the cardiovascular system chapter 14 and 15
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the primary function of the cadiovascular system?
the transport of material to and from all parts of the body;
nutirents, water and gases that enter the body from the external environment
materials that move from cell to cell within the body
waste products that the cells eliminate
The cardiovascular system is composed of?
heart
blood vessels
cells and plasma of blood
What are arteries?
blood vessels that carry blood away from the heartto the body's tissues.
What are veins?
blood vessels that return blood to the heart from the body's tissues.
What causes the blood to flow only in one direction?
the valves in the heart and veins preventing backflow
the heart is divided by …, into left and right halves. each halve functions as an independent … that consists of an … and a …
The heart in divided by a septum, into left and right halves. Each half functions as an independent pump that consists of an atrium and a ventricle.
What is the function of the atrium?
The atrium receives blood returning to the heart from the body and lungs.
What is the function of the ventricle?
The ventricle pumps blood out of the heart to the lungs and the rest of the body.
The right side receives blood from the … and sends it to the lungs for …. . The left side of the heart receives … blood from the lungs and pumps it to …..
The right side receives blood from the tissues and sends it to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart receives newly oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to tissue throughout the body.
What is the pulmonary circulation?
the blood vessels that go from the right ventricle to the lungs and back into the left atrium.
What is systemic circulation?
the blood vessels that carry blood from the left side of the heart to the tissues and back to the right side of the heart.
What are the divisions of the aorta?
coronary arteries —> nourish the heart muscle; blood from these arteries flows into capillaries, into the coronary veins, which empty directly into the right atrium at the coronary sinus
ascending branches —> these go to the arms, head and brain
abdominal aorta —> suplies blood to the trunk, the legs and the internal organs, liike the liver, digestive tract and the kidneys.
what is a portal vein?
a vein between 2 capillary beds
what causes blood to flow out of the heart?
The contraction of the heart muscle during systole creates a high pressure that forces blood into the arteries.
liquids and gasses flow down pressure gradients from regions of higher pressur to regions of lower pressure
What is pressure(in fluid)?
the force exerted by tthe fluid on its container
What is hydrostatic pressure?
the exerted pressue when a fluid is not moving. the force is exerted equally in all directions
What causes pressure to fall over a distance when fluid is moving?
pressure falls over a distance as energy is lost because of friction
What are the 2 pressures excerted by moving fluid?
dynamic —> kinetic energy
lateral —> hydrostatic pressure(potential energy) exerted in the walls of the system
What is driving pressure?
the pressure created in the ventricles. it is the force that drives blood through the blood vessels.
When the walls of the fluid-filled container expand, the pressure exerted on the fluid … .
When the walls of the fluid-filled container expand, the pressure exerted on the fluid decreases.
What is a major factor that influences blood pressure?
volume changes of the blood vessels
Flow through the tube is directly proportional to the … .
Flow through the tube is directly proportional to the pressure gradient.
the relationship says that the higher the pressure gradient, the greater the fluid flow

Fluid flows only if there is ….?
fluid flows only when there is a positive pressure gradient
Flow depents on?
the pressure gradient, not on the absolute pressure. when the delta P is equal the flow is equal
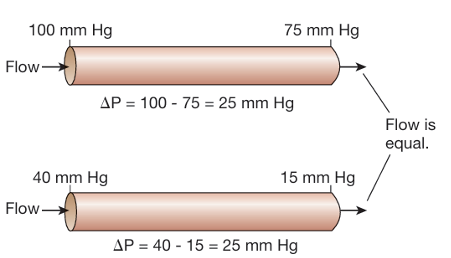
What is the systems resistance to flow?
the tendency of the cardio vascular system to oppose blood flow.
blood flowing through blood vessels encounters friction from waal of the blood vessels and from cell within the blood rubbing against one another as they flow.
Blood flow takes the path with the … . An increase in the resistance of a blood vessels results in a … in the flow through that vessel.
Blood flow takes the path with the least resistance. An increase in the resistance of a blood vessels results in a decrease in the flow through that vessel.
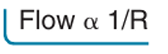
flow is inversely proportional to?
resistance
if the resistance increases, flow decreases
By whcih 3 components is resistance influenced?
the radius of the tube —> teh amin variable that effects resistance in the systemic circulation
the lenght of the tube —> is detemined by anatomy of the system and is constant
viscosity(tickness) of the fluid —> determined by ration of red blood cells to plasma and by how much protein is in the plasma. this is normally constant
Poiseuille’s law show the relationship of these factors; (middle of page 4)
middle of page 4