Chapter 10 Microbiology Smartbook
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What is an antibiotic?
Natural agents used only against bacterial infections
A drug isolated then modified in the lab is called?
Semisynthetic
Semisynthetic drug
Natural antibiotic chemically modified in the lab
Prophylaxis
Use of a drug to prevent infection
Antimicrobial chemotherapy
Use of drugs to control infections caused by microbes
All-inclusive term for infection-fighting drugs
Antimicrobial
Natural metabolic product made by microbes to reduce competition
Antibiotic
Drug wholly made by chemical synthesis
Synthetic
Antimicrobial entirely produced chemically
Synthetic
Use of a drug to prevent infection
Prophylaxis
Kirby-Bauer test measures ___?
Antibiotic susceptibility
General term for using drugs to control infection
Antimicrobial chemotherapy
Major bacterial sources of antibiotics
Streptomyces and Bacillus
3 factors before selecting drug
Nature of microbe
Sensitivity
Patient condition
Susceptibility testing needed when…
Pathogen commonly shows resistance
Drug testing NOT used for
Prions
E-test function
Gives MIC value
MIC
Minimum inhibitory concentration (highest dilution that inhibits growth)
MBC
Minimum bactericidal concentration
Therapeutic index
Ratio: toxic dose / therapeutic dose
Therapeutic window
Blood drug range where effective without toxicity
Largest zone of inhibition (image)
Tetracycline
All inclusive infection control drug
Antimicrobial
Why do susceptibility tests?
Pathogen commonly shows resistance
Natural Antimicrobial: definition
Antibiotic
Drug testing used for all except
A. Bacteria
B. Protozoa
C. Fungi
D. Prions
D. Prions
A drug produced chemically =
= Synthetic
Kirby-Bauer determines ___susceptibility
Antibiotic
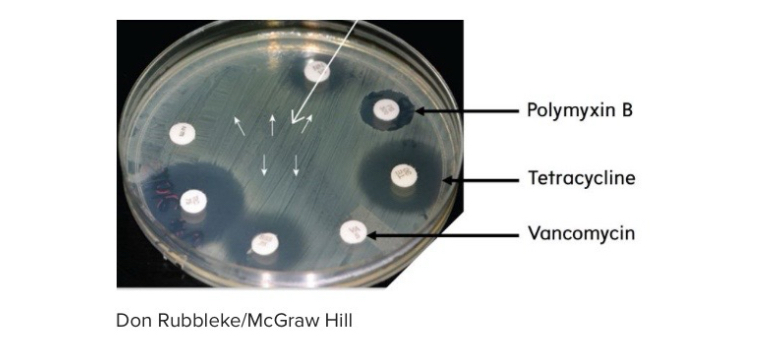
In this image of a Kirby-Bauer Test, the zone of inhibition is greatest for the antibiotic _____
Tetracycline
Which genus of fungus is not a major source of antibiotics?
A. Penicillium
B. Cephalosporin
C. Aspergillus
C. Aspergillus
Factors before selecting Antimicrobial?
Nature of microbe, sensitivity, medical condition
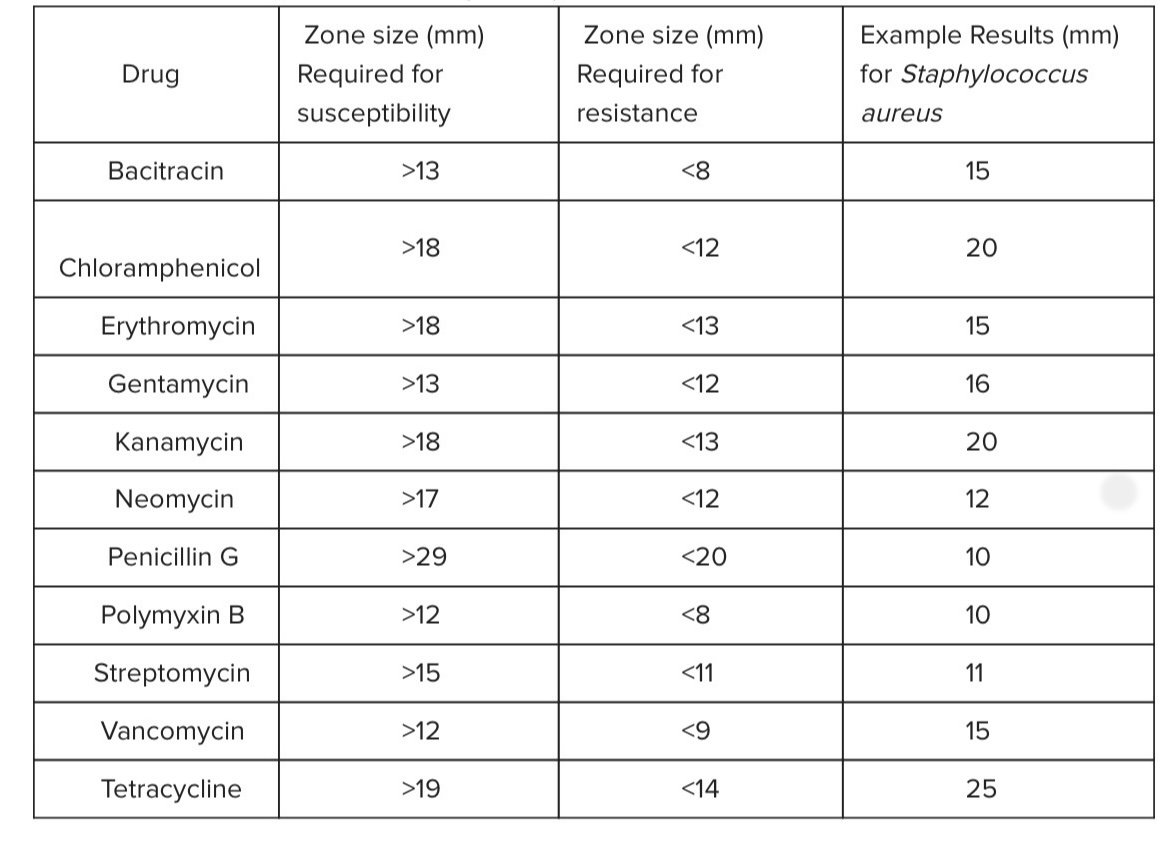
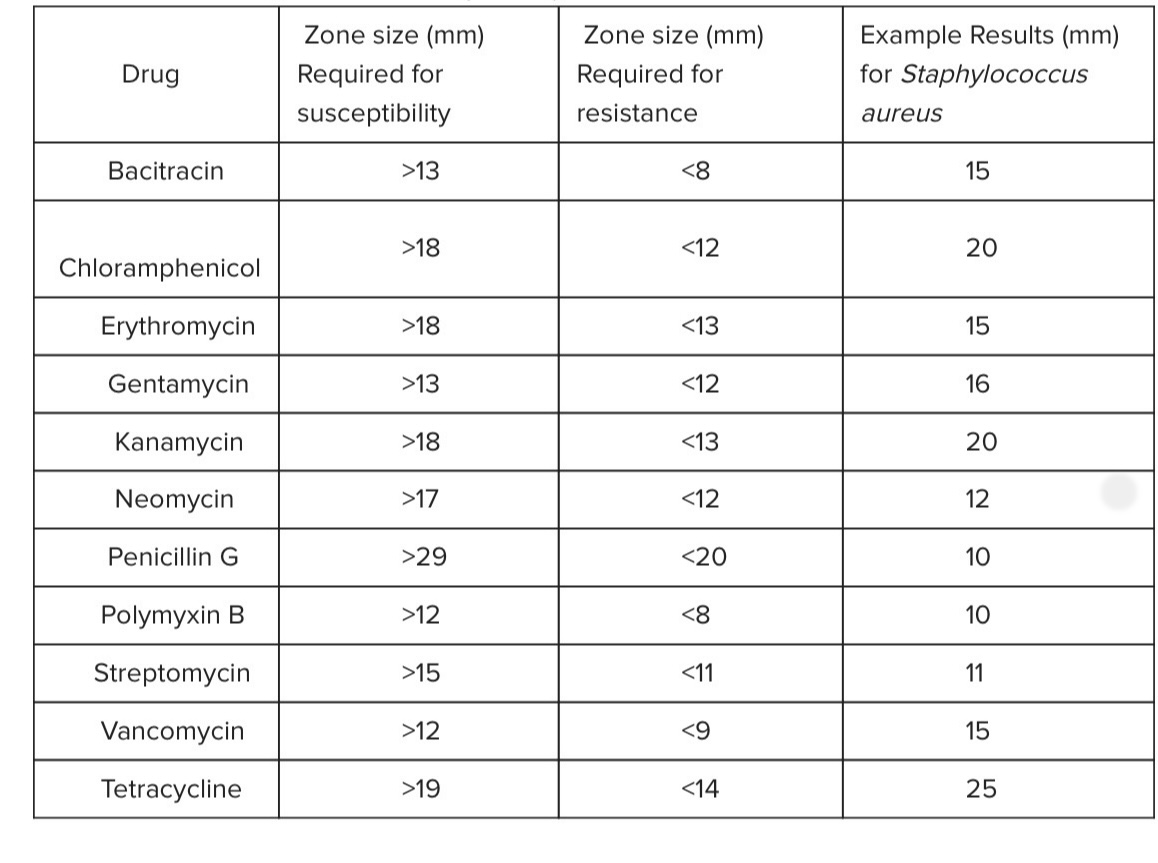
Based of the information in the table below, which of the antibiotics would be good choice to treat an infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus?
Chlorampenicol
Essential to test all infectious agents
False
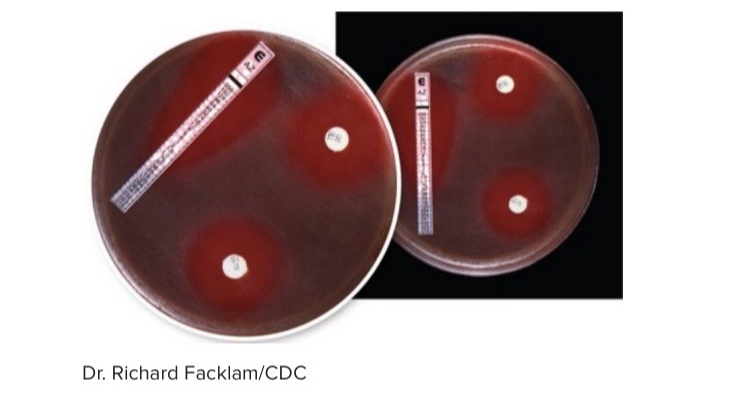
The image shows a diffusion procedure known as the _____ -test, which can establish the minimum inhibitory concentration for a microbe
E
Drug testing is unwarranted for fungi/protozoa
False
Lowest concentration inhibiting growth =
= MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration)
The ____ technique is an agar diffusion test used to determine antibiotic susceptibility of a particular bacterial strain.
Kirby-Bauer
Purpose of MBC
Determine if microbes were killed
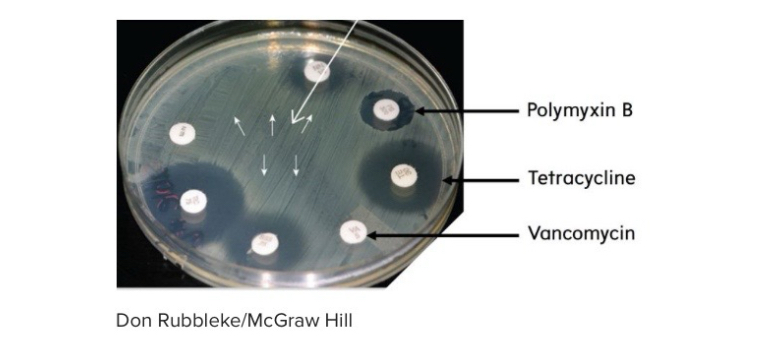
Examine the Kirby-Bauer antibiotic susceptibility plate shown below. Based on the zones of inhibition, which antibiotic is this bacterial strain resistant to?
VA—Vancomycin
Which drug would be a poor choice for treating this infection?
Penicillin G
E-test advantage?
Provides MIC
Drug failure may be due to resistant bacteria?
True
MIC definition?
Highest dilution that still inhibits growth
Smallest concentration to kill =
= MBC
Therapeutic index = ratio of
Toxic dose / therapeutic dose
MIC
Minimum inhibitory concentration
Which antibiotic has the broadest spectrum of activity?
A. carbapenems
B. tetracyclines
C. Streptomycin
D. Penicillins
tetracyclines
Therapeutic window =
Range where drug is effective without toxicity
Tetracycline mechanism?
Blocks tRNA on A-site → inhibits protein synthesis
Beta-lactam ring is part of?
Penicillin
Drug inhibiting translocation?
Erythromycin
Drugs can’t penetrate what?
Biofilms
Synercid targets?
Protein synthesis
Fungal drugs toxic because both are?
Eukaryotic
Which inhibit helicase?
Fluoroquinolones
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics
Isoniazid, Polymyxin
Antifungals (drug groups)?
Azoles, Macrolide polyenes
Active part of penicillin?
Beta-lactam ring
Azoles MOA?
Interfere with sterol synthesis
Biofilm bacteria express different?
Genes
Echinocandins interfere with?
Fungal cell wall synthesis
Drugs that are effective against fungi have a strong possibility of being toxic to humans because both organisms are eukaryotes.
True
Fluoroquinolones stop transcription of DNA by inhibiting unwinding enzymes called
Helicase
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics
Isoniazid, Polymyxin
Antifungals (drug groups)?
Azoles, Macrolide polyenes
Active part of penicillin?
Beta-lactam ring
Azoles MOA?
Interfere with sterol synthesis
Biofilm bacteria express different?
Genes
Echinocandins interfere with?
Fungal cell wall synthesis
Quinine is a drug used to treat the protozoan infection known as
malaria
Quinine has been replaced by the synthesized quinolones, mainly ____ and primaquine, for treatment of malaria, because they have less toxicity in humans.
chloroquine
Drugs blocking influenza fusion?
Oseltamivir, Zanamivir
Common antimalarials today?
Chloroquine, Primaquine
SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication inhibitor?
Remdesivir
Ivermectin + praziquantel treat?
Helminths
Adaptive tolerance = drug ____?
Resistance
Why viral infections hard to treat?
Rely on host cells for molecular processes
Antifungal that blocks cell wall?
Echinocandin
Major antiviral modes of action?
Block entry, block replication, block maturation
Influenza entry blockers?
Oseltamivir, Zanamivir
Which antibiotics inhibit protein synthesis?
Streptomycin
Drug for penicillin allergy?
Aztreonam
Bacteria persisters do what?
Slow/stop metabolism
Beta-lactamase role?
Drug inactivation
Horizontal transfer mechanisms?
Conjugation, Transduction, Transformation
Gene silencing RNA?
Interfering RNA (RNAi)
Correct statements about gene sharing?
Transposons move resistance; viruses can transfer resistance genes
Epigenetic resistance in fungi is?
Reversible
Resistance genes from chromosomal mutation?
True
R factor is a type of?
Plasmid
Erythromycin/clindamycin resistance from altered?
50S ribosomal subunit
Natural selection applies pressure from?
Environment
RNAi is explored for?
RSV, Hepatitis C virus
CRISPR used to cut?
Antibiotic resistance genes
Post-antibiotic era =
= Some infections untreatable
Probiotics are?
Preparations of live microbes
Major drug side effects categories?
Toxicity, Allergies, Flora disruption
Nephrotoxic drugs damage?
Kidneys
Drug reaction when immune system activated =
= Allergy
Damage from drugs can be?
Permanent or reversible