[1.1] Anti-cancer drugs
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Cancer
neoplastic disease
term used for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and can invade other tissues due to mutations in the DNA of cells
Cyst
abnormal sac or closed cavity filled with liquid or semisolid matter; movable
Tumor
mass that is observed as a lump in a body; neoplasm; non-movable
Inflammatory breast CA
no lump; but is still cancer
makes the skin on the breast look red and feel warm
the affected breast may become larger or firmer, tender, or itch
Signs and Sx of Inflammatory Breast CA
sudden visible enlargement
discoloration
tenderness and pain
inward turning of nipple
Abilities of cancer cells
melts the collagen and connective tissues
capable of intravastion
capable of extravasation
capable of angiogenesis
Angiogenesis
process involving the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels
Cancer tx
Surgery
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Hormone therapy
Stem cell transplant
Chemotherapy
treatment of cancer by using cytotoxic and other drugs
Goals of chemotherapy
palliation
cure
adjuvant
neoadjuvant
Palliation
alleviation of symptoms; prolong life
Adjuvant
surgery and/or radiotherapy then chemotherapy; done after initial tx
Neoadjuvant
chemotherapy then surgery and/or radiotherapy
Most common side effects of chemotherapy
affects all rapidly proliferating cells
hair loss
loss of appetite
N/V
diarrhea
bone marrow suppression
fatigue
Sx manifest cell death*
Chemotherapuetic agents
Cell-cycle
phase-sppecific
phase-nonspecific
Cell-cycle non-specific
Phases of Cell Cycle
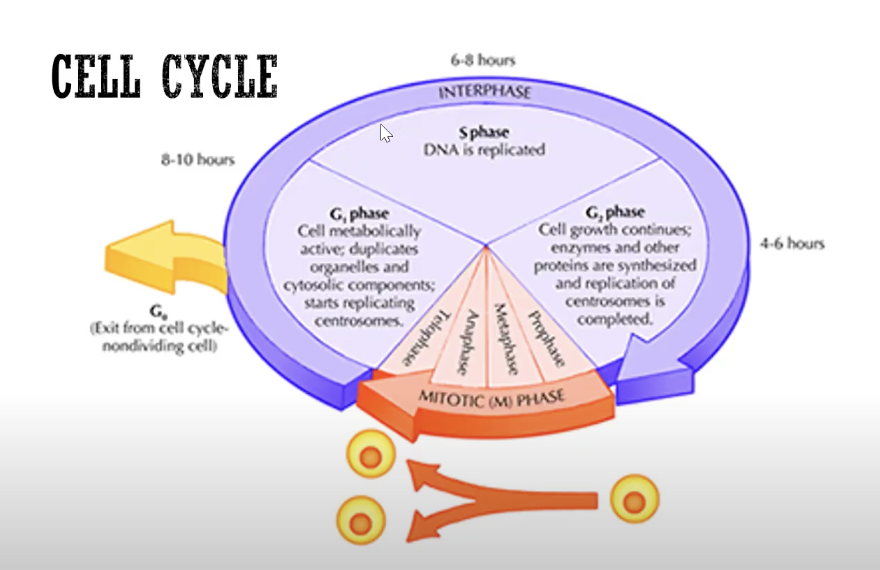
Phase-specific agents
most active against cells that are in a specific phase of the cell cycle
Drugs used for M-phase
Vinca alkaloids
Drugs used for G1-phase
Asparaginase
Prednisone
Drugs used for S-phase
Antimetabolites
Drugs used for G2-phase
Bleomycin
Etoposide
Phase-Non specific agents
effective while cells are in the active cycle but do not require that the cell be in a particular phase
Drugs used for Phase-Non specific
Alkylating agents
Antitumor antibiotics
Cisplatin
Cell-cycle Non-specific agents
effective in all phases including G0
Drugs used for Cell-cycle Non-specific
Nitrosoureas
Radiation
Plant alkaloids
Vinca alkaloids - microtubule damaging agents
Taxanes - microtubule damaging agents
Camptothecins - topoisomerase inhibitors
Podophyllotoxins - topoisomerase inhibitors
Vinca alkaloids
starts with “vin-”
Vincristine
Vinblastine
Vindesine
Vinorelbine
Vinca alkaloids MOA
promote depolymerization (disassembly) and prevent the rescue of microtubules
*detailed explanation:
blue tubulin (GDP-bound tubulin) is more unstable than green tubulin (GTP-bound tubulin)
prevent the rescue of destroyed microtubules → inhibiting mitotic spindle formation, chromosomal migration, and cell division
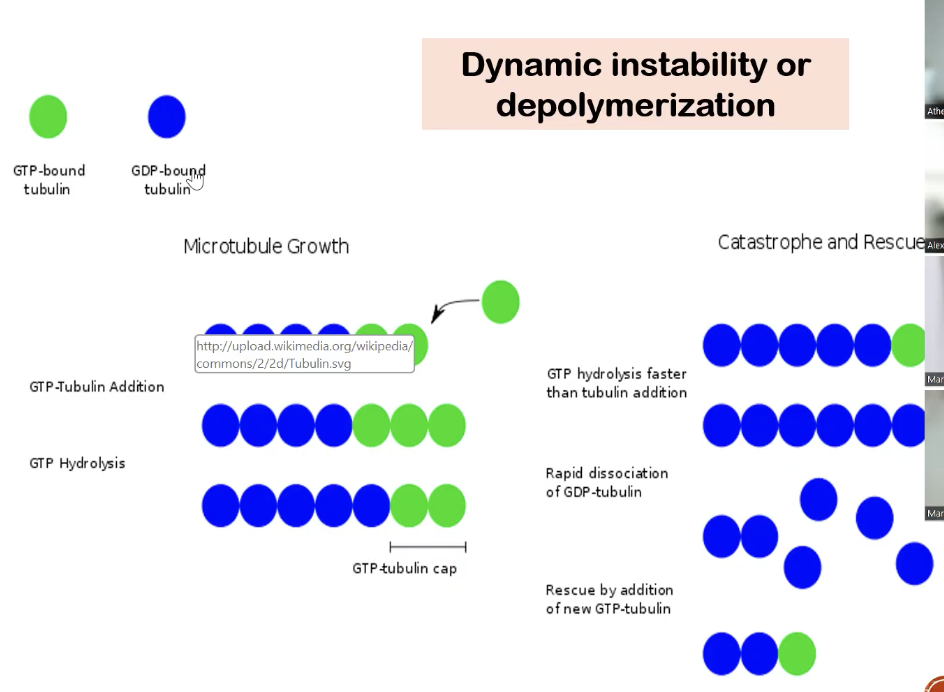
Vinblastine
used to treat testicular cancer which can cause alopecia, bone marrow suppression, N/V
Vincristine
used to treat Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Wilm’s tumor which can cause neurotoxicity or peripheral neuropathy
Taxanes
ends with “-taxel”
Docetaxel
Paclitaxel
Cabazitaxel
Taxanes MOA
bind to and stabilize microtubules by enhancing tubulin polymerization
forming weak polymers, clogged microtubules
Podophyllotoxins
ends with “-side”
Etoposide - G2
Teniposide - late S, early G2
Podophyllotoxins MOA
inhibits topoisomerase II causing double strand DNA breaks
Campothecins
ends with “-tecan”
Topotecan
Irinotecan
Campothecins MOA
inhibits topoisomerase I causing single strand DNA breaks
Irinotecan
pro-drug metabolized to an active topoisomerase I inhibitor, SN-38
Irinotecan
used to treat colon rectal cancer
Antibiotic Anticancer Agents
Anthracyclines
Bleomycin
Dactinomycin
Plicamycin
Mitomycin
Anthracyclines
ends with “-rubicin”
Daunorubicin
Doxorubicin
Idarubicin
Epirubicin
Anthracyclines MOA
intercalation → stabilize / inhibit topoisomerase II after it has cut and unwinded the DNA strand for replication → prevents topoisomerase from reattaching the broken ends of DNA
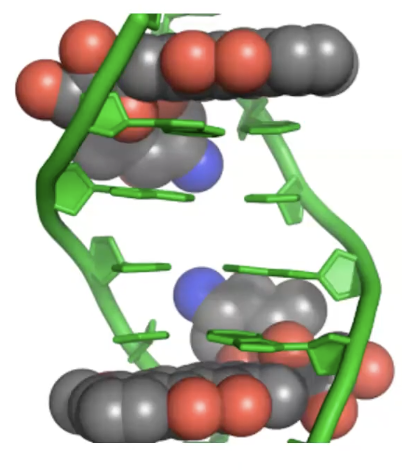
Intercalation
process by which drug slides between DNA base pairs causing additional DNA strand breaks
Anthracyclines
causes cardiotoxicity, total alopecia, bone marrow suppression, red or orange discoloration of the urine
Doxorubicin
used to treat BOLT cancer (breast, ovarian, lung, thyroid)
Daunorubicin, Idarubicin, Doxorubicin
used to treat acute leukemia
Dactinomycin MOA
intercalation between C-G base pairs → block RNA polymerase → inhibit DNA and RNA synthesis
RNA polymerase
an enzyme that is responsible for copying a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence
Dactinomycin
potent vesicant, used in pediatric cancers such as Wilm’s tumor (kidney CA) but may cause radiation recall
Radiation recall
the skin from prior radiation therapy can become red and appear damaged again
hyperpigmentation and thickening of the skin
Plicamycin
formerly Mithramycin used to treat testicular CA
Plicamycin
binds to DNA in the presence of Mg2+ or other divalent cations, where it interrupts RNA synthesis
Plicamycin
may cause bone marrow suppression, liver toxicity, hypocalcemia
Mitomycin
second line agent for metostatic colon cancer
Cervical cancer treatment combination
Bleomycin
Vincristine
Mitomycin
Stomach, pancreas, lung cancer treatment combination
Mitomycin
Doxorubicin
5-fluorouracil
Mitomycin MOA
metabolized intracellularly → binds to guanine residues → cross linking of DNA strands (alkylation)
Bleomycin
outstanding side effect is lung toxicity
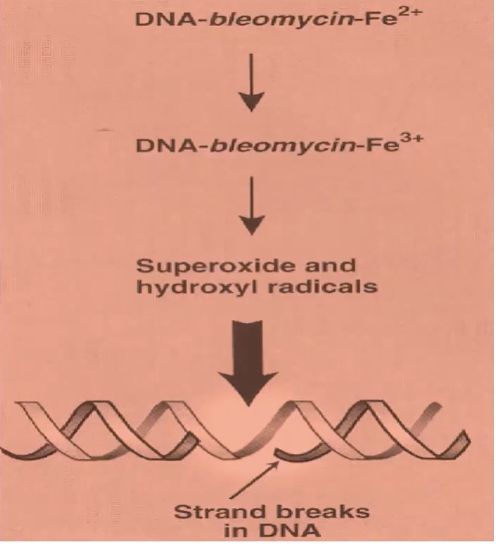
Bleomycin MOA
oxidation of DNA-bleomycin-Fe(II) complex → production of toxic free radicals → inhibit DNA synthesis
Hormonal Agents
SERM agents
SERM
selective estrogen receptor modulators
drug that have estrogen receptor agonist or antagonist properties depending on the target tissue
SERM drugs that have antiestrogen activity
Tamoxifen
Toremifene
Raloxifene
*used to treat breast CA
Tamoxifen, Toremifene, Fulvestrant
used to treat Hormone receptor-positive breast CA
Tamoxifen, Raloxifene
used for risk reduction for women at high risk of breast CA
Raloxifene
used to treat osteoporosis due to its estrogenic activity in bone
*since estrogen is used to increase bone density
Toremifene
may cause QT prolongation
Tamoxifen
may increase the risk for endometrial CA (estrogenic activity in endometrium)
SERM drugs
carry the risk for thromboembolic events
Fulvestrant MOA
estrogen receptor antagonist
detailed:
competitively binds to the estrogen receptor on tumors; blocking the action of estrogen to inhibit tumor growth
increases liver enzymes
SERM drugs, Fulvestrant
may cause hot flashes
Aromatase inhibitors
ends with '‘-zole’
Aminoglutethimide
Anastrazole
Letrozole
Aromatase inhibitors
used to treat breast CA in postmenopausal women
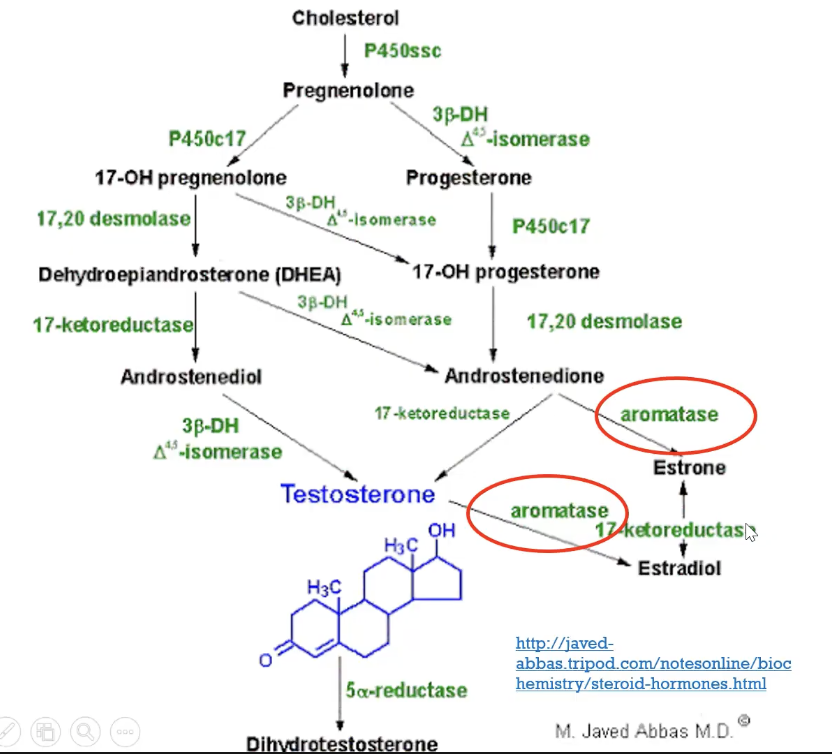
Aromatase inhibitors MOA
inhibits conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone
inhibits extra adrenal synthesis of estrone and estradiol
inhibits aromatase enzyme and prevent the conversion of androstenedione to estrone, testosterone to estradiol (aromatization)
overall: inhibit estrogen formation
Anastrazole and Letrozole
may cause hypercholesterolemia
Aromatase inhibitors drugs
Not benefit postmenopausal women
Increase risk for ischemic CV events
GnRH agonists
Leuprolide
Goserelin
GnRH agonists MOA
initially stimulating FSH and LH → negative feedback → reduced testicular synthesis
long term → suppression of LH and FSH → decrease in levels of testosterone, dihydroxytestosterone, estrogen
Leuprolide, Degarelix
used to treat advanced prostate CA
*MOA is different
*Leuprolide causes tumor flare
Goserelin
used to treat advanced prostate CA, advanced breast CA
Degarelix MOA
GnRH antagonist
acts more quickly than GnRH agonists
may cause wt gain
Degarelix
precaution for ADT (Androgen Deprivation Therapy) since it may increase risk for CV disease
Androgen Synthesis Inhibitors
Abiraterone
Ketoconazole
Androgen Synthesis Inhibitors MOA
inhibits CYP17 → inhibit formation of testosterone precursor
CYP17
enzyme required for androgen biosynthesis
aka 17a-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase
Abiraterone, Ketoconazole, Enzalutamide
used to treat metastatic castration-resistant prostate CA
Abiraterone
causes edema and fatigue
Ketoconazole
causes N&V, skin rash
First generation antiandrogens
ends with “-lutamide”
Flutamide
Bicalutamide
Nilutamide
First generation antiandrogens MOA
inhibit binding of androgens to the androgen receptor → block testosterone effects at the androgen receptor → prevent testosterone stimulation of cell growth in prostate CA
Antiandrogens
used for advanced prostate CA in combination with GnRH agonist or surgical castration
Flutamide
may cause hepatic failure
Nilutamide
may cause interstitial pneumonitis
Second generation antiandrogens MOA
pure androgen receptor signaling inhibitor which leads to cellular apoptosis and decreased prostate tumor volume
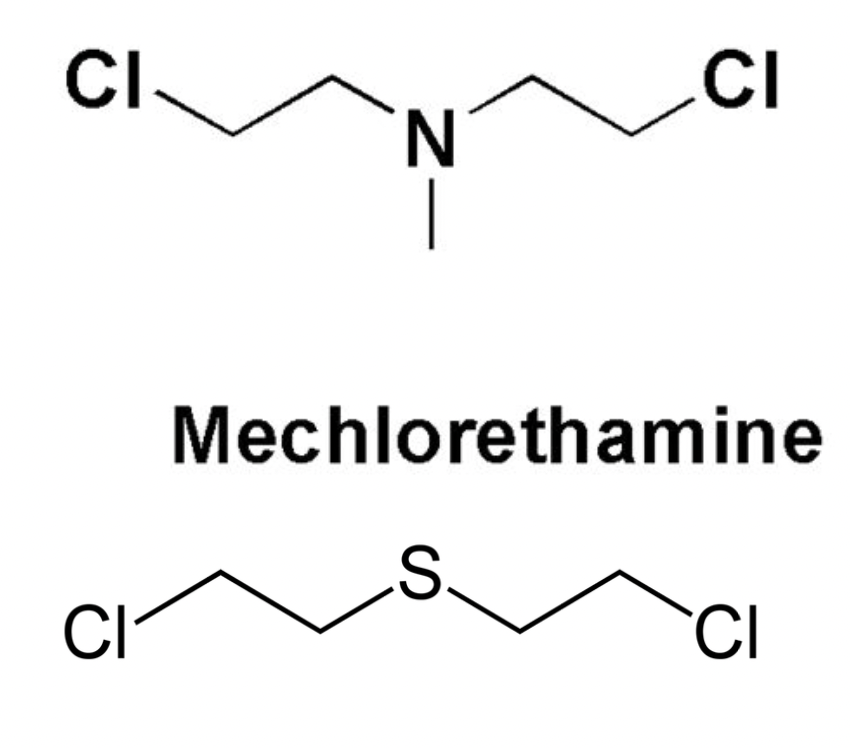
Mechlorethamine
nitrogen based analog of mustard gas - cytotoxic and vesicant agent
Alkylating agents MOA
The alkylating agents involve intramolecular cyclization to form an ethyleneimonium ion and/or carbonium ion (electrophilic center)
They react with a base such as N7 of guanine in DNA producing an alkylated purine
Alkylation of a second guanine residue results in cross linking of DNA strands
Alkylation of guanine can result in miscoding through abnormal base pairing with thymine or results to DNA strand breakage
Alkylating agents
Nitrogen mustards
Nitrosoureas
Alkylsulfonate
Platinum analogs

Mechlorethamine
used to treat Hodgkins lymphoma
Carmustine, lomustine
used to treat Brain tumors, melanoma & lymphoma
Cyclophosphamide
used to treat Breast, testicular, ovarian cancer, non- Hodgkin lymphoma
Ifosfamide
used to treat testicular, sarcoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Cisplatin, Carboplatin
used to treat Lung, ovarian, bladder and testicular cancer, and colorectal (Oxaliplatin)