511 Midterm 3 - Muscles
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the 3 Muscle types?
Striations?
Nucleus/Nuclei
In/Voluntary
Skeletal - striated, multi-nucleated, voluntary
Smooth - not striated, 1 nucleus, involuntary, spindle-shaped
Cardiac - striated, 1 nucleus, involuntary, branched w/intercalated disks
One muscle fiber/cell is surrounded by:
Sarcolemma
A bundle of muscle fibers/cells is called:
Fascicle
Each fascicle is connected by:
And surrounded by:
Endomysium - reticular fibers
Perimysium - reticular + collagen fibers
What is the outermost membrane holding all of the fascicles together?
Epimysium - collagen fibers
Tendons are an extension of what part of the muscle?
All of the collagen fibers of the connective tissue casings
Muscle fobers (cells) are composed of many Myofibrils
What are these Myofibrils made of?
Actin
Myosin
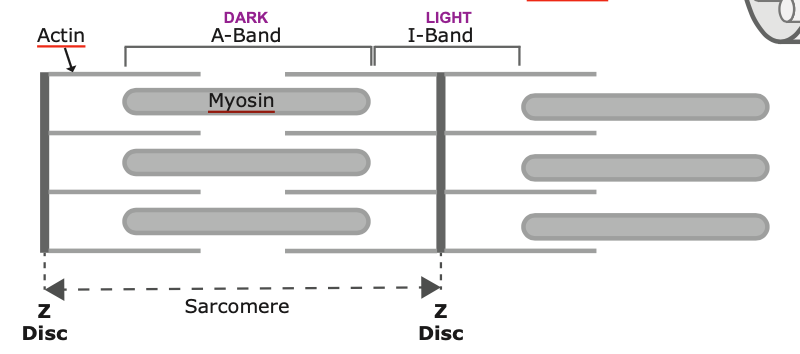
Describe the A-band, I-band, Z-disk, Sarcomere
A-band = Dark band = Myosin + actin overlap
I-band = Light band = Actin only, overlaps z-disk
Z-disk = connection of neighboring sarcomeres
Sarcomere = single contractile unit
Define Motor Unit
A neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
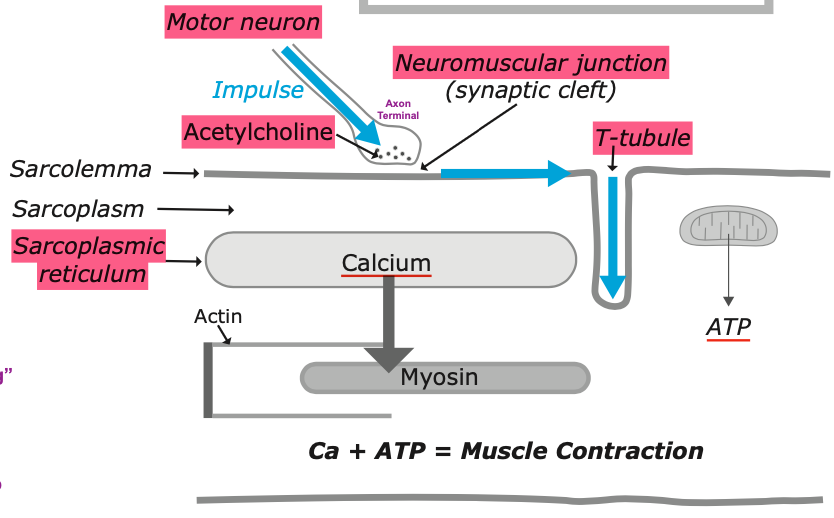
Describe the Physiological process of a Muscle Contraction
1. Motor nerve impulse arrives
2. Acetylcholine is released, transferring impulse across synaptic cleft to sarcolemma
3. Impulse continues along sarcolemma surface then in through T-tubule (line up with z disks)
4. Impulse reaches sarcoplasmic reticulum (which wraps around the sarcomeres) and calcium is released
5. Myosin can now bind actin - “Crossbridging”
6. Energy from ATP allows myosin to pull actin —> sarcomere shortens
What do you call the portion of the SR thats thickened, right along the T-tubule?
Cistern
What steps of muscle contraction require ATP?
Crossbridging (Myosin binding to actin)
Release of Myosin Head
Pump Ca back into Sarcoplasmic Reticulum for relaxation/next contraction
How is the actin and myosin arranged differently in smooth muscle vs. skeletal muscle?
Instead of parallel lines (sarcomere —> striated appearance), filaments/contractile units crisscross around the cell
Instead of Z-disks, Smooth Muscle has…?
Dense Bodies - anchor the actin
What are the 2 types of Smooth Muscle?
Visceral (Single unit) - 1 neuron, multiple muscle cells
-For entire organs/structures that want to contract as a single unit
-Influenced by ANS, or able to contract w/o external stimulation (i.e stretching due to food entering the stomach, intestine, etc)
Multiunit smooth muscle - 1 neuron, 1 or few muscle cells
-Enables individually contracting certain cells/small groups within a larger area/structure
-Contractions require an impulse from the ANS
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) is divided into two sub divisions. Which response does each trigger? How does it affect cardiac and smooth muscle contraction?
Sympathetic (SNS) —> “Fight or Flight” —> inc CV, dec GI
Parasympathetic (PSN) —> “Rest and Digest” —> dec CV, inc GI
What are the 3 methods of ATP Synthesis used by the body?
1. Aerobic metabolism (sufficient O2)
- Aka Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Max energy extracted from glucose
2. Anaerobic metabolism (lack O2)
- Incomplete glucose breakdown
- Lactic acid byproduct (later metabolized when O2s back)
3. Creatine Phosphate - MUSCLES ONLY
- CT is used to convert ADP back to ATP
- Glucose breakdown + O2 —> ATP + CP
What 3 resources do muscles store for themselves? Why?
CP, Glucose as glycogen, O2 as myoglobin (only for a few sec)
Enables muscle to function whenever needed and not depend on the blood stream’s timing
How do muscles play into temperature regulation?
When ATP is burned, Heat is a byproduct (transported via bloodstream)
Eliminating excess heat:
Panting/sweating ; water evaporation uses energy in the form of heat (endothermic), removing heat through the skin surface
Behavioral choices; sit in the shade or only come out at night
Creating heat when cold:
Shivering = Spasmodic muscle contractions that increase heat productions
Tends to occur in larger muscles (skeletal) for most heat production
Side note: Liver = main thermos - heating the body when skeletal muscle contractions aren’t