MCAT Retry
1/545
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All information + tricks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
546 Terms
Avogrado’s #
6×1023
molecular formula
#number of atoms in each molecule
example of a molecular formula
C5H10O5
EMPIRICAL FORMULA
smallest integer ratio of an atom
example of empirical formula
CH2O
Pressure SI Units
105P=760 mmhg=760 torr
volume conversions
1L =1000mL=1000cm3
Temperature SI
K=C+273
what are the 2 exceptions in the central dogma
RNA can be reverse transcribed to DNA
RNA can be copied to RNA (some viruses)
replication
DNA can be copied to DNA
Transcription
DNA can be transcribed to RNA
Translation
RNA can be translated to a protein
UAA, UGA, UAG (Stop Codons)
You Are Annoying
You Go Away
You Are Gone
what are the 3 type of point mutations
silent
missense
nonsense
point mutation
1 nucleotide substitution
2 type of mutations
point
insertion/deletion
missense mutation
results in same aa
nonsense
results in stop codon
insertion/deletion mutation
additions or loss of nucleotides
frameshift
insertion or deletion of a # of nucleotide not deleted by 3
effects on aa from frameshift
alters reading frame
can lead to significant changes in protein sequence
can lead premature stop codon
Nuclear Notation
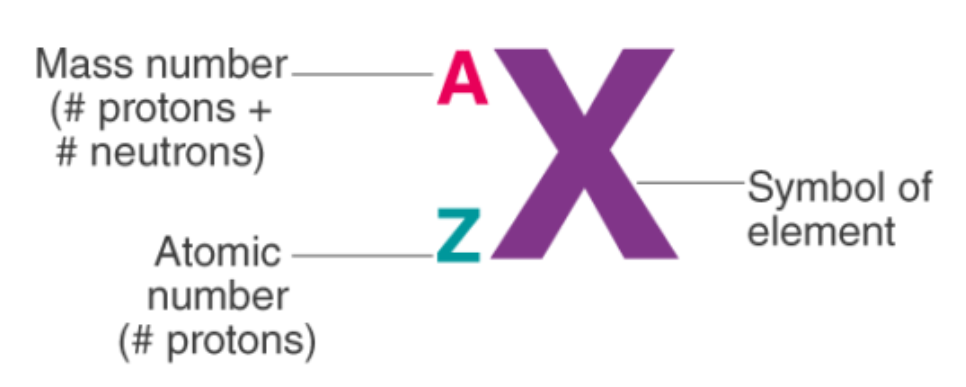
what does the A represent in nuclear notation
Mass #
A=#p +#n
Atomic Mass(Z)
#of protons
Alpha decay
A decreases by 4
Z decreases by 2
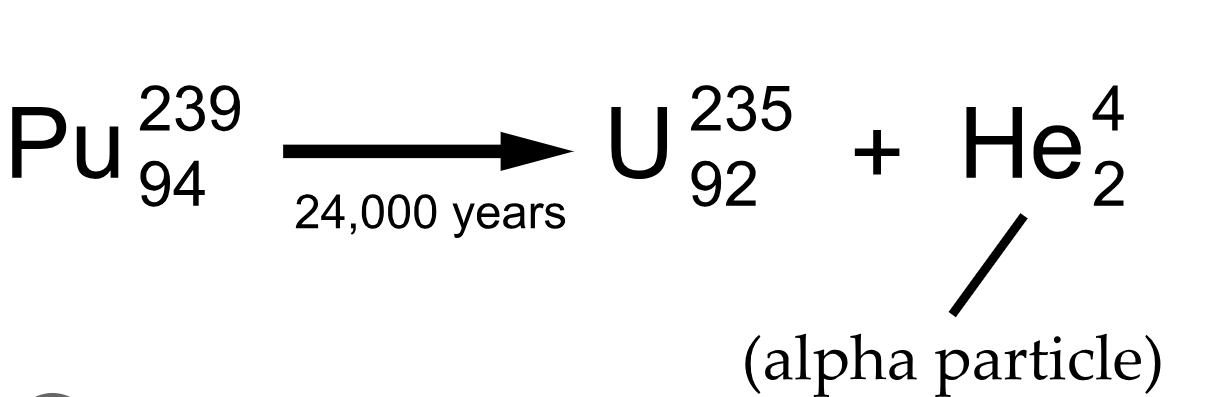
Beta - decay trick
move right on P table
beta - decay
A stays the same
Z increases by 1
occurs with nuclei w/ a high neutron protein ratio
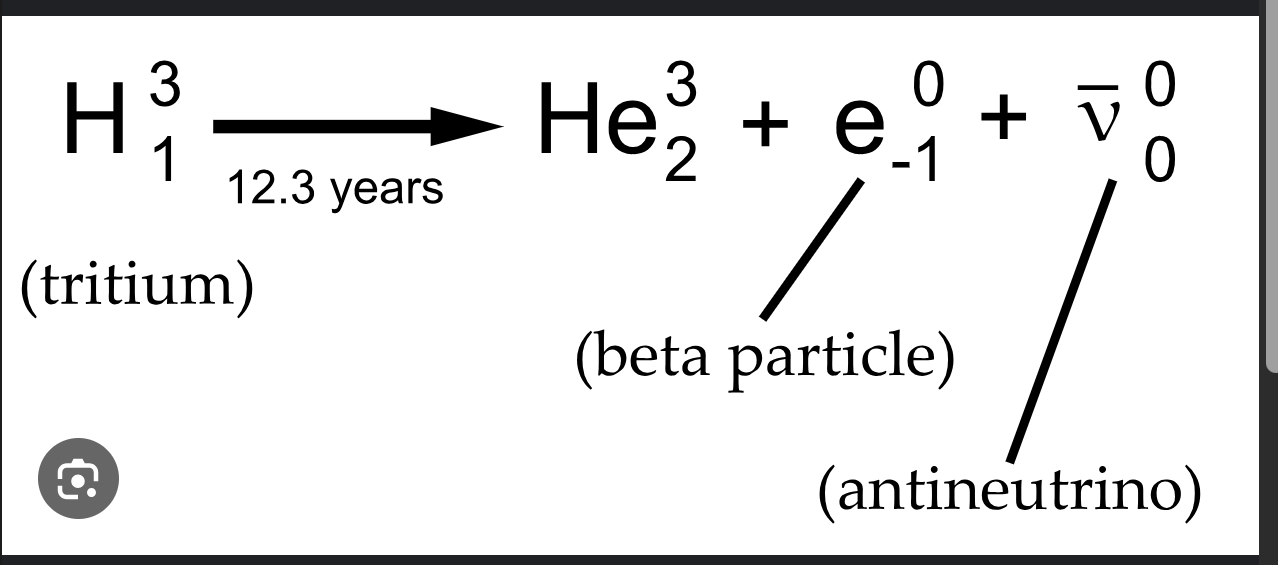
beta plus decay and Electron Capture
A stays same
Z decreases by 1
move to the P table
B+ decay
Electron capture
Gamma decay trick
stays the same
Force Units (N) broken down
(kg*m) / (s2)
Scalar
physical quantities described by only a magnitude
examples of scalar quantities
5 kg
298k
vector
physical quantities w/ both magnitude and direction
vector addition
transcription: Type of RNAs
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
catalytic (ribosomes)
Messenger (mRNA)
codes for protein
Transfer(tRNA)
Carries aa to ribosome/mRNA during translation
Ribosomal (rRNA)
component of ribosome (rna + protein)
Catalytic (ribosome)
Biological enzyme
Mechanism of Transcription
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter (transcription start site)
RNA polymerase unwinds the DBA (helicase activity)
Using the template strands of DNA , RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule
mRNA is complementary to the template strand
mRNA has the same sequence as the coding strand
RNA poly is DNA dependent RNA polymerase
transcription stops when RNA polymerase reachs transcription stop site
RNA polymerase does not have proofreading activity and is error prone
Eukaryotic mRNA processing
the initial RNA molecule synthesized by RNA poly undergoes several modification
5’ capping addition of a methylated guanine at a 5’ end
3’ capping addition of a poly A tail to 3’ end
these 2 modification protect the RNA from degradation and promote translation
where does the modification of RNA molecule occur
nucleus
RNA splicing
noncoding region (introns) are removed & leaving the coding regions (exons)
Alternative splicing
one mRNA molecule multi protein possibilities from 1 gene
Spliceosome
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are complexes of proteins and small small nuclear RNAs(snRNA’s)
snRNPs bind to pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome that carries out splicing
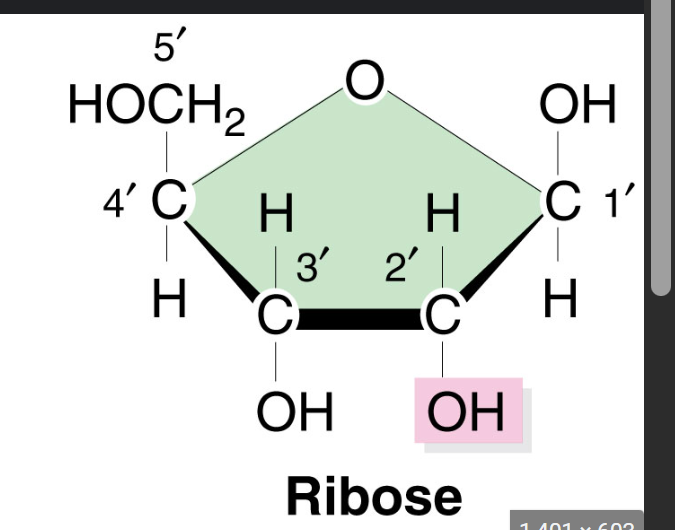
Ribose
2’ and 3’ OH group
backbone of RNA
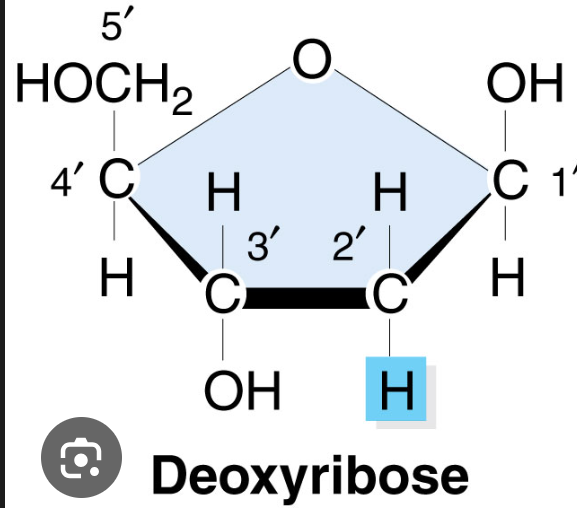
deoxyribose
only has a 3’ OH group
Backbone of DNA
less of 2OH group (higher stability)
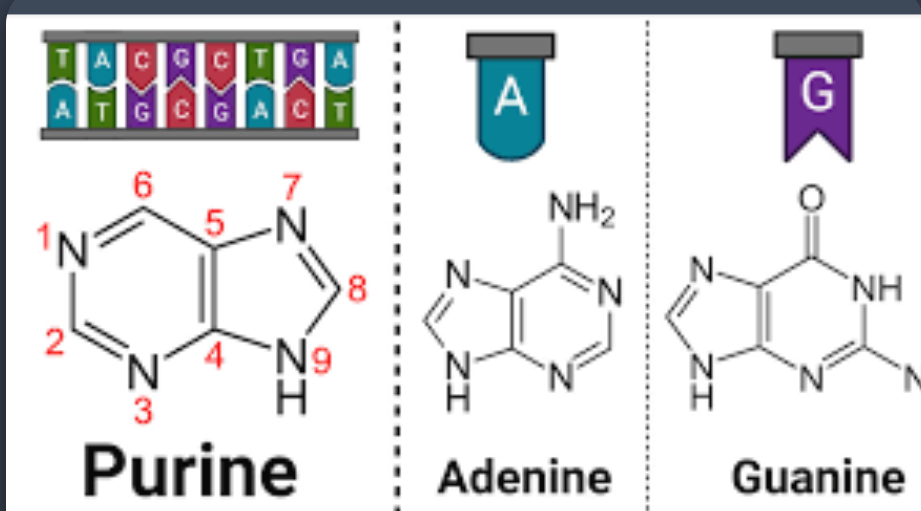
nitrogenous bases
purines
pyrimidines
purines
2 fused rings
(adenine and guanine)
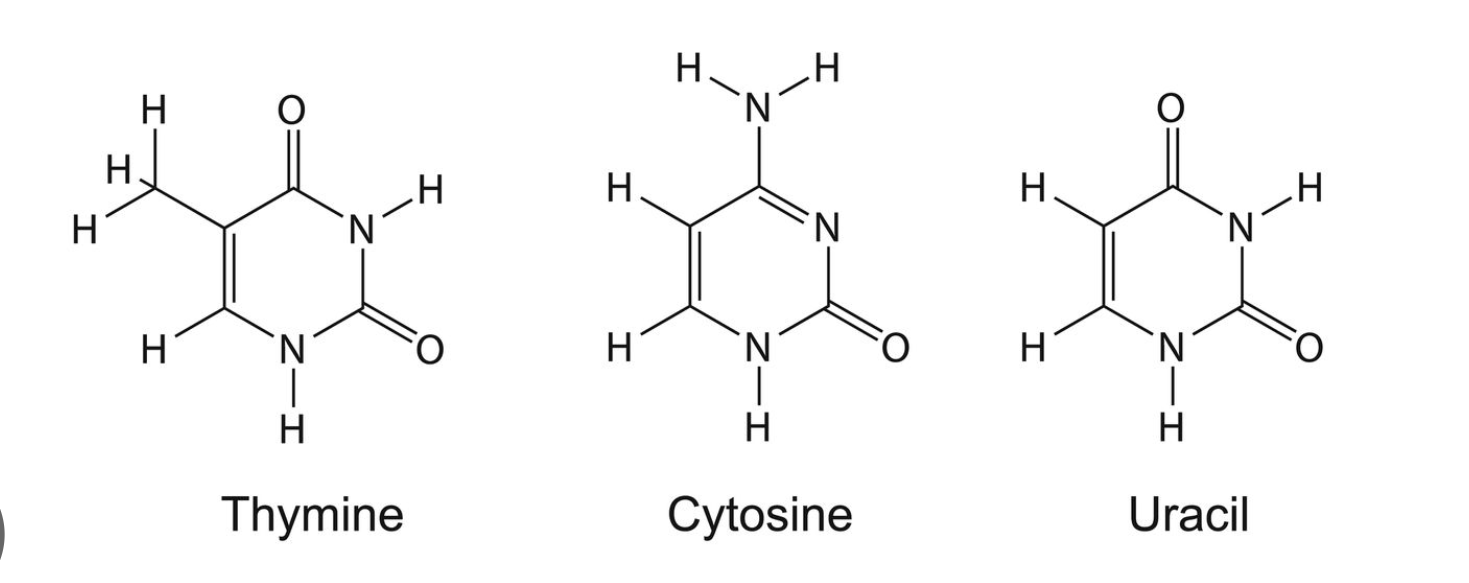
pyrimidines
one ring
cytosine, tyrosine, uracil
Nucleosides
5 carbon sugar + nitrogenous base
nucleotides
5’ carbon sugar +nitrogenous base + phosphate =(nucleoside + phosphate)
building blocks of RNA/DNA
important source of energy for many metabolic processes (ATP)
A-T or A-U have how many hydrogen bonds
2
C-G have how many hydrogen bonds
3
watson crick model of DNA
double helix formed btw 2 antiparallel sing stranded DNA molecule
each single stranded dna molecule is a polymer of deoxynucleotides hold together by phosphodiester bonds sugar phosphate backbone
the single stranded DNA molecule are held together by base stacking and hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bonds
hybridization
process by which a DNA/RNA molecule binds to complement RNA?DNA molecule
exponential decay
occurs when a quantity decreases at a rate proportional to its current amount
half life
amount of time required for a substance to decay to half its half quantity
how much of a 100g sample at radioactive 32P (1/2=14d) would remain after 56 days?
6.25
0 days=100g
14 days=50g
28 days=25g
42 days=12.5 g
56 days= 6.25g
Bohr Model
a model of atoms where electrons follow circular orbits (energy levels shells) location at fixed distances from the nucleus
these energy levels shells increase in energy Away from the nucleus
get progressively closer together away from nucleus
have changes that are quantized
the principal quantum #,n, indicates the energy levels/shells
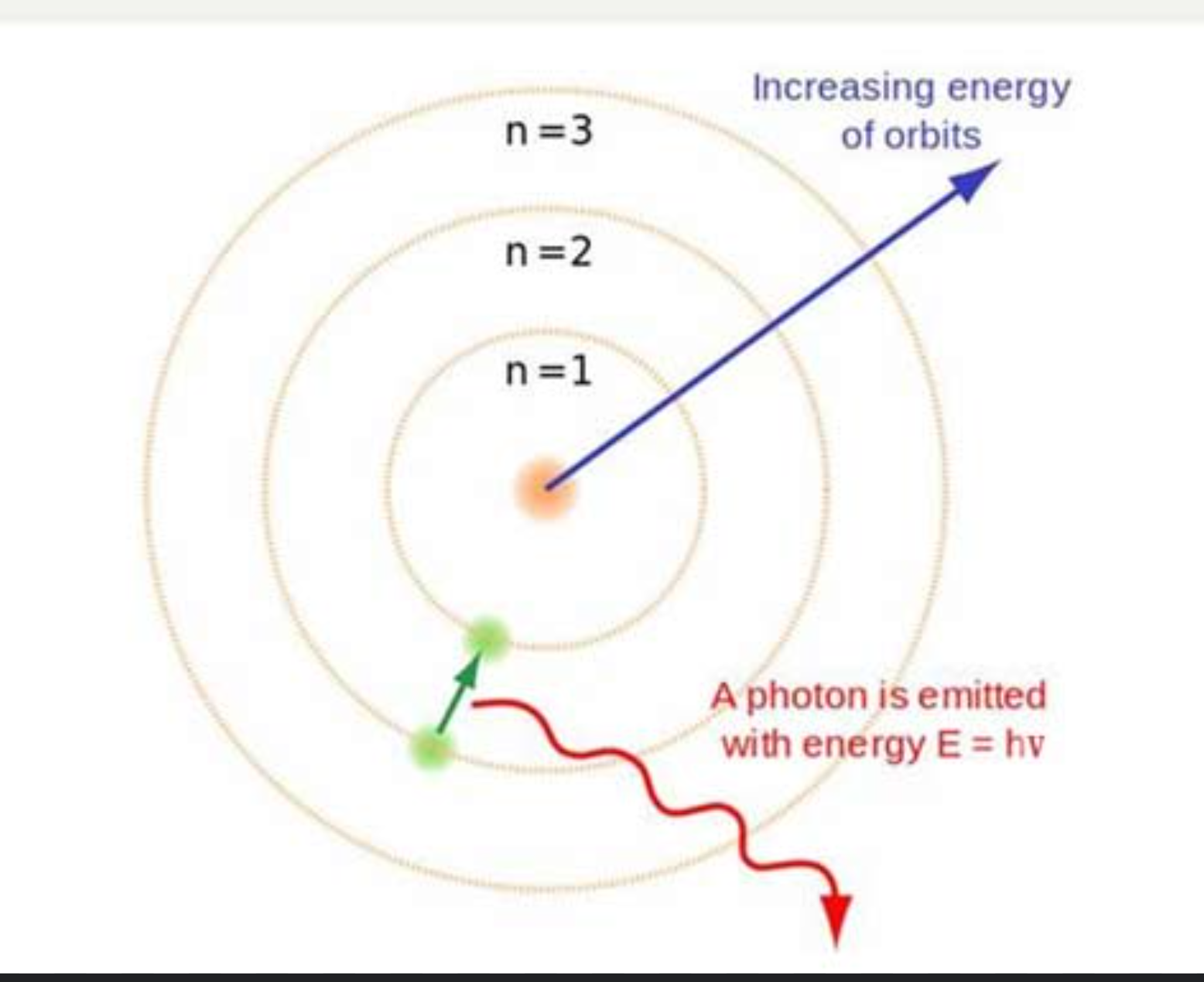
excitation
electrons can move from lower energy level to high energies by absorbing a proton
photon must have an energy= to the difference energy between the two levels
when the e- moves up to a higher energy level, it moves from the ground state into an ___ state
excited
relaxation
electrons in the excited state will spontaneously move from a higher level to a lower energy level by emitting a proton
Planck’s constant
6×10 -34J*S
Energy of photon is ___to frequency of photon
proportional
line spectra
a continuous spectrum contains lights of ALL wavelengths
ex: white light
contains light only discrete wavelengths bonds
absorptions line spectrum
while light is shined onto a sample its ground state
thew sample absorbs same wavelength of light
the unabsorbed light is passed through a prism to produce the absorption spectrum
the dark bands indicate which wavelengths of light waves absorbed by the sample
wave-particle duality
light and matter behaves li\ke both particles nad waves
Sensory memory
storage of sensory information after sensory perception for a very short period of time (ms-s)
Iconic
example of visual sensory memory
echoic
example of audio sensory memory
haptic
example of touch sensory memory
working memory
cognitive system for holding and processing a limited amount of information
short term memory
cognitive system for holding but not manipulating a limited number of chunks of information for a period of seconds (w/o rehearsal)
the # of chunks of info that can ebe held has been claimed to be 7± 2 and 4 ± 1
long term memory
storage of an unlimited amount of information for an indefinite period of time
includes explicit and implicit memory
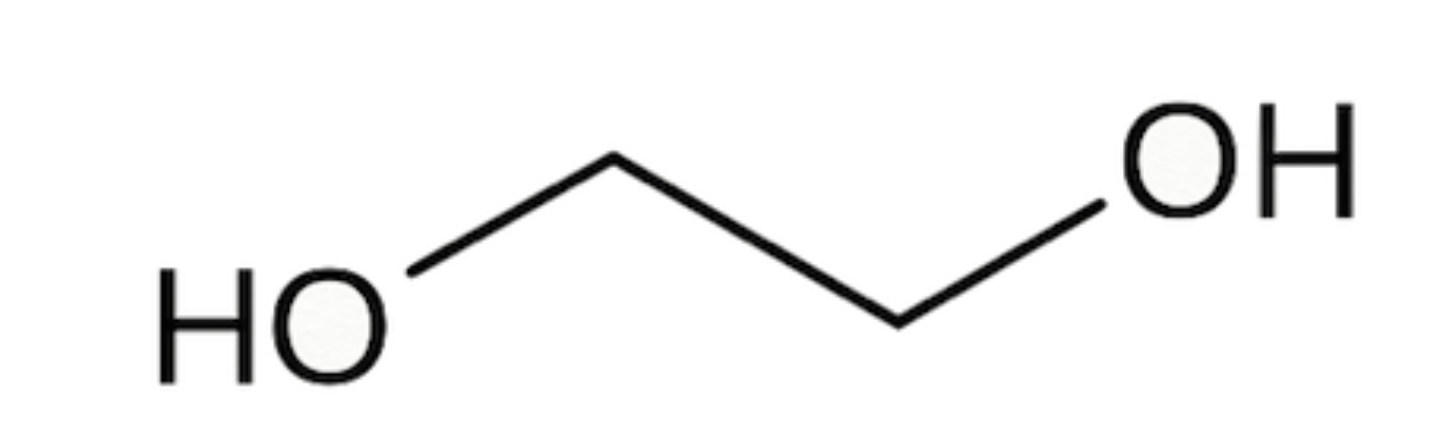
Ethylene glycol is known to most Americans as antifreeze and to some for having a sweet syrupy taste. For scientists, it can be used as a protecting group for carbonyls. Which is the most stable conformer of the compound ethylene glycol depicted below?
a. para conformer
b. guache conformer
c. anti conformer
d. eclipsed conformer
b. guache conformer
Explanation:
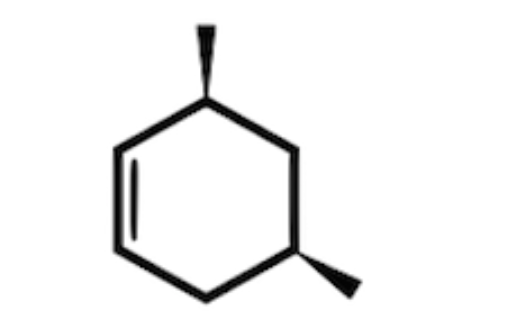
Which of the following cyclic hydrocarbon structures would be NOT categorized as an achiral compound?
is not an achiral compound and will rotate plane-polarized light as a chiral compound due to a lack of a plane or axis of symmetry
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the characteristics of diastereomers, enantiomers, and meso compounds?
D. for a given set of stereoisomers, meso compounds must have at least 2 stereocenters and are diastereomeric to other stereoisomers in the set
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the stereochemistry between the various cyclohexanes?
the conformational isomer sof trans1-2 dichlorocyclohexane are enantiomers, which are not interconvertible but resolvable
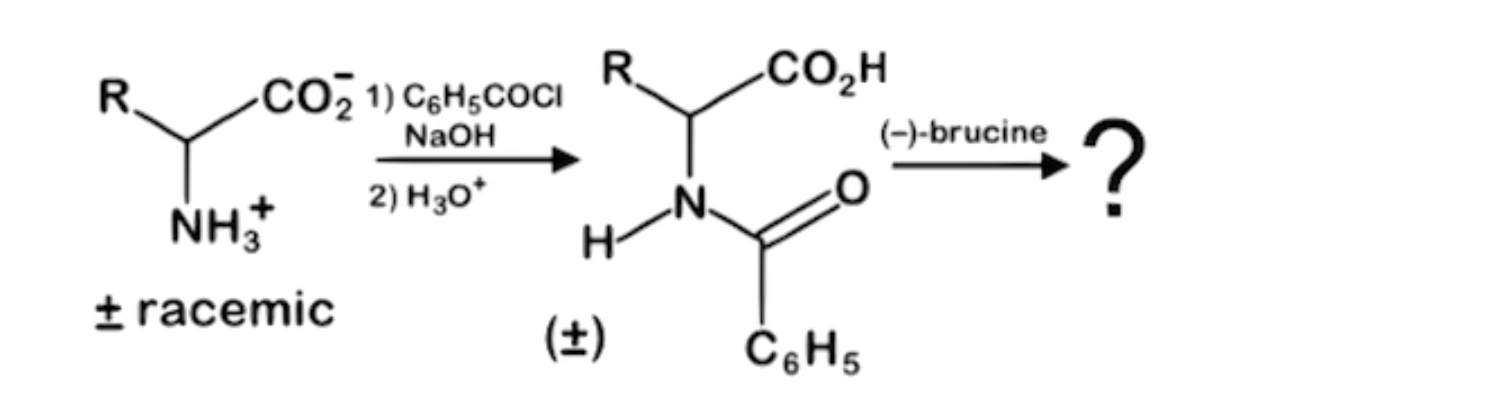
While brucine is a naturally occurring alkaloid related to strychnine and hence poisonous, it can be used as a tool for stereospecific chemical syntheses. Which of the following statements best describes the result of this reaction series with a racemic mixture of an amino acid
the products can be separated using TLC techniques with a chiral stationary phase

Tagalose is a functional sweetener and can be found in milk in small amounts. Commercially, Tagalose is produced from lactose, whereby galactose is isomerized under alkaline conditions to D-tagatose (shown below) by calcium hydroxide. Based on the Fischer projection, which of the following wedge-dash structures correctly represents D-tagatose?
On adjacent stereocenters, when the configurations are the same, such as S, S or R, R, there is a switch from dash to wedge or wedge to dash. So if the configurations change, such as R, S or S, R, there are both dashes or wedges.

Sushi and other culturally Japanese foods have become widely accepted outside of Japan. There are now Japanese restaurants everywhere in the US. There are even American versions of Japanese food, such as the “California roll”. This is an example of:
cultural diffusion
American English commonly uses words that originate from various African, Asian, and non-English-speaking European cultures. This is an example of:
cultural diffusion
In the 1960s, we witness social movements such as the hippie peace movement, the feminist movement, or the green movement. At the time, the norms and values of these social group placed it at odds with the dominant (mainstream) culture. They were referred to as:
Countercultures
definition of cultural lag
refers to how human behavior lags behind technological innovations.
When we get sick, we can type out our symptoms on the computer and search for them. We can even get instantaneous diagnoses and treatment recommendations. According to some new studies, computer diagnostics have been shown to outperform physician judgement in some contexts. However, the majority of the population still prefer paying personal visits to the doctor’s office. This is an example of:
cultural lag
Research shows that our behavior is affected by intentions. In addition to intentions, however, it is also found that whether we have the resources or capacity to carry out these intentions also influence our behavior. This additional factor can be referred to as:
perceived behavior control
A researcher studying student intentions to engage in safer sex practices found that individual attitudes toward wearing condoms, and their friend’s attitudes toward wearing condoms explained the variations in the intent of an individual to use condoms in the short-term. However, the study further showed that the perception of one’s ability to use condoms or of condom availability significantly explained the variation between condom usage and non-usage. This “perception” is an example of:
perceived behavior control
A speaker comes to give a talk on socio-economic inequality. As a listener, you find that the topic is interesting and important. You feel motivated as you listen to the talk, and you think deeply about the topic. After the talk, you thoroughly feel that the talk changed your perceptions and attitudes towards inequality. Which of the following is true, according to the experience?
This is an example of central route to persuasion
A salesperson often gets a customer to agree first to a small request, such as a home-visit appointment, an application form, or a trial period. After this initial small compliance, the salesperson will then ask the customer to do bigger things, such as actual purchases. Based on past small-scale compliance, the customer would be expected to experience cognitive dissonance if he/she switched to non-compliant behavior. This is most accurately an example of:
foot-in the door phenomenon
In a research experiment, shocks were administered to two groups of dogs in barriers. In Group I, there was a button that would deactivate the shock that the dogs could press. In Group II, there was no button. The two groups of dogs were then placed together and shocks were administered with no deactivation button. The dogs from Group I actively looked for ways to escape the shock situation, some by jumping over the barrier blocks. However, the dogs from Group II remained in place without looking for a solution and whimpered. This is an example of:
learned helplessness
In a consumer research study, two groups were asked to make product selections. In Group A, consumers were asked to choose 1 product out of 5. In Group B, consumers were asked to choose 1 product out of 25. The results showed that those in Group A were more satisfied with their choices compared to those in Group B who were presented with more choices. Which of the following is true regarding the study results?
this is an example of they tyranny of choice
In a study, a researcher divided participants into three groups. In Group A, participants were asked to resist pieces of chocolate in a bowl. In Group B, participants were asked to resist pieces of radishes in a bowl. In Group C, participants were given nothing to resist. Afterwards, all of the participants were asked to solve a difficult math problem. The results showed that those who had to resist chocolate were more likely to give up sooner on the problem. This is an example of:
ego depletion
Deindividuation refers to a psychological state that results in non-normative behavior when a person is in the presence of a group. Which of the following typically decreases during the process of deindividuation?
self awareness
Which of the following parental styles is associated with high self-esteem in children?
authoritative parenting style
In which of Erikson’s stages of human development does an individual begin to develop a sense of self?
adolescence
According to Freudian theory, where does self-identity develop?
the ego
How is the Freudian theory of psychosexual development similar to the Eriksonian theory of human development?
both theories focus on stages of development that are characterized by a central crisis that must be resolved
Which of the following is a core principle of Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory of development?
Children are able to reach their highest potential when they are in the presence of skilled and knowledgeable instructors.