Western Front
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What were the conditions in the Western Front?
Poor hygiene
trench foot epidemics
full of rats(plague) & lice(trench foot) - diseases
wet/flooded depending on the weather
Corpses were buried at the side of the trenches
How was life in the trenches?
Daily life was monotonous and often very dull. It involved the cleaning and inspection of weapons; the construction and repair of trench defences; the removal of dead and wounded from trenches and no man's land; the transfer of supplies, food rations and new equipment; observing enemy activity and movement; repairing barbed wire defences; delousing of uniforms.
Characteristics of the trenches
Shallow
Zigzag - prevented soldiers from being able to see/fire directly. however, they were narrow and often blocked.
No electricity
No clean water
- British trenches were badly designed because they believed the war would be short
Why was Britain in disadvantage?
Germany Army was double the size (160,000 soldiers)
German trenches were well-designed
German strategies were better
Front Trench
Where attacks would be made
worst design for trench
Shallowest trench
Support Trench
Aout 80 metres behind the front line
Where troops woulld retreat - in case the front line came into attack
Reserve trench
100 metres behind the support trench
where reserve troops could be mobilised for a counter attack - in case the front line was captured
Communication trench
ran between other trenches
1914: First battle of Ypres
BEF moved to prevent German advances
Germans launched on attack on Britain
12th october - 11th November
Britain lost 50,000 but maintained control, but Germany controlled the edges
1915: Second battle of Ypres
After Hill 60 Battle
22nd April - 25th may 1915
First (German) use of chlorine gas on the Western Front
Germany moves two miles closer
59,000 British men lost
1916: The Battle of the Somme
1st July - 18th November 1916
British: 20,00 men dead and 400,000 injured (By November 1916)
Creeping barrage, banks in warfare
1917: The battle of Arras
Easy to build tunnels
April 1917 - May 1917
24,000 British men were attacked trying to breakthrough
Slow advance
1917: Third Battle of Ypres
british wanted Ypres salient
31st July - 10th November 1917
Moved about 7 miles
245,000 British casualties
1917: Battle of Cambrai
Launched 20th October 1917
Large scale use of tanks
FANY
First Aid Nursing Yeomanry. First women’s voluntary organisation. founded in 1907
RAMC
Royal Army Medical Corps. Branch of army responsible for medical care in 1898.
Chain of evacuation
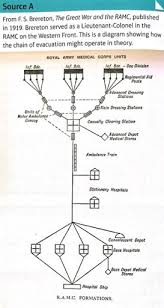
Regimental Aid Posts
Provided immediate first aid and triage for the wounded.
Stabilized soldiers for further evacuation.
Could not perform surgery or keep casualties for long.
Seriously wounded were moved quickly to the next stage.
200 metres from the front
ADS
Continued first aid and triage.
Treated shock and bleeding.
Prepared wounded for further transport.
Could hold the wounded temporarily but was not equipped for surgery.
1km behind the front line
MDS
Further assessment and treatment.
Some minor surgeries and emergency interventions.
Wounded categorized: those who could return to the front vs. those needing further evacuation
1-2 miles behind the front line
CCS
First major surgical facility.
Treated life-threatening injuries.
Carried out operations (e.g., amputations, abdominal surgery).
Stabilized patients before they were moved to hospitals further back.
Prioritized based on triage: most likely to survive with treatment went first.
5-10 miles behind the front line
Base Hospital
Long-term care and recovery.
More complex surgeries.
Convalescence and rehabilitation.
Eventually, wounded were either returned to duty or evacuated to Britain.
many miles from the front
Evacuation to Britain
Severely wounded soldiers were sent to Britain for extended recovery.
Care continued in military or civilian hospitals.
transport by train, barge or ship
Thomas Splint
A tool that prevented your leg from moving untill the surgery
created by Robert Jones and Hugh Thomas
Increased the survival rate from 20% to 82%