Chem 2 Exam 1 UARK
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
VSEPR Theory
helps explain and predict molecular geometry around the central atom
Electron Groups
bonding groups (single, double, and triple bonds each count as one bonding group) and lone pairs of electrons
2 b, 0 lp
Linear
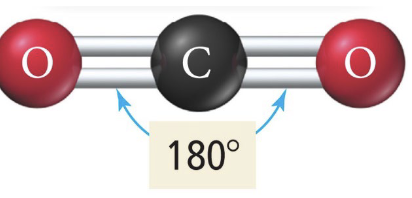
3 b 0 lp
Trigonal planar
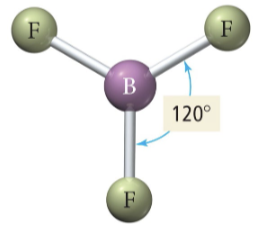
2 b 1 lp
Bent
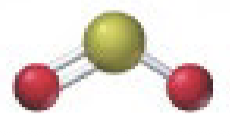
4 b 0 lp
Tetrahedral
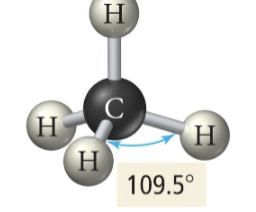
3b 1 lp
trigonal pyramidal
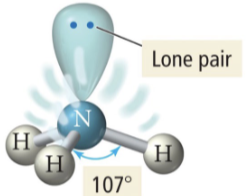
2 b 2 lp
bent
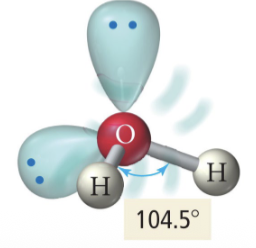
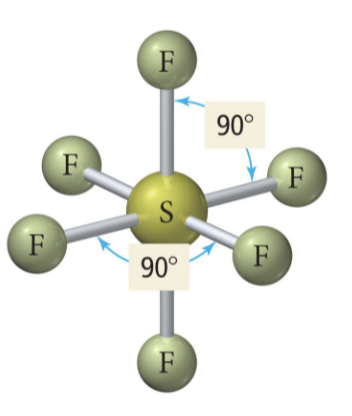
5 b 0 lp
Trigonal bipyramidal
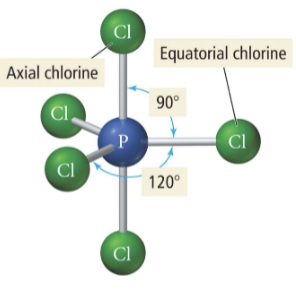
4 b 1 lp
Seesaw
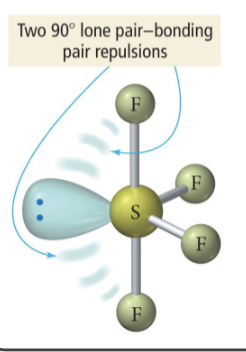
3 b 2 lp
T-shaped
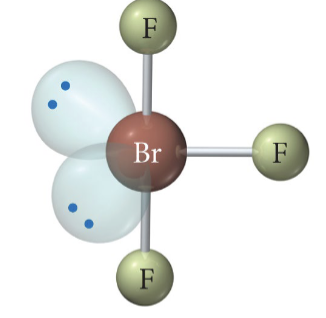
2 b 3 lp
Linear
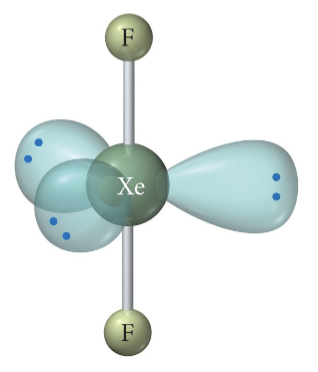
6 b 0 lp
Octahedral
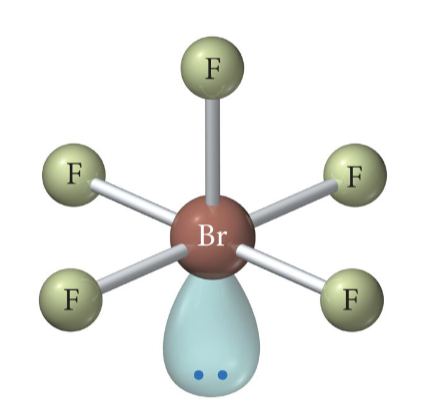
5 b 1 lp
Square pyramidal
4 b 2 lp
Square planar
The 4 most electronegative atoms from highest to lowest
F
O
N/Cl
Most likely result in a non-polar molecule
Linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral
Most likely results in a polar molecule
Bent, trigonal pyramidal, seesaw, t-shape, and square pyramidal
Two geometries that are exceptions and result in nonpolar molecules
Square planar (4 b 2 lp) and Linear (2 b 3 lp)
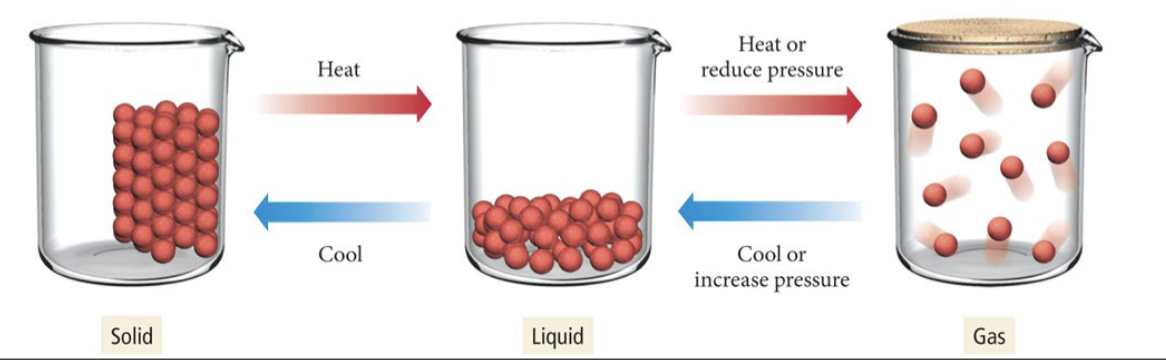
Solids can be __________
crystalline or amorphous
Amorphous solids have
no long-range order
Crystalline solids have
long-ranger order, regular ordered structure
The changes between states
Intermolecular forces are _______ molecules
BETWEEN
Bonds are _____ molecules
within
Bonds are _____
stronger than intermolecular forces
Dispersion Forces
Between all neutral particles, only intermolecular force between nonpolar molecules
increasing with increasing surface area and size
Dipole-dipole forces
between polar molecules
Hydrogen bonding
between particles w N-H, O-H, F-H bond
strongest intermolecular force in a pure substance
Ion-Dipole force
between polar molecule and ion ex. NaCl (aq)
only occur in mixtures
Hydrogen bonding…
increases the boiling point and melting point of molecules
Like dissolves like, so
polar solvents dissolve polar or ionic solutes
nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes
As molar mass increases,
boiling point, melting point, and viscosity increase
As intermolecular forces increase
boiling point, melting point, viscosity, and surface tension increase
Vaporization
the process by which thermal energy can overcome intermolecular forces and produce a state change from liquid to gas
The rate of vaporization increases with
increasing temp, surface area, and decreasing strength of intermolecular forces
Volatile
liquids that vaporize easily
Nonvolatile
liquids that do not vaporize easily
Vaporization is
endothermic (+)
Heat of vaporization of enthalpy of vaporization means
the heat required to vaporize 1 mole of liquid to gas
increases with increasing intermolecular forces
Dynamic equilibrium
rate3 of condensation = rate of vaporization
Vapor pressure
pressure of a gas in dynamic equilibrium with its liquid
depends on temp and intermolecular forces
When a system in dynamic equilibrium is disturbed,
the system responds so as to minimize the disturbance and return to a state of equilibrium
Boiling point
temp at which the liquid’s vapor pressure equals the external pressure
Normal boiling point
the temp a which the vapor pressure equals 1 atm
As elevation increases,
the boiling point of water decreases
Once the boiling point of a liquid is reached,
additional heating only causes more rapid boiling; it does not raise the temp of the liquid above its boiling point
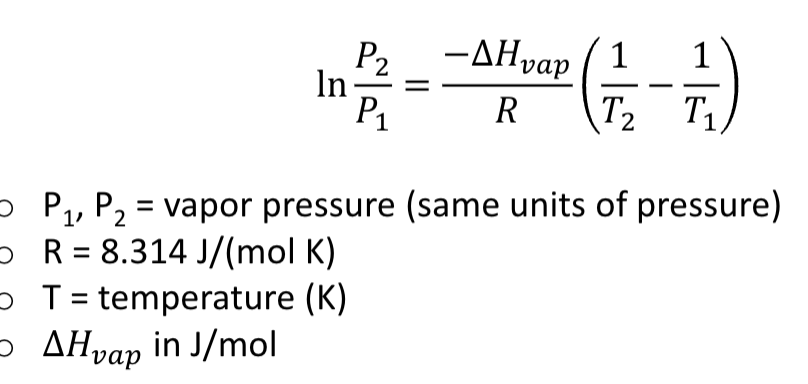
Clausius-Clapeyron equation
compares vapor pressure at two different temperatures
Supercritical fluid
neither a liquid nor gas
Critical temperature
the temp at which the transition to a supercritical fluid occurs Tc
Critical Pressure
the pressure at which the transition occurs Pc
Sublimation
transition from solid directly to gas
ex. dry ice at room temperature
Deposition
transition from gas directly to solid
Melting or fusion
transition from solid to liquid
Freezing
transition from liquid to solid
Heat of fusion, or enthalpy of fusion
the heat required to melt 1 mole of a solid
requires intermolecular forces to be partially overcome
generally increases with increasing intermolecular forces
fusion is positive b/c melting in endothermic
Heating Curve for water

Three main regions of phase diagram
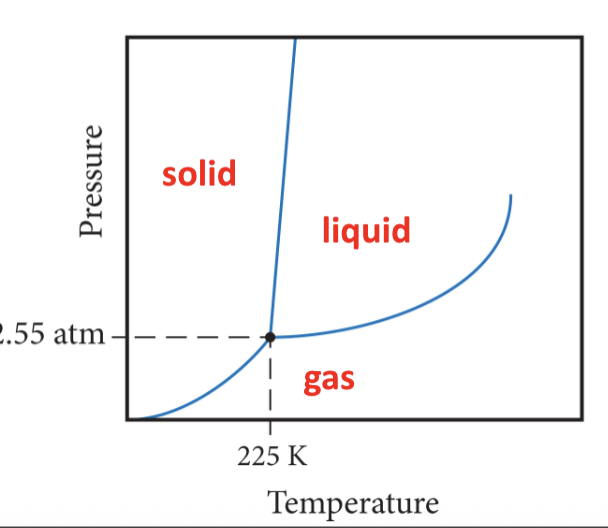
Curves in Phase diagram
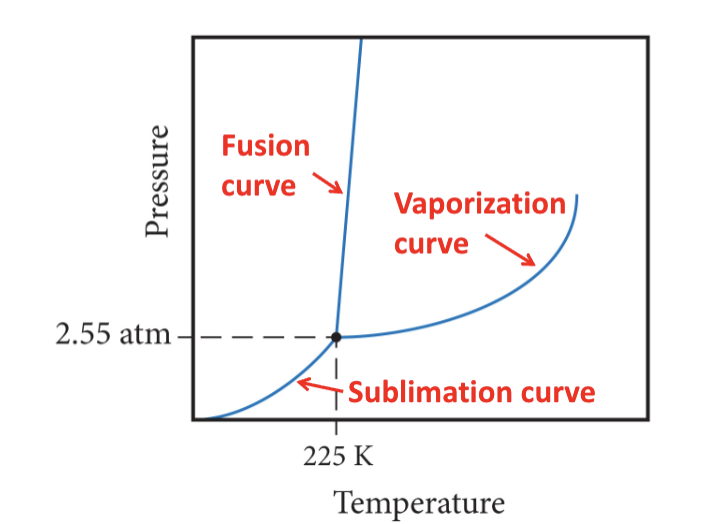
Triple point
set of conditions at which three states are equally stable and in equilibrium
Critical point
represents the temp and pressure above which a supercritical fluid exists
If the fusion curve has a positive slope,
the solid state is more dense
If the fusion curve has a negative slope,
the liquid state is more dense
Crystalline solids
Molecular solids, Ionic solids, and Atomic solids
Molecular solids
composite units are molecules
low melting point
ex. ice
Ionic solids
composite units are cations and anions
high melting points
ex. table salt, NaCl
Atomic solids
nonbonding, metallic, and network covalent
Nonbonding
held together by dispersion forces
low melting point
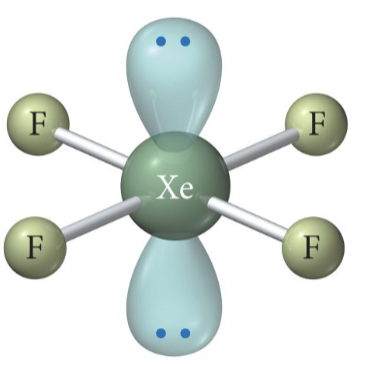
ex. solid xenon
Metallic
held together by metallic bonds
variable melting points
ex. gold
Network covalent
held together by covalent bonds
high melting points
ex. quartz
Solubility
the amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent
Aqueous solutions have what as the solvent
water
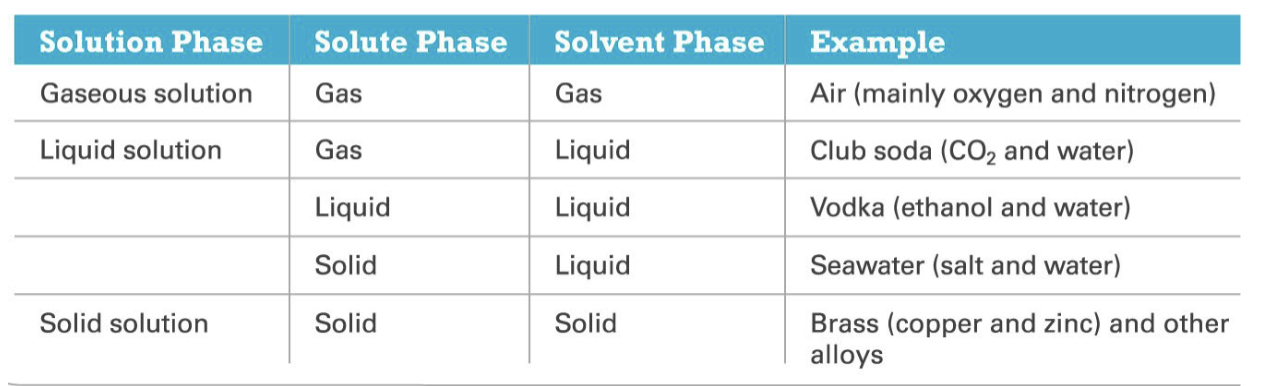
Type of Solutions
Entropy
a measure of energy randomization or energy dispersal in a system
increases when the gases mix
spontaneous process
Intermolecular forces exist between
solvent-solute
solvent-solvent
solute-solute
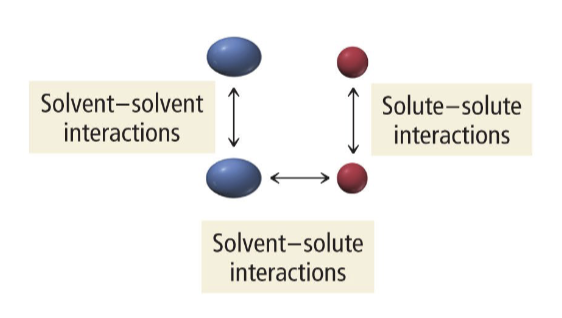
Solvent-solute interactions > solvent-solvent and solute-solute then
solution genrally forms
Solvent-solute interactions = solvent-solvent and solute-solute then
Solution generally forms
Solvent-solute interactions < solvent-solvent and solute-solute then
Solution may or may not form, depending on relative disparity
Common Polar solvents
Water (H20), Acetone (CH3COCH3), Methanol (CH3OH), and Ethanol (CH3CH2OH)
Common Nonpolar solvents
Hexane (C6H14), Diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3), Toluene (C7H8), Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)
Miscible
when two liquids form a homogeneous solution in all proportions
Enthalpy of solution
overall enthalpy change of solution formation
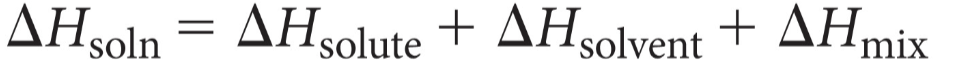
Know this?

Heats of hydration
energy change that occurs when 1 mole of the gaseous solute ions are dissolved in water
exothermic for ionic compounds
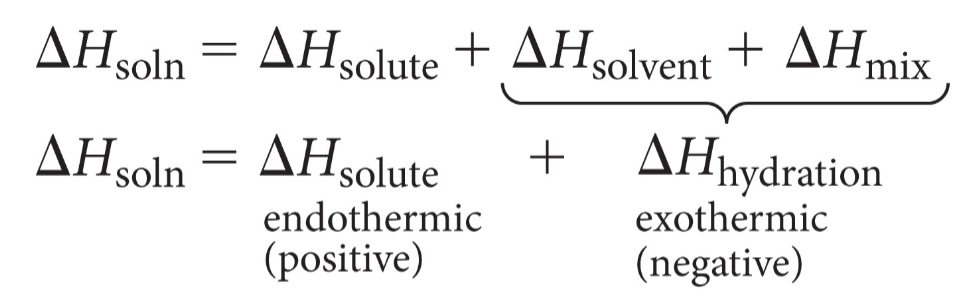
Heats of Hydration…
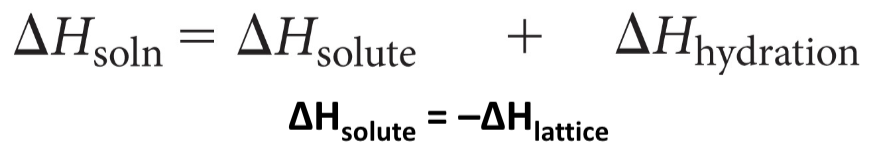
Know this?

Saturated solution
has exactly the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in the solvent
Unsaturated solution
has less than the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in the solvent
Supersaturated solution
more than the maximum amount of solute that cen be dissolved in the solvent
Solubility decreases with
increasing temperature
Solubility increases with
increasing pressure
Henry’s Law
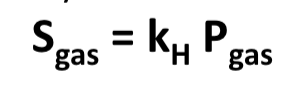
Molarity (M)
amount solute ( in mole)/ volume solution (in L)
mol/L
Morality (m)
amount solute (in mole)/ mass solvent (in kg)
mol/kg
Percent by mass
multiplications factor = 100 %
Mole fraction (x)
amount solute (in mol)/ total amount of solute and solvent (in mol)
Parts per million by mass (ppm)
multiplication factor = 106
Parts per billion by mass (ppb)
multiplication factor = 109
If given molarity (M),
assume 1 L solution
If given molality (m)
assume 1 kg solvent