UTZ Prelim
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Ultrasound
employs high frequency sound waves
Ultrasound
Sound waves with frequencies above the normal human range of hearing
Ultrasound
Sound waves with frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
mechanical and longitudinal
Ultrasound is technically a ______ and ______ wave
2-10 MHz
frequency of medical UTZ
1 ms
Duration of the pulse is about ____
1000 times per second
pulses are repeated about ______
high intensity
Strong echoes are said to be
Strong echoes
appear as brighter dots on the screen
Transducer
A device that converts mechanical energy from and to electric energy
Relatively low cost of equipment
Non-ionizing and safe
Scanning can be performed in any plane
Can be repeated frequently
Detection of blood flow, cardiac and fetal movement
Portable equipment
Aids biopsy and drainage procedure
ADVANTAGES OF ULTRASOUND
Operator dependent
Inability of sound to cross interface with gas or bone causing unsatisfactory visualization of underlying structure
Scattering of sound in the presence of fat`
DISADVANTAGES OF ULTRASOUND
coronal section

saggital section
transverse section
Lazzaro Spallanzani
He experimented with bats and found that the maneuvered through the air using the hearing rather than sight.
ecolocation
the use of sound waves to determine distances or locate objects
Lazzaro Spallanzani
forms the basis for ultrasound physics
1793
Lazzaro Spallanzani discovered that bats navigate themselves with the help of sound whistles while flying in darkness.
SONAR
A system that uses the reflection of underwater sound waves to detect objects.
piezoelectric crystal
An integral component of the ultrasound transducer that converts electrical energy into sound energies of various frequencies above the human audible range. These crystals also convert sound energy (echoes) into electrical signals that become the sonographic image
Radio Detection and Ranging
RADAR
Sound Navigation and Ranging
SONAR
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
LASER
20 Hz
the lowest frequency humans can hear
1540 m/s
Speed of sound in soft tissue
Jean-Daniel Colladon
Swiss physicist/engineer who discovered sonography with an underwater bell in 1826. He accurately determined the speed of sound.
1826
Jean-Daniel Colladon, Swiss physicist/engineer who discovered sonography with an underwater bell
Pierre & Jacques Curie
discovered piezoelectricity
Pierre & Jacques Curie
They observed that an electric potential would be produced when mechanical pressure was exerted on a quartz crystal . This gave us the ability to create ultrasonic waves.
Transducer
A device that converts electric energy to ultrasound energy and vice versa
1880
The first scientific publication describing the phenomenon
Tourmaline, quartz, topaz, cane sugar and Rochelle salt
Crystals in experiment of Pierre & Jacques Curie
Paul Langevin
He invented the hydrophone to detect icebergs. The hydrophone was later used to detect submarines in World War I. This marked a significant milestone in the history of ultrasound.
1912
After the sinking of the Titanic, Paul Lagevin invented the hydrophone to detect iceberg.
1912
The sinking of the Titanic inspires Paul Langevin and Constantinoski to invent an ultrasound machine to detect iceberg.
Dr. Karl Dussik
An Austrian psychiatrist, who was the first to use ultrasound pictures in an attempt to diagnose brain tumors in the late 1930s.
Hyperphonography
First procedure done by Dr. Karl Dussik using ultrasound pictures in an attempt to diagnose brain tumors
heat sensitive paper
Dr. Karl Dussik used _____ paper to record echoes
1942
First to use ultrasound as a diagnostic tool to locate brain tumor and the cerebral ventricles.
neurologist
Dr. Karl Dussik is a _____from the University of Vienna.
Dr. George Ludwig
In 1940s, he was the first records and studied the difference in sound waves as they traveled through tissues, organs, muscles and gallstones in animals.
1948
Dr. George Ludwig was the first records and studied the difference in sound waves as they traveled through tissues, organs, muscles and gallstones in animals.
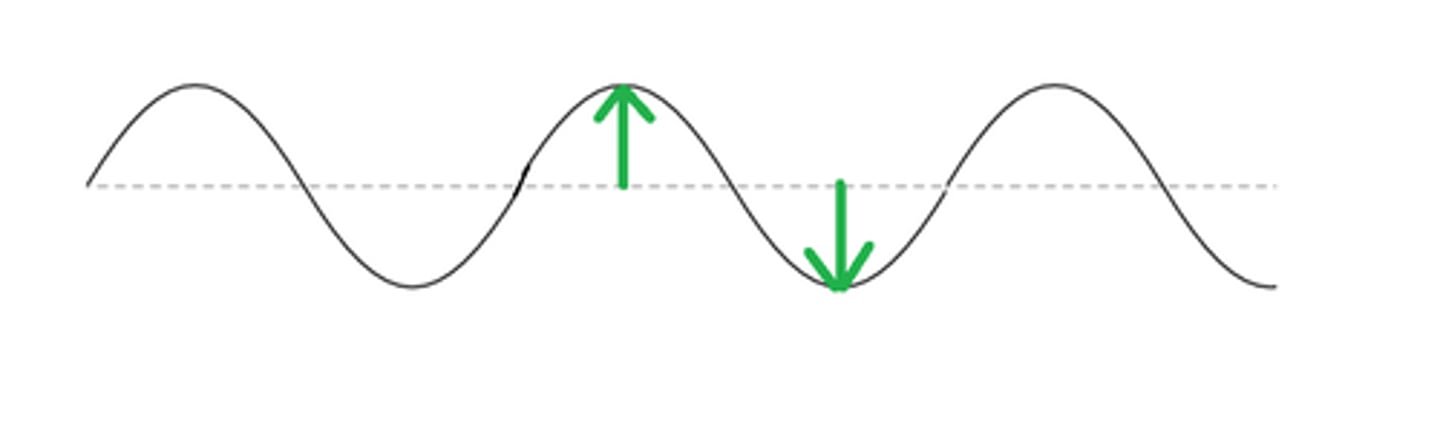
Amplitude
A mode
343 m/s
speed of sound
hydro
water
sound
phone
Inge Edler and Hellmuth Hertz
in 1953, they performed the first successful echocardiogram by employing an echocardiogram test control device from a Siemens shipyard.
1953
Inge Edler and Hellmuth Hertz performed the first successful echocardiogram by employing an echocardiogram test control device from a Siemens shipyard.
Dr. Ian Donald
During World War II, he became interested in radar and sonar.
Dr. Ian Donald
Father of Obstetric Ultrasound.
Dr. Ian Donald
He also invented the B-mode scanner, and he was able to detect a twin pregnancy.
1958
Dr Ian Donald, during World War Two, invented the B-mode scanner.
Douglas Howry and Joseph Holmes
In the 1950s and 1960s they improved the B mode scanner. Up until then, the patient had to be submerged and water to produce images.
Douglas Howry and Joseph Holmes
They invented a transducer that was put in direct contact with the patient.
Bright mode
B-mode
amplitude
height or loudness of the wave
velocity
speed of the wave
wavelength
distance traveled by a wave in a single cycle
cycle
repetition of the back and forth motion of the motion of the molecules
amplitude
wavelength
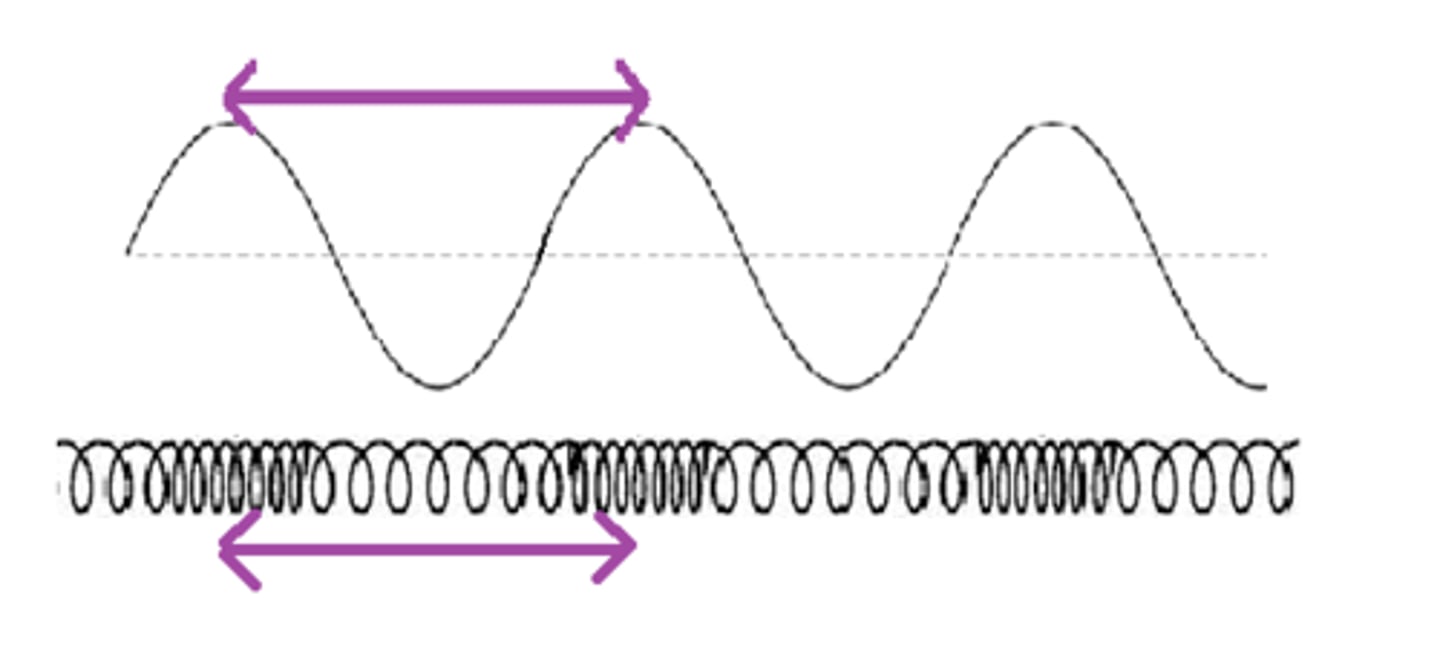
inversely proportional
wavelength is _____ proportional to frequency
time
measurement of cycle
low frequency
frequency used for deeper structure
high frequency
frequency used for superficial structure
high frequency
frequency who exhibits high quality image
3.5 probe
used for abdominal UTZ
refraction
bouncing back or reflection of the sound wave
shorter wavelength
wavelength that gives BETTER RESOLUTION, CLEARER IMAGE and MORE DETAILS on the screen
focusing
Ultrasound waves can be focused either by lenses and mirrors or electronically in composite transducers.
narrow focused beam
images a thin section of tissue, gives better detail and sharper resolution
unfocused beam
gives hazy images
composite focus
Variable focal length which can be adjusted to the required depth.
annular array sector transducer
adjustable focusing in all planes
narrow acoustic beam
thinner image section, high quality, clearer image and have more information
fixed focal distance
Most transducers have a _______ in at least one plane
annular array sector transducer
The only transducer who have an adjustable electronic focus in all planes.
latitude
range of contrast
short latitude
have fewer shades of grey and more details
long latitude
more shades of grey
21 shades of grey
visible shades of grey human eye can see
hyper
high
iso
mid
hypo
low
echoic
term that describes memory of sounds
dense
term used in CT scan
intense
term used in MRI
radiolucent
radiopaque
terms used in xray
attenuation
partial or total absorption of the energy of an x-ray beam as it traverses an object
higher frequency
more absorbed and scattered