Neurological emergencies and Weak'n'dizzy
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I love getting patients away from me :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Is our homie walking, talking, using the limbs, feel sensation, appear normal; any focal or general deficit, GCS, gradual or acute onset (protect the airway and stop progression)
Preliminary Neuro Workup - put ur eyeballs on the patient
Under 4 hours
Neuro deficits that present to the hospital ___________ from the onset is a STROKE ALERT
4 points (spontaneous, to speech, to pressure, no response)
GCS - eye opening
5 points (Alert/oriented, disoriented/confused, words only, sounds only, nothing)
GCS - verbal response
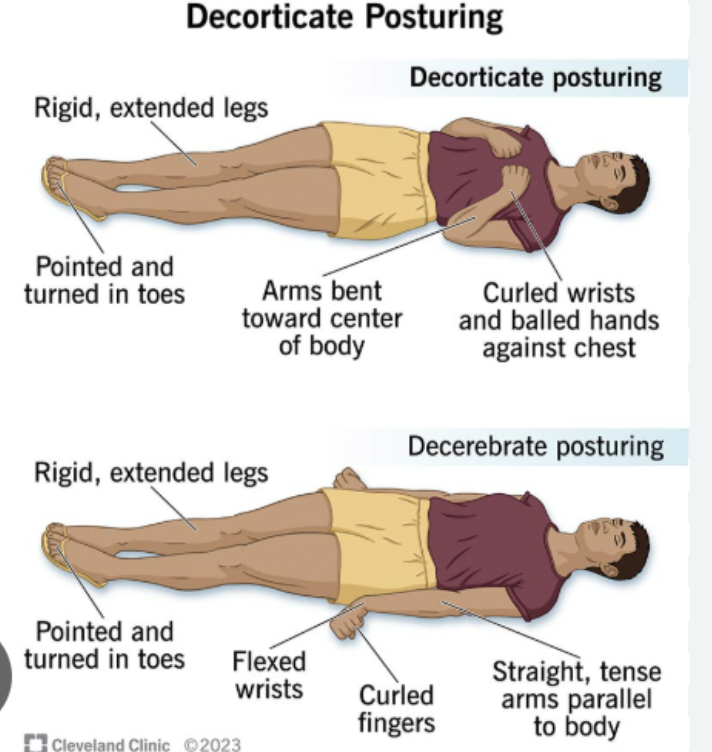
6 points (follows commands, purposeful movements to stimuli, flexion/withdrawal, abnormal flexion (decorticate), abnormal extension (decerebrate), no response)
GCS - motor response
Head CT (no contrast), CT angio (aneurysm), Brain MRI (cerebellar stroke - signs of central vertigo), spine CT/MRI, FINGERSTICK GLUCOSE, CBC, CMP, coags, lumbar puncture, ammonia, urine tox, ETOH, ASA, APAP, O2 supplementation, NPO (until dysphagia screen)
Neuro ED workup
O2 supplementation, NPO, monitor for airway
Protective measures in the ED
Strokes don’t affect the entire nerve (forehead and palpebral fissures are spared)
What is the difference between a stroke and bell’s palsy?
motor, sensory, cognition (responsiveness)
Focal neuro deficits of acute onset include
CT head no contrast (ACLS protocol is to have this done in 20 min, read in 45)
How do we differentiate ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic stroke?
Fingerstick glucose, Non-contrast CT, CBC, PT/INR, CMP, troponins (MIs can be concurrent), Tox screen, ETOH pregnancy, EKG, MRI (if cerebellar stroke is suspected), NIH stroke scale
Ischemic stroke workup
protect airway, elevate the head of the bed 30 degrees, manage HTN, Maybe thrombolytics
Management game plan for an ischemic stroke
Nicardipine, labetalol, esmolol (easily titratable)
Medications used to lower bp in a stroke
Over 220/120 (only lowered 15% in the 1st 24 hr)
In an ischemic stroke, the BP should only be lowered IF
BP above 185/110, Active bleeding, Last known well 4+ hours, acute intracranial hemorrhage, symptoms/signs of a SAH, CT has obvious hypodensity, prior ischemic stroke/head trauma (w/in 3 months), Acute posttraumatic brain infarction, intracranial/intraspinal surgery (w/in 3 months), GI malignancy or bleeding w/in 21 days platelets under 100k, current endocarditis, arterial puncture w/in 7 days, any anticoag usage
Exclusion criteria for thrombolytics
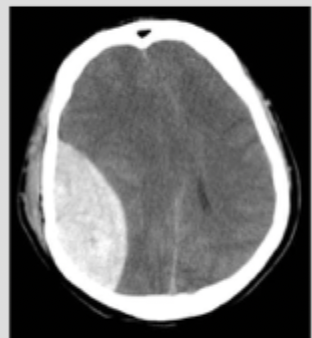
Epidural
What type of intracranial hemorrhage is characterized by LOC with a blow to the head followed by a lucid period and then a mental decline
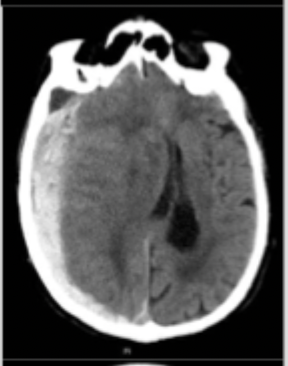
Subdural
What type of intracranial hemorrhage is characterized by an acceleration-deceleration injury sheering veins and more common in the elderly due to atrophy
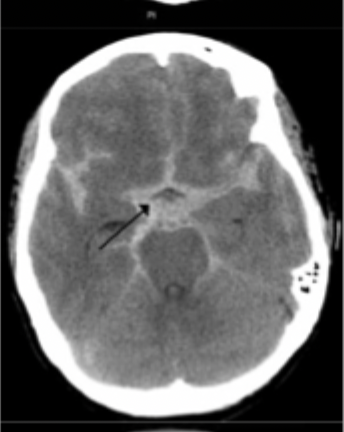
Subarachnoid
What type of intracranial hemorrhage is characterized by thunderclap HA, neck stiffness, star signs on CT and xanthochromia on lumbar puncture
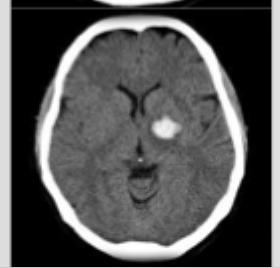
Intracerebral (intraparenchymal)
What type of intracranial hemorrhage that occurs due to hypertensive emergency, bleeding mass, or tumors
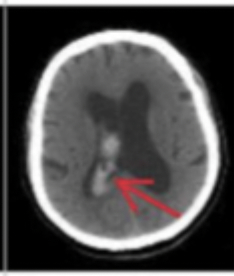
Ventricular
What type of intracranial hemorrhage is associated with both intraparenchymal and SAH?
Brain CT no contrast, fingerstick glucose, CBC, PT/INR, bleeding time, platelet function testing, CMP, troponin, tox screen ETOH, pregnancy, EKG, lumbar puncture (if CT is neg and a SAH is suspected)
Diagnostics for a hemorrhagic stroke
Elevated head of the bed to 30 degrees, protect the airway (get a full neuro before sedating), reverse any anticoagulation (FFP or whatever), blood pressure management, ICP management (mannitol or hypertonic saline), Hyperventilation (PaCO2 of 30-35), maybe a burr hole
Game plan for a hemorrhagic stroke
SBP of 140-160
In a hemorrhagic stroke, the BP should be lowered to
Opioids
What are we avoiding in HA treatment?
meningitis, encephalopathy, intracranial hemorrhage, mass-occupying lesion, temporal arteritis, CO poisoning, acute angle glaucoma
Must catch HAs in the ED
Traumatic/sudden/with exertion onset, AMS, seizure, fever, neurologic deficits, visual changes (unless a hx of migraines), anticoags, recent abx, immunosuppressants, no hx of similar symptoms, progressive symptoms, current/recent pregnancy, lupus, vasculitis, cancer
HA red flags
AMS, fever, neck stiffness, papilledema, focal neuro deficits
Red flag physical exam findings with a HA
CT brain w/o contrast (~100% sensitive for SAH within 6 hours)
Imaging for a HA (based on red flags)
RBC clearing (confounded by traumatic LP), xanthochromia, measure opening pressure as well
Lumbar puncture findings for a SAH (used after 6 hours)
1L of IV fluid, Toradol IV (after a CT), tylenol PO, reglan (metoclopramide) IV, Benadryl IV
Phase I of HA treatment in the ED
Mag IV, Solu-medrol (methylprednisone) IV
Phase II of migraine treatments
Pulsatile, one-day duration, unilateral, N/V, disabling intensity
What is the POUND mnemonic for migraines?
Altered mental status (AMS)
A change from baseline that can be the end state of almost any disorder
fingerstick, ABG/VBG, EKG, CBC, CMP, lipase, UA, urine tox, ETOH, ammonia, CK, ASA/APAP, troponin, lactate, anti-epileptic med levels (if there’s a hx), LP (AFTER HEAD CT), Head CT, Cervical CT, CXR, EEG
Work up for AMS in the ED - wide net (no reliable historian)
Spell lunch backwards → then look for an altered mental status or fluctuating course, Check inattention, is there an altered level of consciousness, Check for disorganized thinking
Describe the delirium triage screen
known epileptic not taking their medications
Most common cause of seizures
r/o toxicity or metabolic causes and punt to the PCP
What are we doing after our patients 1st seizure?

punt to neuro
What are we doing after our patients 2nd seizure?

brain trauma, infection, severe metabolic derangement, mass lesion, stroke
A secondary seizure can be an indication of
febrile (think meningitis)
Which type of generalized seizure typically occurs in patients 6-60 months, last less than 15 min and does not recur within 24 hours?
Eclampsia, pre-existing epilepsy, trauma
Seizures in pregnancy can be due to
intracranial hemorrhage (at the very least its a sign of a TBI)
A post traumatic seizure is what until proven otherwise?
Seizure precautions (tape blankets to bed rails), O2, IV access, vitals, fingerstick, check seizure med level (see if sub-therapeutic), r/o other conditions (infections, med, electrolytes)
Treatment plan for uncomplicated seizures
Status epilepticus
A single seizure lasting over 5 min OR 2+ with no recovery of consciousness between seizures
Lorazepam/diazepam IV + phenytoin/fosphenytoin or keppra (levetiracetam)
5-10 minute status epilepticus game plan

Versed bolus followed by drip 🥇, propofol/ketamine/phenobarb, intubate, EEG
15+ minute status epilepticus game plan

Fingerstick, ABG/VBG, EKG, CBC, CMP, UA, urine tox, CK, ETOH, Ammonia; MAYBE a head CT followed by an LP, lactate, antiepileptic medication levels
New onset seizure workup
LOC, disorientation, confusion, blank stare, poor balance, gait, post-traumatic seizure
What do we need to find out in the possible concussion hx?
NEXUS, Canadian C-spine rule (reminder C-spine can only be cleared on a sober, conscious patient)
What is used for adult cervical spine r/o?
PECARN (under 18), Canadian CT head algorithm (16+)
What are some algorithms for Head trauma
Punt to PCP, physical and cognitive rest, tylenol prn for 2 days, ondansetron prn for 2 days, beware of a 2nd head injury
Discharge instructions for a concussion

facial/scalp bruising, boggy scalp hematoma (goose egg), evidence of a depressed or open skull fracture, hemotympanum, “racoon eyes”, “battle signs,” otorrhea, rhinorrhea of CSF (halo sign)
Physical exam findings to look for for head trauma
under 13
Children with a GCS under _____________ should get imaging (general agreement per the book)
Muscle weakness is a neuro deficit, Fatigue/malaise is nonspecifc
Why is it important to determine what our patients mean by “weakness”
anemia, hypovolemia, orthostatic hypotension
Lightheadedness is often due to…
Vertigo
the loss of balance or the feeling that the room is spinning
CBC, CMP, TSH w/ T4, pregnancy, urine tox, cardiac eval, CXR, PFTs (outpatient)
General diagnostics for “weakness”
Anemia, HF, inability to oxygenate (V/Q mismatch), systemic infection, adrenal crisis, myxedema coma (super low thyroid hormone)
Emergent concerns for weakness
Location (general or localized), progression (acute, slow, remit/relapse)
What do we need to figure out about the weakness?
R/o stroke, spinal injury, or peripheral nerve injuries, secure the airway (1st priority), punt to a specialist
ER gameplan for weakness

Central vertigo
A dysfunction of the brain or brain stem leading to a mis-interpretation of peripheral stimuli
Peripheral vertigo
A dysfunction of the inner ear or vestibular nerve creating incorrect stimuli that is sent to the brain
vestibular migraine (most common), cerebellar/brainstem stroke (MOST IMPORTANT), posterior circulation TIA, cerebellar hemorrhage
Causes of central vertigo
BPPV (most common), vestibular neuritis, labyrinthitis, Meniere’s, perilymph fistula, superior canal dehiscence, vestibular schwannoma
Causes of peripheral vertigo
Associated Cranial nerve deficits, vertical nystagmus, ataxia
Central vertigo signs and symptoms
unilateral hearing loss, tinnitus, fatigable on repeat Dix-hallpike maneuver (aka nystagmus will slow), more intense, positional
Peripheral vertigo signs and symptoms
Head impulse test, nystagmus, test of skew, hearing loss
The HINTS+ exam can help determine peripheral vs central vertigo, what are the parts?
STROKE ALERT (if w/in 4hr window), brain CT no contrast, MRI (gotta check the cerebellum), admit
If central vertigo is suspected, what are we doing?
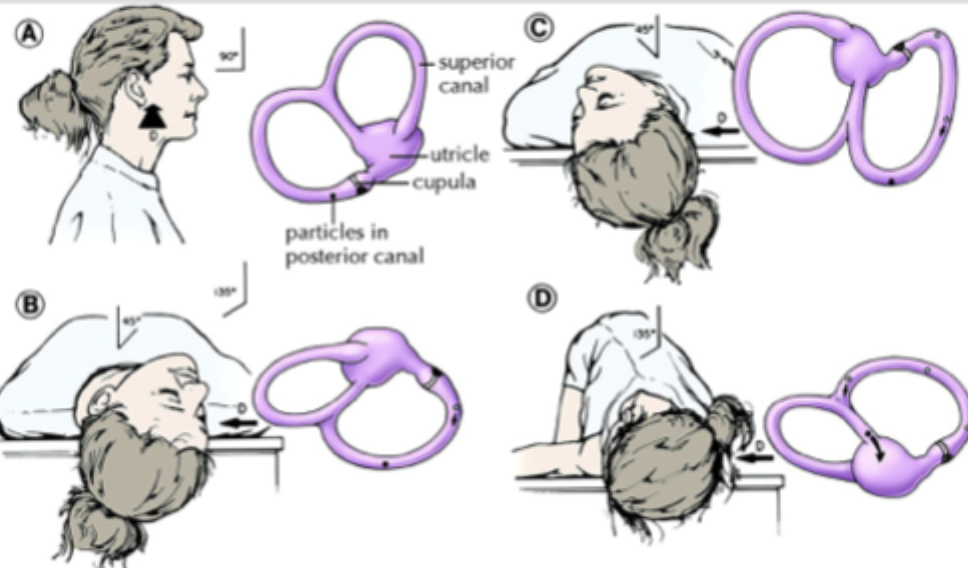
Epley maneuver (BPPV), antiemetics (meclizine), Anticholinergics (Scopolamine), benzos
Gameplan for peripheral vertigo
LOC or near-loc, recovery, family hx of sudden death, chest pain, palpitations, previous episodes
What should we find out in our hx if the chief complaint is “passing out?”
Vasovagal (situational syncope)
The loss of consciousness after a psychologically stressful event due to an increase in vagal tone leading to bradycardia, hypotension, and a lack of brain perfusion
syncope/presyncope
The LOC not related to psychologically stressful event
fingerstick, pregnancy, detailed physical (focus on cardiac and neuro), supplemental O2, vitals, IV access, EKG, CT head or spine if trauma
Work up for the syncopal patient
Congestive Heart Failure, Hematocrit (under 30%), EKG abnormality (nonspecific - prolonged QT, BBB, etc), SOB, SBP under 90
What is the San Francisco Syncope Rule?
Cardiogenic (structural, dysrhythmias), Reflex mediated (vasovagal, situational), Neurological (TIA, migraine, subclavian steal), orthostatic, psych, medication induced, seizure
DDX of syncope
SAH or ICH
Syncope + HA =
CVA/TIA or ICH
Syncope + neurologic deficit =
seizure, ICH, CVA
Syncope + confusion =
MI, PE, Aortic dissection
Syncope + chest pain =
AAA
Syncope + back/abdominal pain in an elderly patient =
ectopic pregnancy
Syncope + positive Hcg
punt to PCP if low risk, punt to hospitalist if high risk, NO exercise until a stress test, seizure precautions (no driving, swimming, etc)
Disposition for syncope
