econ curves
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
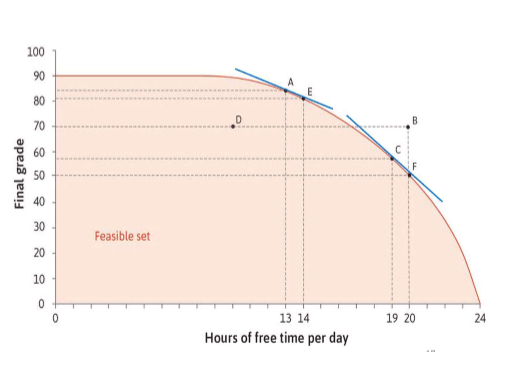
production frontier
MRT
transforming 2 inputs
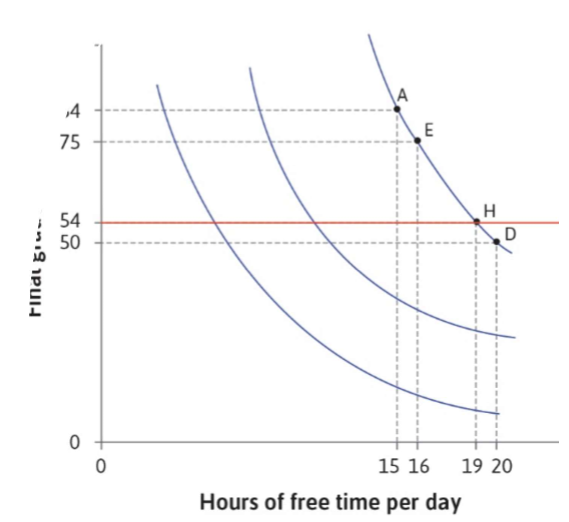
indifference curves
MRS
tradeoffs willing to make
preference/ utility
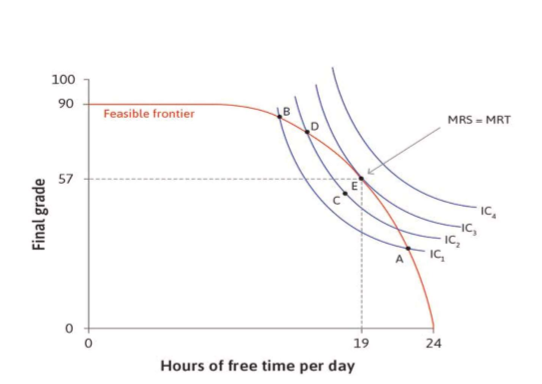
optimal choice
where MRS=MRT
(output= utility)
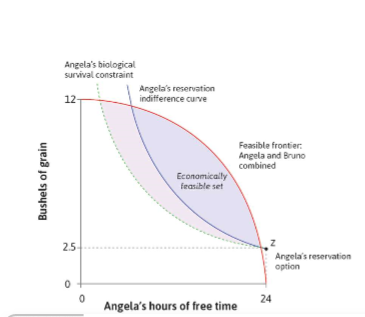
suboptimal choices and institutional effects
where MRS =/ MRT
reservation indifference curves → legal rights
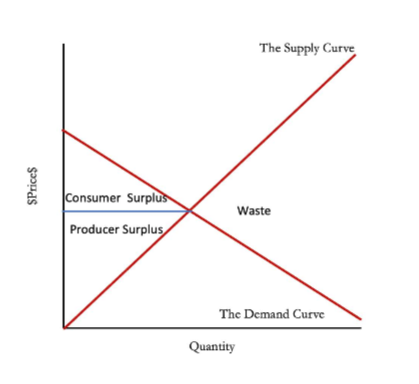
supply and demand curve
gains from trade
supplier and consumer shares
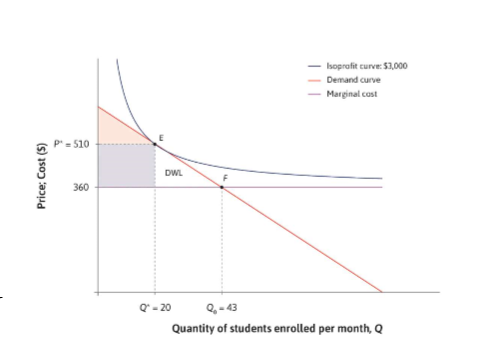
DWL
caused by price increases, production cuts
by companies with market power (non competitive)
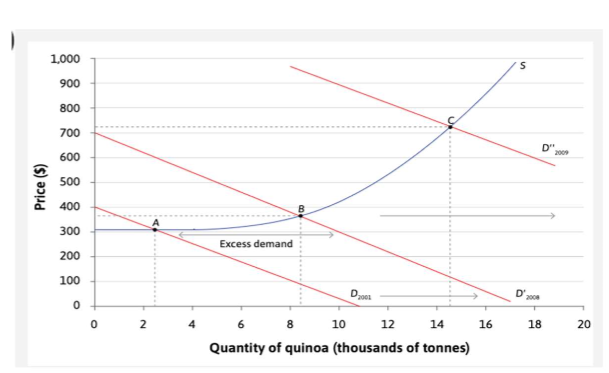
demand shocks
increased demand moves curve to the right
further up the supplu curve → increase in prices.
decreased demand= reverse.
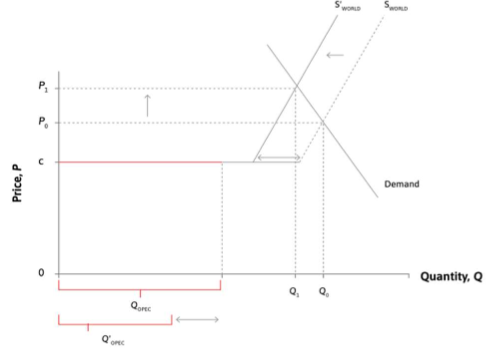
supply shocks
reduced supply moves to curve to the left.
and further to the demand curve (prices rise)
increase supply = reverse.
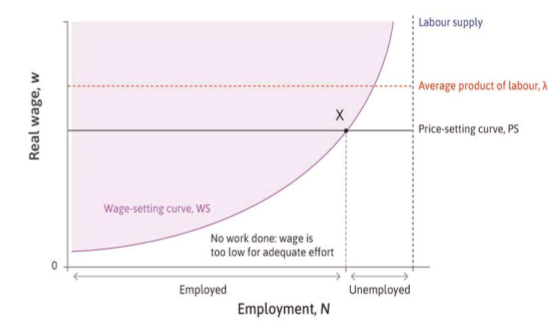
wage setting & price-setting curves
WS= what companies want to pay (minimum possible)
PS= cost of labour in final product (real prices)
impact on unemployement
impact company profits
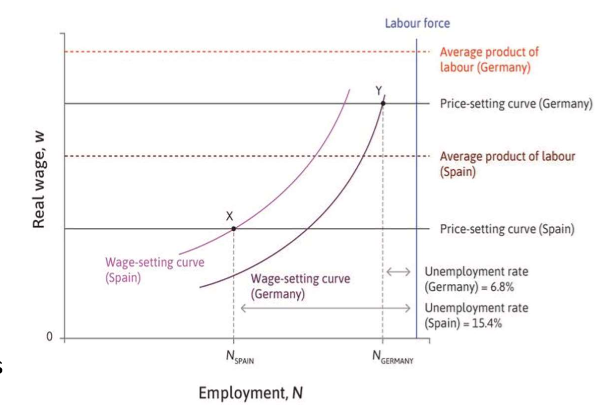
WS & PS curves
productivity effect on curves → higher real wages and lower unemployement
requires coordination institutions.
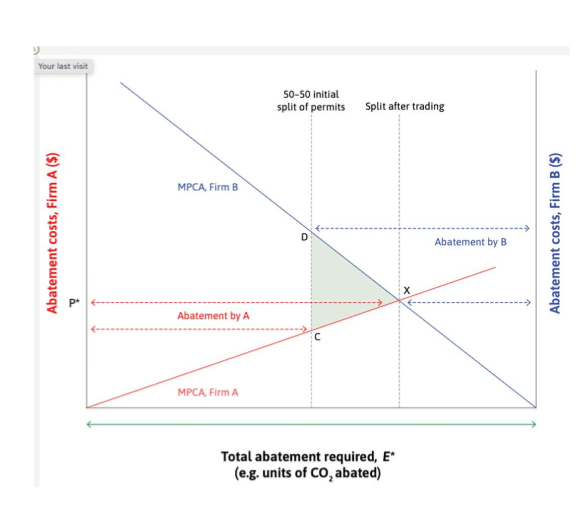
trading pollution permits between 2 companies
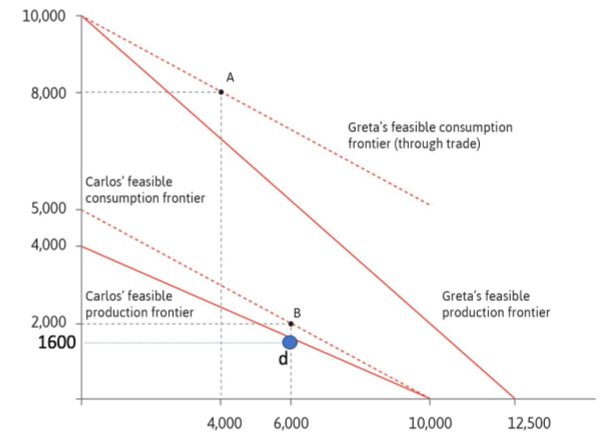
trading choices
consumption frontiers change under trade.
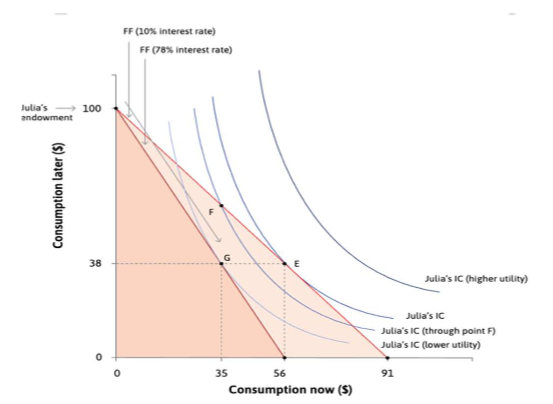
borrowing choices
consumption today vs. later
based on interest rate and IC
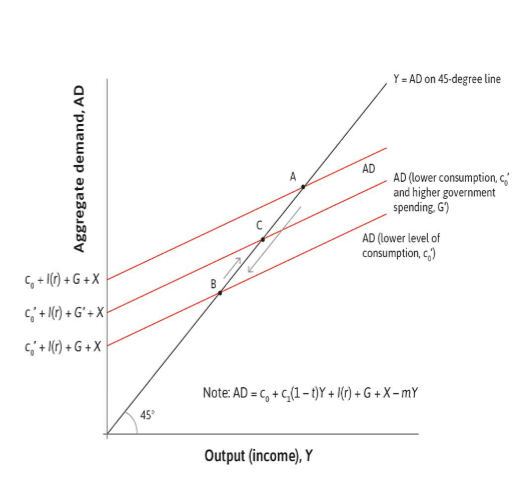
Aggregate demand (C+I)
moves up as economy improves, down with deterioriation.
fiscal policy and interest rate changes have similar effects moving AD line.