Biology Khanacademy Unit 4: Cell communication and cell cycle
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
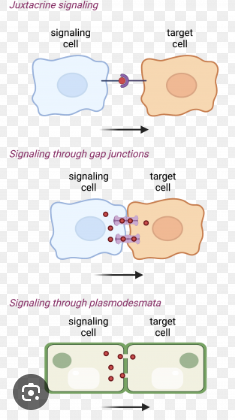
Direct Signaling/Direct Contact Cell-Cell Communication
Communication between cells facilitated by direct contact between them. In this type of signaling the ligands only travel from the environment of the first cell to the other.
A type of signaling used by multicellular organisms.
Paracrine Signaling
Cells communicating with multiple cells in a close proximity without coming into contact with them. Usually this is done by cells releasing molecules that diffuse through the space between the cells communicating.
In this type of signaling multiple signaling molecules are released (in order to communicate with multiple other cells). In addition to this the ligands released move from the releasing cells environment to an intermediate environment before binding to the other cell (and potentially being absorbed into its environment).
A type of signaling used by multicellular organisms.
This type of signaling is especially important during development when nearby cells have to tell each other what to do.
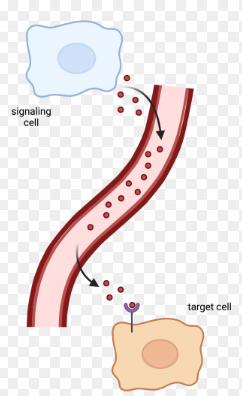
Endocrine Signaling
Communication through the release of hormones that travel through the blood stream and act on distant target cells. All cells get message in this type of signaling but not all cells will respond as some will not have the right proteins to bind to the signaling hormone.
A type of signaling used by multicellular organisms.
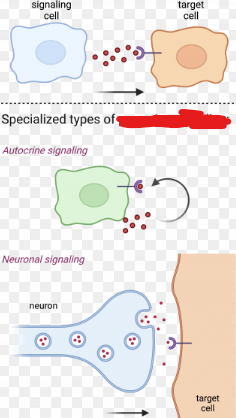
Autocrine Signaling
A cell signaling process that allows a cell to signal itself. Ligands are released by the same cell that holds receptors to which the ligands bind.
A type of signaling used by multicellular organisms.
This type of signaling is also important during development to reinforce the identity of cells.
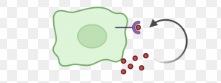
Receptors
Places where communicator molecules bind to on other molecules.
Ligand
Another name for a signaling molecule released by a cell.
Signal Transduction
The process of a ligand binding to a membrane receptor and exhibiting an intracellular response. Upon ligand binding receptor changes conformation and activates intracellular signaling molecules.
Hormones
Signals that are produced in one part of the body and travel generally far away in order to reach targets.
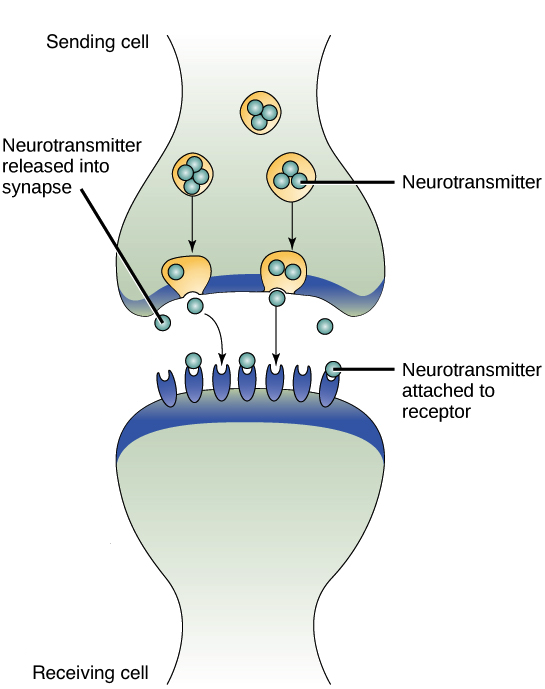
Synaptic Signaling
A type of paracrine signaling in which nerve cells transmit signals.
Quorum Sensing
A form of cell-cell signaling used by unicellular organisms. In this sensing unicellular organisms monitor the density of a population and when this density reaches a threshold level all members change their behaviour or gene expression together. This type of sensing produces and detects autoinducers.
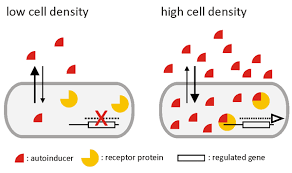
Autoinducers
Signaling molecules continually secreted by bacteria to announce their presence to neighbors (typically of the same species). Each species of bacteria have their own ______ with a matching receptor however some autoinducers can be produced and detected by multiple species of bacteria.
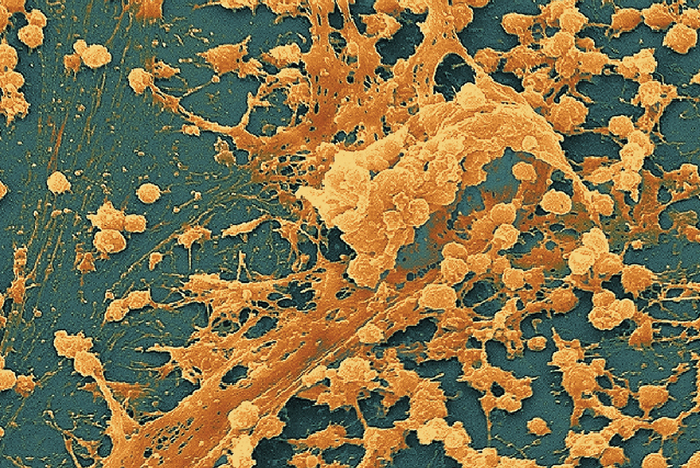
Biofilms
Surface attached communities of bacterial cells that stick to one another and to their substrate (underlying surface).
The picture attached is an example of a ________.
Paracrine Hormones
Hormones that are regionally active, made in one part of the body, and work with a small distance of the site of synthesis.
Autocrine Hormones
Hormones made at one cell and working on the same cell or cells in very close proximity. Closer proximity than paracrine hormones.
Endocrine Hormones
Hormones that get into the blood stream and work over a long distance.
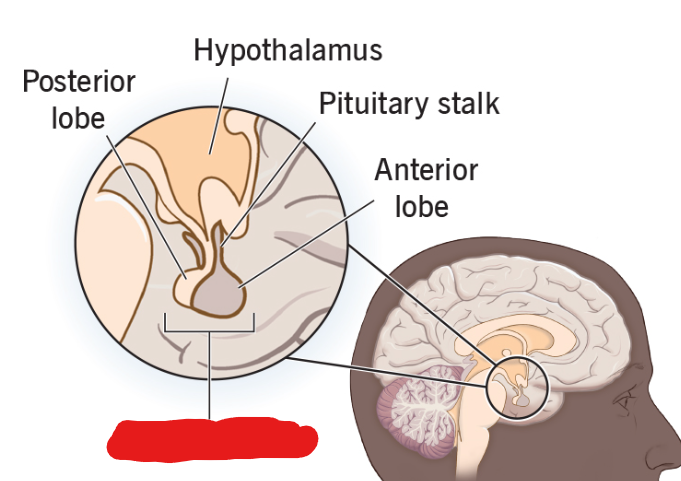
Pituitary Gland
Called the master gland. A part of the endocrine system. Makes hormones that work on other organs.
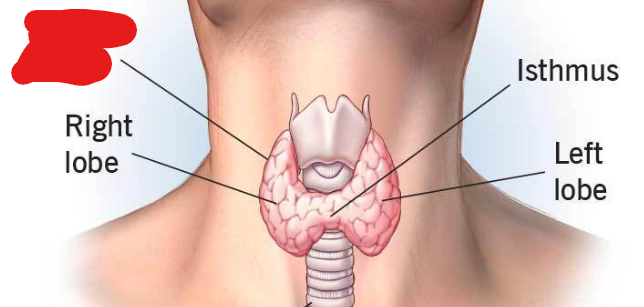
Thyroid Gland
Responsible for metabolism and other functions. Part of the endocrine system. This gland receives instructions from the pituitary gland.
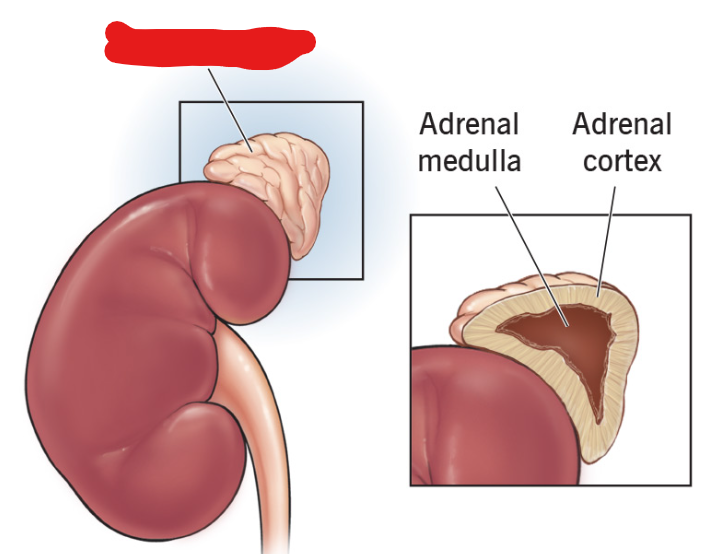
Adrenal Gland
Responsible for adrenaline functions and makes steroid hormones. Receives instructions from pituitary gland.
Pancreas
Responsible for making insulin and glucogon as well as other endocrine hormones. Receives instructions from pituitary gland.
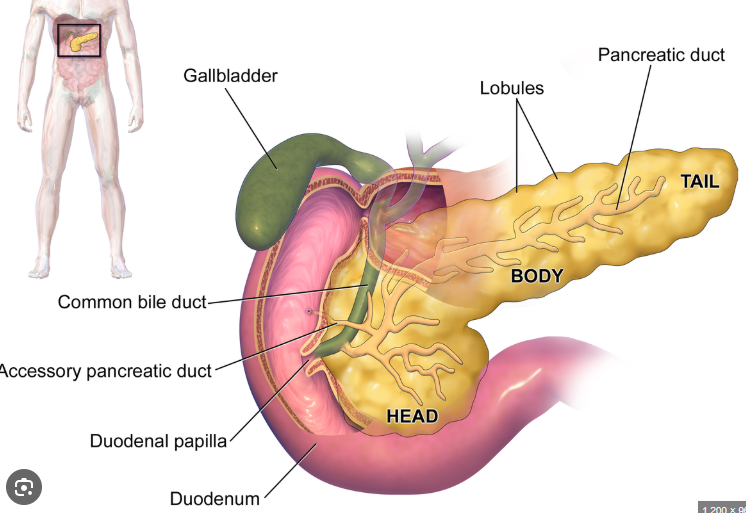
Plasmodesmata
Specialized junctions in a plant cell that allow direct cytoplasmic exchange between 2 cells. These contain a thread of cytoplasm extending through them and an even thinner thread of ER reticulum. They can also selectively dilate to allow passage of certain large molecules.
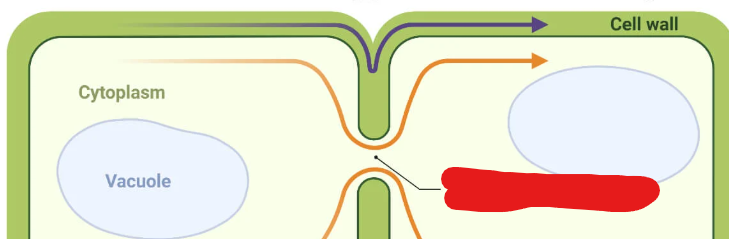
Vertebrates
Animals which posses a backbone or spinal column.
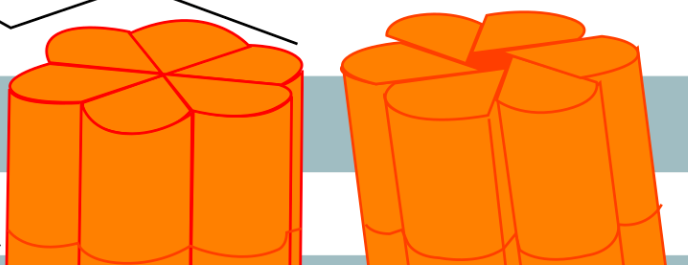
Gap junctions
Junctions between adjacent animal cells created as a result of 2 connexons, one on each of the cells, connecting. Connexons are themselves made up of 6 connexins.
When these open up in order to allow molecules through, they rearrange their configuration slightly sliding past each other and opening up a channel.

Connexons
Transmembrane integral proteins that connect in order to make gap junctions. These are made up of 6 connexins.
Connexins
Membrane proteins that, with 5 other of the same proteins, combine in order to form connexons that are used to make gap junctions between vertebrate animal cells.
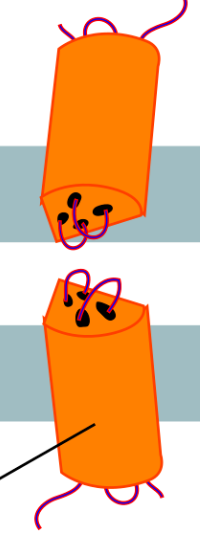
Tight Junctions
Junctions that create watertight seals between adjacent animal cells. At their site these junctions hold adjacent cells tightly against each other by using many individual groups of tight junction proteins called claudins which rearrange themselves in a structural way.
These junctions keep liquid from escaping cells.
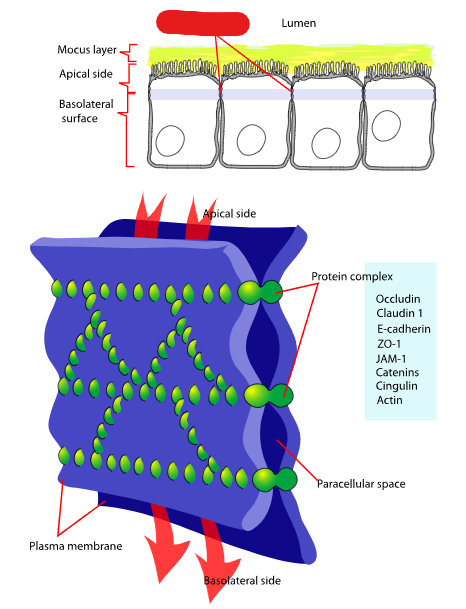
Claudins
Tight junction proteins that hold adjacent cells together and that rearrange themselves into a structure allowing them to do so.
Desmosomes
Molecules in animal cells that act as spot welds between adjacent epithelial cells. These are used to keep stretchy things like skin together.
Cadherins
Specialized adhesion proteins which are found on the membranes of 2 cells adjacent and which interact in the space between them, holding the membrane together.
_____ attach to the cytoplasmic plaque which connects to filaments that help anchor the junction.
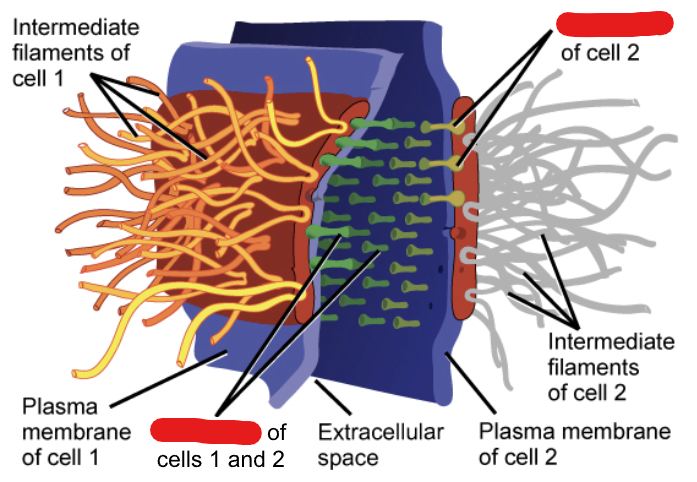
Cytoplasmic Plaque
A place on which cadherins attach to.
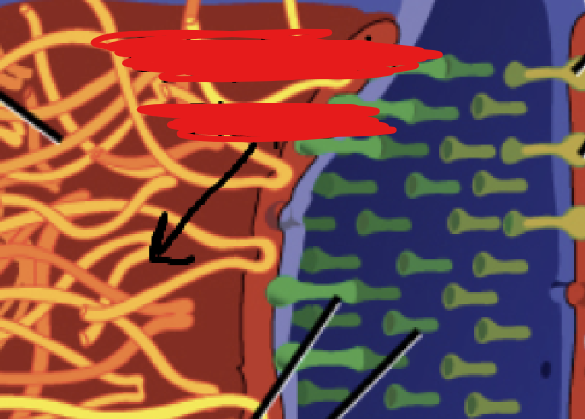
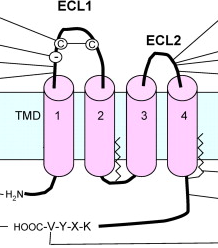
Membrane Receptors
Integral proteins embedded in the cell membrane and that take part in cell communication with outside environment. Many drugs target ___ ____. Different cells have different ____ ____. Each _____ _____ can only bind to a few ranges of liquids.
All ____ ____ are grouped into 3 types: Ligand gated ion channels, G-Protein coupled receptors and enzyme linked receptors.
The image attached outlines what ____ ____ are usually drawn to look like.
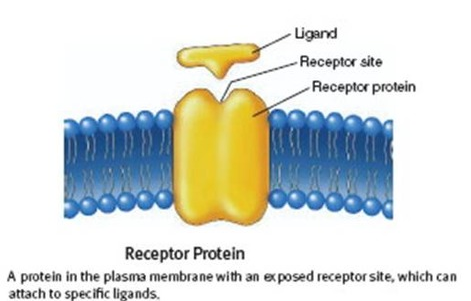
Ligand Gated Ion Channels
One of the 3 categories of membrane receptors. These are cell surface receptors that open (creating a channel) whenever a ligand binds to the channel. This allows ions to flow down their concentration gradient.
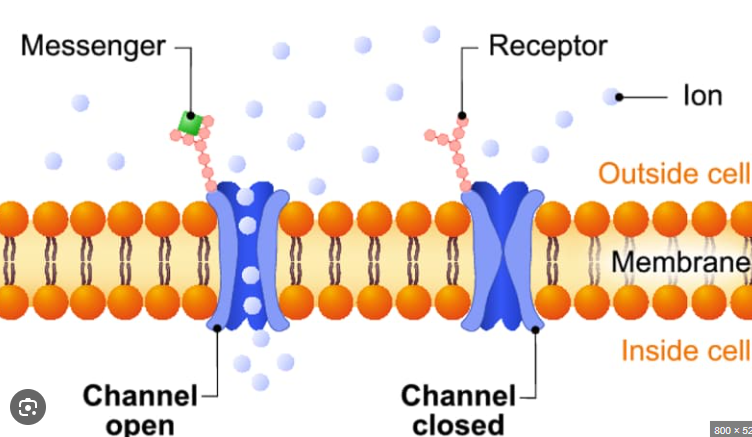
G-Protein Coupled Receptors/7 Transmembrane receptors
One of the 3 categories of membrane receptors. These are a large family of cell surface receptors that share a common structure and method of signaling.
These go through the plasma membrane 7 times hence one of their alternate names.
These interact with G proteins and are coupled to them hence on of their other alternate names.
When a ligand binds to these they undergo a conformational change, thus allowing G proteins to exchange a GDP molecule for GTP and thus becoming turned on.
Enzyme Linked Receptors
One of the 3 categories of membrane receptors. These are cell-surface receptors with intracellular domains associated with an enzyme.
Intracellular Receptors
Receptors found inside of the cell (in the cytoplasm or nucleus). In most cases their ligands are small and hydrophobic since they need to cross the plasma membrane.
These receptors cause change directly, i.e. by binding to the DNA and altering transcription themselves.
Cell Surface Receptors
Receptors found in the plasma membrane. These are membrane-anchored proteins and their ligands do not need to cross the plasma membrane.
They have, typically, 3 domains: an extracellular ligand binding one, a hydrophobic domain extending through the membrane, and an intracellular domain which transmits a signal.
G-Proteins
Proteins that bind to nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to form a nucleotide guanosine diphosphate (GDP). _ ____ attached to GTP is active, while ones bound to GDP are off. Some GPCR’s have already G-proteins bound to them.
These proteins are able to bind to GTP when GPCR (G-Protein Coupled Receptors) are activated via a ligand.
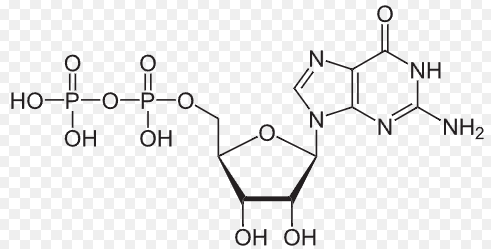
Nucleotide Guanosine Triphosphate - GTP
A molecule that is created by G-Protein coupled receptors from GDP.
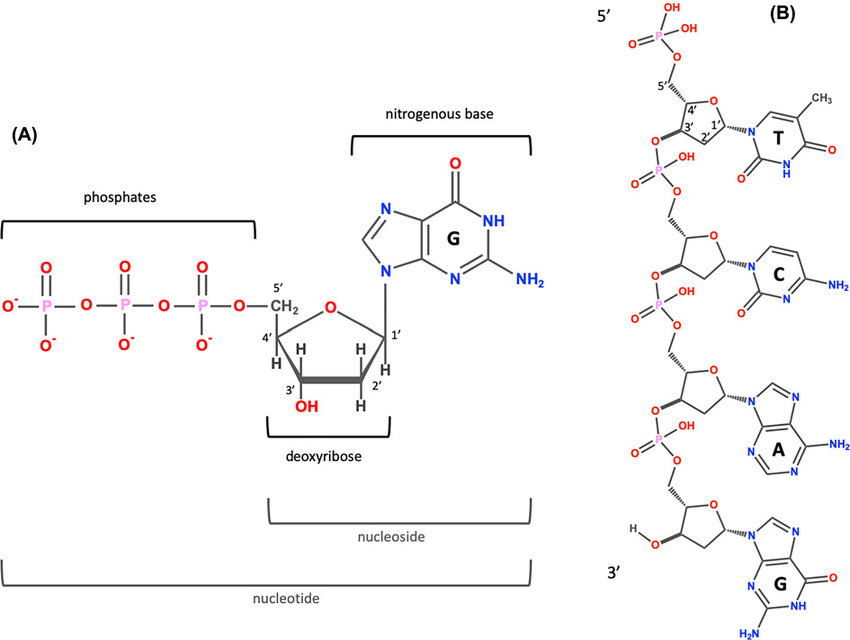
Nucleotide Guanosine Diphosphate - GDP
A molecule that is phosphorylated by G-Protein coupled receptors creating GTP.
Heterotrimeric G proteins
G proteins that associate with GPCR’s These hydrolyze GTP into GDP when they are turned on. These are turned on when a conformational change occurs in G Protein Coupled Receptors.
These have 3 substructures. Alpha, beta, and gamma. Alpha and Gamma units are lipid bound whereas beta is enclosed by the two.
When GPCR’s bind to a ligand they undergo a conformational change. The alpha unit of these proteins then let go of GDP and bind to GTP and become active. The beta and gamma units make a beta gamma dimer.
Alpha unit then finds a protein to regulate the function of. Most of the time it is the alpha unit which does this but it can also be the beta and gamma dimer created.
The targeted protein then relays the signal.
This process ends when the ligand on the GPCR is unbounded, and a new ____ ____ ____ that is inactive, and has a GDP molecule, binds to the GPCR. The cycle then restarts.
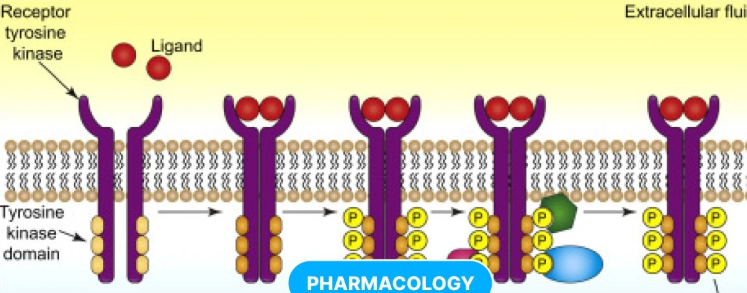
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
A class of enzyme-linked receptors found in humans and other species.
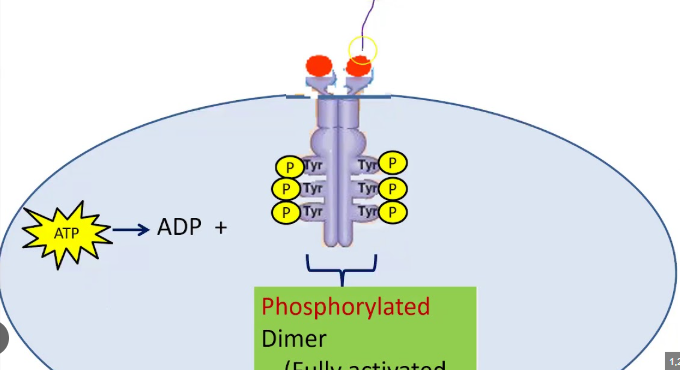
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling (RTK Signaling)
Process of signaling molecules binding to a pair of nearby receptor tyrosine kinases and the two RTK’s dimerizing, attaching phosphates to each others tyrosines in their intracellular domains, with the new phosphorylated tyrosine transmitting the signal to other molecules in a cell.
Steroid Hormones
Small hydrophobic ligands that can pass through the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors in the nucleus or cytoplasm.
These can be primary messengers.
Image attached shows examples of a few of these.
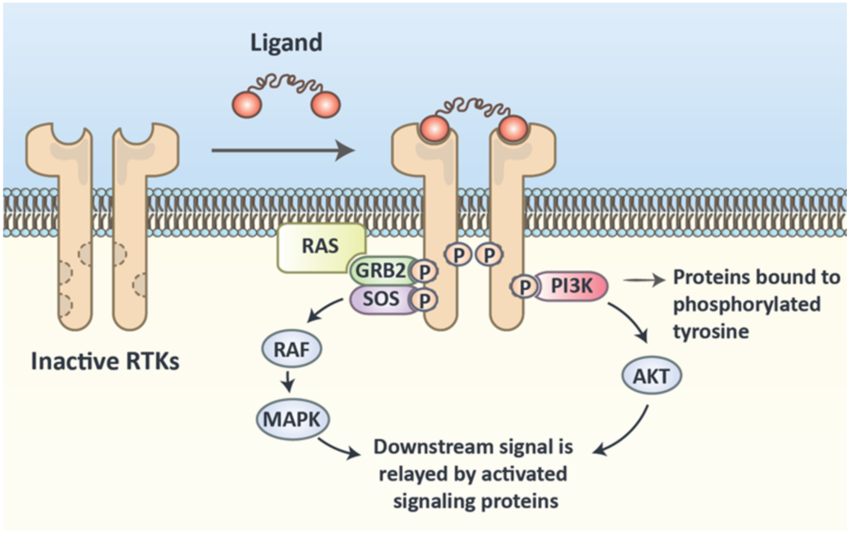
Intracellular signal transduction pathways
The chain of molecules that relay signals inside a cell. Binding of ligands initiates there. Basically ligands bind to receptor which releases ligands that binds to another receptor and so on.
Image attached outlines an example of a ___ ___ __ __
Upstream
Molecules and events that come earlier in the relay chain.
Downstream
Molecules and events that come later in a relay chain.
Phosphorylation
One of the most common tricks through which molecules turn on and off. This reaction is catalyzed by kinases. _____ can both activate or deactivate.
Image attached shows an example of the _____ of ADP.
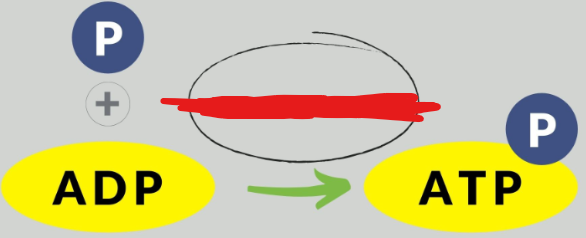
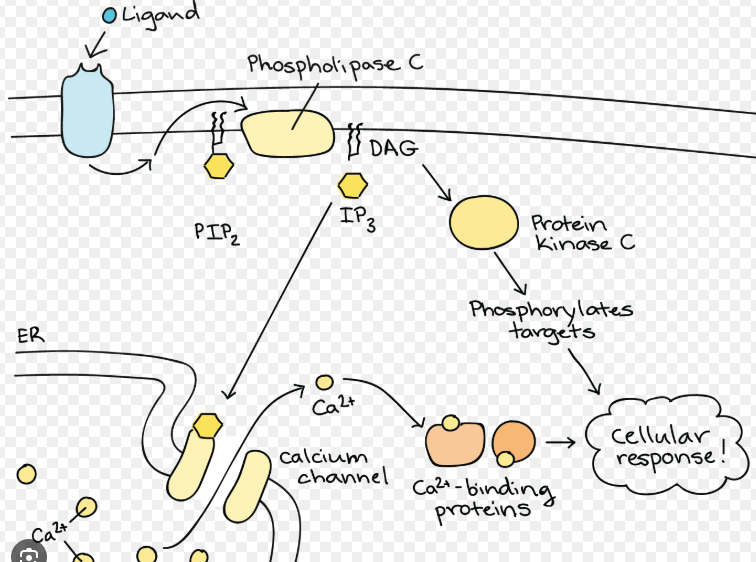
Second messengers
Small non-protein molecules that pass along a signal initiated by the binding of a ligand to its receptor. Ca2+ is an example. These are secondary and used after the ligand binds to the main receptor.
Hormones that can’t cross the plasma membrane use these messengers.
Phosphatidylinositols
Phospholipids which can be phosphorylated and snipped in half releasing 2 fragments which act as second messengers.
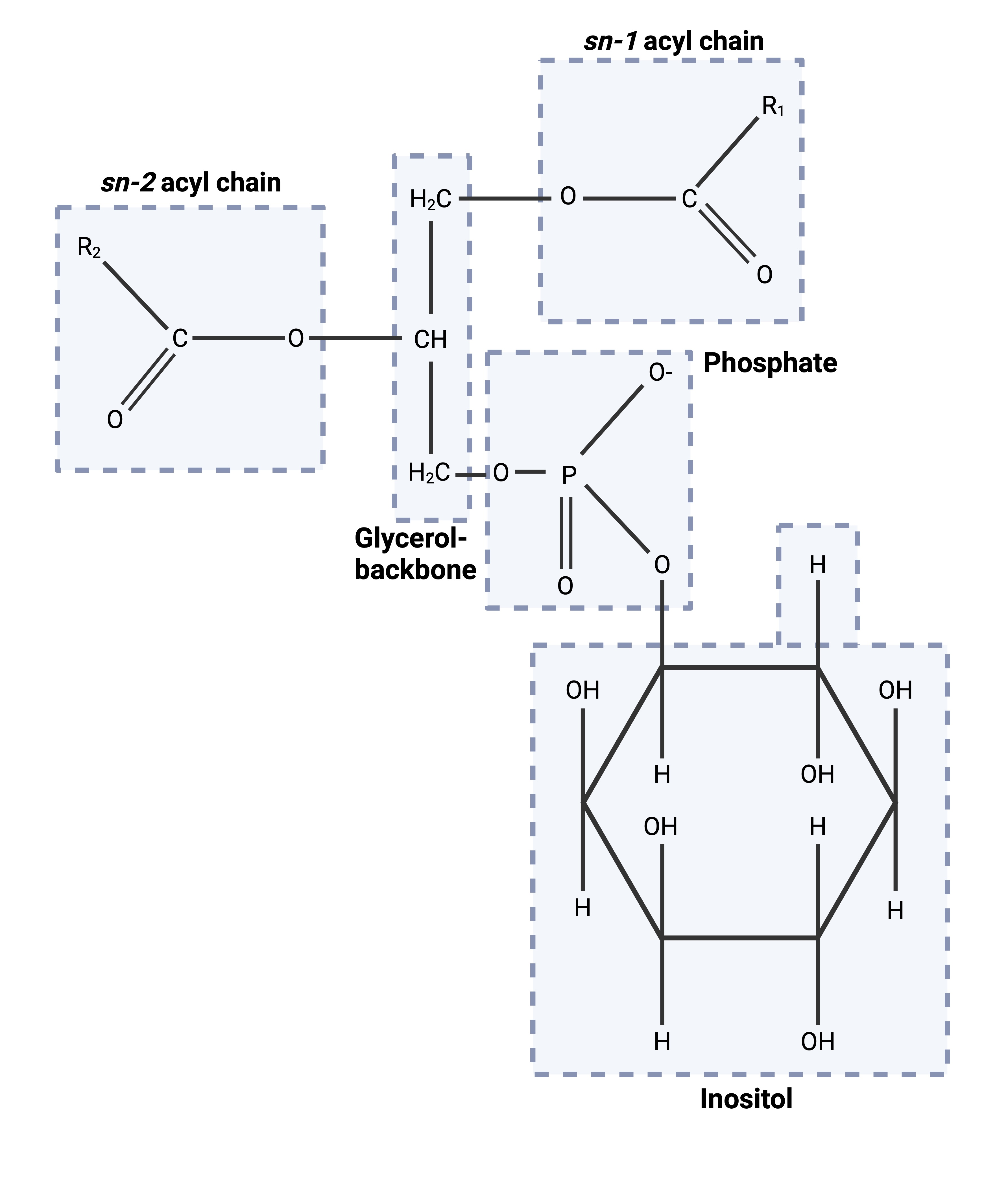
Signal Amplification
The process of a hormone binding to a receptor and setting off a chain reaction producing a lot of a secondary messenger and resulting in less hormone being required to activate the original signal/signal the original hormone that was the target.
Primary Messengers
Messengers that are able to cross the plasma membrane without the need to use secondary messengers.
Gene expression
The process in which information from a gene is used by the cell to produce a functional product.
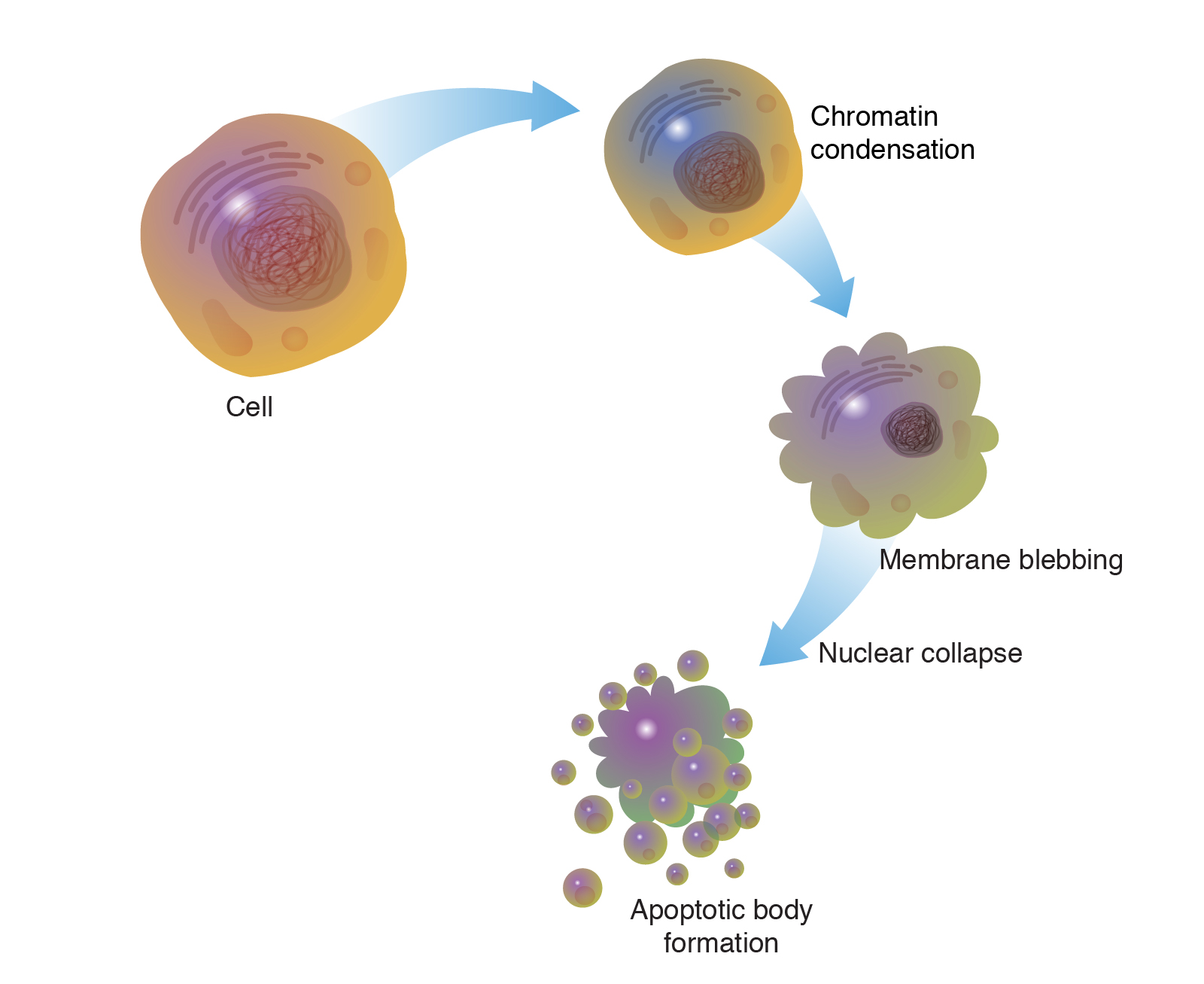
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death. Allows the cell to die in a controlled manner preventing the release of potentially damaging molecules from inside the cell.
Homeostasis
The process by which humans maintain a constant internal temperature, constant blood pressure, and in general regulate their own bodies. The tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant, internal environment. This can also affect human behaviour.
Negative Feedback Loop
Loops that act to oppose stimuli, or cues, that trigger them. Used in homeostasis to bring values back to set points. The process of these are stimulus→sensor→control→effector.
In general there exist 2 ____ ____ loops for each variable. One to lower it and one to raise it.
Set Points
In the context of homeostasis. A set value at which a certain variable, relating to the body, must stay, i.e. internal temperature has a ____ ____ of 37.0 degrees celcius. These can vary slightly over 24 hours.
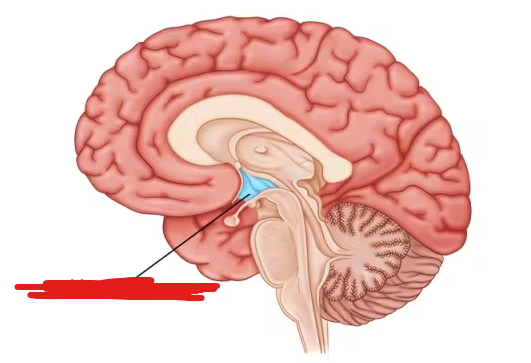
Hypothalamus
The region of the brain that maintains a constant temperature of the body, and in general, performs homeostasis/regulates it.
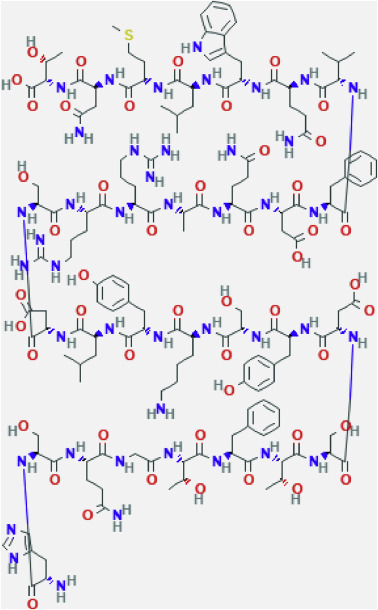
Insulin
A molecule that decreases the concentration of glucose in the blood. Converts glucose into glycogen, a storage molecule in the liver. Released by beta cells in the pancreas.
Picture attached shows a fragment of the molecule.
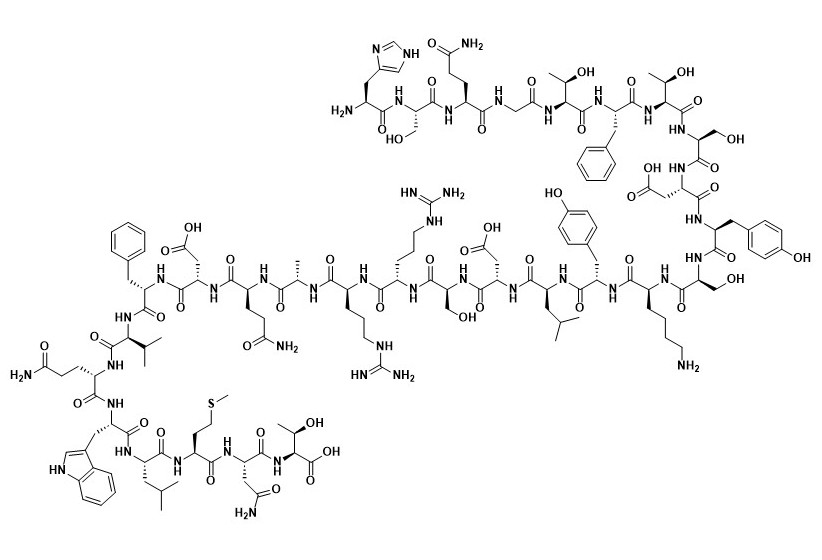
Glucagon
The opposite of insulin. Increases the concentration of glucose in the blood if one hasn’t eaten in a while. Released by alpha cells in the pancreas.
Picture attached shows a fragment of the molecule.
Positive Feedback Loop
Loop that amplifies a starting signal. Found in the processes that need to be pushed to completion. An example of such loops is in child birth when oxytocin increases uterine contractions.
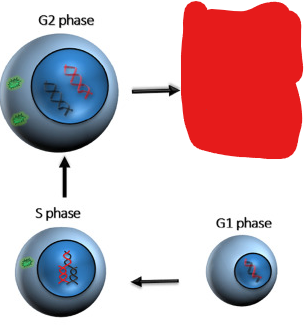
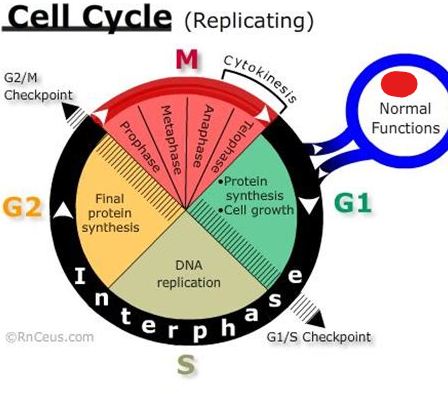
Interphase
Th stage of a cell’s life cycle at which it spends most of its time. Consists of different sub-phases. This phase is categorized by the cell both replicating its DNA and growing in preparation for cell division.
Mitosis
The process by which the nucleus of a cell turns into 2 nuclei and a cell is replicated.
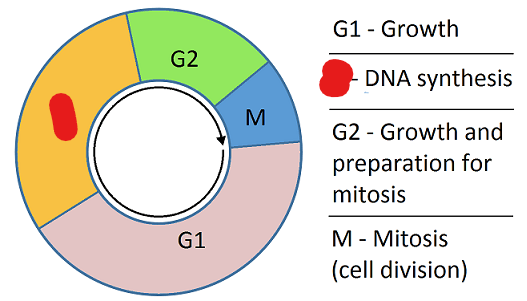
First Gap Phase/G1 Phase
The sub-phase of interphase wherein a cell grows in size for the first time.
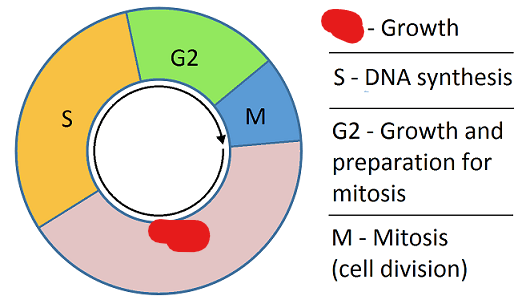
Synthesis Phase/S-Phase
The phase at which genetic info i.e. DNA is replicated and so are chromosomes. During this phase centrosomes are also replicated all to prepare for mitosis.
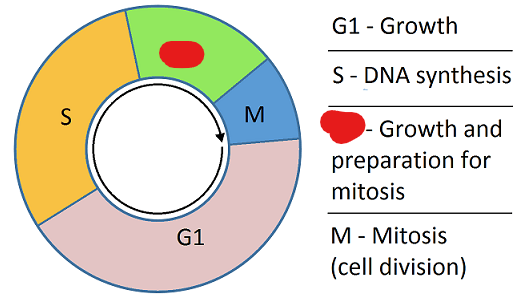
Second Gap Phase/G2 Phase
The second growth sub-phase during interphase. Occurs after the S-Phase. After this sub-phase mitosis is able to occur. This phase is done in preparation for mitosis.
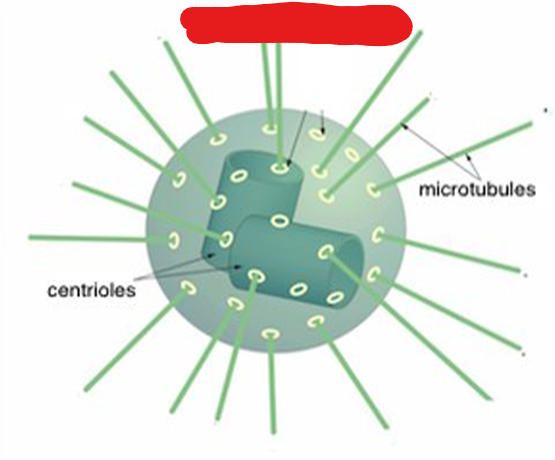
Centrosome
An important part in a nucleus needed for mitosis to occur. Plant cells typically don’t have these but rather a have a type of microtubule organizing centre.
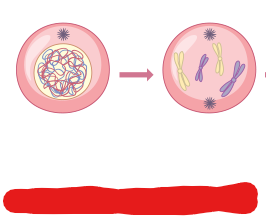
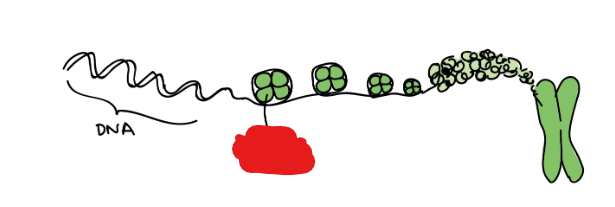
Chromatin
A complex of DNA ,RNA, and protein found in eukaryotic cells. This complex serves to package long DNA molecules into compact linear strands also called chromatids or chromosomes. These strands serve important roles during the S-Phase.
These also include histones.
Chromatid
Compat and dense linear strand of DNA created by Chromatins. These are replicated during the S-Phase of interphase resulting in two sister ______.
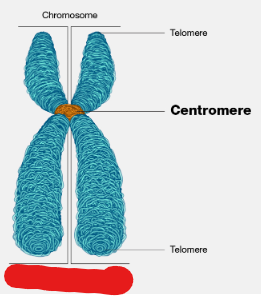
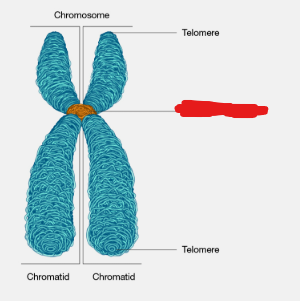
Chromosome
One, or, depending on the phase of the cell life cycle, a pair of chromatids bound together by their centromere, that are, themselves, made up of DNA.
Image attached outlines a ______ that consists of 2 sister chromatids.
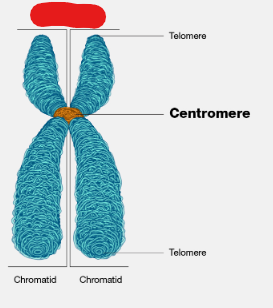
Centromere
The site at which two sister chromatids are bound together in a chromosome made up of two chromatids.
0th Gap Phase/G0 Phase
The phase that cells which divide slowly, or not at all, enter. In this phase a cell is not growing but just performing its regular functions. This phase is permanent for some cells. Cells sometimes enter this phase from the first gap phase i.e. G1 phase.
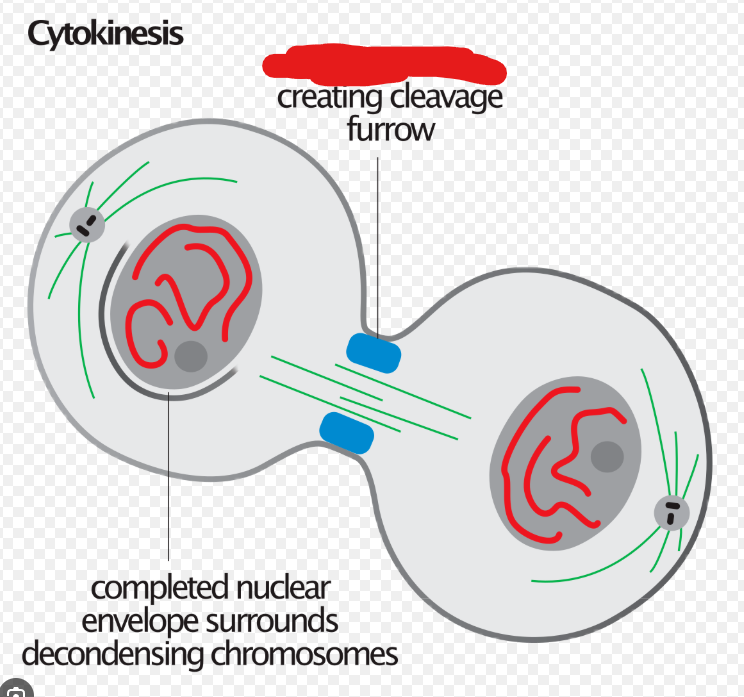
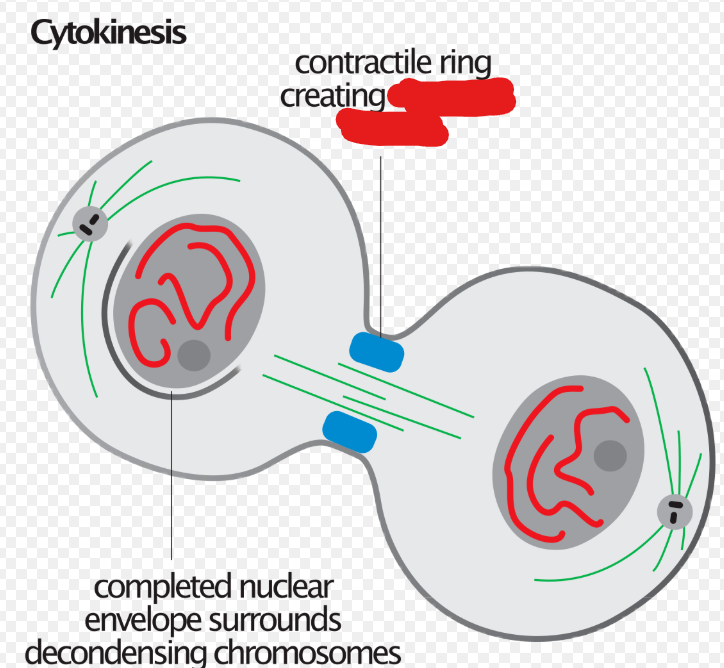
Cytokinesis
The duplication of the cytoplasm of a cell. Usually begins just as mitosis is ending sometimes with little overlap. There are 2 types of ______. Animal ____ and Plant _______
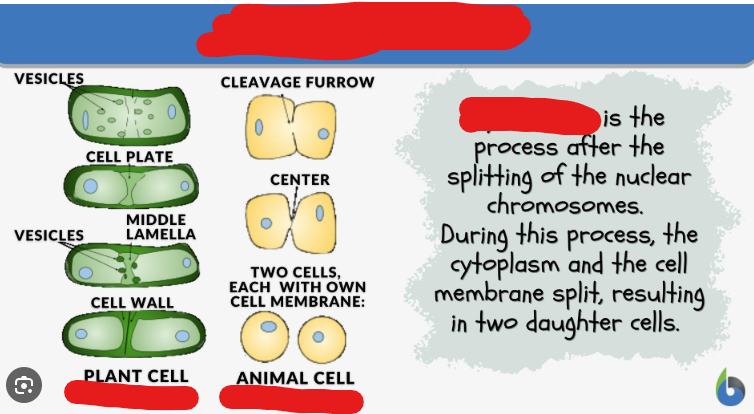
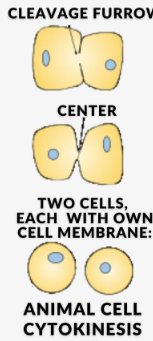
Animal/Contractile Cytokinesis
The cytokinesis that occurs in animal cells. In this process contractile rings, which are a band of cytoskeletal fibers, contract inwards and pinch the cell into 2.
Plant Cytokinesis
The building of a new structure down the middle of a plant cell, this structure being called the cell plate, that then sections off the two different parts and allows them to become 2 fully new autonomous cells.
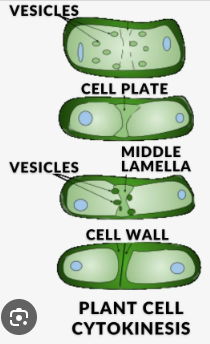
Cell Plate
A structure made up of plasma membrane and cell wall components that is built during plant cytokinesis and serves to section off 2 areas that will be new cells.
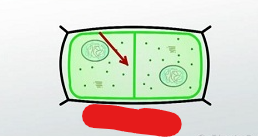
Actin/Contractile Ring
A band of cytoskeletal fibers that contract inward and pinch animal cells in 2 to duplicate them.
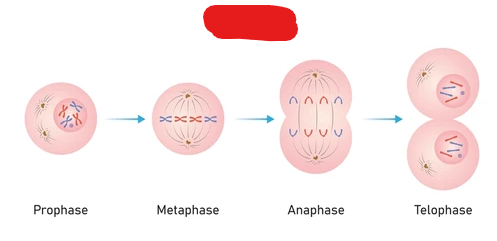
Prophase
The phase during mitosis at which chromatin turns into chromosomes, centrosomes move to opposing sides of the cell, and the nuclear envelope starts to disappear. Additionally the mitotic spindle begins to form and capture as well as organize chromosomes.
Centrioles
Cylindrical like structures present in pairs within centrosomes.

Microtubules
Structures that resemble ropes which are used by centrosomes on centromeres in order to pull apart sister chromatids.
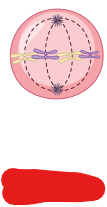
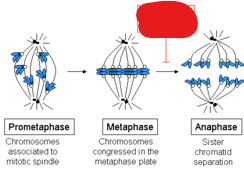
Metaphase
The phase at which chromosomes are in the middle, the nuclear envelope has fully disappeared, and centrosomes have their microtubules attached to centromeres.
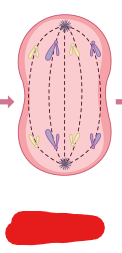
Anaphase
The phase categorized by the splitting apart of sister chromatids by the microtubules of centrosomes.
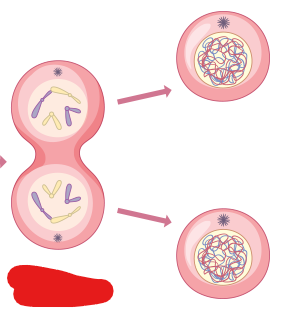
Telophase
The phase categorized by the forming of new nuclear membrane around separate chromatids on 2 sides of the cell. This phase is performed to create 2 new nuclei. Additionally chromosomes de-condense back into chromatin and the mitotic spindle breaks down.
Mitotic Spindle
A structure made of microtubules that begins to form during prophase. This grows between 2 centrosomes as they begin to move apart and then captures and organizes chromosomes.
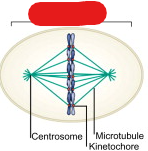
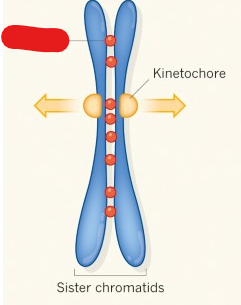
Kinetochore
A patch of proteins found on the centromere of each sister chromatid. Microtubules bind to these in metaphase and use them to pull chromosomes apart in the anaphase.
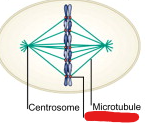
Kinetochore Microtubules
Microtubules that bind to a chromosome during mitosis.
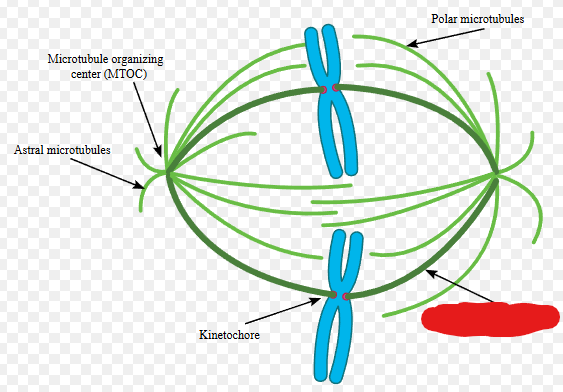
Metaphase Plate
A term for the plane where chromosomes line up during metaphase.
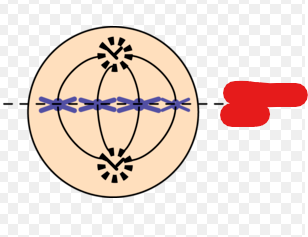
Spindle Checkpoint
The point at which checking is done by a cell. This point is during metaphase and right before anaphase in order to ensure all chromosomes are on the metaphase plate with kinetochores attached to microtubules.
This checkpoint checks for
Chromosome attachment to spindle at metaphase plate
Cleavage Furrow
The indentation made on a cell as the actin/contractile ring acts on it during cytokinesis.
Genome
A cell’s set of DNA. Most often all cells in an organism share it and hence you can say the organism’s ________.
Histones
Specialized proteins that help organize DNA and give it structure. These proteins are present within chromatin where negatively charged DNA can wrap around them.
Diploid
Consisting of one or multiple pairs of chromosomes (not necessarily homologous). A ______ cell has 2n amount of chromosomes where n is any positive integer.
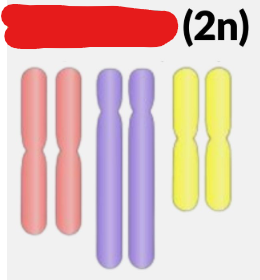
Haploid
Consisting of one or multiple chromosomes which are not in pairs. A ______ cell has n amount of chromosomes where n is any positive integer.

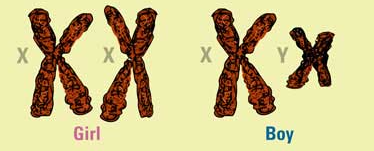
Sex Chromosomes
The chromosomes that determine a person’s biological sex.
In humans: XX for female, XY for male. A rare exception to the rule of homologous pairs of chromosomes in the context of humans.
The picture attached outlines the ____ ____ present in humans.
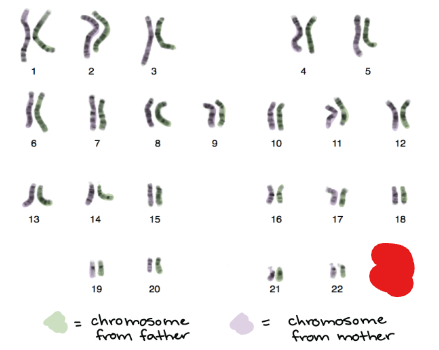
Autosome
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. In the context of humans the other 44 ones.
The picture attached outlines the _______ present in humans.
Cohesins
Proteins that keep sister chromatids attached to each other.
G1 and S Phase Checkpoint
The checkpoint activated before the S phase and at the end of the G1 phase in order to prevent malfunctions when going into synthesis.
During this checkpoint cyclins D and E activate CDKs 4 and 2 respectively which phosphorylate Rb. Inhibiting DNA replication.
After this Cyc A is produced and binds to CDK 2 which activates DNA replication and allows the S phase to occur.
If CDK 2 is not activated by Cyc A cell will go into G0 Phase which is a regulatory phase. Some cells stay in this phase forever while some go to the S phase if conditions become right again.
This checkpoint checks for
Cell size
Nutrients
DNA Damage
Growth Factors
G2 and M Phase Checkpoint
The checkpoint activated before mitosis and during the G2 phase in order to prevent malfunctions when going into mitosis.
During this checkpoint Cyc B is produced which binds to CDK 1 and allows mitosis to occur.
This checkpoint checks for
DNA Damage
DNA Replication Completeness
If errors are detected cell pauses at the G2 checkpoint to allow for repairs. If errors are unrepairable apoptosis will occur most of the time.
Kinase
A molecule that adds a phosphate group to another molecule.
Cyclin-Dependent Kinases - CDK
Kinases that are dependent on cyclins in order to activate. These, like other kinases, phosphorylate other molecules.
These are also present in the checkpoints that regulate the cell cycle.
Cyclin
Molecules that activate ____-dependent kinases which phosphorylate other molecules.
These are present in the checkpoints that regulate the cell cycle.
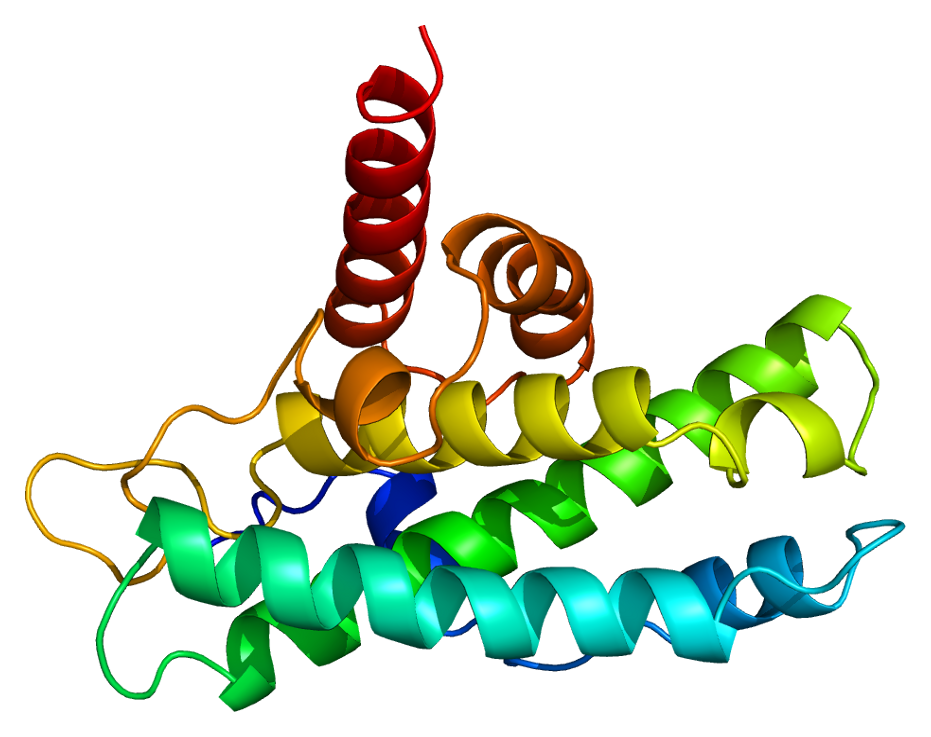
Retinoblastoma protein - Rb
A protein that is activated to prevent a cell from dividing and inactivated to allow for DNA replication. This includes the DNA replication that occurs during the S phase of interphase. This is a tumor suppresant molecule.
Picture attached outlines the structure of this protein.