7 Scientific Racism and History of Life
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
race
not a genetic category, because:
There is more human diversity within races than between races
Much human diversity is restricted to small populations
Human genetic diversity is a subset of African genetic diversity
Most of human history took place in Africa
Non-Africans branched off from a small population of Africans
Predictions based on race aren’t very good
humans
~99.9% identical on the DNA level: the whole species has less genetic diversity than a typical group of 55 chimpanzees
The diversity they do have is mostly outside of protein-encoding genes. Some of their diversity changes amino acid sequences or the “copy number” of sequences.
whole genomes
Except for a few very rare genetic variants, all alleles are found in multiple human populations. Still, the allele frequencies differ from population to population.
Y chromosome
Passed on from father to son. Paternal lineages can be tracked through the __, but only in sons of sons of sons...
mitochondrial genome
Mitochondria contain their own genes that are inherited exclusively through the mother. We can trace maternal lineages through the __.
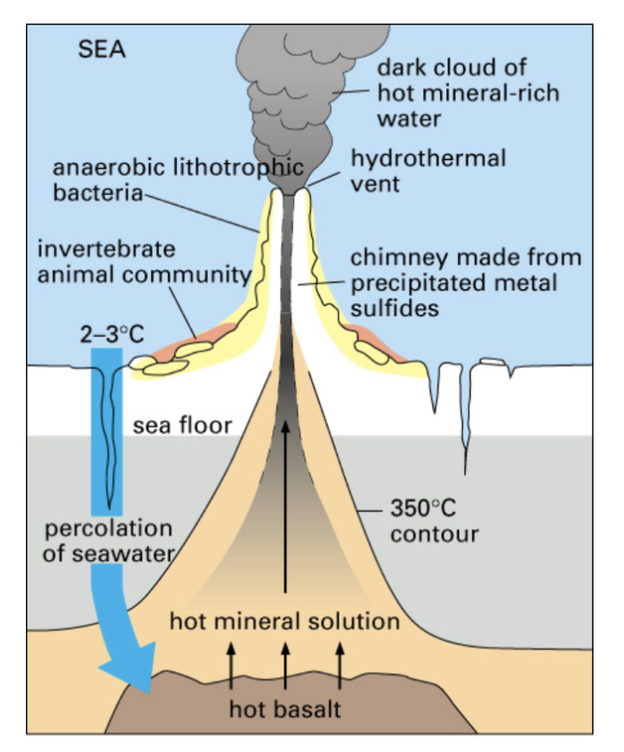
deep sea vents
possible location for the beginning of life
High pressures and steep temperature gradients near __ could have permitted accumulations of complex molecules where they would have also been protected from cosmic radiation.
At __, H2 and CO2 are often available for chemical conversion to CH4 (methane) and water. This releases energy and provides building blocks for life. This is also how many bacteria still make a living.
transition to life
requires matter that
Contains the information needed for replication
Can provide the catalysis required to copy itself
Proteins are excellent catalysts, but cannot act as templates for their own production
DNA can act as a template for itself, but is not catalytic
RNA can act as a template and can act as an enzyme!
ribozymes
RNA is a molecule that can store information AND act as an enzyme.
Even though RNA has only 4 bases, it is single stranded and it can fold into so many different shapes that several RNA enzymes have been discovered.
Two of these, ribosomal RNA and RNAs that self-splice, have been found in nature. Many others have been randomly generated and then selected in the laboratory.
enzyme
The first step in creating a more complex life form than a single, self-replicating ___ would be a collection of __s that can cooperate (e.g. a ribozyme that can copy itself and other ribozymes and ribozymes needed for releasing energy from inorganic molecules)
animals
Related to a group of protists called choanoflagellates. These single cell organisms filter bacteria and other foods from sea water. These organisms grow as multicellular colonies in the presence of bacteria. They resemble collared cells that filter food from water inside sponges.