Development of B Lymphocytes (13)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is the pathway of B cell development in primary lymphoid organs?
Stem cell, Pre-B cell, Immature B cell (IgM+), and Mature B cell (IgM+ , IgD+)
What are the outcomes of B cell development in secondary lymphoid organs?
IgM, IgG, Memory B cell, IgA, and IgE
What occurs to allow mature B cells to develop into IgG, Memory B cells, IgA, and IgE?
Isotype switching and somatic mutations
B cell development in primary lymphoid organs is?
Antigen independent
B cell development in secondary lymphoid organs is?
Antigen-dependent
Immature B cells undergo selection process to become [blank]
self-tolerant
Multivalent self-antigen undergo apoptosis after what?
Clonal deletion
Soluble self-antigen IgM migrate to periphery to become?
Anergic B cells
No self-reaction with IgM migrate to the periphery to become?
Self-tolerant mature B cells
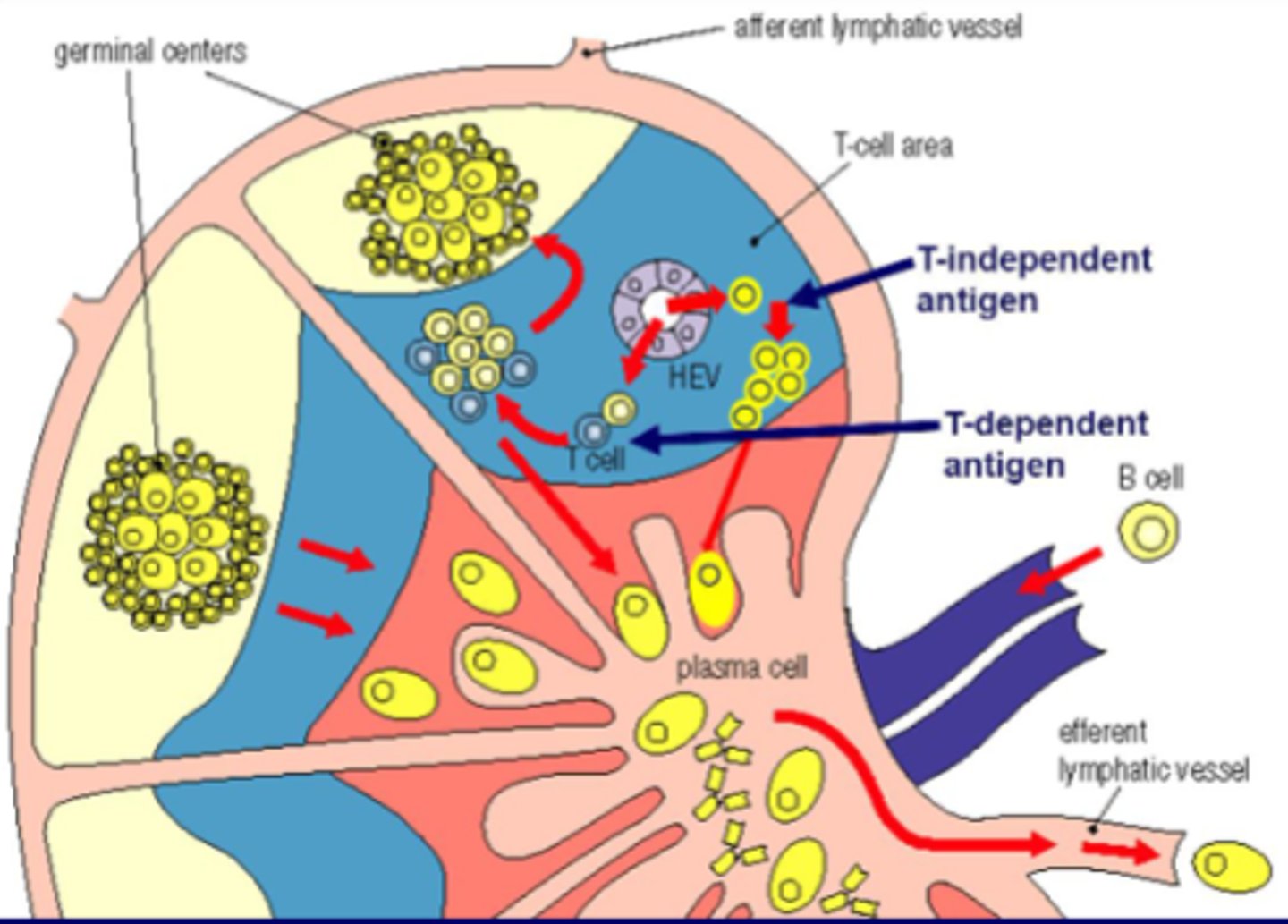
Describe the circulation of naive B cells in lymph nodes
Blood vessels, HEV, T-cell area, B-cell area, primary lymphoid follicle, T cell area, medullary cords, efferent lymphatic vessel
What are the two types of antigens for B-cell stimulation?
Thymus-dependent (TD) antigens and Thymus-independent (TI) antigens
-Need T-cell help for activation of B cells and production of antibodies
-Usually are protein or glycoprotein antigens
Thymus-dependent (TD) antigens
-Can induce antibody production in the absence of T-cell help
-Usually these are bacterial capsular polysaccharides with highly repetitive structures or B-cell mitogens such as LPS
Thymus-independent (TI) antigens
Effect of specific antigen on B cell migration and differentiation