Speciation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
species
A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
fertile offspring
capable of producing viable offspring
reproductively isolated
when a group of organisms is prevented from interbreeding with other groups
Pre-zygote barriers
mechanisms that prevent mating or fertilization between species
post-zygote barriers
mechanisms that occur after fertilization, preventing the development of viable or fertile offspring.
Habitat isolation
Two species might prefer different habitats and thus be unlikely to encounter one another
temporal isolation
Two species might reproduce at different times of the day or year and thus be unlikely to meet up when seeking mates
Two species might have different courtship behaviors or mate preferences and thus find each other "unattractive"
Behavior isolation
Two species might produce egg and sperm cells that can't combine in fertilization, even if they meet up through mating.
Gametic isolation
Two species might have bodies or reproductive structures that simply don't fit together.
Mechanical isolation
Reduced hybrid fertility
The condition where hybrid offspring are sterile and cannot reproduce, preventing gene flow between the parent species.
Reduced Hybrid Viability
(survivability) Parents have incompatible genetics and the hybrid offspring fails to develop
speciation
The evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species, often due to reproductive isolation.
sexual selection
The process by which certain traits increase an individual's chances of reproducing based on preference by one sex for certain characteristics in individuals of the other sex.
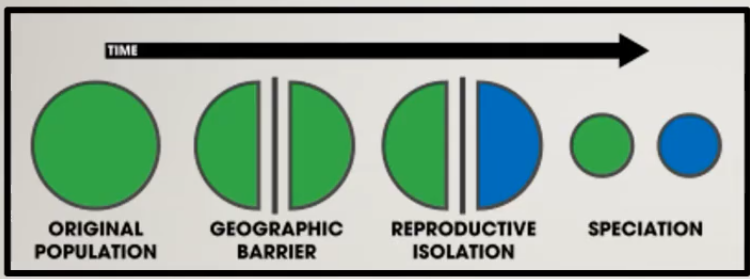
Allopatric speciation
when two different populations are living in different geopgraphic regions, which prevent sgene flow and thus speciation occurs when they are geographically isolated.
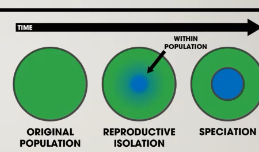
Sympatric speciation
Occurs when two different populations living in the same environment and different isolation mechanisms prevent gene flow
Punctuated equilibrium
Evolution occurs after a long period of stasis (a period of little to no change) and followed by a rapid bursts of speciation
Gradualism
The theory that evolution occurs slowly and steadily over time, with gradual changes leading to speciation.
divergent evolution
populations become seperated by geographic barriers and evolve indepedntly into their own species. Different habitats and become more different over time. Same common ancestor
convergent evolution
the process by which unrelated species evolve similar traits or adaptations due to similar environmental pressures, despite having different ancestors.
adaptive radiation
A type of divergent evolution where a group of organisms quickly diverge into new species. Different niches are occupied, leading to a rapid evolution of diversity.
It is possible for complex molcules to be built from inorganic molecules
origins of life