5 psy therapies - CBT
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
combination of cognitive and behavioral therapies
that helps people change negative thought patterns, beliefs, and behaviors to manage symptoms and live more productive, less stressful lives.
What is Cognitive-Behavior Therapy (CBT)?
the idea that emotions and behaviors result from cognitive processes,
and that these processes can be modified
to achieve different feelings and behaviors.
What is Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) based on?
psychoeducational model
emphasizes (therapy as a learning process) involving:
new skills
new ways of thinking
effective coping strategies
What kind of model is CBT, and what does it emphasize?
combines cognitive and behavioral therapies.
generally short-term
focuses on helping clients deal with specific problems.
What does CBT combine, it’s genuine time and what is its main focus?

Aaron Beck
in the early 1960s as a result of his research on depression.
Who developed Cognitive Therapy and when?
He was a psychoanalytic psychotherapist.
a prominent psychologist and psychiatrist
What was Aaron Beck’s original therapeutic background?
depression results from hostility turned inward the self.
What psychoanalytic concept did Beck test regarding depression?
contained
fewer themes of hostility
more about defectiveness (النقص), deprivation, and loss
What did Beck discover about the dreams of depressed patients?
negative bias in how they interpreted life events,
leading to cognitive distortions.
What negative pattern did Beck observe in depressed clients?
because of its focus on thinking
now called (CBT) since it also includes behavioral techniques.
Why did Beck name his approach “cognitive therapy,” and what is it now called?
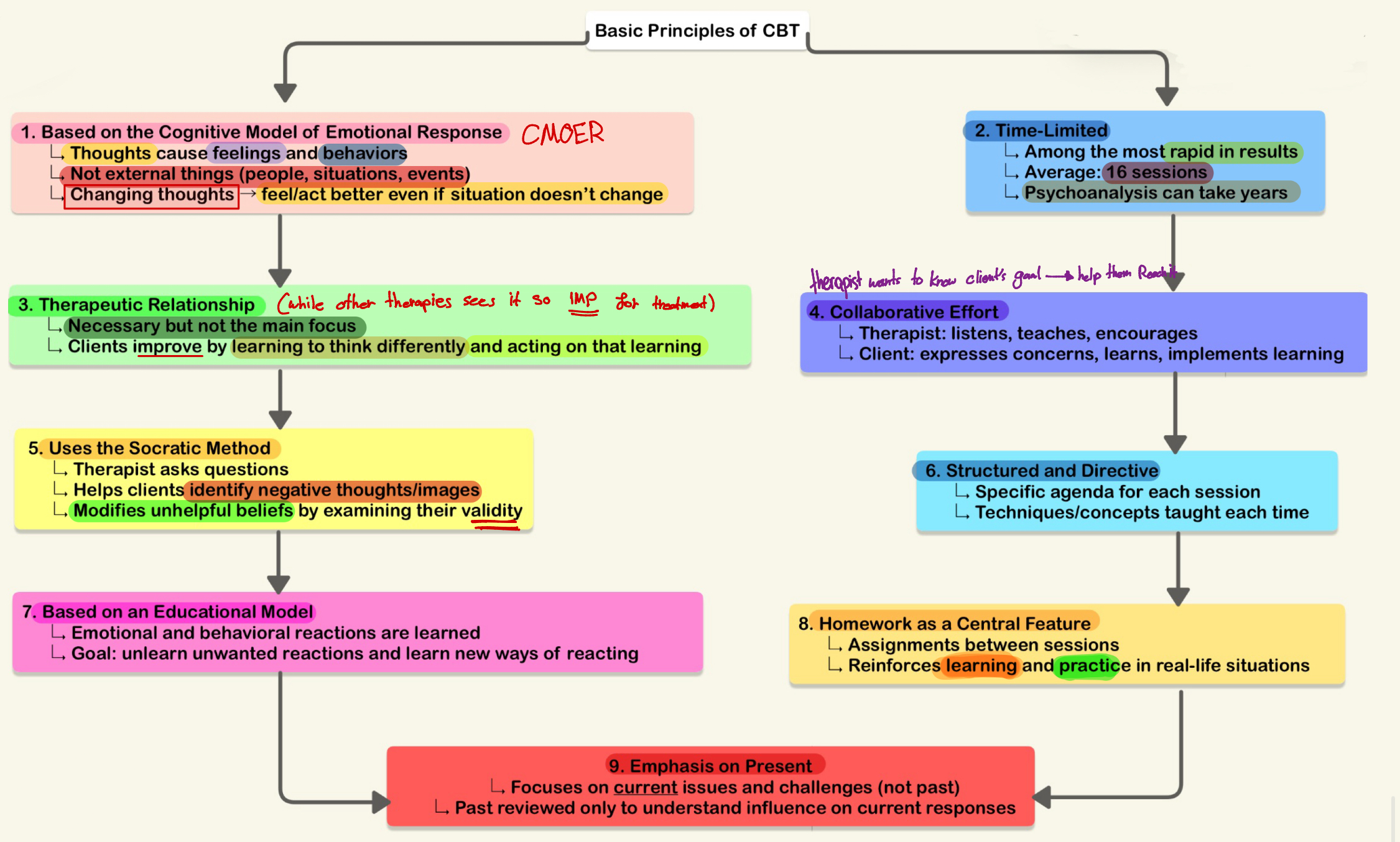
Mention the principles of CBT?
A = Activating Event → an initial situation or event that leads to a thought.
What does “A” stand for in the ABC Model?
B = Beliefs → the thought or belief that occurs at the time of the event.
What does “B” stand for in the ABC Model?
C = Consequences → the feeling or behavior perceived as resulting from the event or thought.
What does “C” stand for in the ABC Model?
A – Activating Event
“The client failed the exam.” → In the ABC model, is this A, B, or C?
B – Belief
“The client thought she is a failure and not good at anything.” → In the ABC model, is this A, B, or C?
C – Consequence
“Depressive symptoms appeared as a result of that thought.” → In the ABC model, is this A, B, or C?
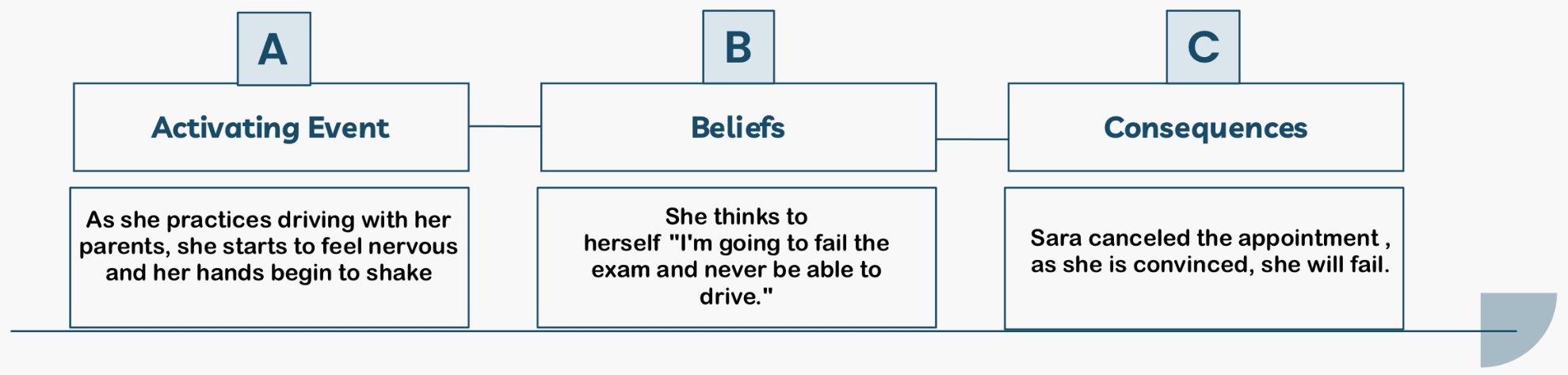
Sara is preparing for her driver's license exam. As she practices driving with her
parents, she starts to feel nervous and her hands begin to shake. She thinks to
herself "I'm going to fail the exam and never be able to drive."On the day of the
exam, Sara canceled the appointment , as she is convinced, she will fail.
Define ABC?
Thoughts that automatically come to mind when a particular situation occurs.
What are automatic thoughts?

What are the qualities of automatic thoughts?
They are cognitive contents from schemas
fundamental جايه من الجذور و افكارنا ومشاعرنا مبنية عليها
inflexible جامدة يعني ما تتغير حتى لو في دليل زي الشخص اللي ينسب نجاحه للحظ
absolute مطلقة يعني ما يفكر انه فاشل بنسبة معينة، يا اسود يا ابيض
generalized beliefs about oneself, others, the world, and the future.
What are core beliefs?
They underlie (تشكل) and produce automatic thoughts.
What do core beliefs produce?
They remain dormant (خامدة) until activated by stress or negative life events.
When are core beliefs activated?
Helpless العجز
worthless
unlovable
What are the categories of core beliefs?
In childhood
When do core beliefs develop?

What are the differences between Core beliefs and Aautomatic Tthoughts ?
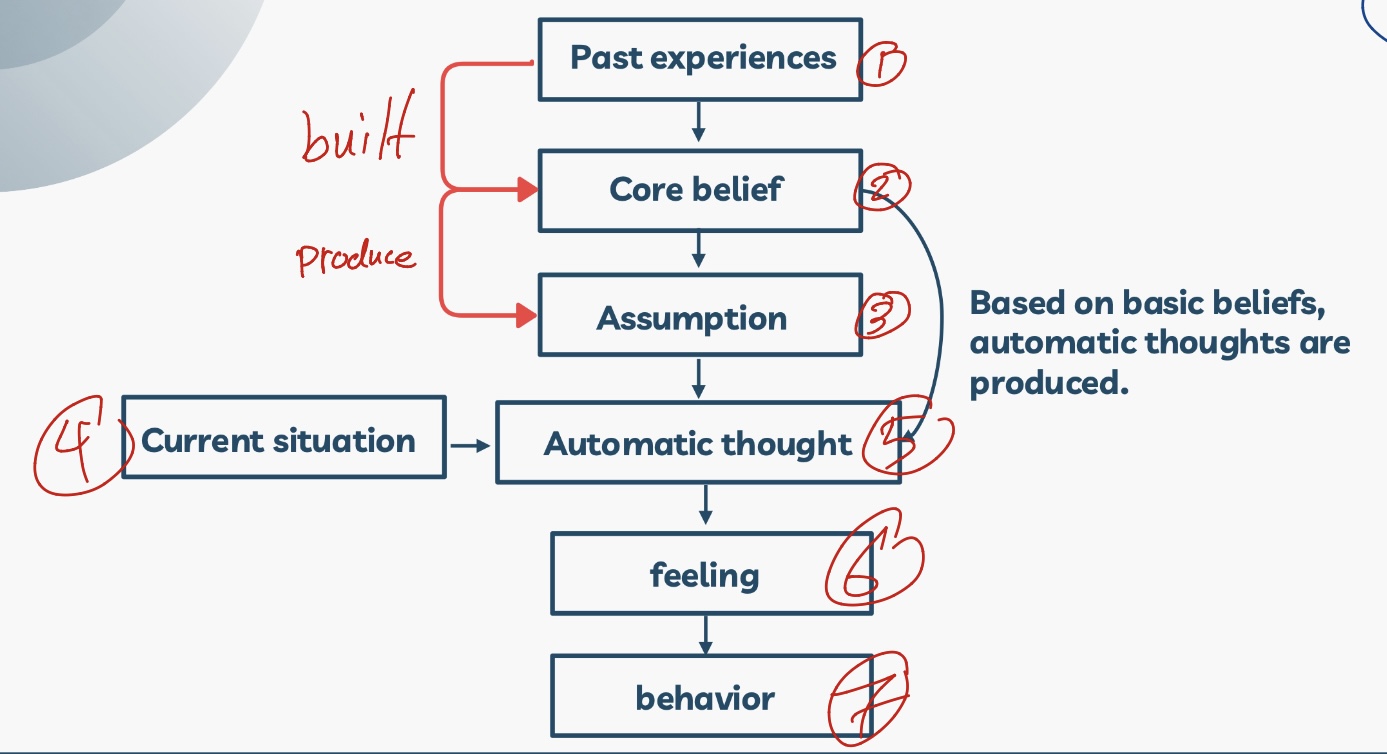
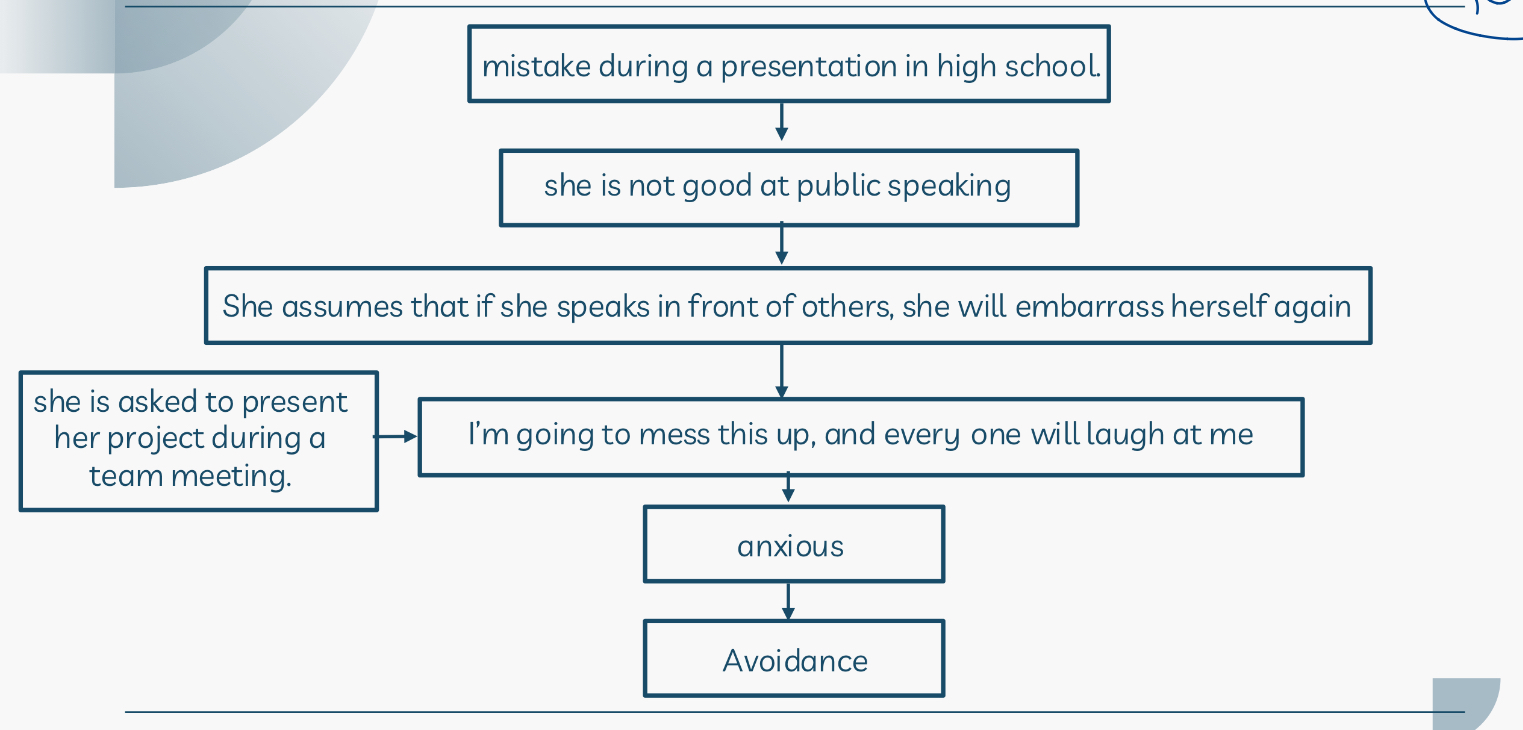
Provide an example on this graph?
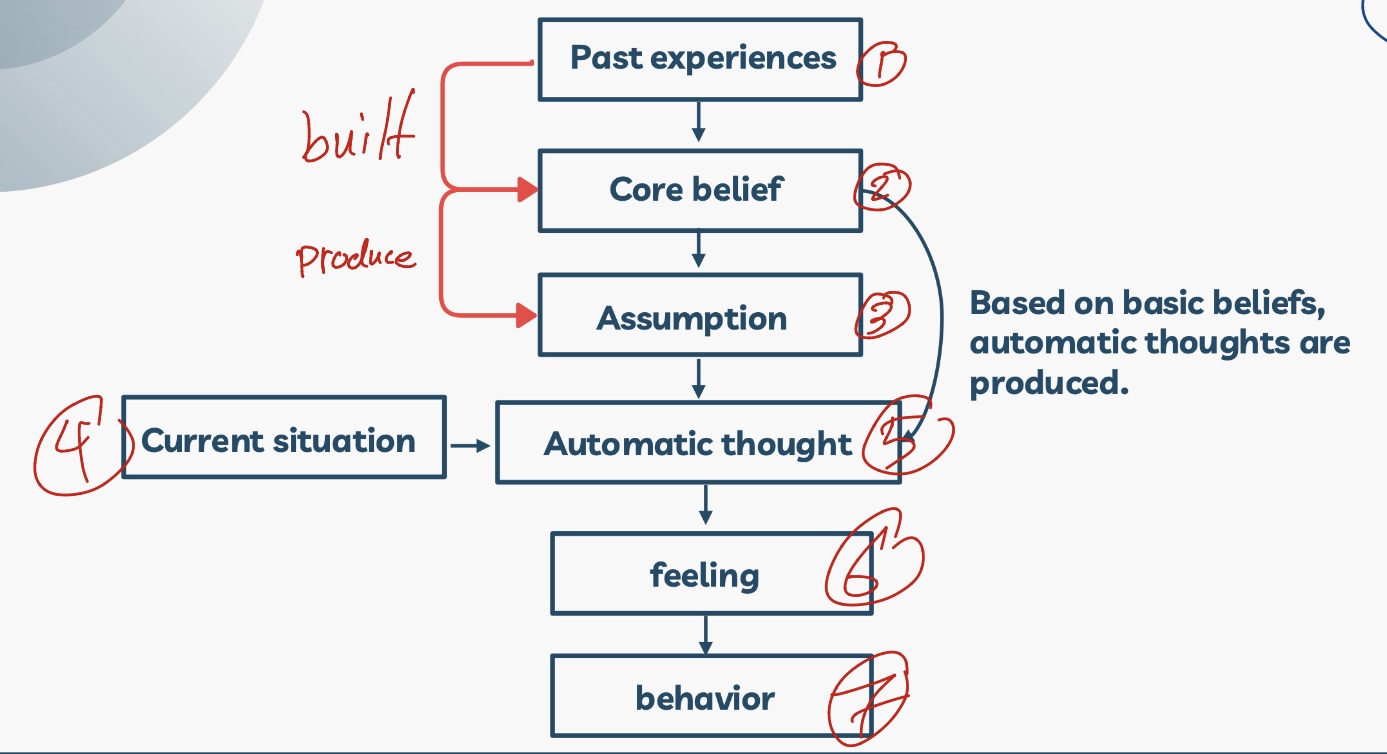

What are cognitive distortions?
Selecting one idea or fact from an event
while ignoring other facts
to support negative thinking.
What is selective abstraction in cognitive distortions?
Focusing on the one negative comment among many compliments
Give an example of selective abstraction?
Holding extreme beliefs based on a single incident and applying them inappropriately to other events.
What is overgeneralization in cognitive distortions?
💡“I failed a test; I am bad at everything.”
Give an example of overgeneralization?
Expecting that the worst will happen or has already happened.
What is catastrophic thinking in cognitive distortions
💡“If I drive my car, I could get into a terrible accident and die.”
Give an example of catastrophic thinking?
When evaluating yourself, another person, or a situation
, you unreasonably magnify the negative and/or minimize the positive.
What is magnification & minimization in cognitive distortions?
💡“I made one mistake in my presentation; now everyone will think I'm incompetent.”
💡“Getting high marks doesn’t mean I’m smart.”
Give an example of magnification & minimization?
catastrophic thinking
I have a headache; it must be a brain tumor, and that means I’m going to die
this is a cognitive distrotion called?
magnification
Example: “I have a headache; it must be a brain tumor
this is a cognitive distrotion called?
It is the tendency to relate external events to oneself even when there is no logical basis for the connection.
What is personalization in cognitive distortions?
💡“My friends didn’t invite me because they don’t like me.”
Give an example of personalization?
An extreme form of generalizing,
where one or two instances or qualities are turned into a global judgment.
What is labeling in cognitive distortions?
“I failed in this task; then I am a failure.”
Give an example of labeling?
Thinking and interpreting in all-or-nothing terms or categorizing experiences into extremes.
What is black-and-white thinking in cognitive distortions?
“If I can't do it perfectly, it's not worth doing.”
Give an example of black-and-white thinking?
implicit or explicit rules we have about how we and others should behave
What is the "Should" cognitive distortion?
⇨ When others break the rules, we feel upset.
⇨ When we break our own rules, we feel guilty.
What happens when others or we break implicit or explicit rules?
“I should always be successful.”
Give an example of the "Should" cognitive distortion?
It is thinking that if we feel a certain way, it must be true
What is emotional reasoning in cognitive distortions?
“I feel guilty, so I must have done something wrong.”
Give an example of emotional reasoning?
concept in cognitive therapy
referring to three core negative beliefs or thought patterns that contribute to mental health disorders like depression.
What is Beck's cognitive triad?

Automatic, spontaneous, and seemingly uncontrollable negative thoughts about:
What does Beck’s cognitive triad involve?
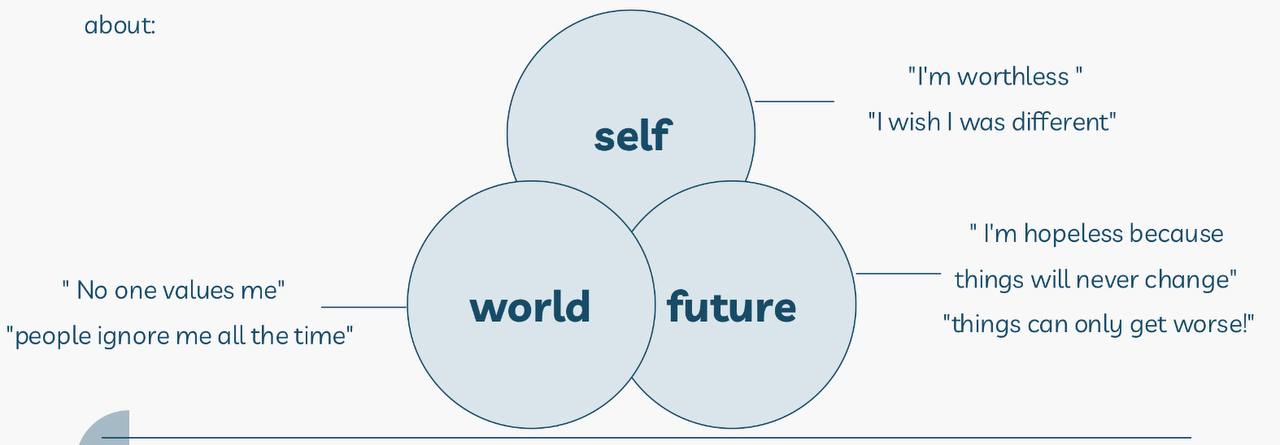
provide examples for each?
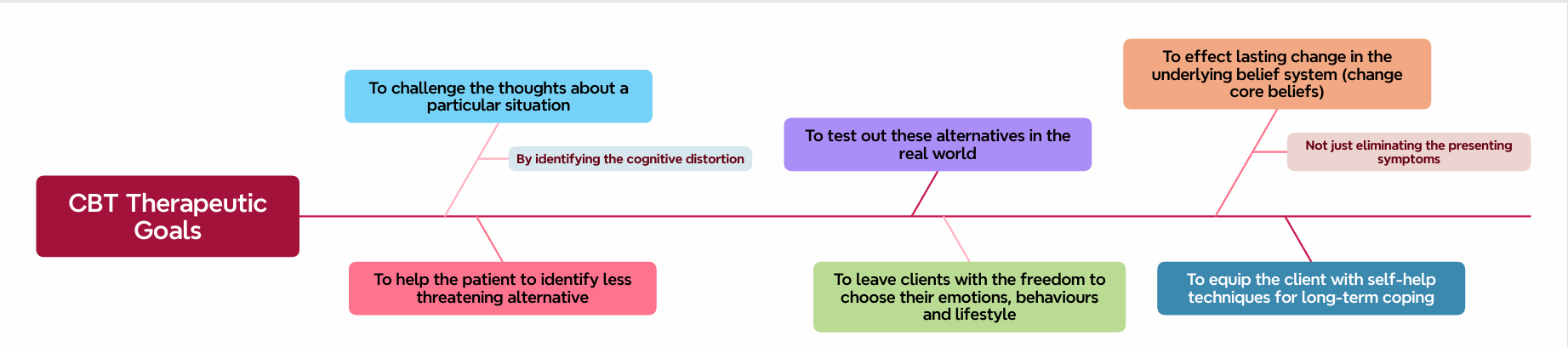
Mention CBT Therapeutic goals?
It’s a therapeutic technique & important element in CT
clinicians educate patients about
therapy
disorder symptoms
session structure
responsibilities
cognitive model.
Agenda setting
Feedback
What is psychoeducation in cognitive therapy? (What are some components patients learn during psychoeducation?)
True
clinicians reinforce learning in psychoeducation By encouraging patients to read cognitively oriented pamphlets or self-help book chapters to apply what they learned in therapy. ✅❌
False
Clinicians reinforce learning in psychoeducation by asking patients to read cognitively oriented pamphlets or self-help book chapters without connecting it to what they learned in therapy✅❌

What is Homework therapeutic technique in CBT and what kind of activities does it include?
A collaborative process to identify specific therapeutic outcomes
that are:
observable
measurable
achievable
relevant to the patient’s problem.
What is goal setting in CBT?
↑ session continuity
objective assessment of therapy progress
helps identify changes
Why is goal setting important in CBT?
identifying broad goals,
therapist & patient determine the most important issues,
arranging them from most to least important
considering prerequisite skills if needed.
How are goals prioritized in CBT?
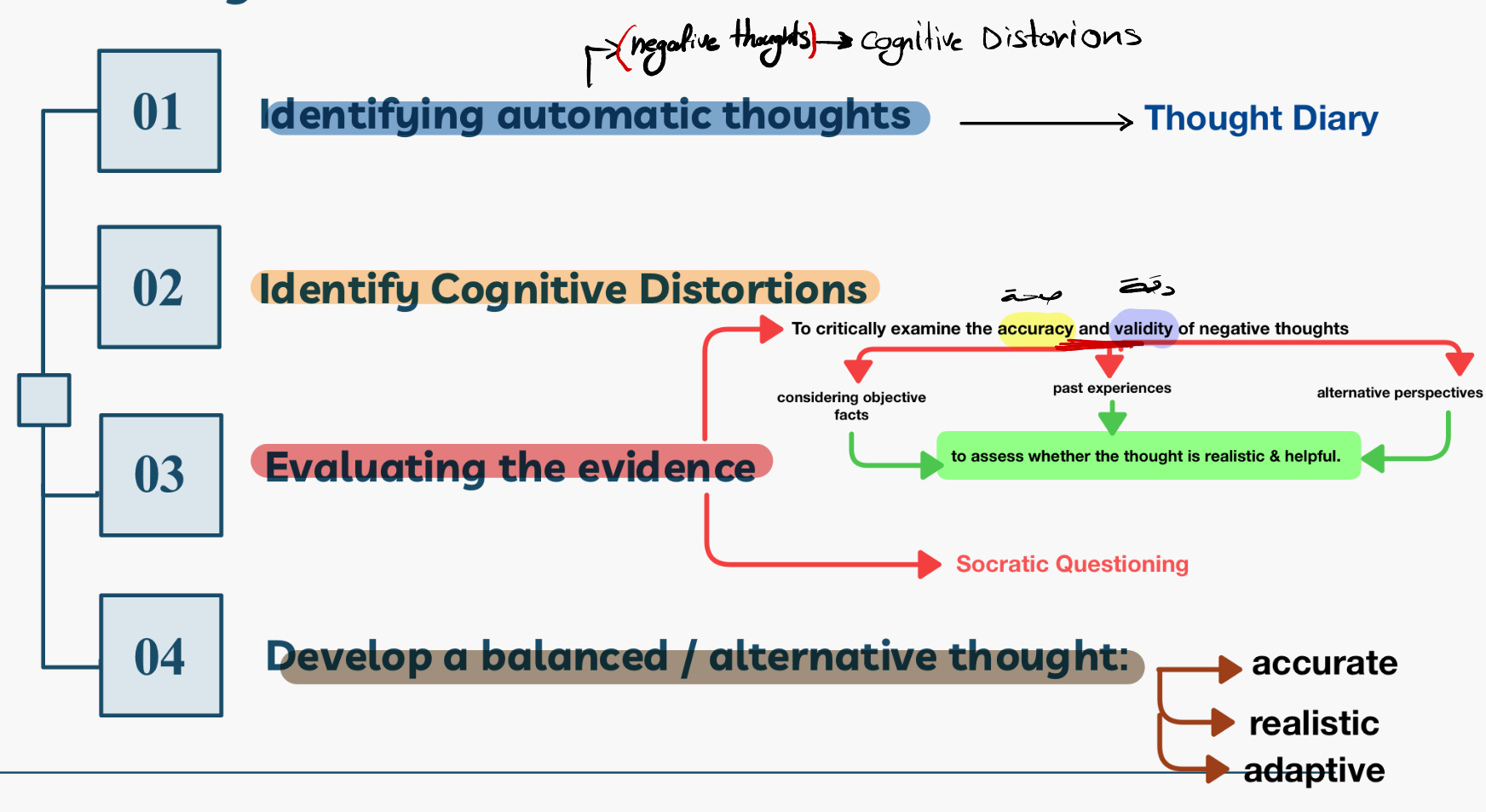
What are the steps of cognitive restructuring?
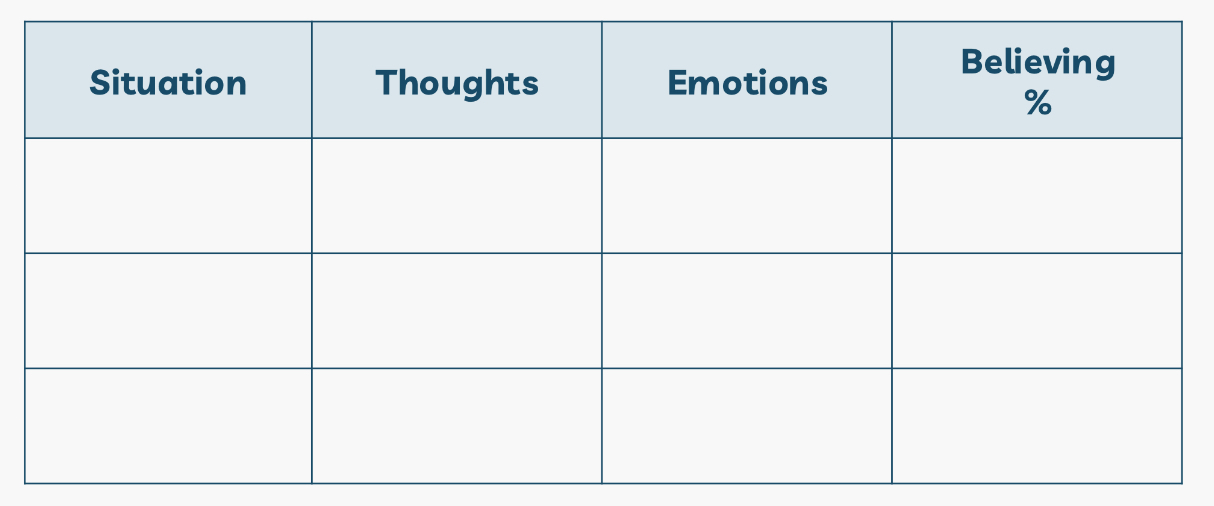
What does Thought diary include? سجل الافكار

probing questions (اسئلة عميقة) used to
examine and challenge negative thoughts
helping individuals uncover:
alternative explanations
Ulternative perspectives.
What is Socratic Questioning in cognitive restructuring? With examples
based on the evidence gathered in the previous steps
should offer a more balanced & constructive view of the situation.
Alternative thoughts in cognitive restructuring should be based on? + should offer ?
tools used to question and evaluate
underlying assumptions and core beliefs
by testing their validity through real-life experiments.
What are behavioral experiments in cognitive therapy?
If someone believes “If I make a mistake, everyone will laugh and ridicule me,”
they might be asked to perform an experiment
to see what actually happens when mistakes are made.
What is an example of a behavioral experiment?
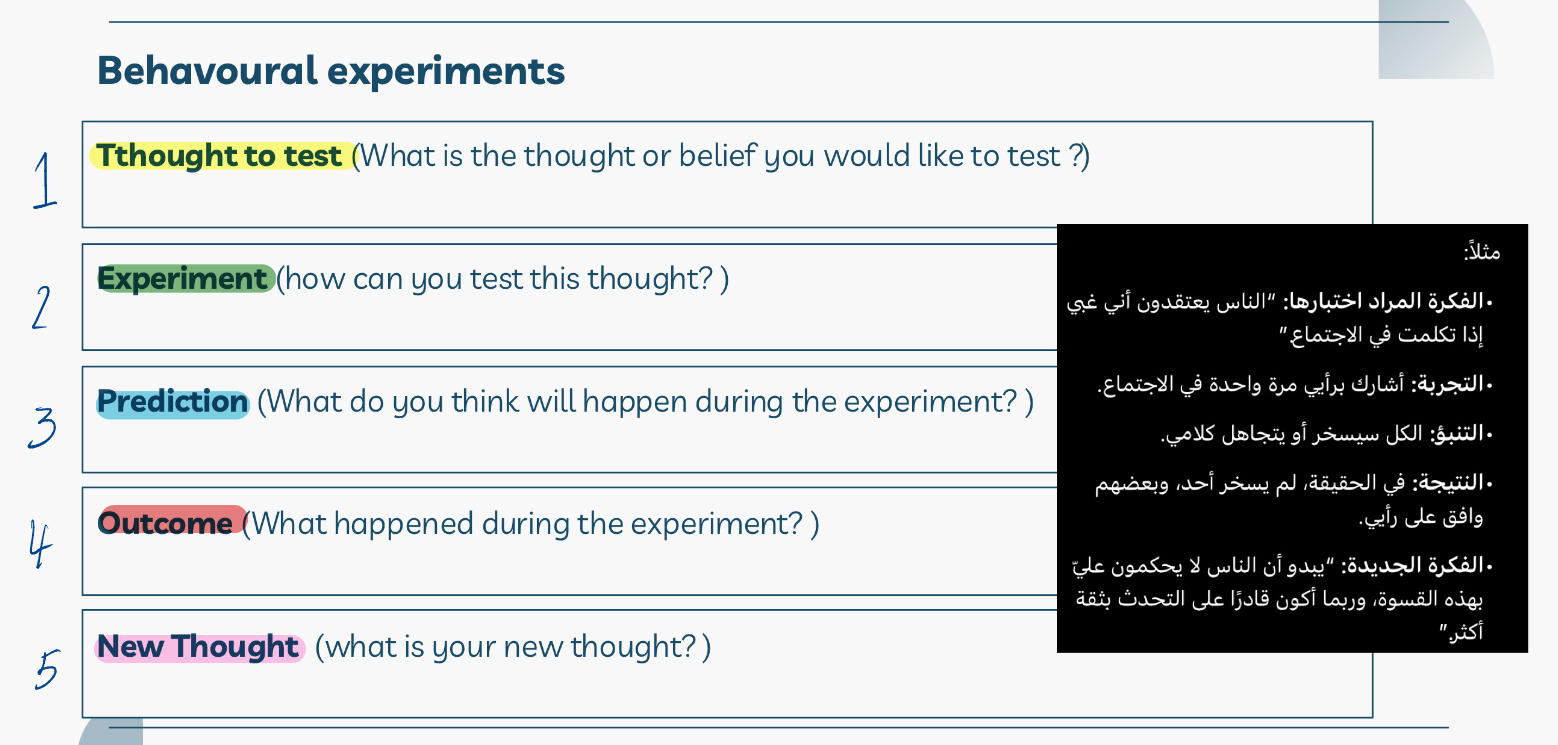
What are the steps of a behavioral experiment?
set of techniques aimed at increasing a patient’s activity
and access to positive, reinforcing situations
that improve mood and functioning.
What is behavioral activation?
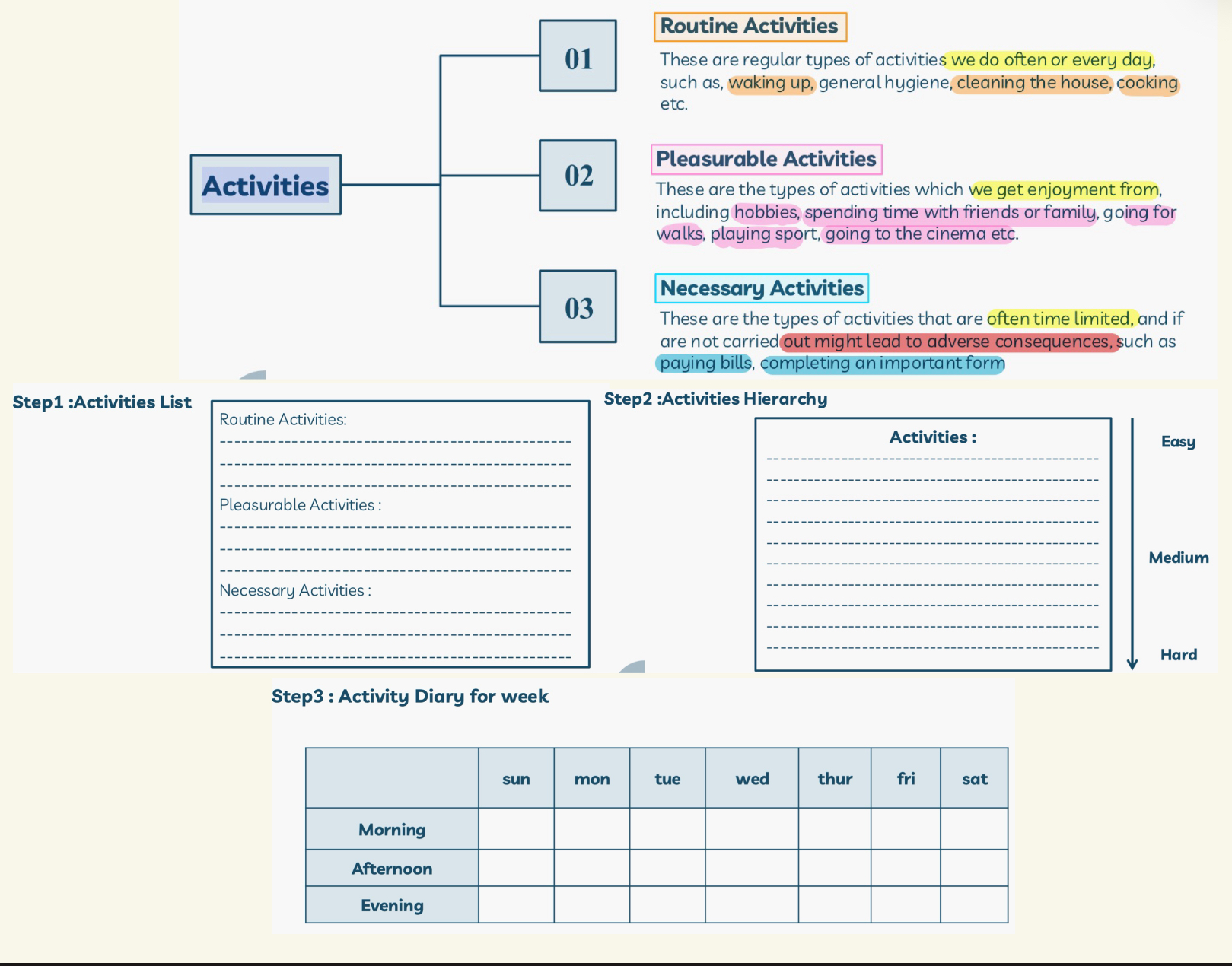
What are the main types of activities in behavioral activation?
A central part of it
where patience bring real life problems to therapy
to work on their practically
What is the role of problem-solving in cognitive therapy?
Because some of their worries are realistic and need to be addressed in a practical way, not just through cognitive change.
Why is problem-solving particularly important for people with low mood or anxiety?
helps identify the problem
find a practical way to manage or deal with it.
What can a problem-solving approach help with?
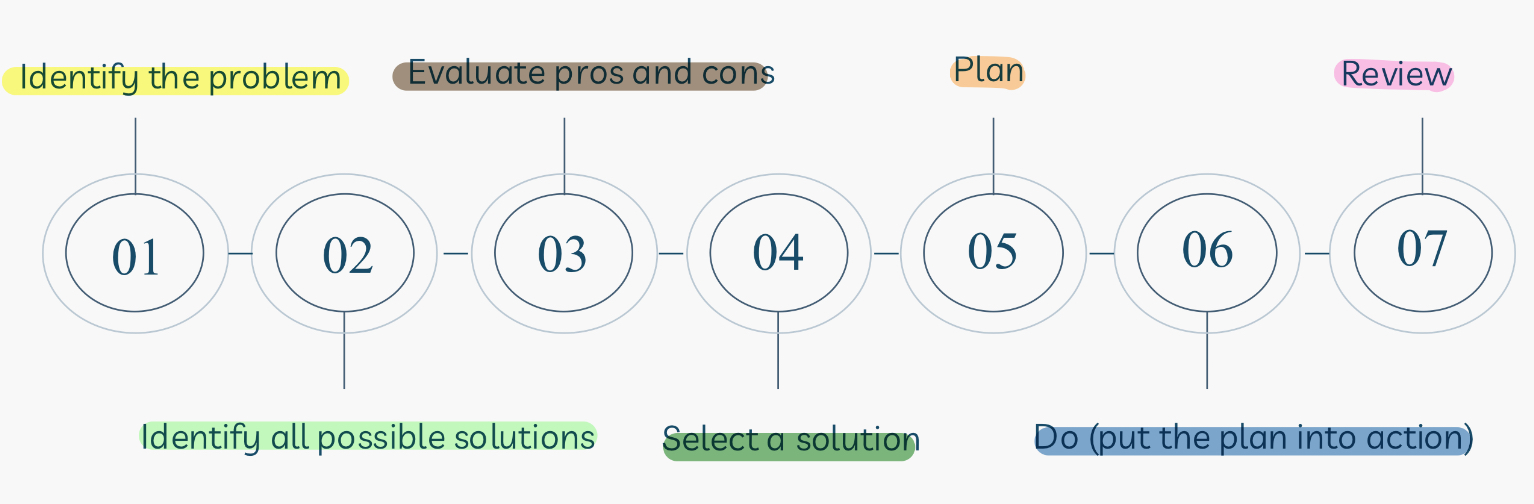
Mention the steps of problems solving?
CBT technique for turning
overwhelming tasks into manageable achievements
by approaching everything step-by-step.
What is a Graded Task Assignment (GTA) in CBT?
By breaking it into smaller goals arranged in the most logical and achievable order.
How is a big goal managed in a GTA?
often feel overwhelmed by large tasks and need to approach problems step-by-step.
Why are Graded Task Assignments (GTA) especially important for depressed patients?

What is the advantages of CBT?

What are the disadvantages of CBT?