forensic-Toxicology-Midterm
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Toxicology-DEF
The study of chemicals/substances effects on living organisms
Responsibilities of a Toxicologist
Detect if any substances/chemicals/drugs are present
Interpret how the drugs work normally outside the scenario
How does the drug affect the specific person
Each person responds different to drugs
Establish if its a legitimate use or exposure
Prescription drugs or workplace exposure
(People)- Marie Larfarge
THE FIRST CRIMINAL who was charged for poisoning her husband with arsenic
Poison- DEF
Any substance/chemical/drug that taken in certain/smaller quantities, can kill or cause major damage to a human
IMPORTANT NOTE: ‘The dosage makes the poison’, meaning that the amount of poison kills you, we have small amounts right now of cyanide and mercury in us, but it doesn’t kill us.
lethality depends on two things?
How much enters your body?
How long it takes to enter your body?
NOTE: Anything is harmful to you if you “overdose”
You can drink too much water and breathe too much oxygen
intoxicant-DEF
Something that would need to be ingested in large amount to serve lethal (Opposite to passion)
EX: Alcohol or carbon monoxide
Collection for Drugs done by?
Collect fluids or tissues from
the body to analyze
Metabolism
The conversion of one chemical into
another by the body
The newly made product is: /// metabolites \\\
EX: When Heroin is injected, it metabolizes back into a metabolite: Morphine
Areas-Entrance site
Places where the substance can enter the body
EX: Injection sites, blood, stomach
Areas-Exit site
This is the substance,that exits our body and already metabolized.
Area-Concentration site
When drugs tend to concentrate at in mass
Entrance site- Blood
Considered an entrance site
toxicologist’s most useful and
accurate substanceContain the traces of the drugs or metabolites
Tells the toxicologist what occurred at the time of death
Concentrations of substances determine levels of intoxication.
Exit site - Urine
Not as accurate as blood,
We have more influence over the concentration of the substance in our urine, given we can drink water to dilute the urine.
Entrance site -Stomach
remove stomach contents by gastric tube
in the contents contain the drugs
The contents are washed and tested
Most useful for detecting poisons and overdoes
Concentration site-Liver
Main organ responsible for metabolizing drugs and toxins
Traces remain longer then blood
Depressants, concentrate in the liver
opium, heroin,morphine, Oxycontin
Drugs that depress or suppress your body
Concentration site- Eyeballs
Vitreous humor( The liquid inside the eyeball) can have traces of drugs
The eyeball is very resistant to decay
Could be the last liquid thing in the body
Accurate but delayed
Tells the story of what was in the blood only 1-2 hours before the eyeball sets in place, and begins decays
Exit site-Hair
absorbs everything; drugs, poisons,
environmental toxins
Gives a good timeline
determine whether poisoning was acute or chronic
Outside site- Insects
drugs will concentrate in the tissues of bugs
that feed on corpses.
known as forensic entomology
Acute poison-Def
Quick intense poisoning
Chronic poison-Def
Small amounts of poison over time
Manner-Accidental
victim unknowingly ingests a lethal
amount of poisonChildren: usually happen at home
Bleach,
adults: product is mislabeled or someone has put it in
the wrong container.Wrong prescription drugs
Other cases are: drug dose miscalculation or dangerous mixtures of drugs
EX: Mixing alcohol and prescription sedatives, casues the lining in a stomach to dissolve
Manner-Succidal
victim intentionally takes their own life
MOST COMMON MANNER
For methods: Carbon Monoxide is most common method followed by prescription drug overdose.
EX: Victim/s take multiple drugs at once.
makes it very hard for the ME to determine what
actually caused the death. Multiple tests must be conducted to find exact levels and effect of the drugs
EX: Carbon monoxide poison
Manner-Homicide
victim is intentionally killed by someone
else.LEAST COMMON MANNER
Most commonly occurs at home.
victim usually knows the killer
Test- Presumptive test
A initial screening to check if a suspected drug is present.
Cheap and easy and less accurate
Done mainly to give a suspicion, doesn’t 100% confirm
EX: Breathalyzer
Test- Confirmatory test
confirms the presence of a drug.
Done after presumptive test
More expensive, accurate, and time consuming
100% confirms presence
EX: Blood tests
Vocab-Stimulant
concentrates in the brain
Increase alertness, attention, and
energy,elevates blood pressure, heart
rate, and respiration.EX: cocaine, nicotine, ecstasy,
adderall, and caffine
Vocab-Stimulant
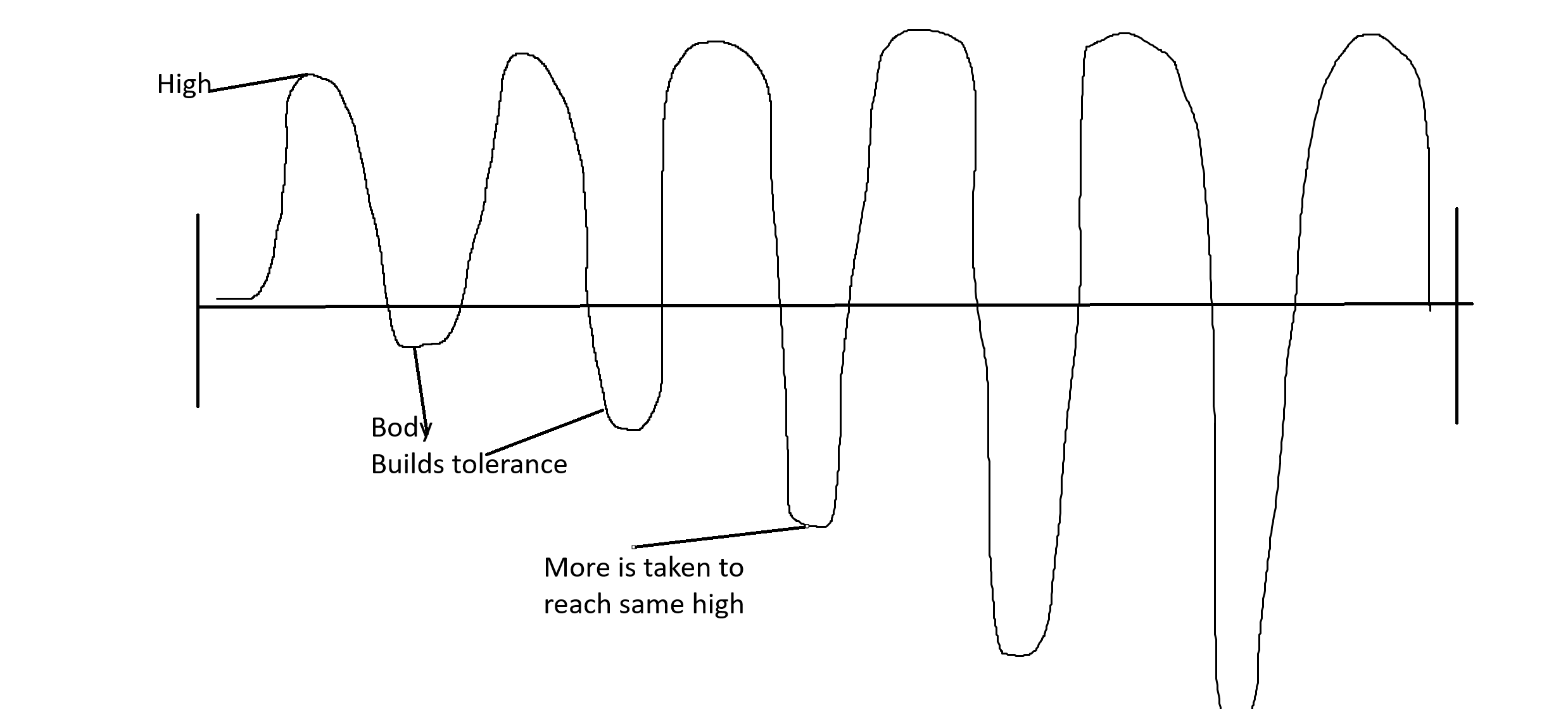
Vocab-Tachyphylaxis
Short: the body builds up a
tolerance to the drug.Long: When taking drugs in general, our body becomes accumulated, and the high/feeling decreases. Users tend/have to take more of the substances in order to sustain that high/feeling
Vocab-Depressant
Slows brain activity and the nervous
system function.Concentrates in liver
alcohol, opioids
Long term alcohol abuse is acute
Drinking 50 beers is chronic
Drug Scheduling
Schedule 1 – no medical use. Most dangerous.
(heroin, LSD, marijuana, meth, MDMA)Schedule 2 – very rare for medical use, still
very dangerous (oxycontin, cocaine, ritalin)
• Schedule 3 – low abuse potential (codine,
steroids)
• Schedule 4 – very low abuse (xanax, ambien)
• Schedule 5 – over the counter drugs
Vocab-Narcotic
Originally referred to a variety of
substances that dulled the senses and relieved pain.Today, it means opioid
Vocab-Benzodiazepines and Barbiturates
Depressants that relieve anxiety, and prevent seizures (Xanax and valium
Vocab-Sedative
sleep producing substances/drug
Vocab-Analgesic
pain relieving/numbing substance/drug
Levels of drug concentration
Normal – expected in the general population
Therapeutic – level that brings about the most
beneficial effect (appropriate use of prescription)Toxic – 1st level that causes harm: nausea, vomiting,
or change in heart rateLethal – level of drug that causes death
Vocab-LD50
Drug/substance blood concentration/level, at which 50% of population will perish if they ingest it

Chromatography?
Physical separation of a mixture into its individual
components.A SPIKE ON THE GRAPH, MEANS A HIGH CONCENTRATION
A BIG DOT ON THIN LAYER CHROMA, MEANS THE SAME
ex: Separate the components of inks and dyes or blood and chemicals in said blood
POSSIBLE TO BE HUNDREDS OF COMPONENTS IN ONE MIXTURE
Vocab-Chromatography-analyte
The substance that is separated during
chromatography ( statistic of blood)
EX: Cyanide,mercury,alcohol,etc separting during the process
Vocab-Chromatography-Stationary phase
when the substance/solute which is fixed in
place for the chromatography procedure
Vocab-Chromatography-solute
The substance actually being dissolved
Think milk powder
The samples we are testing
Vocab-Chromatography-Solvent
The substance that does the disolving
Think water
to any substance capable of
dissolving other substance
Vocab-Chromatography- mobile phase
The actual process in which the solute, and solvent are moving around
consists of the sample being separated/analyzed and the solvent that moves the sample through the column.
Vocab-Chromatography- Retention Factor
The measure of how far the substance it has moved up under certain conditions
quick way of identification
Solvent front: The distance solvent moved up the slide
Usually the entire plate/slide
Solute front: The distance solute moved up the plate
How far the solute moved up the slide
Possible there are multiple solute depending in the mixture
formula: —————>
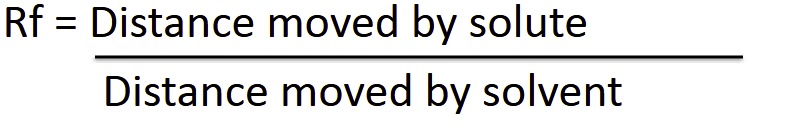
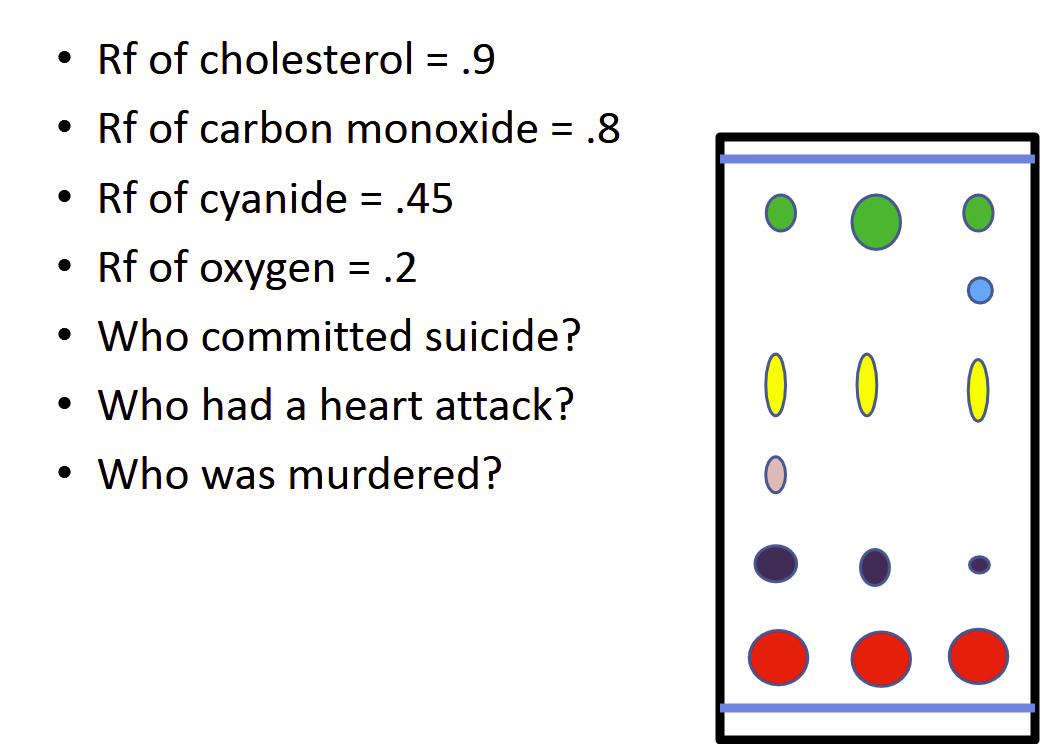
Chromatography-Thin-Layer Chromatography
Uses thin plastic or glass trays to identify
the composition of a mixturecheaper method
A BIG DOT ON THIN LAYER CHROMA, MEANS THE SAME
A SPIKE ON THE GRAPH, MEANS A HIGH CONCENTRATION
Method: Blood (solute) is placed onto the slide that is coverd in a solvent (usually some form of gel), and overtime the solute moves up the slide
The lightest/lowest atomic weight will be at the top of the plate, while the heaviest closest to the blood.
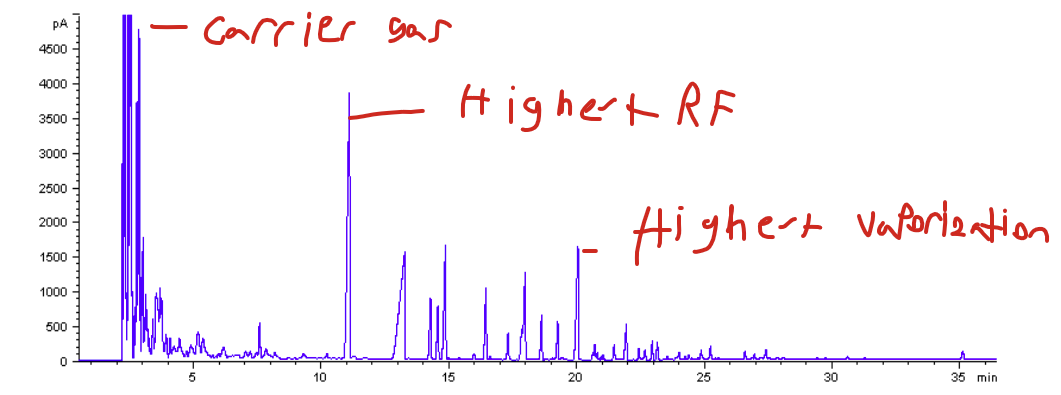
Chromatography- Gas Chromatography
Uses a specalized oven to evaporate a solute (blood), to get diffrent chemical concentrations, through the evaporated vapors
Blood is evaporated, and the vapor that is left over is mercury,cynaide,etc
The vapor is caught by a carrier gas
A very light gas, that is used to hold onto the vapor from the solute
THE PEAKS ON THE CHART ARE ORGANISED BY ATOMIC WEIGHT, HEAVIEST LAST, SMALLEST FIRST.
OPPOSITE TO THIN LAYER,
1st peak: The carrier gas
2nd Peak: Highest RF value
Essentially how far a compound travels
3rd: Highest heat vaporization
The heaviest atomioc weight
Vocab-Chromatography- chromatogram
results for chromatography, but not the statistics of the blood
People-Matthieu Orfila
founder of toxicology