Cell Biology Chapter 20 Flashcard Study Set
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
20-1 Both multicellular plants and animals have _____________________.
(a) cells capable of locomotion.
(b) cells with cell walls.
(c) a cytoskeleton composed of actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments.
(d) tissues composed of multiple different cell types.
(d) tissues composed of multiple different cell types.
plant cells don't have intermediate filaments
20-2 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; use each word or phrase only once.
Plants are sedentary and thus their cells have different needs from those of cells found in motile animals. For example, in plant cells, __________________ generates the turgor pressure that drives cell growth. Plants have cell walls, but cell growth is possible in the developing tissue because the __________________ cell walls are expandable. The __________________ cell walls are deposited once growth has stopped, and can be specially adapted to their function. Fibers made from __________________ (the most abundant organic macromolecule on Earth) are found in plant cell walls, and provide tensile strength. In woody tissues, the __________________ in the cell walls makes the tissue more rigid and waterproof. The deposition of the cell wall is directed by the __________________ cytoskeleton.
actin lignin pectin
cellulose membranous primary
collagen microtubule secondary
epidermis nuclear tertiary
lamin osmosis
20-2 Plants are sedentary and thus their cells have different needs from those of cells found in motile animals. For example, in plant cells, osmosis generates the turgor pressure that drives cell growth. Plants have cell walls, but cell growth is possible in the developing tissue because the primary cell walls are expandable. The secondary cell walls are deposited once growth has stopped, and can be specially adapted to their function. Fibers made from cellulose (the most abundant organic macromolecule on Earth) are found in plant cell walls, and provide tensile strength. In woody tissues, the lignin in the cell walls makes the tissue more rigid and waterproof. The deposition of the cell wall is directed by the microtubule cytoskeleton.
20-3 Which of the following statements about plant cell walls is true?
(a) The microtubule cytoskeleton directs the orientation in which cellulose is deposited in the cell wall.
(b) The molecular components of the cell wall are the same in all plant tissues.
(c) Because plant cell walls are rigid, they are not deposited until the cell has stopped growing.
(d) The cellulose found in cell walls is produced as a precursor molecule in the cell and delivered to the extracellular space by exocytosis.
(a) The microtubule cytoskeleton directs the orientation in which cellulose is deposited in the cell wall.
20-5 Which of the following molecules is not found in plants?
(a) cellulose
(b) lignin
(c) collagen
(d) pectin
(c) collagen
20-6 Which of the following statements about cellulose is false?
(a) Cellulose synthase enzyme complexes are integral membrane proteins.
(b) An array of microtubules guides the cellulose synthase complex as it moves in the membrane.
(c) The sugar monomers necessary for the synthesis of a cellulose polymer are transported across the plasma membrane.
(d) Microtubules are directly attached to the outside surface of the plasma membrane to form tracks that help orient the cellulose polymers.
(d) Microtubules are directly attached to the outside surface of the plasma membrane to form tracks that help orient the cellulose polymers.
20-8 Which of the following is not an example of a connective tissue?
(a) bone
(b) the layer of photoreceptors in the eye
(c) the jellylike interior of an eye
(d) cartilage
(b) the layer of photoreceptors in the eye
20-9 Which of the following statements about animal connective tissues is true?
(a) Enzymes embedded in the plasma membrane synthesize the collagen in the extracellular matrix extracellularly.
(b) In connective tissue, the intermediate filaments within the cells are important for carrying the mechanical load.
(c) Cells can attach to a collagen matrix by using fibronectin, an integral membrane protein.
(d) Proteoglycans can resist compression in the extracellular matrix.
(d) Proteoglycans can resist compression in the extracellular matrix.
20-10 Do you agree or disagree with the following statement? Explain your answer.
Like many other extracellular proteins, newly synthesized collagen molecules undergo post-translational processing inside the cell to convert them into their mature form; they are then secreted and self-assemble into fibrils in the extracellular space.
false
20-11 Which of the following statements about collagen is false?
(a) Collagen synthase organizes the mature collagen molecules into ordered collagen fibrils.
(b) Collagen is synthesized as procollagen and secreted to the outside of the cell in a secretory vesicle.
(c) The terminal procollagen domains are cleaved by a protease in the extracellular space.
(d) Cells can break down a collagen matrix using matrix proteases.
(a) Collagen synthase organizes the mature collagen molecules into ordered collagen fibrils.
20-12 Fibroblasts organize the collagen of the extracellular matrix by ______________.
(a) cutting and rejoining the fibrils.
(b) processing procollagen into collagen.
(c) twisting fibrils together to make ropelike fibers.
(d) pulling the collagen into sheets or cables after it has been secreted.
(d) pulling the collagen into sheets or cables after it has been secreted.
20-13 Match the four lettered lines in Figure Q20-13 with the appropriate numbered label.
Figure Q20-13
1. integrin
2. actin
3. collagen
4. fibronectin
20-13 A—3; B—4; C—1; D—2
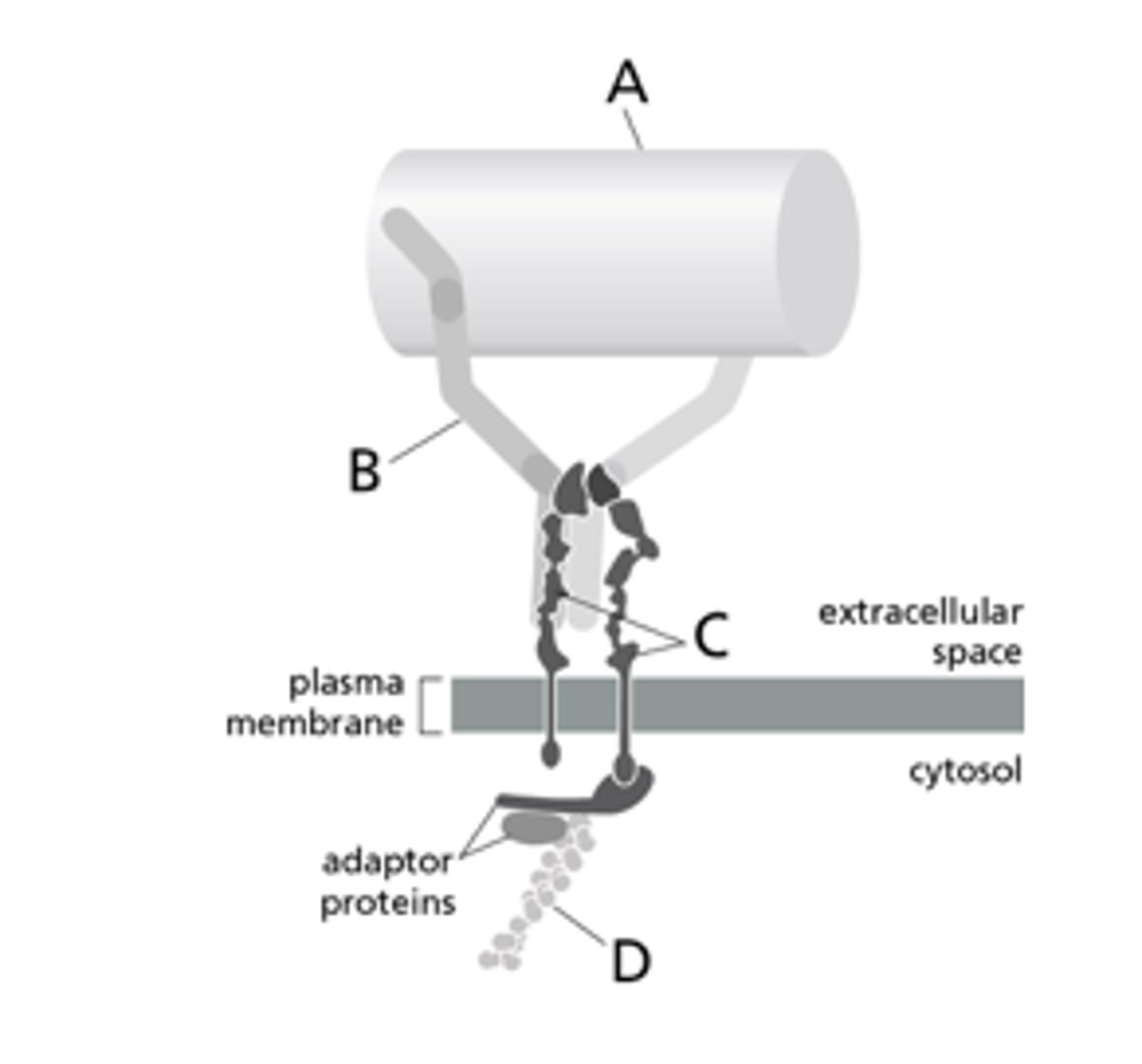
20-14 A cell can crawl through a tissue because of the transmembrane ______________ proteins that can bind to fibronectin outside of the cell.
(a) integrin
(b) collagen
(c) gap junction
(d) claudin
(a) integrin
20-15 Which of the following statements about integrins is false?
(a) Integrins use adaptor proteins to interact with the microtubule cytoskeleton.
(b) Integrins can switch to an activated state by binding to an extracellular matrix molecule.
(c) Integrins can switch to an activated state by binding to an intracellular protein.
(d) An activated integrin molecule takes on an extended conformation.
(a) Integrins use adaptor proteins to interact with the microtubule cytoskeleton.
20-16 Proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix of animal tissues ________________.
(a) chiefly provide tensile strength.
(b) allow cartilage to resist compression.
(c) are linked to microtubules through the plasma membrane.
(d) are polysaccharides composed of glucose subunits.
(b) allow cartilage to resist compression.
20-17 Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Proteoglycans can act as filters to regulate which molecules pass through the extracellular medium.
(b) The negative charge associated with proteoglycans attracts cations, which cause water to be sucked into the extracellular matrix.
(c) Proteoglycans are a major component of compact connective tissues but are relatively unimportant in watery tissues such as the jellylike substance in the interior of the eye.
(d) Glycosaminoglycans are components of proteoglycan.
(c) Proteoglycans are a major component of compact connective tissues but are relatively unimportant in watery tissues such as the jellylike substance in the interior of the eye.
20-19 A basal lamina ______________________.
(a) is a thin layer of connective-tissue cells and matrix underlying an epithelium.
(b) is a thin layer of extracellular matrix underlying an epithelium.
(c) is attached to the apical surface of an epithelium.
(d) separates epithelial cells from each other.
(b) is a thin layer of extracellular matrix underlying an epithelium.
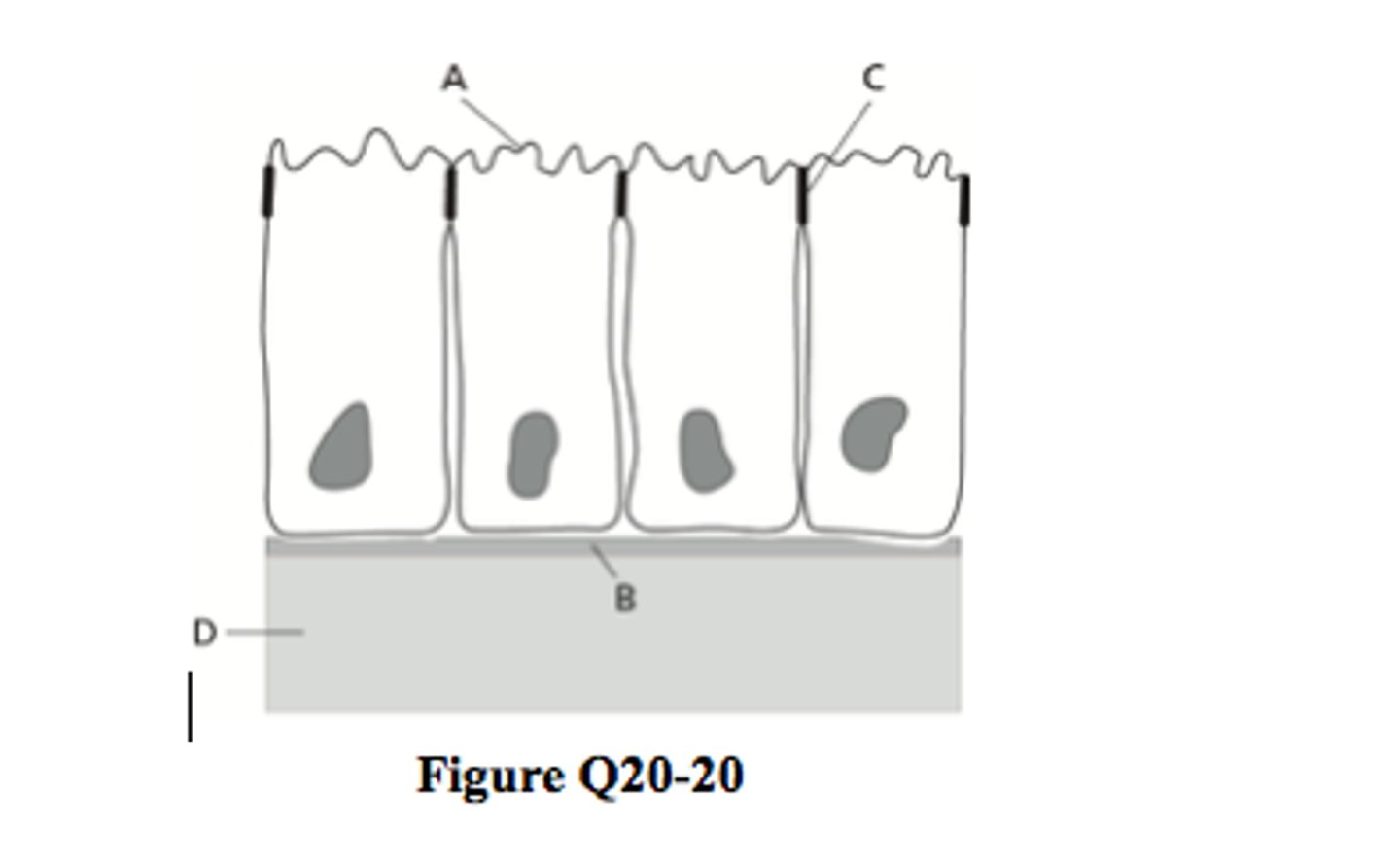
20-20 Match the labeled parts of Figure Q20-20 with the phrase that best matches the part. Each part will only be used once.
Figure Q20-20
basal lamina ______
apical surface _______
cell junction _______
connective tissue _______
basal lamina ___B___
apical surface ___A____
cell junction ___C____
connective tissue ___D____
20-21 Tight junctions ______________________.
(a) allow small, water-soluble molecules to pass from cell to cell.
(b) interact with the intermediate filaments inside the cell.
(c) are formed from claudins and occludins.
(d) are found in cells in connective tissues.
(c) are formed from claudins and occludins.
20-22 Adherens junctions ______________________.
(a) can be used to bend epithelial sheets into tubes.
(b) are most often found at the basal surface of cells.
(c) are found only in adult tissues.
(d) involve fibronectin and integrin interactions.
(a) can be used to bend epithelial sheets into tubes.
20-23 At desmosomes, cadherin molecules are connected to ________________.
(a) actin filaments.
(b) intermediate filaments.
(c) microtubules.
(d) gap junctions.
(b) intermediate filaments.
20-24 Hemidesmosomes are important for ______________________.
(a) tubulation of epithelial sheets.
(b) linkages to glycosaminoglycans.
(c) forming the basal lamina.
(d) attaching epithelial cells to the extracellular matrix.
(d) attaching epithelial cells to the extracellular matrix.
20-25 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; use each word or phrase only once.
__________________ join the intermediate filaments in one cell to those in the neighboring cell. __________________ anchor intermediate filaments in a cell to the extracellular matrix. __________________ involve cadherin connections between neighboring cells and are anchorage sites for actin filaments. __________________ permit the passage of small molecules from one cell to its adjacent cell. __________________ prevent the leakage of molecules between adjacent cells.
adherens junctions gap junctions highway junctions
desmosomes hemidesmosomes tight junctions
20-25 Desmosomes join the intermediate filaments in one cell to those in the neighboring cell. Hemidesmosomes anchor intermediate filaments in a cell to the extracellular matrix. Adherens junctions involve cadherin connections between neighboring cells and are anchorage sites for actin filaments. Gap junctions permit the passage of small molecules from one cell to its adjacent cell. Tight junctions prevent the leakage of molecules between adjacent cells.
20-28 A major distinction between the connective tissues in an animal and other main tissue types such as epithelium, nervous tissue, or muscle is _______________.
(a) the ability of connective-tissue cells such as fibroblasts to change shape.
(b) the amount of extracellular matrix in connective tissues.
(c) the ability of connective tissues to withstand mechanical stresses.
(d) the numerous connections that connective-tissue cells make with each other.
(b) the amount of extracellular matrix in connective tissues.
20-30 Which of the following statements about gap junctions is false?
(a) Gap junctions are made of connexons.
(b) Molecules up to 1000 daltons in molecular mass can move across gap junctions.
(c) Because gap junctions do not allow ions to pass through, they are not used for electrically coupling cells.
(d) Gap junctions can close in response to extracellular signals.
(c) Because gap junctions do not allow ions to pass through, they are not used for electrically coupling cells.
20-31 Which type of junction involves a connection to the actin cytoskeleton?
(a) adherens junctions
(b) desmosomes
(c) tight junctions
(d) gap junctions
(a) adherens junctions
20-32 Which type of junction contributes the most to the polarization of epithelial cells?
(a) adherens junctions
(b) desmosomes
(c) tight junctions
(d) gap junctions
(c) tight junctions
20-33 Cadherins ______________________.
(a) are used to transfer proteins from one cell to another.
(b) mediate cell-cell attachments through homophilic interactions.
(c) are abundant in the plant cell wall.
(d) bind to collagen fibrils.
(b) mediate cell-cell attachments through homophilic interactions.
20-34 Plasmodesmata ______________________.
(a) permit small molecules to pass from one cell to another.
(b) are found only in animal cells.
(c) are closed by the neurotransmitter dopamine.
(d) provide tensile strength.
(a) permit small molecules to pass from one cell to another.
20-35 The plasmodesmata in plants are functionally most similar to which animal cell junction?
(a) tight junction
(b) adherens junction
(c) gap junction
(d) desmosome
(c) gap junction
20-39 Cells that are terminally differentiated ______________________.
(a) will undergo apoptosis within a few days.
(b) can no longer undergo cell division.
(c) are unable to move.
(d) no longer produce RNAs.
(b) can no longer undergo cell division.
20-40 When a terminally differentiated cell in an adult body dies, it can typically be replaced in the body by a stock of ________.
(a) proliferating precursor cells.
(b) cells more apically located than the terminally differentiated cells.
(c) Wnt proteins.
(d) induced pluripotent cells.
(a) proliferating precursor cells.
20-41 An adult hemopoietic stem cell found in the bone marrow ______________________.
(a) will occasionally produce epidermal cells when necessary.
(b) can produce only red blood cells.
(c) can undergo self-renewing divisions for the lifetime of a healthy animal.
(d) will express all the same transcription factors as those found in an unfertilized egg.
(c) can undergo self-renewing divisions for the lifetime of a healthy animal.
20-42 A pluripotent cell _________.
(a) can only be produced in the laboratory.
(b) can give rise to all the tissues and cell types in the body.
(c) can only give rise to stem cells.
(d) is considered to be terminally differentiate
(b) can give rise to all the tissues and cell types in the body.
20-43 Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells ______________________.
(a) can only be produced through therapeutic cloning.
(b) can give rise to all tissues and cell types in the body except germ cells.
(c) can be implanted in foster mothers to produce cloned cows and other animals.
(d) come from the inner cell mass of early embryos.
(d) come from the inner cell mass of early embryos.
20-44 How do reproductive cloning and therapeutic cloning differ?
(a) The DNA in the nucleus of cells produced for therapeutic cloning is genetically identical to the donor genome, whereas in cells produced for reproductive cloning it is not.
(b) Reproductive cloning requires a supply of fertilized donor egg cells, whereas therapeutic cloning requires unfertilized egg cells.
(c) Therapeutic cloning requires nuclear transplantation, whereas reproductive cloning does not.
(d) Embryos are placed into foster mothers during reproductive cloning but not during therapeutic cloning.
(d) Embryos are placed into foster mothers during reproductive cloning but not during therapeutic cloning.
20-45 An individual that arises by reproductive cloning has a nuclear genome that is identical to __________.
(a) the female who donated the egg.
(b) the adult who donated the cell for nuclear transplantation.
(c) both the female who donated the egg and the adult who donated the cell for nuclear transplantation.
(d) the foster mother in which the embryo is placed.
(b) the adult who donated the cell for nuclear transplantation.
20-46 Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells ______________________.
(a) are created by the expression of a set of key genes in cells derived from adult tissues so that these cells can differentiate into a variety of cell types.
(b) require a supply of donor egg cells, such as embryonic stem cells.
(c) can differentiate into a greater variety of adult tissues than embryonic stem cells.
(d) are created by nuclear transplantation.
(a) are created by the expression of a set of key genes in cells derived from adult tissues so that these cells can differentiate into a variety of cell types.
20-47 The artificial introduction of three key ______________ into an adult cell can convert the adult cell into a cell with the properties of ES cells.
(a) chromosomes
(b) viruses
(c) hormones
(d) transcription factors
(d) transcription factors
20-50 A malignant tumor is more dangerous than a benign tumor because ______________________.
(a) its cells are proliferating faster.
(b) it causes neighboring cells to mutate.
(c) its cells attack and phagocytose neighboring normal tissue cells.
(d) its cells invade other tissues.
(d) its cells invade other tissues.
20-51 A metastasis is _________.
(a) a secondary tumor in a different part of the body that arises from a cell from the primary tumor.
(b) a cell that is dividing in defiance of normal constraints.
(c) a part of the primary tumor that has invaded the surrounding tissue.
(d) the portion of the cancerous tumor that displays genetic instability.
(a) a secondary tumor in a different part of the body that arises from a cell from the primary tumor.
20-52 Which of the following statements about cancer is false?
(a) Viruses cause some cancers.
(b) Tobacco use is responsible for more than 20% of all cancer deaths.
(c) A mutation in even a single cancer-critical gene is sufficient to convert a normal cell into a cancer cell.
(d) Chemical carcinogens cause cancer by changing the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
(c) A mutation in even a single cancer-critical gene is sufficient to convert a normal cell into a cancer cell.
20-54 Which of the following genetic changes cannot convert a proto-oncogene into an oncogene?
(a) A mutation that introduces a stop codon immediately after the codon for the initiator methionine.
(b) A mutation within the coding sequence that makes the protein hyperactive.
(c) An amplification of the number of copies of the proto-oncogene, causing overproduction of the normal protein.
(d) A mutation in the promoter of the proto-oncogene, causing the normal protein to be transcribed and translated at an abnormally high level.
(a) A mutation that introduces a stop codon immediately after the codon for the initiator methionine.
20-55 Which of the following statements about tumor suppressor genes is false?
(a) Gene amplification of a tumor suppressor gene is less dangerous than gene amplification of a proto-oncogene.
(b) Cells with one functional copy of a tumor suppressor gene will usually proliferate faster than normal cells.
(c) Inactivation of tumor suppressor genes leads to enhanced cell survival and proliferation.
(d) Individuals with only one functional copy of a tumor suppressor gene are more prone to cancer than individuals with two functional copies of a tumor suppressor gene.
(b) Cells with one functional copy of a tumor suppressor gene will usually proliferate faster than normal cells.
tumor suppressor gene is recessive, so cell behaves normally
20-57 Ras is a GTP-binding protein that is often defective in cancer cells. A common mutation found in cancer cells causes Ras to behave as though it were bound to GTP all the time, which will cause cells to divide inappropriately. From this description, the normal Ras gene is _______.
(a) a tumor suppressor.
(b) an oncogene.
(c) a proto-oncogene.
(d) a gain-of-function mutation.
(c) a proto-oncogene.
20-65 APC is a tumor suppressor and acts in the Wnt signaling pathway to prevent the TCF complex from turning on Wnt-responsive genes. Mice that lack the gene encoding TCF4 do not have the ability to maintain the pool of proliferating gut stem cells needed to renew the gut lining. What do you predict will happen in mice that lack the APC gene?
(a) Mice lacking the APC gene will be like the mice lacking TCF4 and not be able to renew the gut lining.
(b) Mice lacking the APC gene will have inappropriate proliferation of gut stem cells.
(c) Mice lacking the APC gene will have a hyperactive Wnt receptor even though there is no Wnt signal.
(d) Mice lacking the APC gene will be like normal healthy mice, since APC is a tumor suppressor and thus not needed unless there is a tumor present.
(b) Mice lacking the APC gene will have inappropriate proliferation of gut stem cells.