Short-Run and Long-Run Aggregate Supply Quiz Review
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Aggregate Demand (AD)
the amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchased at all possible price levels
What causes aggregate demand to shift?
Consumer spending, Investment spending, Government spending, Net exports
Aggregate Supply; Short-Run (SRAS)
A curve repersenting the total ouptut of a society at various prices levels. This short run curve shows that output can vary with price.
What causes aggregate supply to shift?
R.A.P.
Resource prices
Government action
Productivity
Aggregate Supply and Demand
Rightward shift in AD:
Increase Price level
Increase Real GDP
Leftward shift in AD:
Decrease Price level
Decrease Real GDP
Rightward shift in SRAS:
Decrease Price level
Increase Real GDP
Leftward shift in SRAS:
Increase Price level
Decrease Real GDP
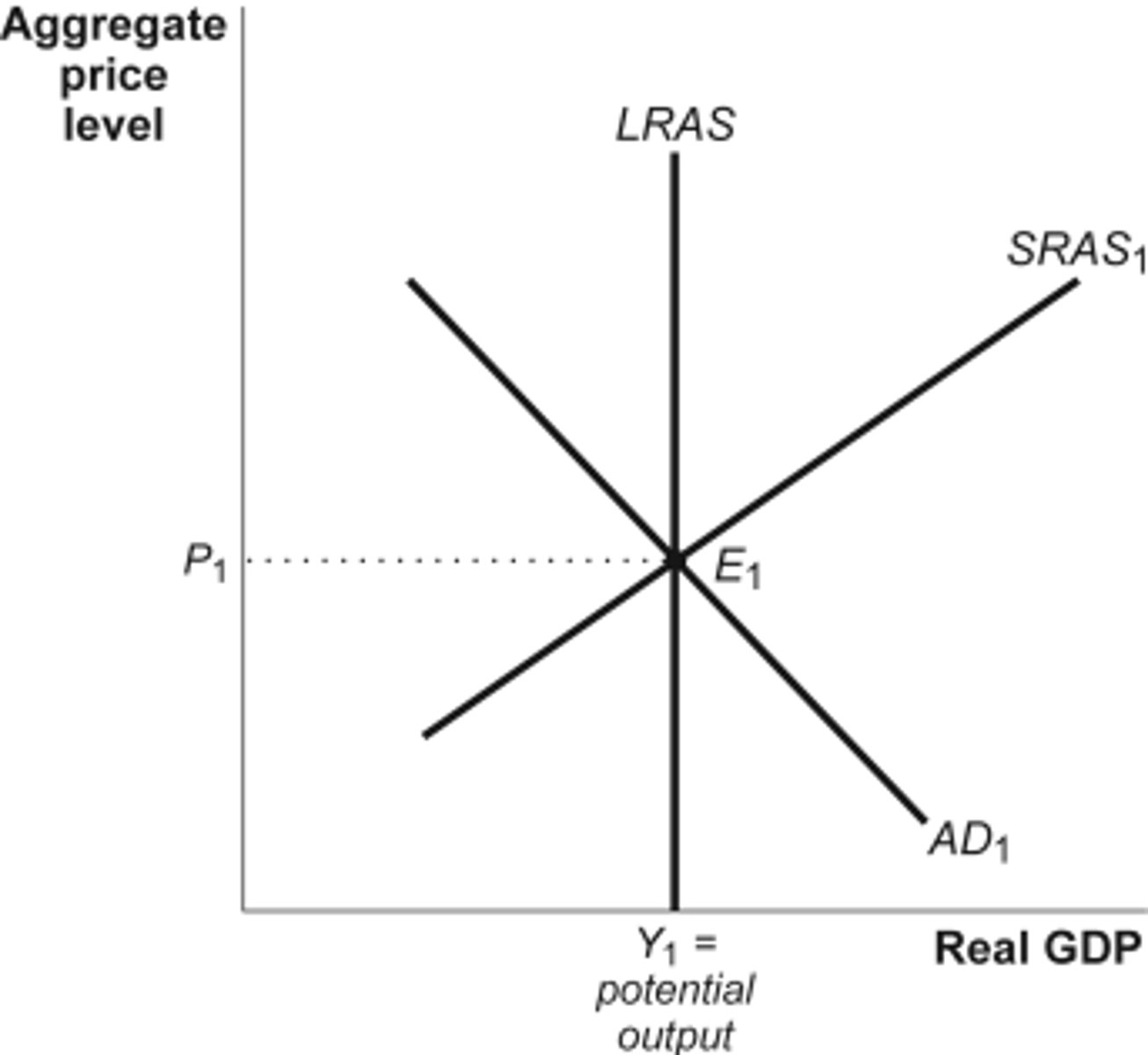
Long Run Aggregate Supply
Potential Real GDP
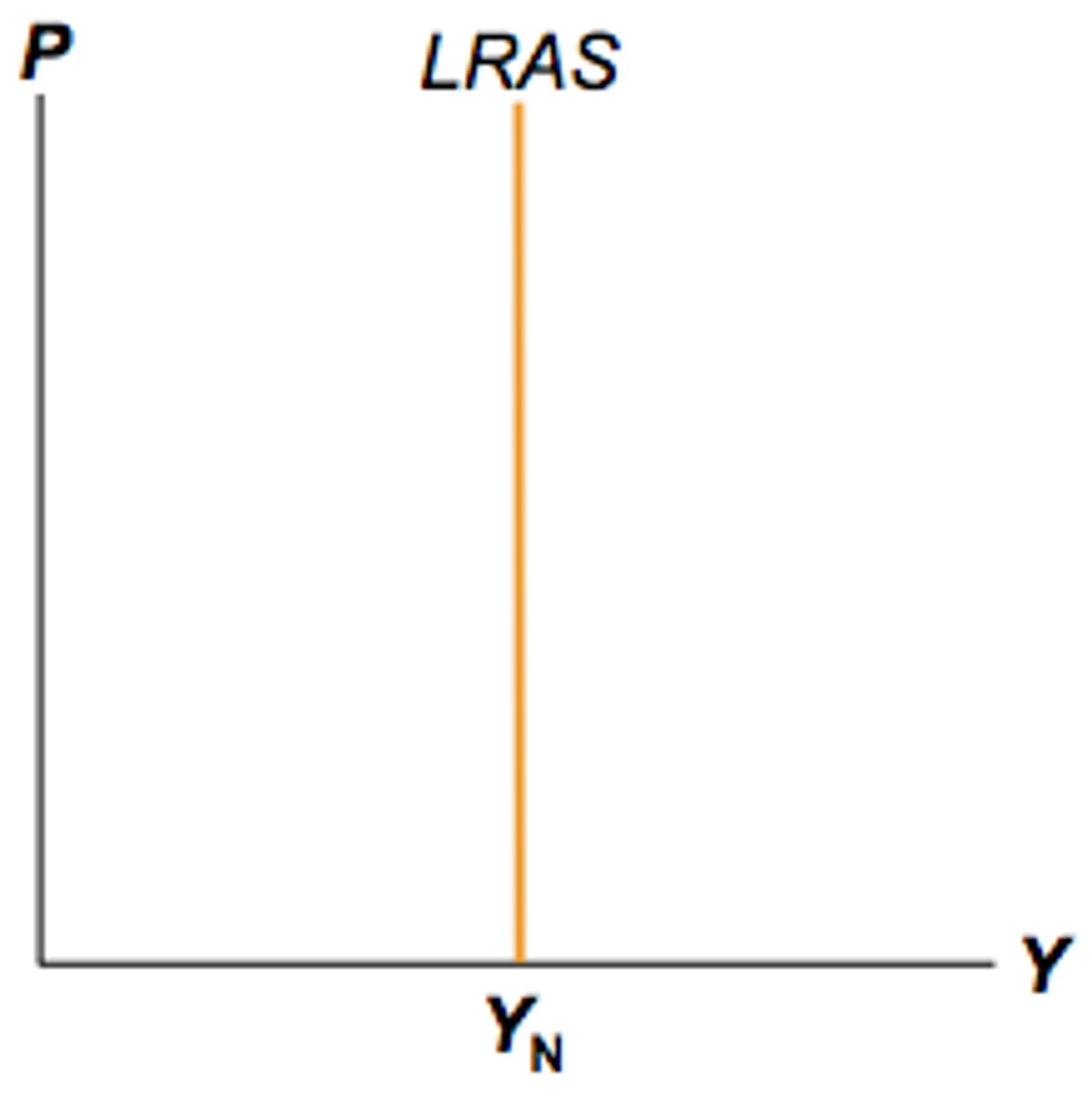
How is the Long-Run Aggregate Supply different from the Short-Run Aggregate Supply?
The long run aggregate supply doesn't depend on price level, but the short run aggregate supply is upward-sloping.
What happens in a recessionary gap?
the real GDP is lower than the potential GDP at the full employment level (less demand for goods and services than there is available supply)
What happens in a inflationary gap?
the real GDP is higher than the potential GDP at the full employment level (more demand for goods and services than there is available supply)
How does the economy self-correct in the long run?
Wage adjustments:
During a recession, when unemployment is high, wages tend to fall making labor cheaper and encouraging businesses to hire more workers, thus stimulating production and bringing the economy back to full employment
Price adjustments:
When there's excess demand in the economy, prices naturally rise, which can discourage consumers from buying as much, while simultaneously incentivizing producers to increase supply, leading to a market equilibrium.
(Wages ↓ leads to SRAS ↑ when not at equilibrium)
(Price ↑ leads to SRAS ↓ when not at equilibrium)
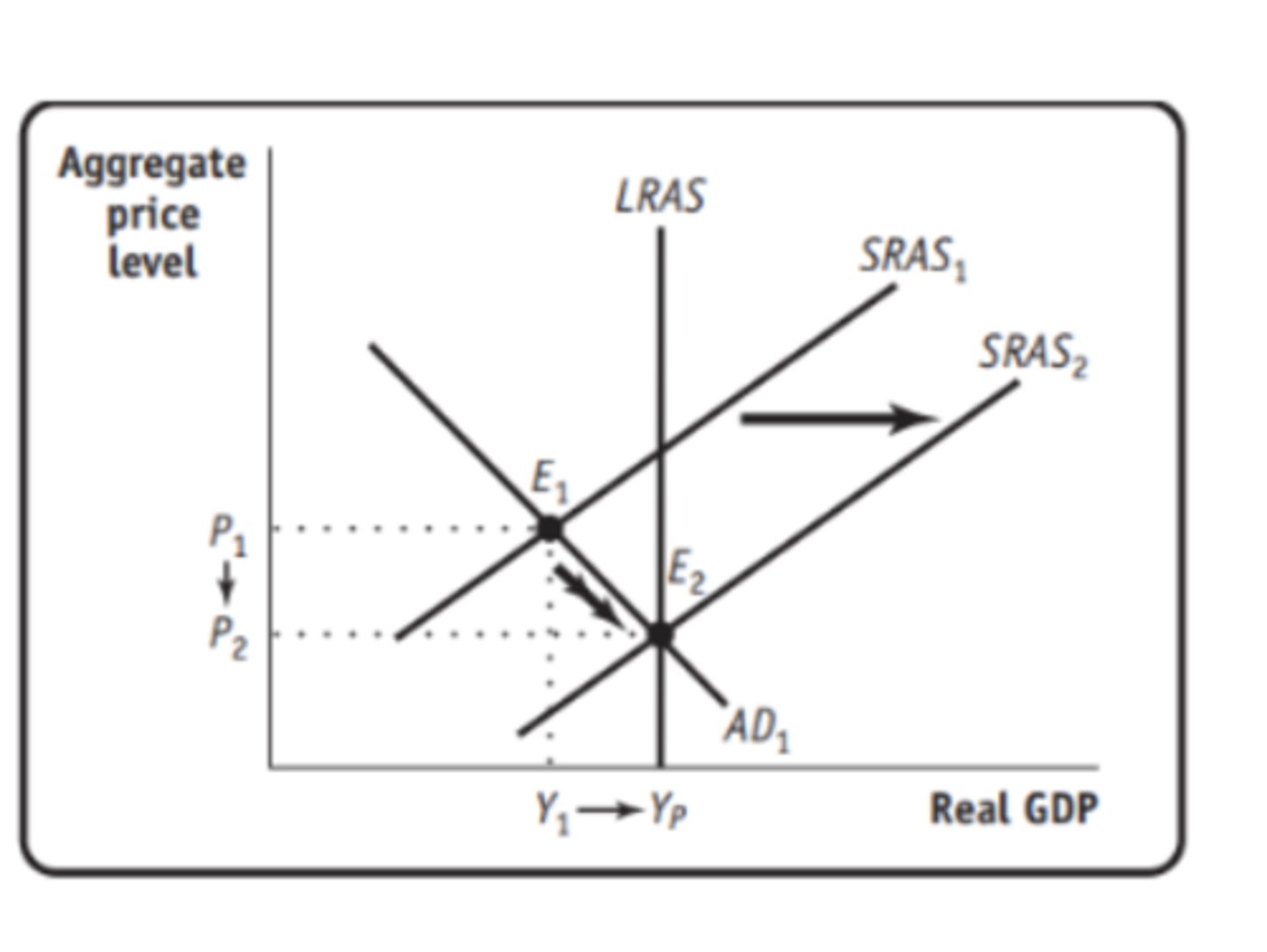
Demand Shock
an event that shifts the aggregate demand curve left or right temporarily
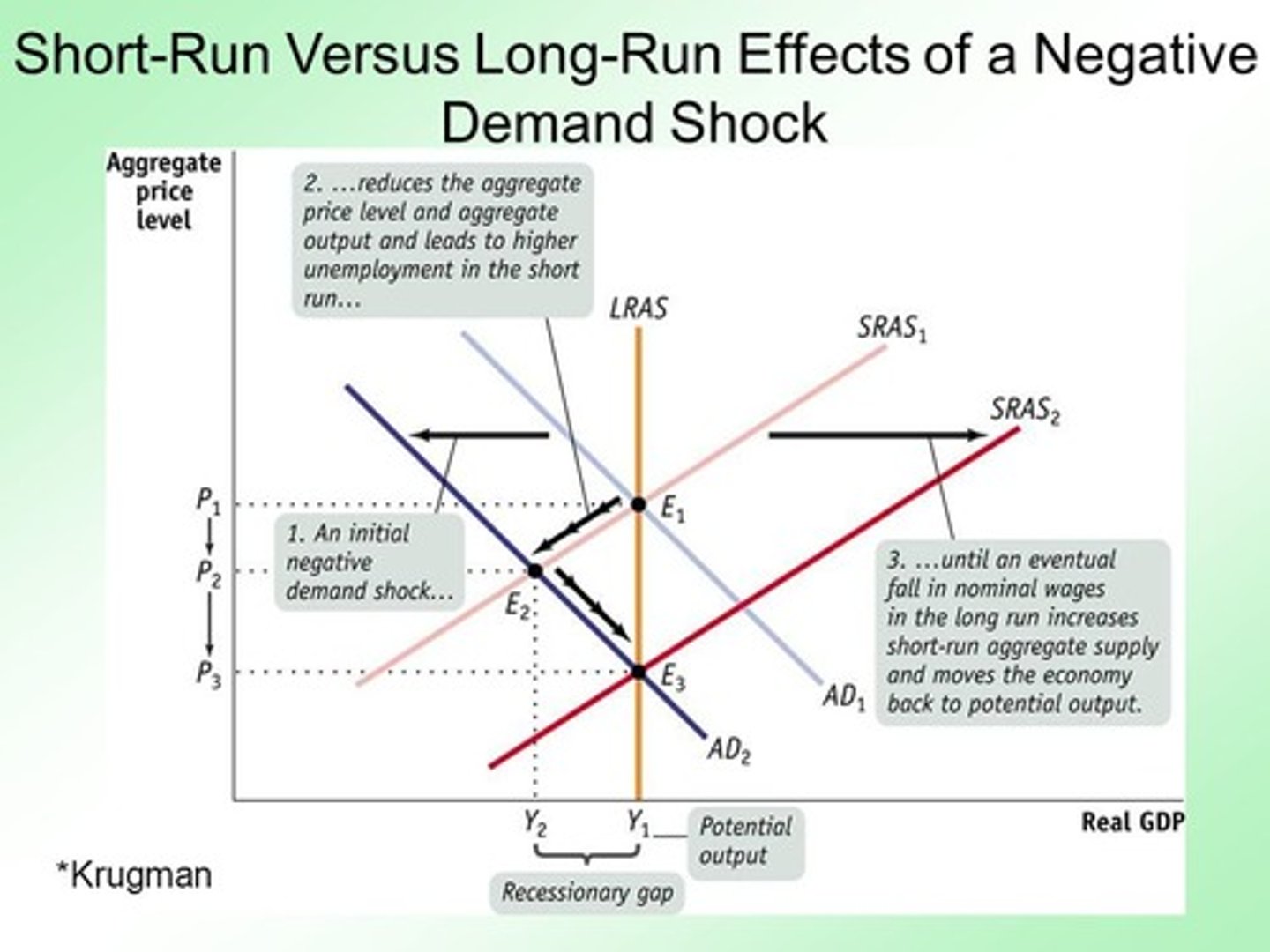
Inflationary and recessionary gaps are closed by self-correcting adjustments that shift
A. the SRAS curve.
B. the AD curve.
C. the LRAS curve.
D. both the SRAS curve and the LRAS curve.
E. both the AD curve and LRAS curve.
A. the SRAS curve.
(The demand shocks shift AD and that causes the recessionary or inflationary gap. Then, SRAS changes as a result of the forces in the economy (surplus/shortage). Finally, the shift of SRAS intersects AD back at a point along LRAS.)
Reminder:
The economy is ALWAYS in some form of short run equilibrium, but long run equilibrium is dependent on shifts from wages and price adjustments after demand shocks
An increase in investment spending leads to _______ in the price level and _______ in real GDP in the short run.
A. an increase; no change
B. a decrease; no change
C. no change; no change
D. an increase; an increase
E. a decrease; a decrease
D. an increase; an increase
A decrease in resource prices shifts the _________ to the _________.
A. long-run aggregate supply curve; left
B. aggregate demand curve; left
C. short-run aggregate supply curve; right
D. aggregate demand curve; right
E. short-run aggregate supply curve; left
C. short-run aggregate supply curve; right
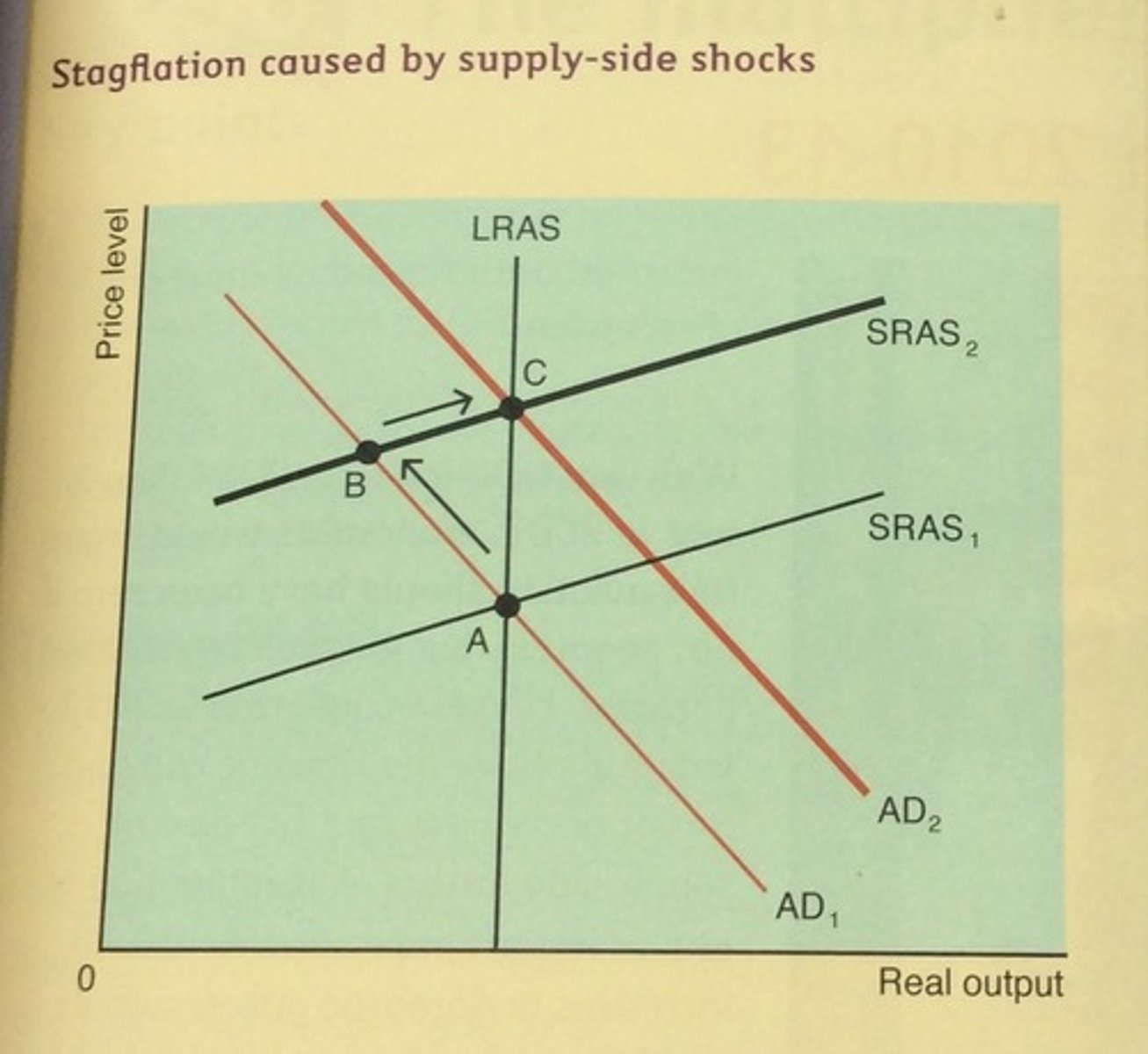
What happens to PL and equilibrium output when a supply shock shifts SRAS to the left?
A. Aggregate price level rises and RGDP falls
B. Aggregate price level falls and RGDP falls
C. Aggregate price level rises and RGDP rises
D. Aggregate price level falls and RGDP rises
A. Aggregate price level rises and RGDP falls
Supply Shock
An unexpected event that causes the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left or right
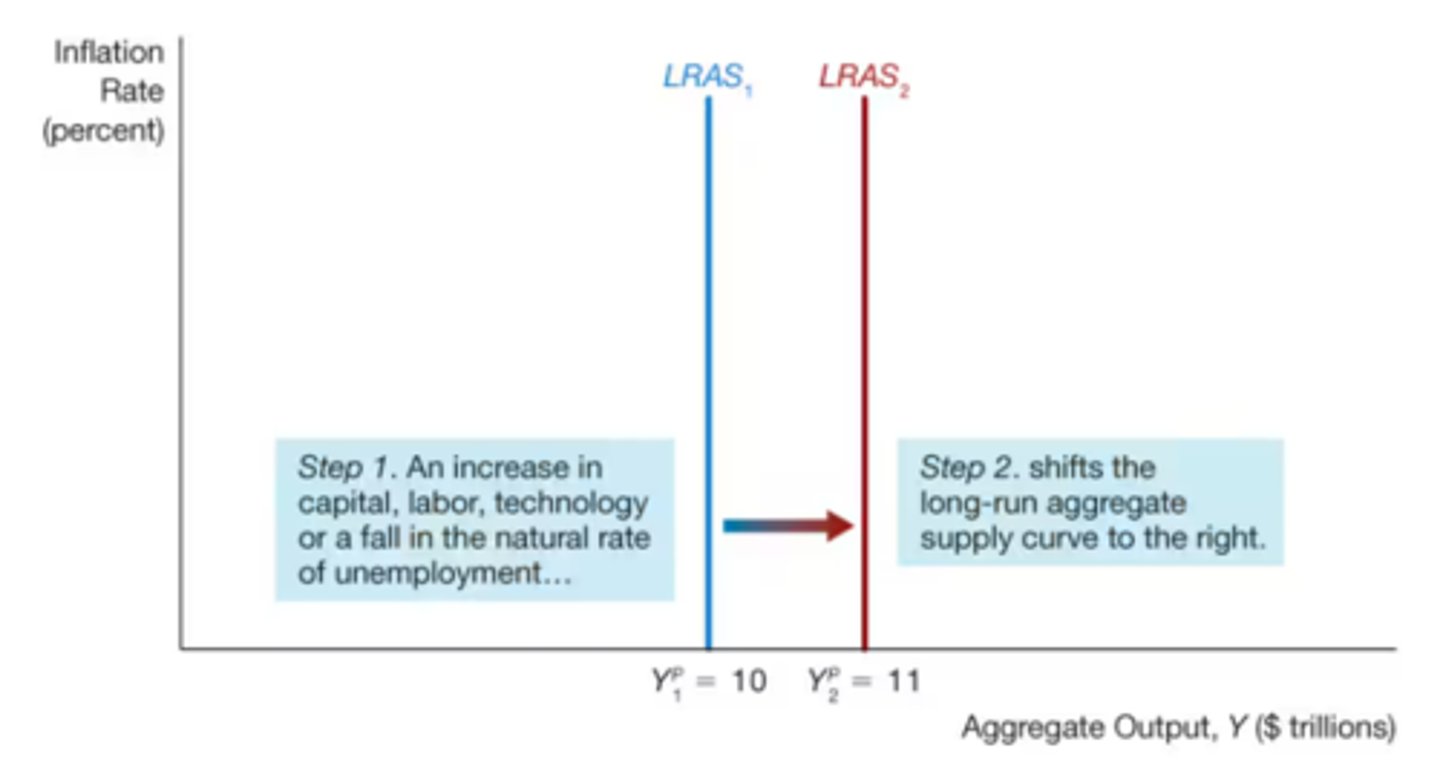
What shifts the Long-run Aggregate Supply Curve?
Technology changes in the labor force, or capital stock (similar to PPC Graph Shifts)