Vital Signs and body temperature
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Vital signs
measurements of the body’s basic functions.
Vital signs
They provide critical and necessary information about the state of health of an individual/
body temperature
pulse rate
respiratory rate
blood pressure
four main vital signs
Body temperature
measure of the ability of the body to generate or get rid of heat
Thermoregulation
the body has the ability to maintain its temperature at safe range so cells may function normally even large variations of temperature occurs externally or from the environment itself. This process is called ___
Thermoregulation
the balance between the body’s mechanisms of heat production and heat loss to maintain a constant body temperature
sensors and controllers
The body temperature is regulated by a coordinated system of __ in the body
-
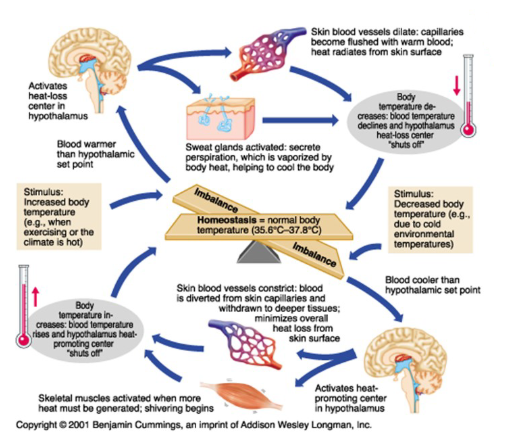
homeostasis = 35.6C-37.8C (avg of 37C or 98.6F)
= normal body temperature
Vasoconstriction
Thermogenesis
Hormonal thermogenesis
If the body is too cold, it needs to warm up through:
Vasoconstriction
The blood vessels under the skin narrows which decreases the blood flow to the skin, thereby retaining heat inside the body.
Thermogenesis
The organs of the body produces heat in variety of ways, for example the muscle shivers to produce heat
Hormonal thermogenesis
The thyroid gland releases hormones to increase metabolism which increases the energy the body makes and the amount of heat it produces.
Vasodilation
Sweating
if the body is too warm, it needs to cool down through:
Vasodilation
The blood vessels under the skin widens which increases the blood flow to the skin, releasing the inner heat from the body through radiation.
Sweating
The sweat glands are activated, releasing sweat which cools the skin as it evaporates, thereby lowering the core temperature
core temperature
the temperature of the deep tissues of the body
surface temperature
the temperature of the skin layers and subcutaneous tissues
Age
Exercise
Hormones
Circadian rhythm/Diurnal variations
Stress
Environment
Presence of disease of illness
Factors Affecting Body Temperature
carbohydrate and fat breakdown
Muscle activity increases metabolism by increasing ___. Any form of exercise can therefore increase heat production and thus, can increase body temperature.
high; low
The body temperature is usually __ during night-time and usually __ during sleep hours in the midnight to morning. (Circadian rhythm/Diurnal variations)
Hyperpyrexia; hypothermia
__ or fever can occur during infections, too much heat can depress the hypothalamus causing heat stroke, or prolonged exposure to cold temperature can cause __
Digital thermometers
Glass mercury thermometers
Electronic ear thermometers
Forehead thermometers
Plastic strip thermometers
Pacifier thermometers
different types of thermometers
Digital thermometers
These are considered to be the fastest and most accurate type of thermometers. It can be used through oral, axillary or rectal route.
Glass mercury thermometers.
These are old types of thermometers usually placed under the tongue or at the armpit and wait for the mercury to rise until it stops.
Electronic ear thermometers
These use infrared to measure body temperature.
Forehead thermometers
These thermometers also uses infrared to measure body temperature and are also lesser accurate than digital thermometers.
Plastic strip thermometers
These are plastic strips placed on forehead which can detect presence of fever, however does not accurately quantify the exact body temperature.
Pacifier thermometers
These thermometers resembles an actual pacifier and are predominantly used in babies older than three months.
0.3-0.6°C (0.5-1°F)
A rectal and ear temperature is __ higher
0.3-0.6°C (0.5-1°F)
axillary and forehead temperature is ___ lower than the average normal body temperature
rectal temperatures
In general, __ are considered to more accurate when checking for a fever in a young child
fever (pyresis)
is the temporary increase in the body’s temperature in response to a disease or illness.
fever of undetermined origin (FUO).
Unexplained fevers persisting for continuous days or weeks are called as __
hyperpyrexia
refers to the extremely high rise of body temperature equal to or greater than 41.5°C (106.7°F).
41.5°C (106.7°F)
hyperpyrexia refers to the extremely high rise of body temperature equal to or greater than ___. It may indicate an underlying serious medical disorder in the body.
Hyperthermia
refers to the uncontrolled rise in body temperature due to excessive body heat production and the body cannot loose enough heat to maintain the normal core temperature.
hypothermia
occurs when the body loses heat faster that it can produce, causing dangerously low body temperature.