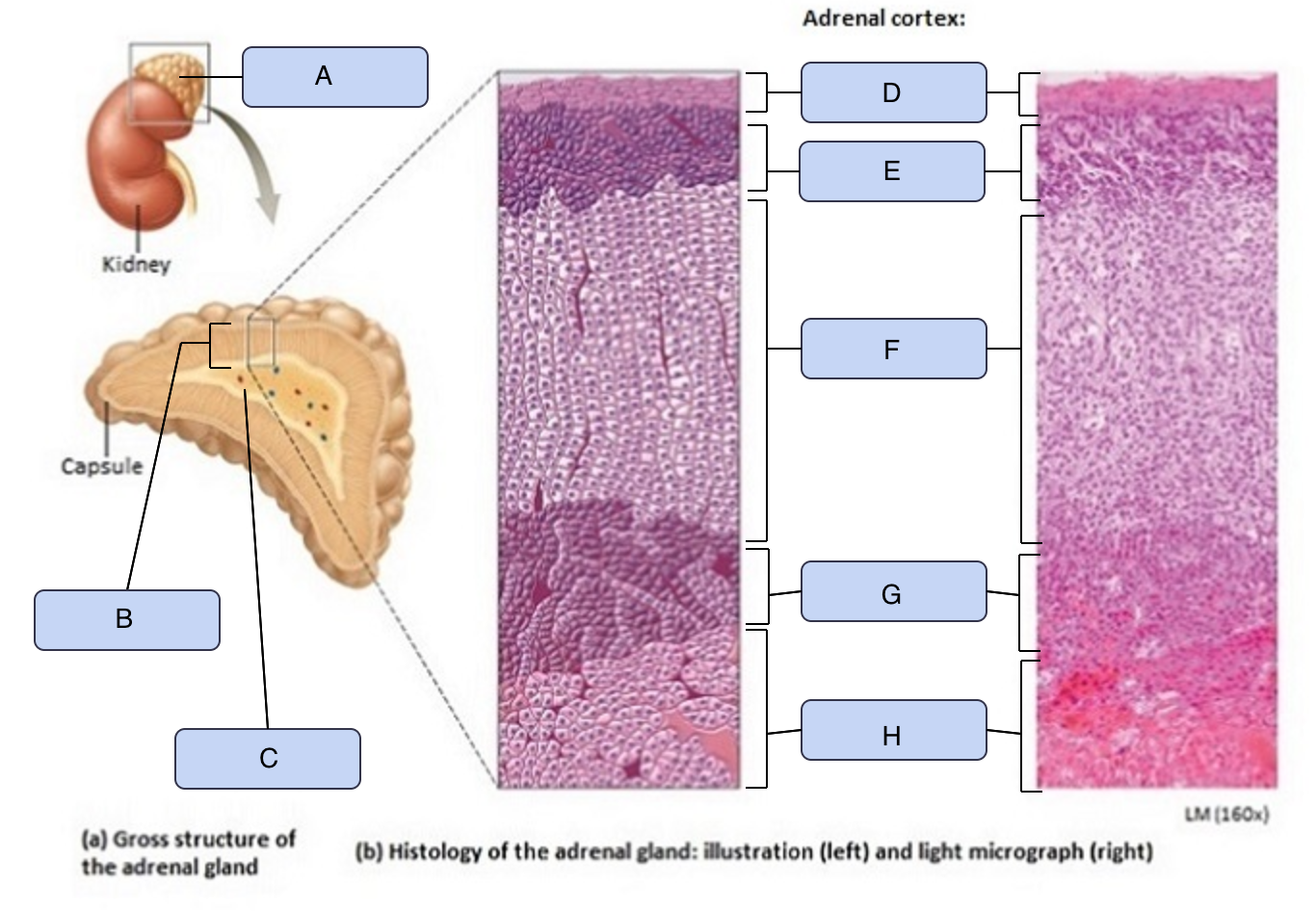
What is E
Zona glomerulosa
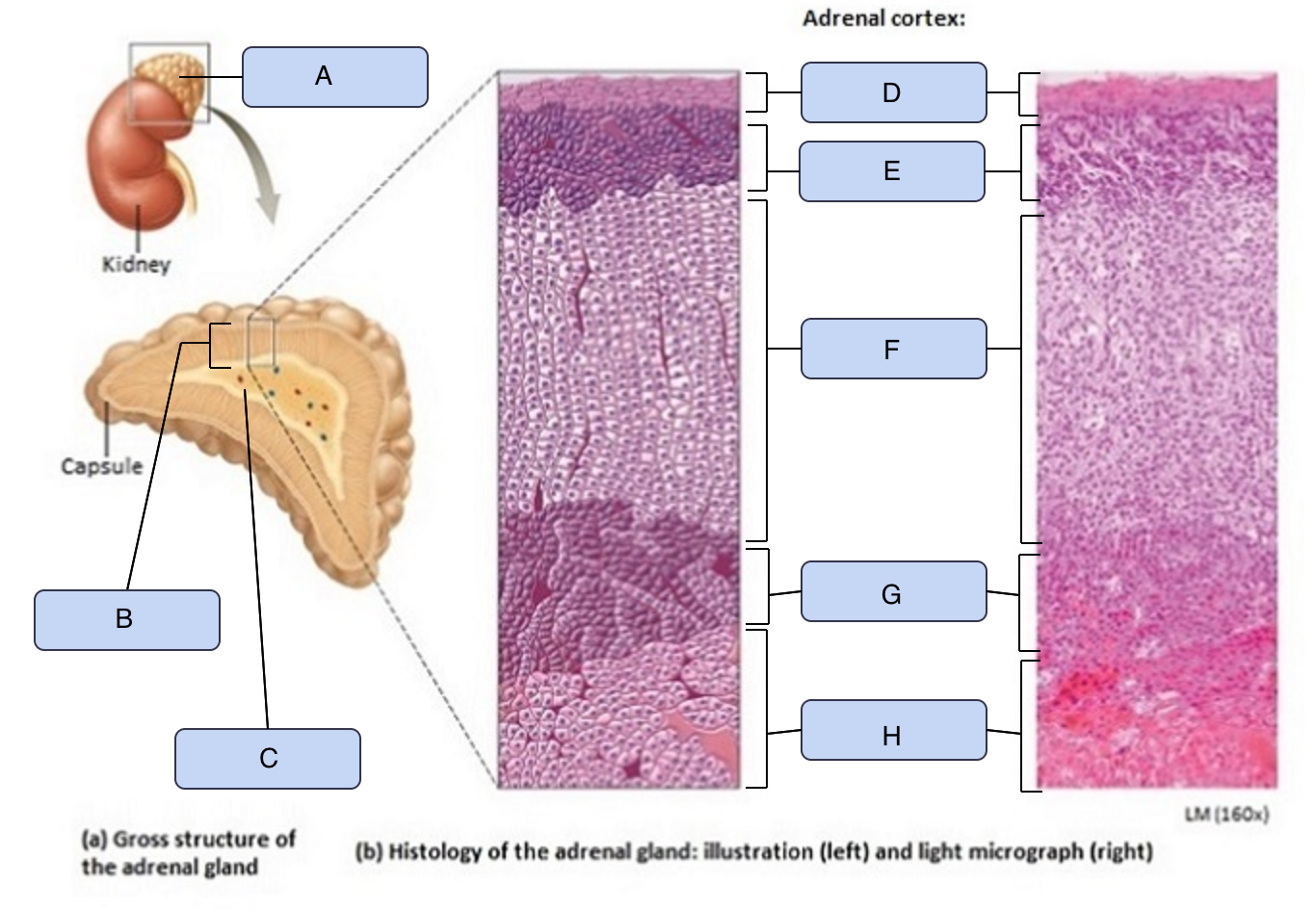
What is F
Zona fasciculata
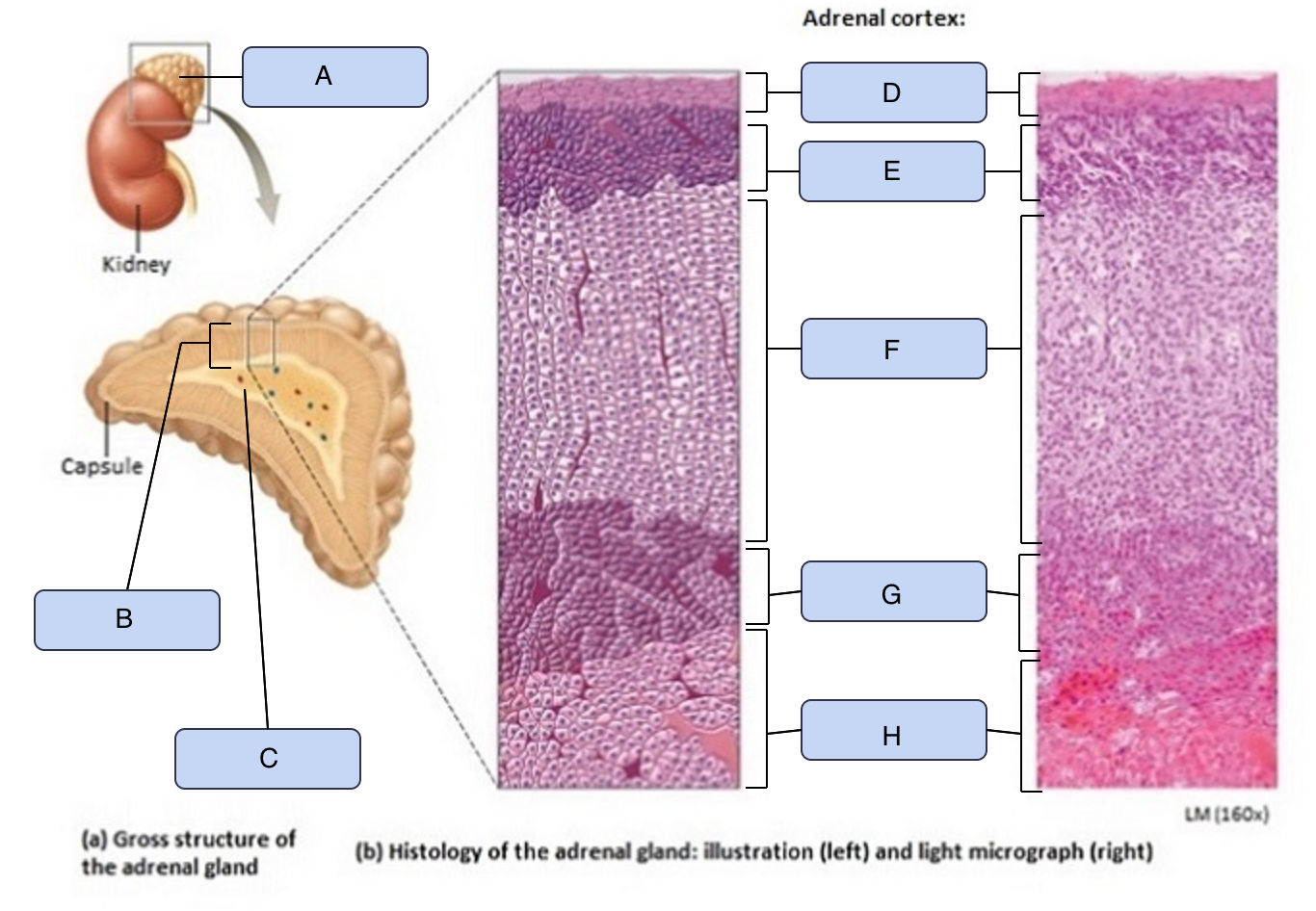
What is G
Zona reticularis
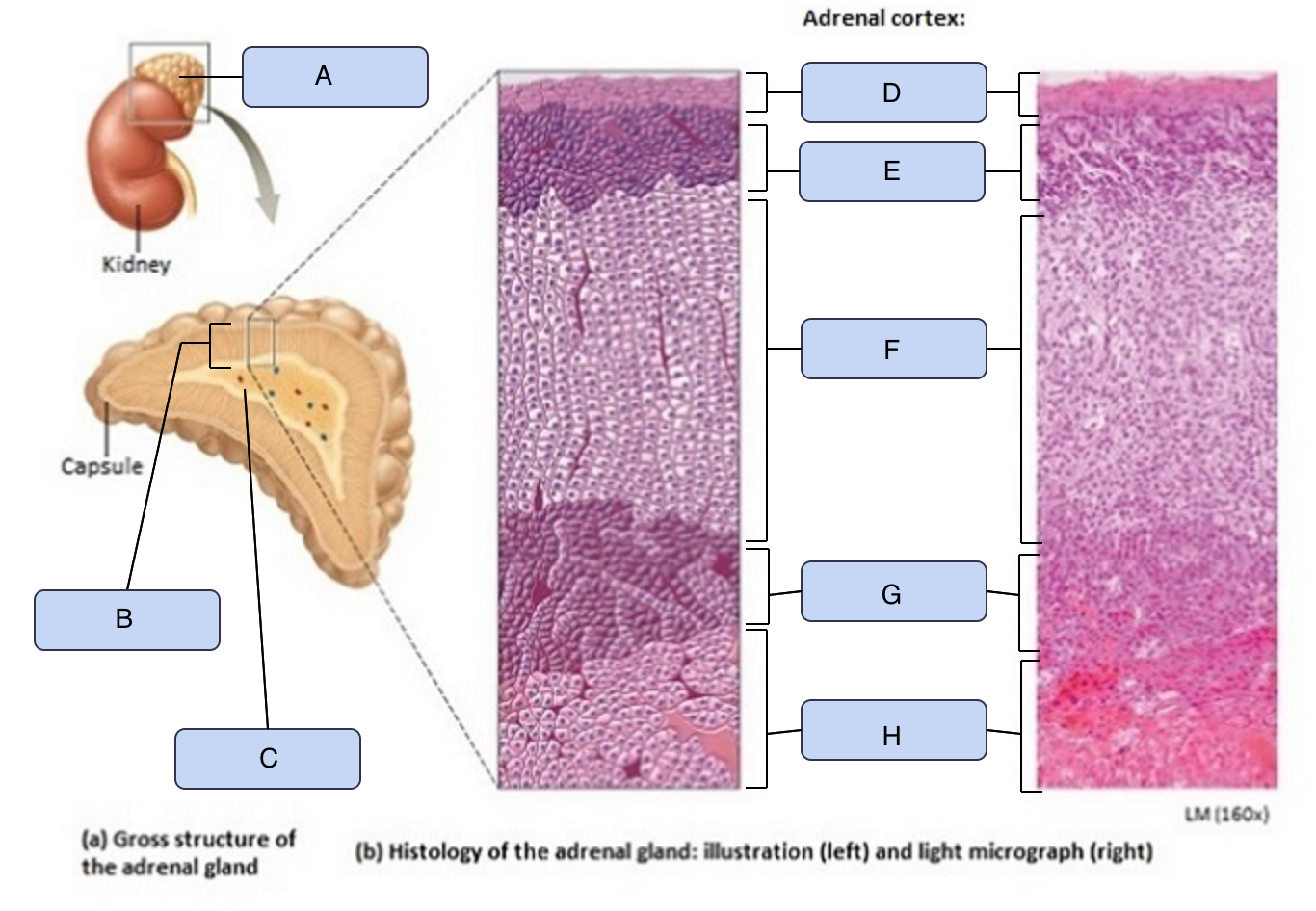
What is H
Adrenal medulla
Aldosterone regulates
extracellular sodium and potassium ion levels
Some potassium-sparing diuretics increase urination without the loss of potassium by working against receptors for:
Aldosterone
What first tier hormone stimulates cortisol production?
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Excess cortisol could result in:
High blood glucose levels
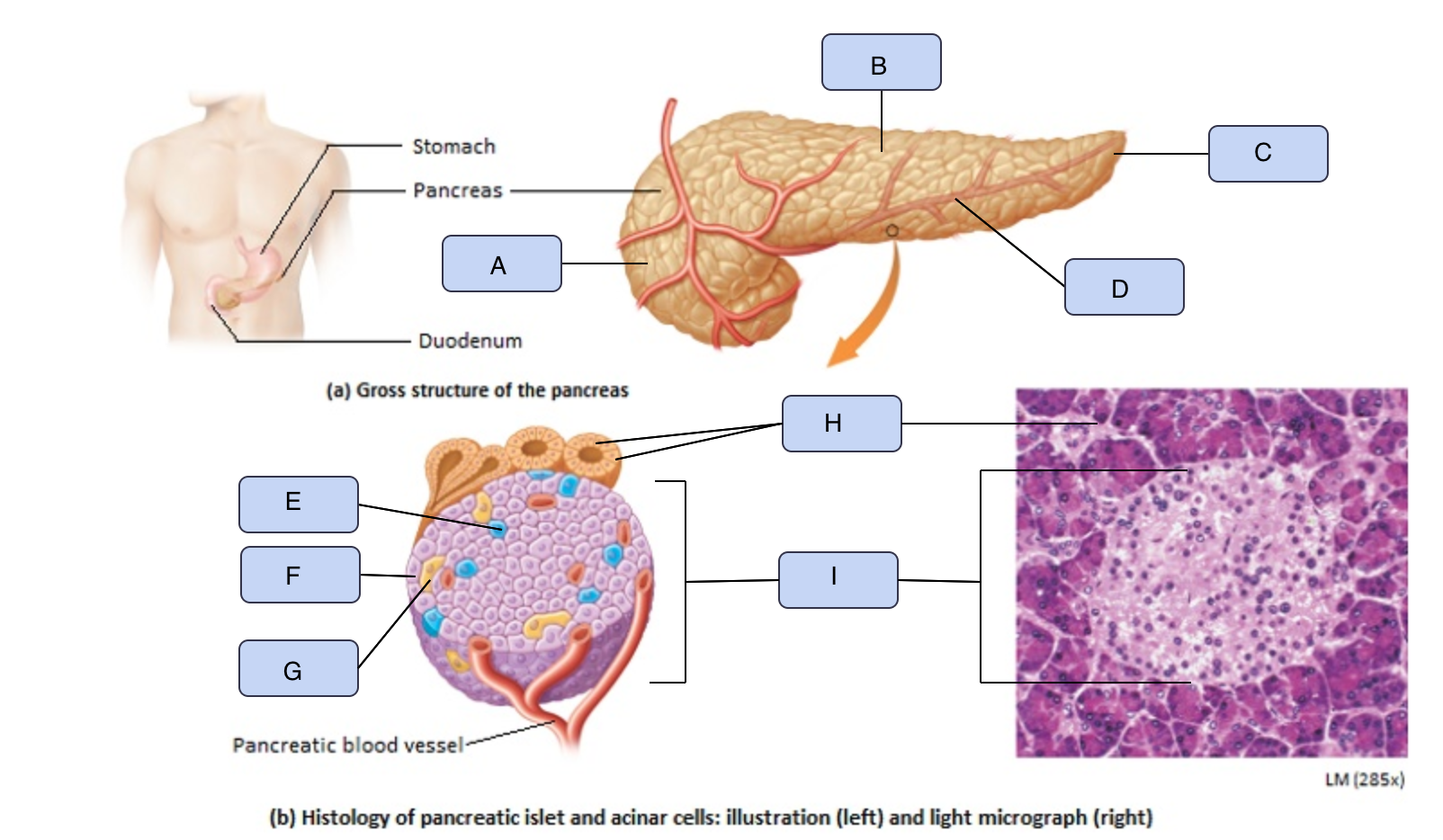
What is A
Head of pancreas
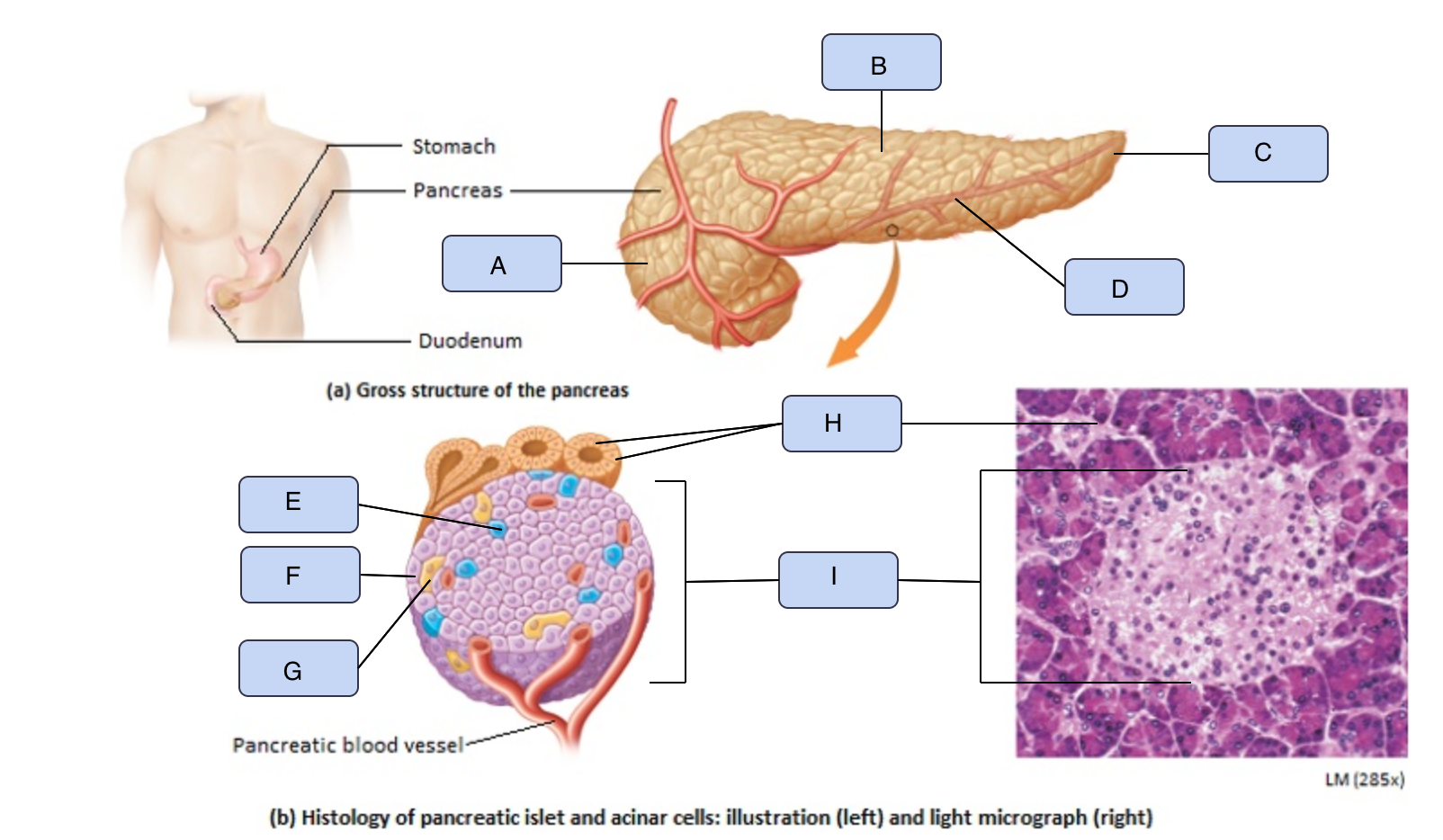
What is B
Body of pancreas
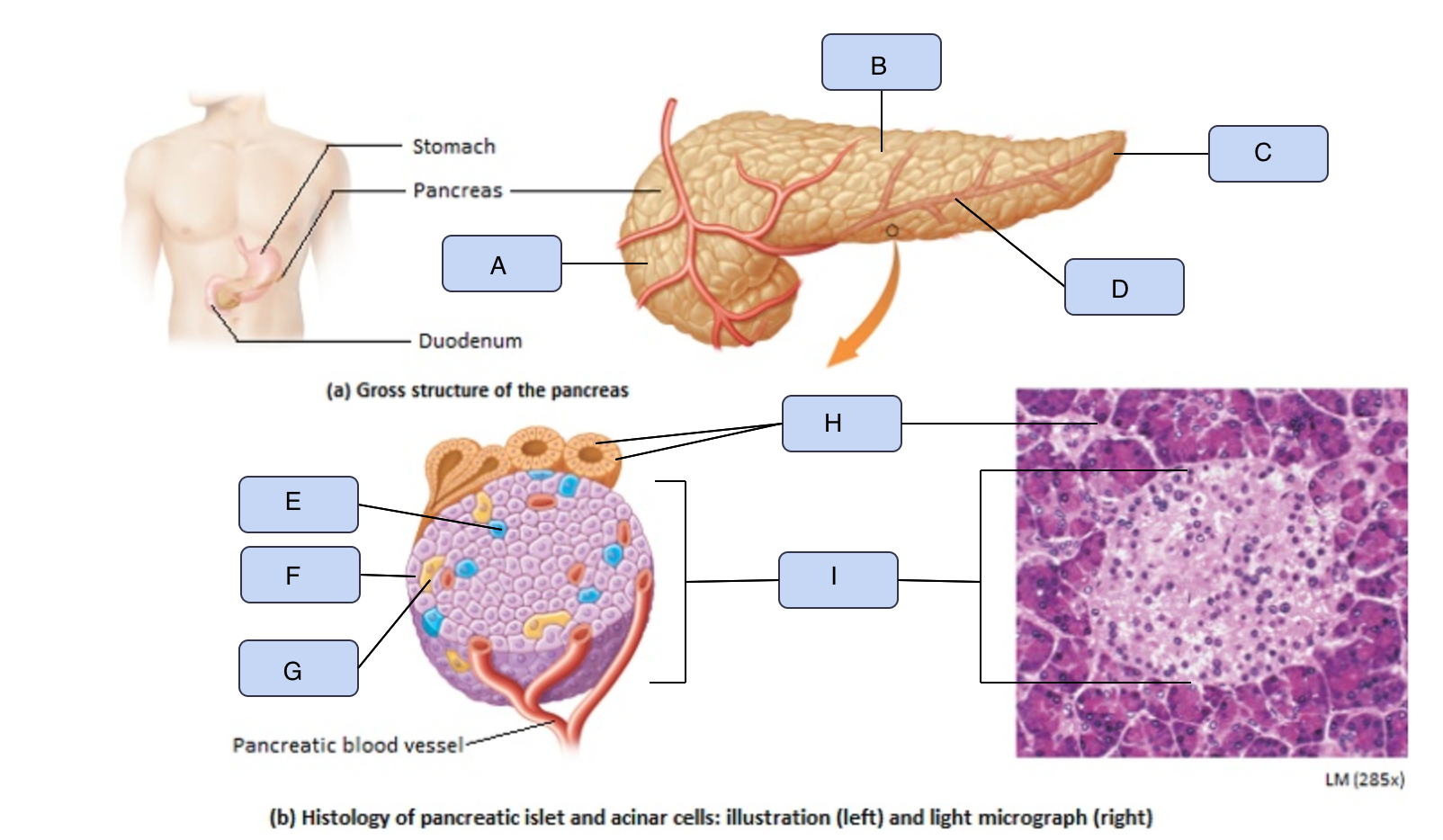
What is C
Tail of pancreas
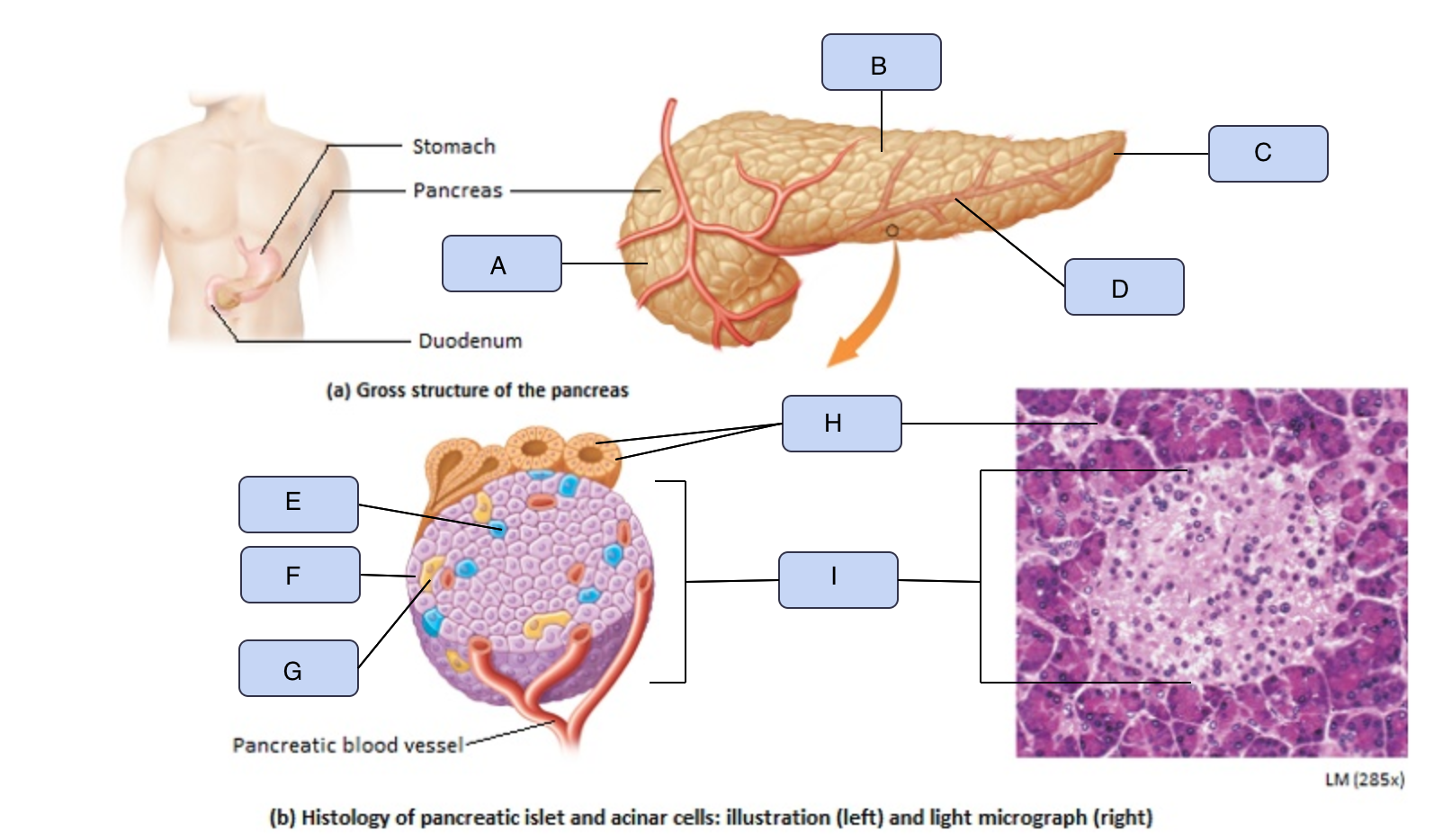
What is D
Pancreatic artery
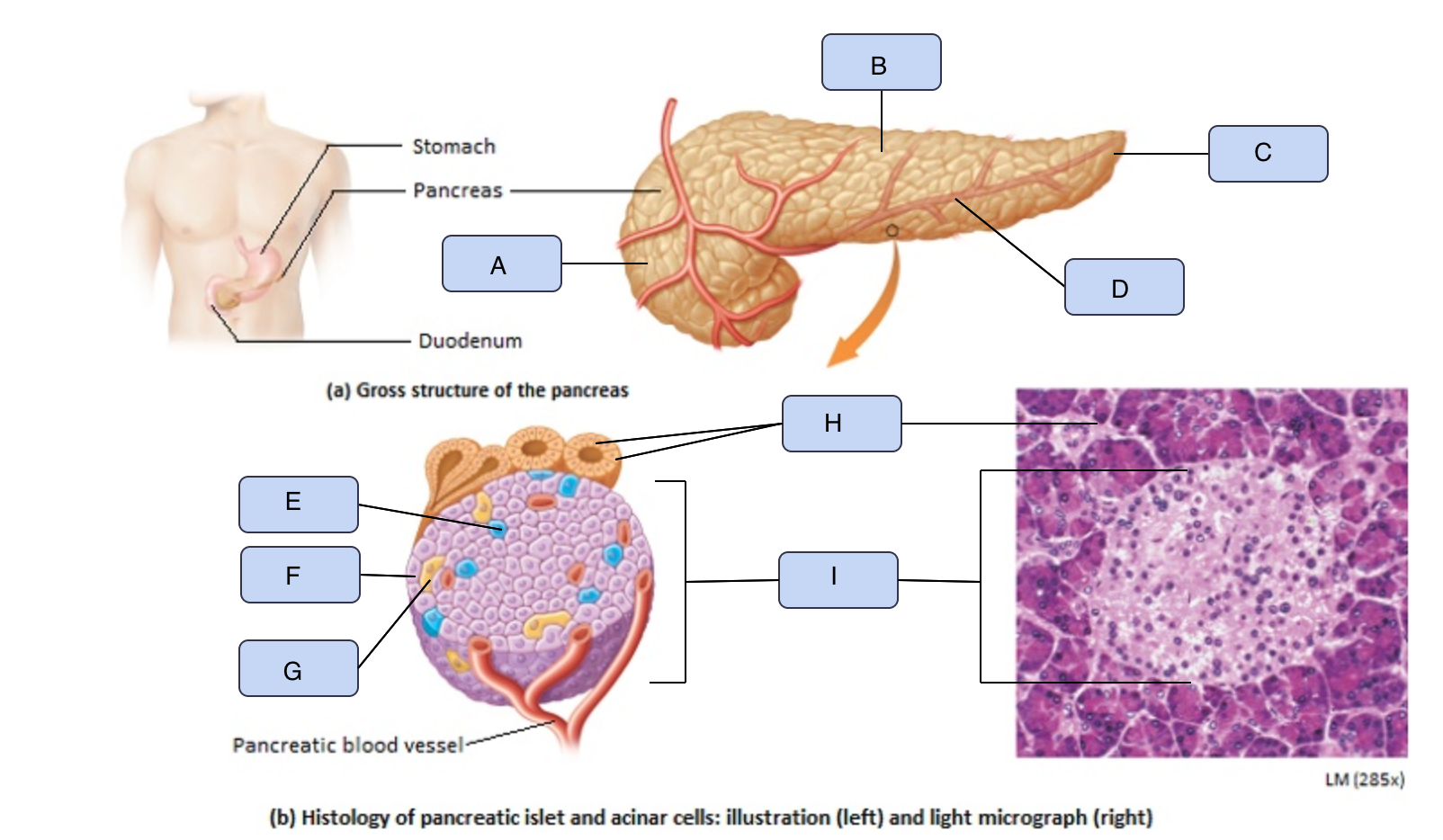
What is E
Alpha cell
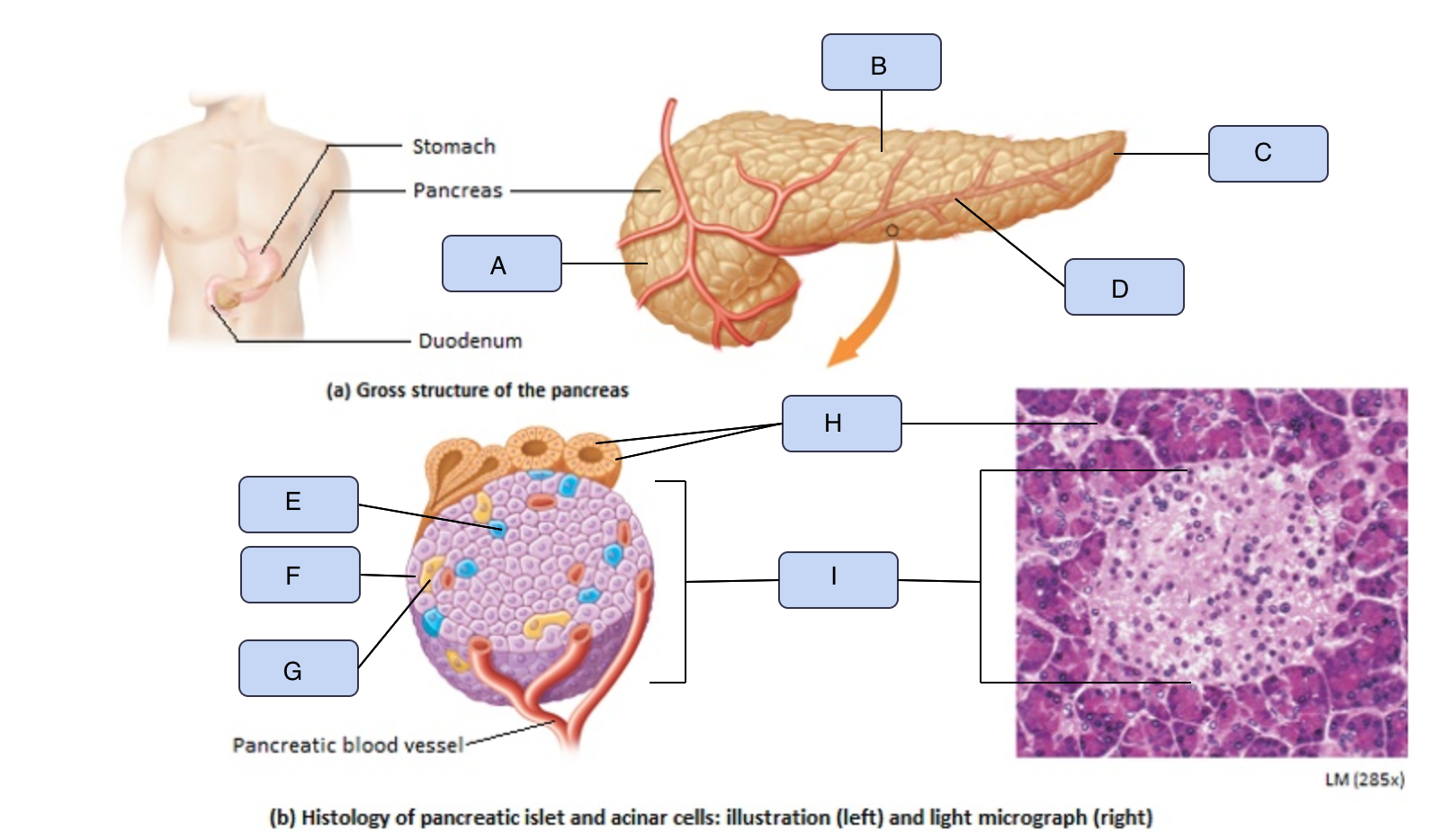
What is F
Beta cell
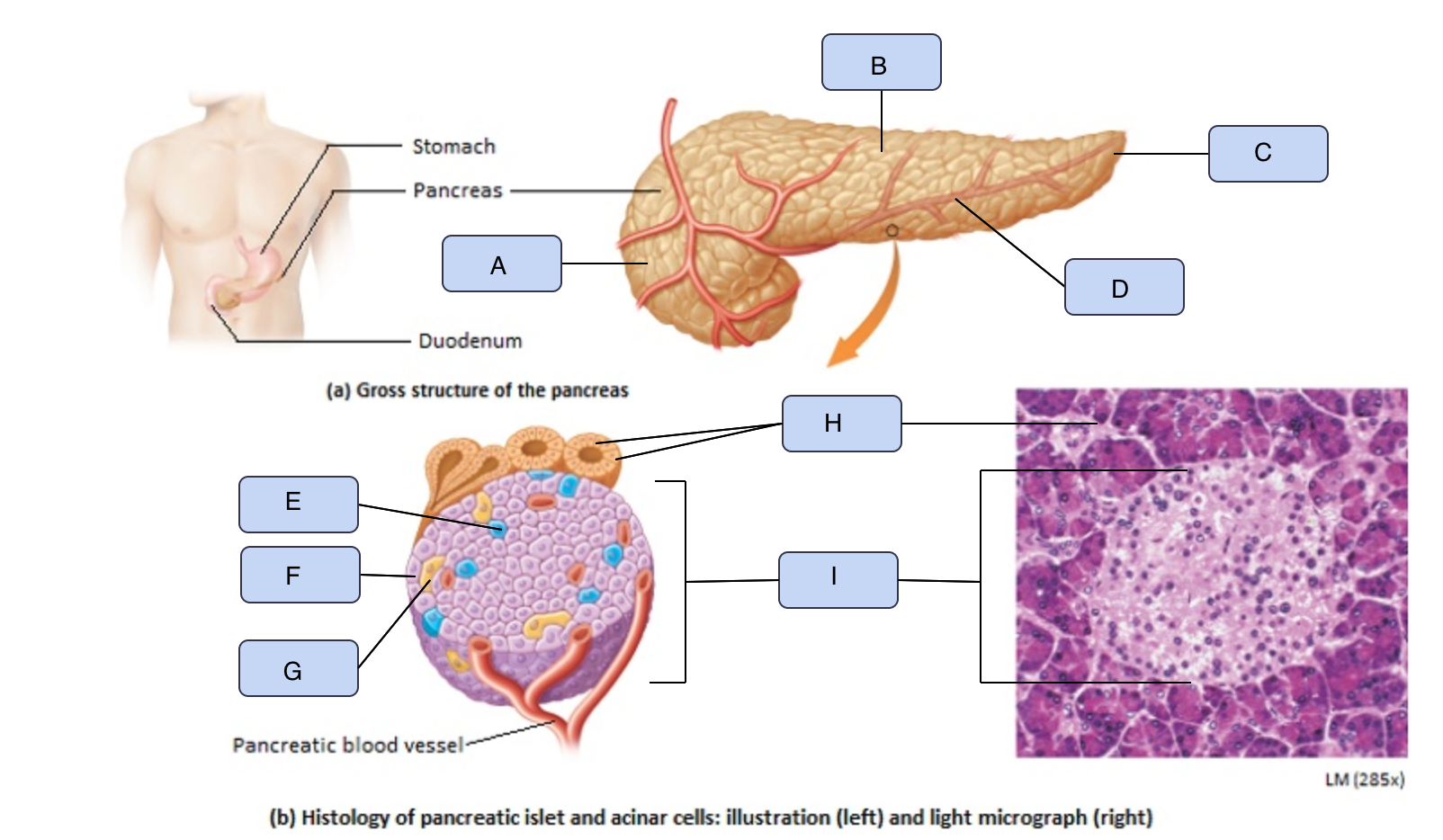
What is G
Delta cell
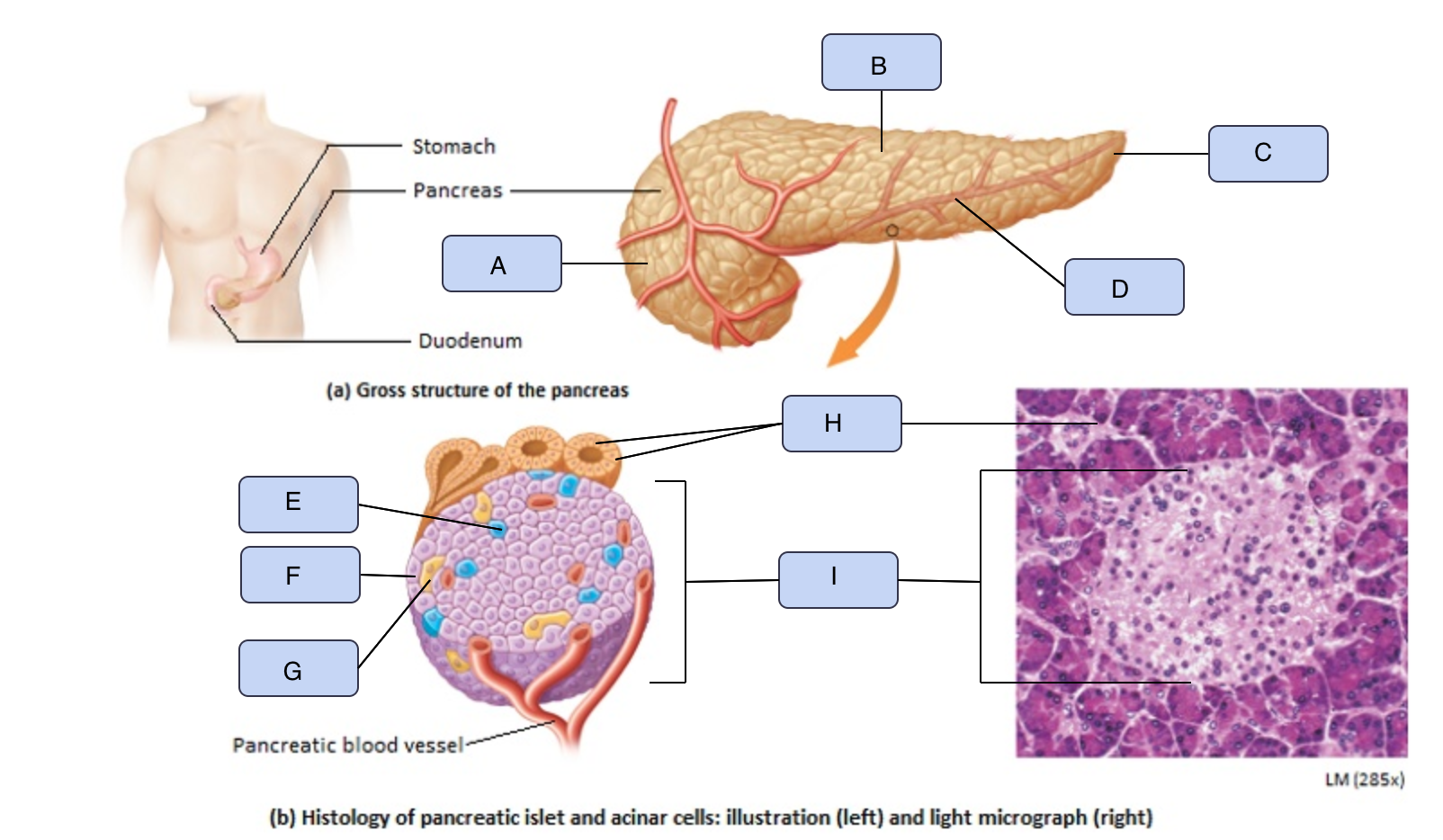
What is H
Acinar cells
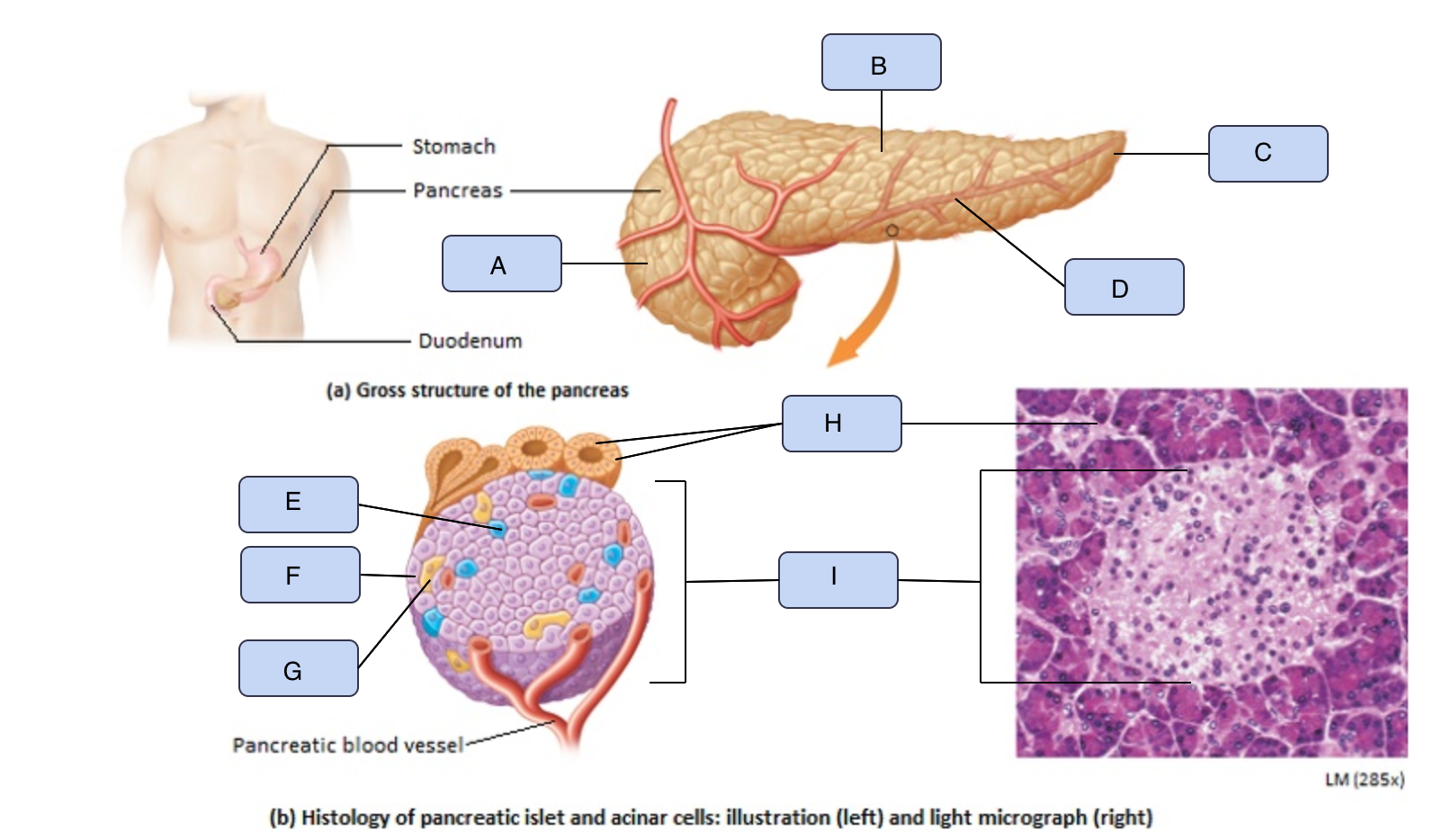
What is I
Pancreatic Islet
When blood glucose levels are high
The pancreas releases insulin
A liver cell responds to insulin by
Taking in glucose and converting it to glycogen
What cells in the body respond to glucagon by breaking down glycogen and releasing glucose?
Liver cells
Body cells that respond to insulin include
liver cells as well as most other cells in the body
When blood glucose levels are low
The pancreas releases glucagon, which eventually causes blood glucose levels to increase
The body's tendency to maintain relatively constant internal conditions is called
Homeostasis
Which of the following effects is NOT associated with the hormone insulin?
Glycogen synthesis
Stimulation of cells to uptake and utilize glucose
Gluconeogenesis in the liver
Synthesis of fat
Gluconeogenesis in the liver
Which pancreatic cells release insulin and glucagon?
Pancreatic islets
What is the main functions of glucagon?
Raise blood glucose levels
The pineal gland produces the hormone
Melatonin
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) promotes:
Vasodilation
High levels of testosterone inhibit the release of:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Which of the following hormones is a part of the rapid response (rather than the prolonged response) to stress?
Epinephrine
In response to stress, which of the following changes would happen?
Decreased insulin secretion
Decreased or difficulty breathing
Decreased sweating
Decreased cardiac output
Decreased insulin secretion
Which of the following are symptom(s) of pheochromocytoma?
Slow heart rate
Heart palpitations
Low blood glucose
Cool, dry skin
Heart palpitations
Choose which condition has all of the following symptoms: hypertension, hyperglycemia, and a “moon face.”
Pheochromocytoma
Cushing’s disease
Addison’s disease
Cushing’s disease
What hormone also aids the stress response by promoting water retention and acting as a vasoconstrictor?
Cortisol
ADH (vasopressin)
Angiotensin II
Aldosterone
ADH (vasopressin)
Reproductive system regulation often needs to be slower and more long-lasting. The main system that allows for such regulation is the:
Endocrine system
Which of the following is an example of a negative feedback loop?
During childbirth, pressure on the cervix stimulates the release of oxytocin. This causes contractions, and therefore puts more pressure on the cervix. This cycle continues until the baby is born. |
During lactation, as an infant suckles, it stimulates the release of prolactin in the mother. Prolactin causes more milk to be produced for the infant to suckle. This continues until the infant stops breast feeding. |
Baroreceptors in the arteries send a signal to the brain that the blood pressure is low. The brain sends a chemical signal to the heart to increase its rate of pumping. This continues until the baroreceptors sense a normal blood pressure. |
During blood clotting, chemicals are secreted by wounded tissues that recruit platelets to the area. As the platelets arrive, they secrete more of the same chemicals, recruiting more platelets to the wound. This continues until the wound is clotted. |
Baroreceptors in the arteries send a signal to the brain that the blood pressure is low. The brain sends a chemical signal to the heart to increase its rate of pumping. This continues until the baroreceptors sense a normal blood pressure
A tumor has appeared on the hypothalamus of a seven-year-old boy, causing increased secretion of GHRH. The increase of GHRH has in turn increased GH and IGF levels. If left untreated, the young boy
Will suffer from gigantism since his epiphyseal plates have not closed
Leptin
Produced by adipocytes; able to cross blood-brain barrier where it interacts with neurons in hypothalamus; induce satiety and prevent overfeeding
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Increase vessel diameter (vasodilation), enhance excretion of sodium ions from kidney (natriuresis), and these decrease blood volume and blood pressure
Eryhtropoietin (EPO)
Produced in response to decreased blood oxygen levels; increase oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
Renin
Converts plasma protein angiotensinogen to angiotensin I; vital component of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system which maintains blood pressure