Organization of Computers Midterm
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What two things can a computer do?
Store state and manipulate state
How many bytes (byte-addressable) can a k-bit address specify?
2^k
What is a register file?
A synchronous RAM
What is the write data port in the register file?
The data that will be written
What is the write address port in the register file?
The location the data will be written to
We need to build a RAM that can store 128, 64-bit words and
has one write port and three read ports
How many address bits does my RAM need for its write port?
7
We need to build a RAM that can store 128, 64-bit words and
has one write port and three read ports
How many data bits does my RAM need for each read port?
64
What are the 3 parts of a register file?
The Storage: An array of registers
The Read Ports: Output the data of the register indicated by read addresses
The Write Port: Selectively write data to the register indicated by write address
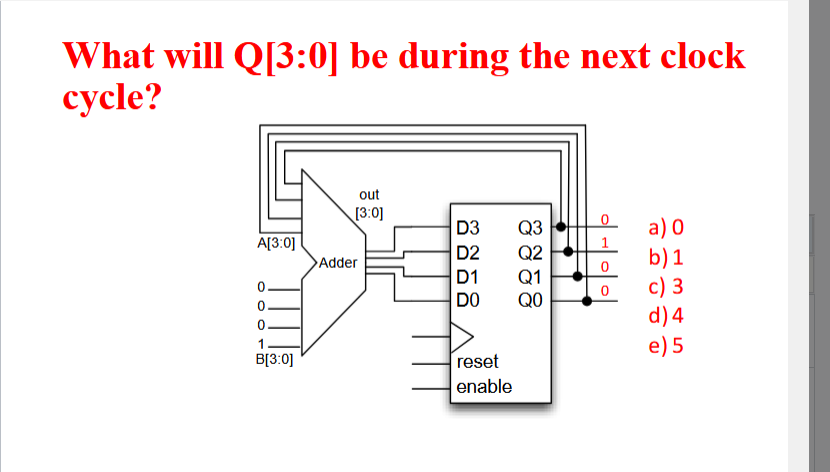
5
How many registers does a 4 × 16-bit register file have?
4 registers (2 bits)
How many data bits does a 4 × 16 register file have?
16 bits
What is the key feature that distinguishes a computer processor from other digital systems?
Programmability
What is a processor?
A hardware system controlled by software
What is an Instruction Set Architecture?
Describes the interface between the software and the hardware. ISA specifies what operations are available. ISA specifies the effects of each operation.
What do instructions consist of?
Operation code: names the operation to perform
Operands:Names the data to operate on
What are register instructions?
R-Type. Require all values to be stored in registers
What is the size of the MIPS register file?
32 × 32 bits
add $14, $18, $3
Which registers are being added together, and in what order?
$18 + $3
add $14, $18, $3
Which register stores the result?
$14
add $14, $18, $3
What is another name for $18?
rs
add $14, $18, $3
What is another name for $3?
rt
add $14, $18, $3
What is another name for $14?
rd
What are I-Type Instructions?
These instructions allow you to specify an immediate value for the second source instead of a register
addi $15, $1, 4
Which values are being added together, and in what order?
$1 + 4
addi $15, $1, 4
Which register stores the result?
$15
addi $15, $1, 4
What is another name for $15?
rt
addi $15, $1, 4
What is another name for $1?
rs
How could a constant be written to a register?
addi $15, $0, 4
How does sign extension work?
The most significant bit of the input is used to extend the number of bits to represent that value
Where are values store in an I-Type Instruction?
rt
Where are values stored in an R-Type instruction?
rd
What are valid addresses for MIPS Instructions?
0,4,8, 12, etc
What is the Program Counter (PC)?
The PC contains the address of the next instruction to execute
Why can the 2 LSb's of the PC be neglected?
Since the only valid instruction addresses are divisible by 4, the first 2 bits will always be 00
Explain the format of the jump instruction
j target_label. Uses a label to tell where in the code to jump to
How many bits are allotted for the address in a J-Type instruction?
26 bits
Where do the other 6 bits come from for the address in a J-Type instruction?
The bottom two bits are always 00 and the 4 MSb’s are the MSb’s of the PC
What is the format for beq? And what is the comparison?
beg rs, rt, target_label
R[rs] == R[rt]
What type of instruction are branch instructions?
I-Type
How is the target label_stored in branch instructions
The constant field is not an address, but an offset from the current PC to the target address.

What is the value stored in L?
3, Since the PC points to the next instruction, you dont count' from the instruction being run, but from where the PC is pointing

How many bits is the PC incremented by to reach label L?
3×4 = 12 bits. The PC moves forward 12 bytes in memory
What is the range of the j instruction?
256 MB
Why would you want to use the jr instruction?
If you want to jump outside the bounds of the j instruction
What is another name for the register that is used in jr?
rs
How does jr allow you to leave the bounds established by j?
jr is provided with a register. This register contains an address to jump to. Allows you to fill the entire register with the desired address
What type of instruction is jr?
R-Type
How large is the immediate in I-Type instructions?
16 bits
What does the lui instruction do?
loads the highest 16 bits of a register with a constant, and clears the lowest 16 bits to 0’s
What is the format of lui?
lui $rt, Imm
What value is stored in $12?
lui $12, 0×3D
ori $12, $12, 0x900
0x003D 0900
What type of instruction is lui?
I-Type
What is the format of slt?
slt rd, rs, rt
What is the format for slti?
slti rd, rs, imm
How much storage does the MIPS architecture have by default?
2^(32) * 8 = 4GB
In data memory, what is the operation if word_we = 0 and byte_we = 0?
Read from the address in ADDR
In data memory, what is the operation if word_we = 0 and byte_we = 1?
Write a byte in ADDR
In data memory, what is the operation if word_we = 1 and byte_we = 0?
Write a word in ADDR
How large is a word in MIPS?
32 bits
What does lw do?
Transfers one word of data from the data memory to a register
What does sw do?
Transfers one word of data from a register into main memory
lw $12, 4($3)
What is another name for $12?
rt
sw $12, 4($3)
What is another name for $12?
rt
lw $12, 4($3)
What is another name for $3?
rs
sw $12, 4($3)
What is another name for $3?
rs
What is the unit of the offset in lw/sw/lbu/sb?
bytes
What does lbu do?
Transfers one byte of data from the data memory to a register and zero extends it
What does sb do?
Transfers one byte of data from a register into main memory
Which byte is transferred in sb?
The LSB