PHARM II: EXAM #3 (LEARN HIV/STI)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Which HIV protein has an affinity for CD4 receptors?
Glycoprotein 160
What protein takes the RNA genome of HIV and converts it to DNA?
Reverse transcriptase
What are the main phases of HIV infection?
Acute
-Acute retroviral syndrome or mononucleosis-like illness
-Latent period
-Chronic
Terminal (AIDS)
-AIDS defining illness (PCP, Kaposi's sarcoma, etc.)
How do you monitor HIV?
-CD4 cell count
-Viral load
What indicates the magnitude of replication of HIV?
Plasma HIV RNA
What indicates the extent of immune damage from HIV?
CD4 count
What are the main drug classes for HIV treatment?
-Integrase inhibitors (InSTI)
-Nucleoside (nucleotide) reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NtRTIs)
-Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)
-Protease inhibitors (PI)
-Entry/Fusion inhibitors
-Coreceptor inhibitor
What are the Nucleoside (Nucleotide) Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors?
What are the 4 general classes of them?
Thymidine analogs
-Stavudine (d4T) (Zerit)
-Zidovudine (AZT or ZVD) (Retrovir)
Deoxycytidine analogs
-Emtricitabine (FTC) (Emtriva)
-Lamivudine (3TC) (Epivir)
Deoxyguanosine analogs
-Abacavir (ABC) (Ziagen)
Deoxyadenosine
-Didanosine (ddI) (Videx)
-Tenofovir(TDF) (Viread)
MOA of the Nucleoside (Nucleotide) Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NtRTIs)
-Require phosphorylation to the triphosphate form
-Competes with endogenous deoxyribonucleotides for catalytic sites on reverse transcriptase
-Prevents DNA elongation once incorporated into DNA strand since it lacks necessary components for sugar-phosphate linking
Which NtRTIs have more pronounced AEs due to actions on mitochondrial RNA/DNA synthesis?
stavudine (thymidine)
didanosine (Deoxyadenosine)
zidovudine (Thymidine)
Which NtRTIs lack as many side effects
tenofovir (Deoxyadenosine)
emtricitabine (Deoxycytidine)
Abacavir (Deoxyguanosine)
lamivudine (Deoxycytidine)
AEs of the NRTIs
Peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, lipoatrophy, myopathy, anemia, lactic acidosis with fatty liver
Which NtRTI can be tested for hypersensitivity before therapy start?
Abacavir
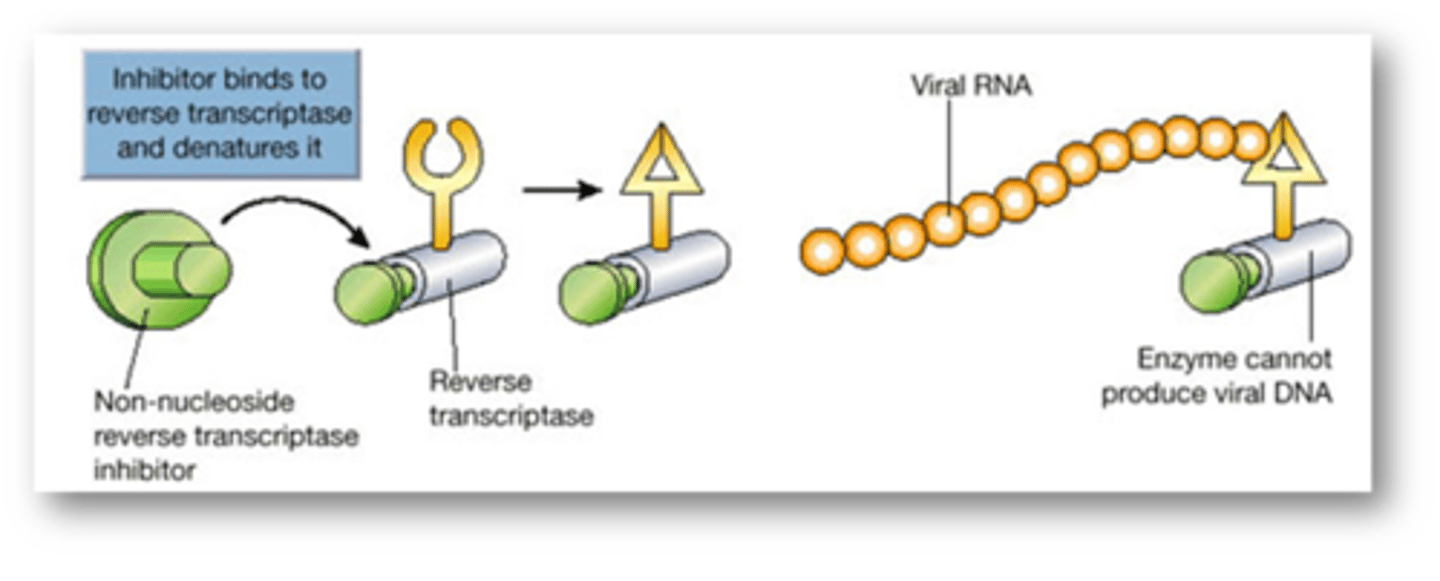
MOA of the Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTI)
Bind to reverse transcriptase adjacent to catalytic site and force a conformational change preventing DNA production
Delavirdine (DLV) (Rescriptor)
Efavirenz (EFV) (Sustiva)
Nevirapine (NVP) (Viramune)
Etravirine (ETR) (Intelence)
Rilpivirine (RPV) (Edurant)
Class
AEs
Resistance
Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTI)
AEs: Rash, Transaminitis (LFTs)
Single viral mutation can confer resistance to entire class (except etravirine)
Which NNRTI is less prone to resistance?
Etravirine
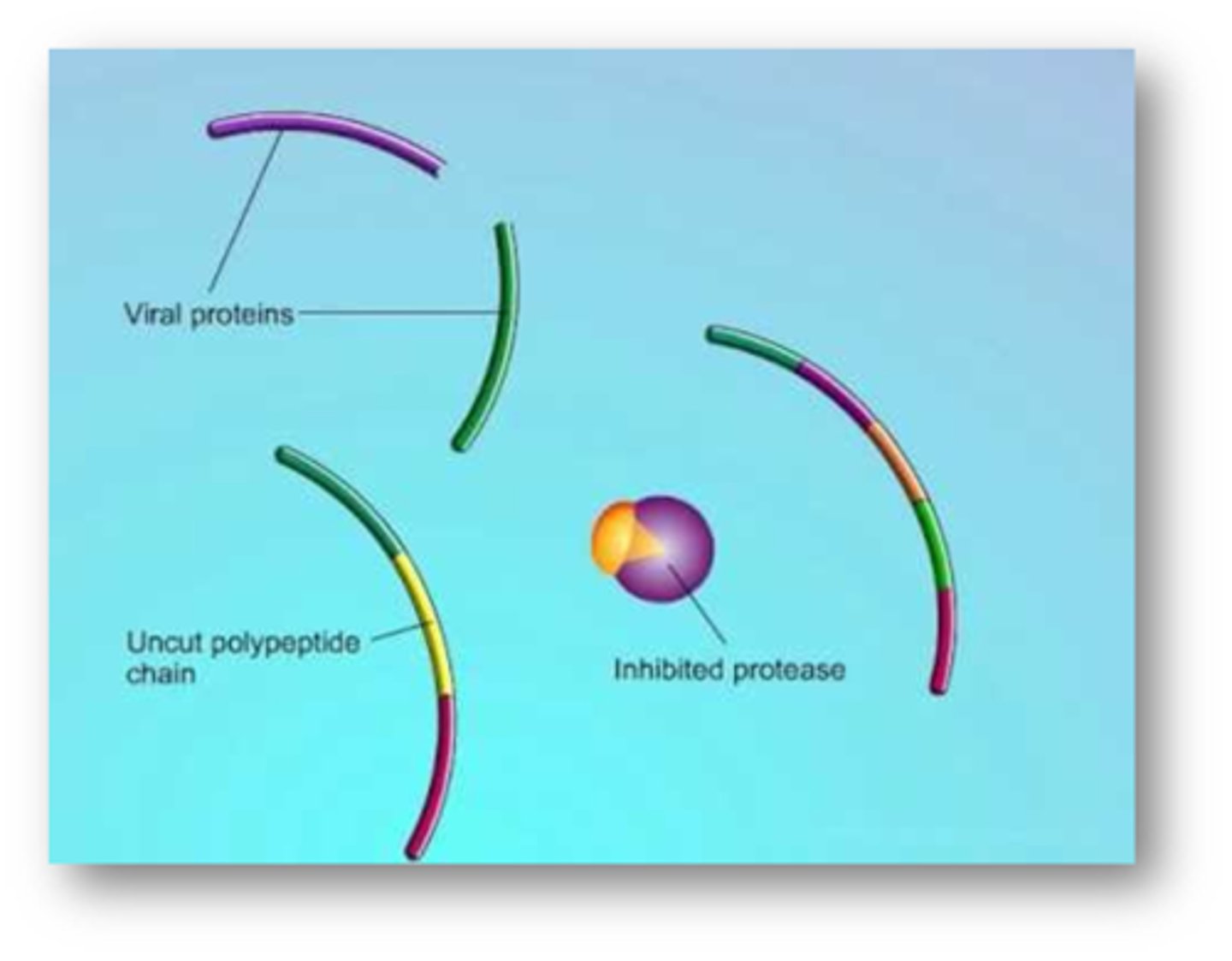
MOA of the protease inhibitors
Inhibit protease enzyme preventing virus from making mature proteins
Atazanavir (ATV) (Reyataz)
Darunavir (DRV) (Prezista)
Fosamprenavir (FPV) (Lexiva)
Indinavir (IDV) (Crixivan)
Lopinavir (LPV) (Kaletra w/ Ritonavir)
Nelfinavir (NFV) (Viracept)
Ritonavir (RTV) (Norvir)
Saquinavir (SQV) (Invirase)
Tipranavir (TPV) (Aptivus)
Class
AEs
Protease inhibitors!
Adverse effects
-GI distress
-Increased lipids
-Glucose intolerance
-Altered fat distribution (lipodystrophy)
What drugs are the protease inhibitors often given with and why?
Often given with low dose ritonavir or cobicistat
-CYP3A4 inhibitors
-Lead to higher drug levels
-Less frequent dosing
-Look at other interacations!
Enfuvirtide (ENF) (Fuzeon)
Class
MOA
AEs
Fusion inhibitor
MOA: Inhibits HIV-1 envelope fusion (NO activity against HIV-2)
AEs:
-No oral administration
-Injection site reactions very frequent (Pain, erythema, nodules)
Maraviroc (Selzentry)
Class
MOA
ADRs
CCR5 antagonist
MOA:
-Works on HIV-1/2
-Blocks HUMAN receptor and NOT the virus
-Can only be used on The correct strain of virus (Testing must be done prior to therapy start)
ADRs: Rash and hepatotoxicity
Raltegravir (RAL) (Isentress)
Dolutegravir (DTG) (Tivicay)
Elvitegravir (EVG) (Viteka)
Bictegravir
Class
MOA
ADRs
Integrase inhibitors
MOA: Bind to integrase and prevent viral DNA from being incorporated into chromosomal DNA
ADRs: Rash, nausea, HA
What is Elvitegravir (Viteka) often co-formulated with?
Cobicistat (CYP3A4 inhibitor)
What is Bictegravir often co-formulated with?
Emtricitabine (NtRTI) and tenofovir (Biktarvy) (NtRTI)
Which HIV drugs INDUCE CYP3A4?
Efavirenz, etravirine, and nevirapine (NNRTIs)
What class of HIV drugs generally inhibits CYP3A4?
Protease inhibitors
General treatment rules for HIV
Initial treatment should be managed with a minimum of 3 antiretroviral agents including a 2 NtRTI backbone
Example initial regimens:
Integrase inhibitor + 2 NRTI
-Raltegravir + tenofovir + emtricitabine
PI + 2 NRTI
-Darunavir (Boosted by ritonavir) + tenofovir + emtricitabine
NNRTI + 2 NRTI (less preferred)
-Efavirenz + tenofovir + emtricitabine
What are the two types of testing that can be done to assess HIV resistance?
Phenotype and genotype testing
HIV phenotype testing
Determines concentration of drug to inhibit 50% replication of the virus (IC50)
-Results are compared to wild type virus
-Provides resistance information for complex mutation patterns
-Higher cost, slower turnaround
HIV genotype testing
-Checks for specific genetic mutations that are known to confer resistance to specific drugs
-Not as informative as phenotyping
HIV in pregnancy
-Generally is treated as a non-pregnant patient
-Maximal viral suppression can limit exposure to fetus
-Breastfeeding is avoided where possible
Which HIV drug can cause neural tube defects?
Efavirenz (NNRTI)
Which HIV drug is recommended intrapartum and for the fetus for 4-6 weeks post-birth?
Zidovudine (NtRTI thymidine analog)
What drugs are often given to healthcare workers for HIV postexposure prophylaxis?
Tenofovir, emtricitabine, raltegravir for 4 weeks
-Started as early as possible
What HIV drug is used for pre-exposure prophylaxis?
Who requires pre-exposure prophylaxis?
Daily tenofovir/emtricitabine (Truvada)
-Men who have sex with men (MSM)
-Sero-discordant couples
-IV drug abusers
-Patients need to be seronegative prior to initiation
How is HIV treatment evaluated?
-Baseline CD4 and HIV RNA load
-HIV resistance test is recommended at initiation
-Monitored every 3 months until HIV RNA is undetectable
When should you change the HIV regiment?
-Intolerable side effects
-Treatment failure (viral RNA > 200 copies/mL)
-Documented resistance to agents
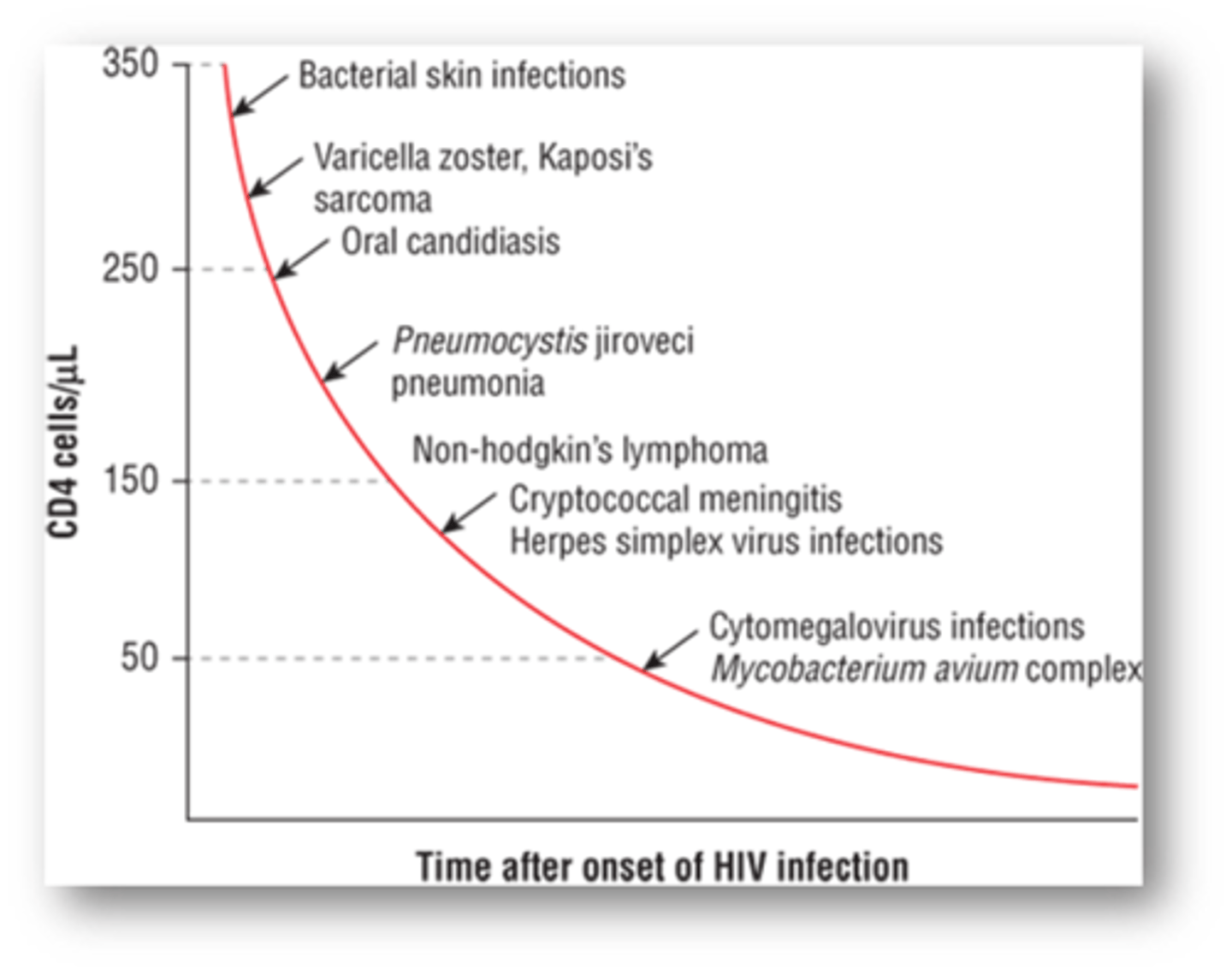
At what CD4 levels are certain opportunistic infections probable?
-Bacterial skin infection (<350)
-Oral candidiasis (<250)
-CMV/MAC (<50)
-PJP (<250)
Immune reconstitution syndrome (IRIS)
Associated with ART therapy initiation with underlying OI
-Worsening fever and OI manifestations
-Occurs due to major increase in inflammatory cascade to smoldering infection
What is the most common life-threatening OI in AIDs pts?
PJP
-a fungus with protozoal characteristics
-Insidious onset of Tachypnea, non to mildly productive cough occurring over weeks
Tx and prophylaxis for PJP
Tx: sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (Bactrim) for 21 days
-Started IV for more severe cases then switched to oral
Prophylaxis:
-Prophylaxis indicated when CD4 < 200 cells/mm3 or history of oropharyngeal candidiasis
-Secondary prophylaxis indicated for anyone with previous case of PCP pneumonia
-Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim given thrice weekly
Candidiasis (Thrush)
Tx
-Fluconazole (Diflucan) IV/PO for 7-21 days (depending on oral vs. esophageal infection)
-Nystatin oral liquid, swish and spit/swallow 4 times daily (Not recommended for esophageal candidiasis)
Why is Neisseria gonorrhoeae difficult to control?
What complications can Gonorrhoeae cause in women?
Difficult to control due to rapid incubation and high number of asymptomatic individuals
Complications more pronounced in women due to non-specific signs and symptoms that delay seeking treatment
-Pelvic inflammatory disease --> infertility/ectopic pregnancies
-Systemic infections
-HIV spread more easily in patients with gonorrhea
Tx for gonorrhea
What is treated along with it?
CDC only recommends IM, single dose ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 250 mg
Due to high rate of chlamydial co-infection, recommended to treat both at the same time
-Azithromycin (Zithromax) 1 g PO once
-Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID for seven days
No good alternatives for cephalosporin allergies (Maybe gemifloxacin or IM gentamicin
What is used to treat gonorrheal eye infections in infants?
Topical erythromycin ointment
Chlamydia trachomatis
Tx
More frequently asymptomatic than gonorrhea
Tx:
-Azithromycin (Zithromax) 1g PO
-Doxycycline PO BID x7days
-Tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones can be used as secondary agents, but should be avoided in pregnancy
Topical erythromycin recommended for chlamydial ophthalmia in children
Tx for syphilis
Treatment – parenteral penicillin G
-T. pallidum reproduces slowly, so single doses of short acting meds won’t eliminate infection
-Benzathine penicillin G (Bicillin) is effective for single dose therapy
-PCN allergy – doxycycline or tetracycline for 2-4 weeks
-Aqueous penicillin G (IV) given intermittently or continuously for more advanced cases or neurosyphilis
What is the MC cause of genital ulceration in the US?
Genital herpes (HSV)
-HSV-1 is with oropharyngeal disease
-HSV-2 is associated with genital disease
How to treat pain and discomfort in genital herpes?
-Warm saline baths, analgesics, antipyretics, antipruritics
-Good hygiene can prevent bacterial superinfection
Tx for Genital herpes (HSV)
First episode infections
-Acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir for 7-10 days reduces viral shedding, duration of symptoms, and time to healing
-Earlier treatment is more effective
-Topical treatment not recommended
-Immunocompromised patients or those with severe disease may need hospitalization and IV acyclovir
Episodic therapy: Initiated in 6-12 hours after prodromal symptoms begins, no more than 24 hours after lesion appears
Chronic suppressive: Reduces frequency by 70-80%
Tx for trichomoniasis
-Metronidazole (Flagyl)
-Tinidazole – anti protozoal toxicity by damaging DNA
-Single 2 g dose of either
-Treating partners leads to better cure rate
Hepatitis A
Transmission
Infection traits
Prevention
-Often self-limiting, Rarely fatal
-Fecal-oral route most common source of infection (shed in feces, contaminated water is a common mode of transmission)
Infection traits:
-Infection is usually acute, self-limiting and confers immunity
-Nearly all individuals will resolve within 6 months with the majority doing so in 2 months
Prevention: Hepatitis A vaccine recommended at 12 months (HAVRIX and VAQTA)
-Routine hand washing
-IG available for postexposure prophylaxis
Hepatitis B virus
-Transmission
-Chronic infection duration
Transmission:
-Chronic infection is major reservoir for transmission and risk for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
-Can be spread sexually, parenterally, or perinatally
Chronic infection: Patients with persistent antigen levels > 6 months have chronic HBV and cure is not possible at that point (Most common in Perinatal infections)
Prevention/Prophylaxis for Hepatitis B infection
Prevention:
-HBV vaccine (Recombivax and Engerix-B)
-TWINRIX (covers both HAV and HBV)
-Vaccine response is low and requires three doses for optimal protection
Prophylaxis: Vaccine or HBV IG
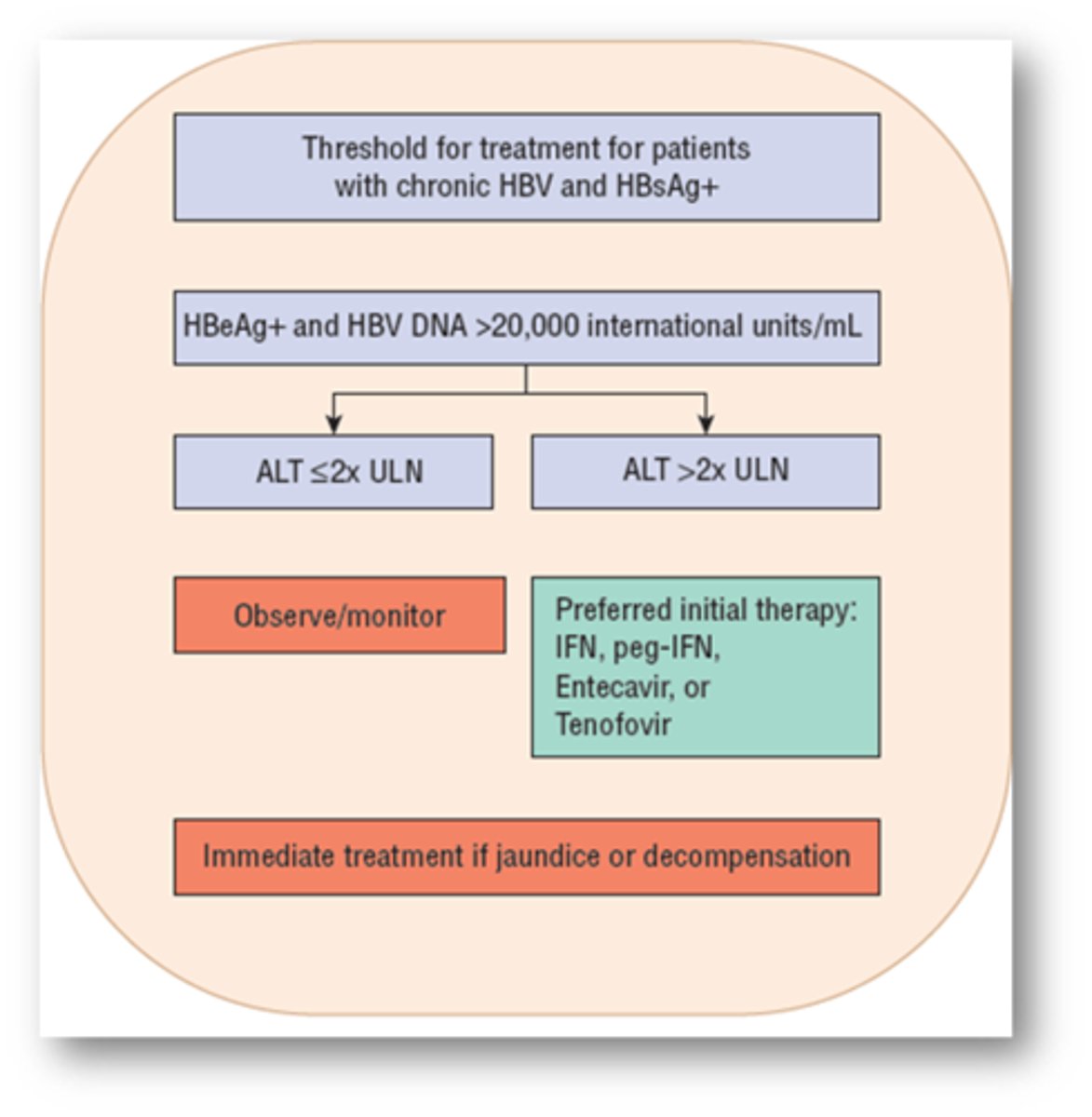
Who should receive HBV treatment?
-Many patients should first undergo serial monitoring of hepatic function and serological markers of viral infection
-Decision to treat is based on risk of liver-related morbidity and mortality in the foreseeable future
ALT <2x: Observe
ALT >2x: IFN, peg-IFN, Entecavir or tenofovir
Or, Immediately treat if jaundiced or decompensating
Interferon-alfa (IFN-alfa) (Intron A)
Use
MOA
Use: First approved therapy for HBV and improved long-term outcomes and survival
MOA:
-Acts as a host cytokine
-Antiviral, antiproliferative, and immunomodulatory effects in chronic HBV
-Stimulates host immune system to mount a defense against HBV
Adverse effects of Interferon-alfa (IFN-alfa)
-Risk for infection in decompensated cirrhotic patients
-Hepatic flares and precipitate hepatic decompensation in cirrhotic patients
-Black box warnings for fatal or life-threatening neuropsychiatric, autoimmune, ischemic, and infectious disorders
-Anaphylactic risk, flu like symptoms
-Depression, suicidal ideation, aggression
-Blood dyscrasias
Optimal duration of Tx is possibly 24 months.
Which HBV drug can be given indefinitely, but has relapse/resistance problems?
Lamivudine (Epivir)
Adefovir (Hepsera)
-Similar mechanism to lamivudine
-Activity against lamivudine resistant HBV
-Monitor serum creatinine as nephrotoxicity has been reported
Entecavir (Baraclude)
Telbivudine
Tenofovir (Viread)
Entecavir: Considered First line for HBV due to safety and low resistance. Used in lamivudine-resistant strains
Telbivudine: More effective than lamivudine, but high rate of resistance
Tenofovir (Viread): Also considered first line for HBV with low resistance rates
What is the most common subtype of HCV in the US?
GT1-6
Daclatasvir (Daklinza)
Use
MOA
Use: Effective against HCV
MOA: Prevents viral RNA replication and virion assembly by binding to NS5A. Distorts structure of protein and impairs function
-No adjustment in renal/hepatic insufficiency
Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni)
Use
MOA
Use: HCV
MOA:
-Ledipasvir inhibits NS5A to block viral replication
-Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide prodrug that inhibits NS5B RNA polymerase (acts as a chain terminator once incorporated into viral RNA)
-NO organ dose adjustment needed
Simeprevir (Olysio)
Use
MOA
ADRs
Use: HCV
MOA: Inhibits NS3/4A protease (Enzyme responsible for forming mature, functional HCV proteins (virus can’t make NS4A, 4B, 5A, and 5B))
-Used with Sofosbuvir or IFN/ribavirin
ADRs: rash/photosensitivity, pruritus, nausea
Ombitasvir
MOA
Combination
MOA: NS5A inhibitor
Used in combination with:
-Paritaprevir – NS3/4A inhibitor
-Ritonavir - boost drug levels of paritaprevir
-Technivie®
-Given with or without dasabuvir (combination with above 3 is Viekira®
Ribavirin (Rebetol)
MOA
ADRs
MOA:
-Decreased gaunosine triphosphate
-Increases RNA mutation rate leading to “error catastrophe”
-Immunostimulatory
-Given frequently with interferon in the past
ADRs:
-suicidal ideation, depression, insomnia, dyspnea,
-Hemolytic anemia (10-13%) (Within 1-2 weeks of start)
What pregnancy category is Ribavirin?
What should women use after Tx with ribavirin and for how long?
Pregnancy category X
Females should use 2 forms of birth control for up to 6 months after discontinuation
Which patient populations will generally receive Ribavirin?
Continues to be used in difficult to treat patients (Prior treatment experience, underlying cirrhosis)
-It is very difficult to achieve sustained virologic response in cirrhotic pts.
Treatment tips for HCV
Treatment experienced patients
-May require longer treatment or use of ribavirin
-Consider resistance testing
Acute exposures
-Up to 50% of patients will spontaneously clear HCV within 6 months
-May defer therapy until then
Compliance
-Any delay can lead to resistance and failure
-Must ensure patients can receive their medication EVERY month