Aviation- Final Exam Review
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
On what date did the Wright Brothers make the first successful/controlled manned, heavier than air powered flight?
The Wright Brothers made their infamous flight on December 17, 1903.
Why is it critical for aviatiors to know the value of density altitude?
To make decisions regarding aircraft performance, such as determining takeoff and landing distances, climb rates, and fuel consumption.
According to the Bernoulli Principle, how does an airfoil generate lift?
The air pressure below the airfoil is greater than the pressure above as a result of its shape, causing an upward force.
According to Newton’s Laws, how does an airfoil generate lift?
The tilted shape of the airfoil pushes air downwards so the wings are pushed against. This is the angle of attack.
What is the angle of attack?
The angle between the oncoming airflow and the chord line of an airfoil. This determines the lift and drag characteristics of the airfoil.
What is critical angle of attack?
The angle at which an aircraft's wing generates maximum lift before it stalls. It is the angle between the chord line of the wing and the relative wind.
What is ground effect?
The phenomenon in which an aircraft experiences increased lift and reduced drag when flying close to the ground or water surface. This occurs due to the compression of airflow between the aircraft and the ground, resulting in a cushion of air that enhances lift.
What is the danger of a steeply banked turn?
This can lead to an increased risk of stalling or losing control of the aircraft, because the increased angle of bank causes a higher load factor on the wings, potentially exceeding the critical angle of attack. As a result, the aircraft may experience a loss of lift and enter into a stall, leading to a loss of control or a potential spin.
What is a spin in aviation?
Occurs when an aircraft enters an uncontrolled downward spiral motion. It typically occurs when the aircraft's angle of attack is too high and the airflow over the wings becomes disrupted. This can lead to a loss of lift and a rapid descent.
Who was the first man to break the sound barrier?
Captain Charles "Chuck" Yeager.
What type of weather is generally associated with a high-pressure system?
Clear skies and calm weather conditions.
In the northern hemisphere, what is the wind circulation around a high-pressure area?
In the northern hemisphere, the wind circulation around a high-pressure area is clockwise. This is known as anticyclonic flow.
What does it mean when an airport's rotating beacon is operated during daylight hours?
The weather is below VFR minimums, so the airport is providing a visual aid for pilots.
How are airport taxiway edge lights identified at night?
Taxiway edge lights outline the edges of taxiways. This lights are blue.
What is a temporary flight restriction?
A restriction imposed by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) on the airspace for a specific period of time. These can restrict aircraft from entering or operating within a designated area, altitude, or time frame, and are typically communicated through NOTAMs.
What is the type of navigation where the aircraft is navigated solely by using an aeronautical chart and reference to visible landmarks?
Pilotage
Which of the following electronic navigation aids form federal airways?
Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR)
What is hypoxia?
A condition characterized by a deficiency of oxygen supply to the body's tissues. It occurs due to factors such as high altitude, lung diseases, heart conditions, etc. , with symptoms of confusion and dizziness.
What is spatial disorientation?
A condition where an individual loses their sense of direction and perception of their position in space. It commonly occurs when there is a mismatch between the sensory information received by the body and the individual's perception of their surroundings.
What is load factor?
This refers to the ratio of the average load on a system to the maximum load that the system can handle. In the context of transportation or aviation, this refers to the ratio of the average passenger load to the maximum passenger capacity of a vehicle or aircraft.
Pitch
Elevator, Lateral
Roll
Aileron, Longitudinal
Yaw
Rudder, Vertical
Roles of the CAA
Facilitate ATC
Certify airmen and aircraft
Rule enforcement
Development of new airways
Federal aid airport program
Roles of the CAB
Rulemaking to enhance safety
Economic regulation of airlines
Accident investigation
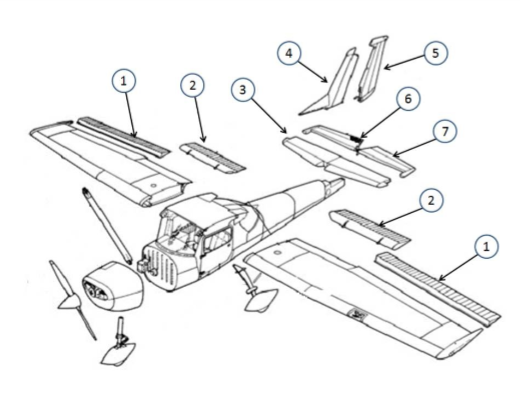
#1
This is the aileron, which is used to control the roll of the aircraft by changing the lift distribution over the wings.
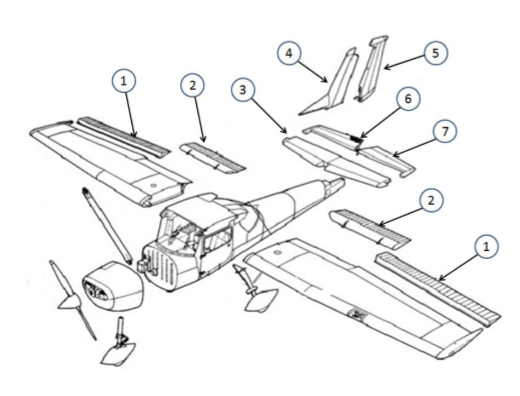
#2
These are the flaps. They allow for a steeper approach without gaining airspeed
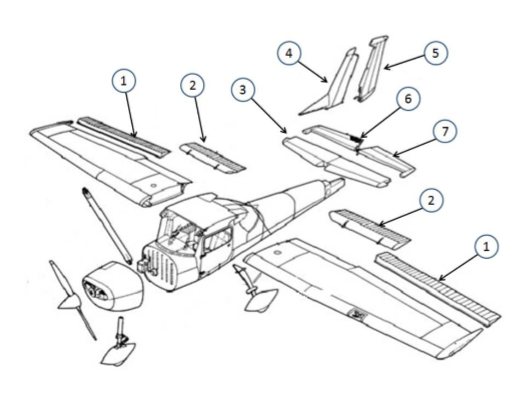
#3
This is the horizontal stabilizer. It provides stability and control. It helps maintain balance by counteracting the pitching motion. It also houses the elevator, which controls the aircraft's pitch.
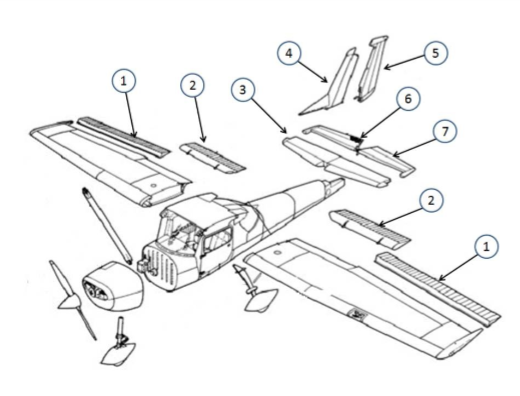
#4
This is the vertical stabilizer. It provides stability and control by preventing yawing, which is the side-to-side motion of an aircraft. The vertical stabilizer houses the rudder, which is used to control the yawing motion and maintain the aircraft's heading.
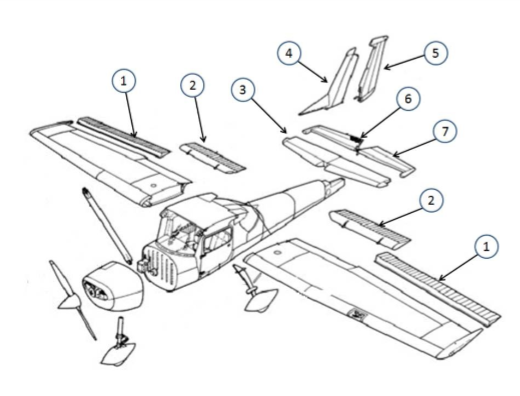
#5
This is the rudder. It helps in steering and controlling the direction of movement. (Yaw, Vertical)
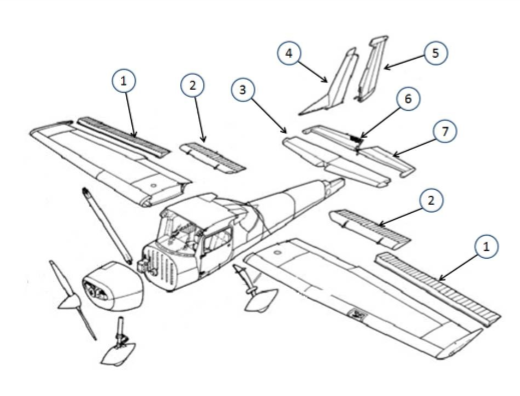
#6
This is the elevator. It is responsible for controlling the pitch or the up and down movement of the aircraft. It is located on the tail of the aircraft and can be moved up or down to change the angle of the aircraft's nose.
Primary flight controls
Elevator, aileron, rudder, canard
Secondary flight controls
Flaps, trim tabs, slats, spoilers
Airmen category
Airplane, rotorcraft, glider, lighter-than-air
Aircraft category
Transport, normal, utility, acrobatic, limited, restricted, and provisional
Airmen class
Single/multiengine, land/sea, gyroplane, helicopter, airship, free balloon
Aircraft class
Airplane, rotorcraft, glider, balloon, landplane, seaplane
First woman to break the sound barrier
Jaquelin Cochran