2.1 Demand
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Demand
the willingness and ability of buyers to pay for a good or service at a given point in time and at a given price level
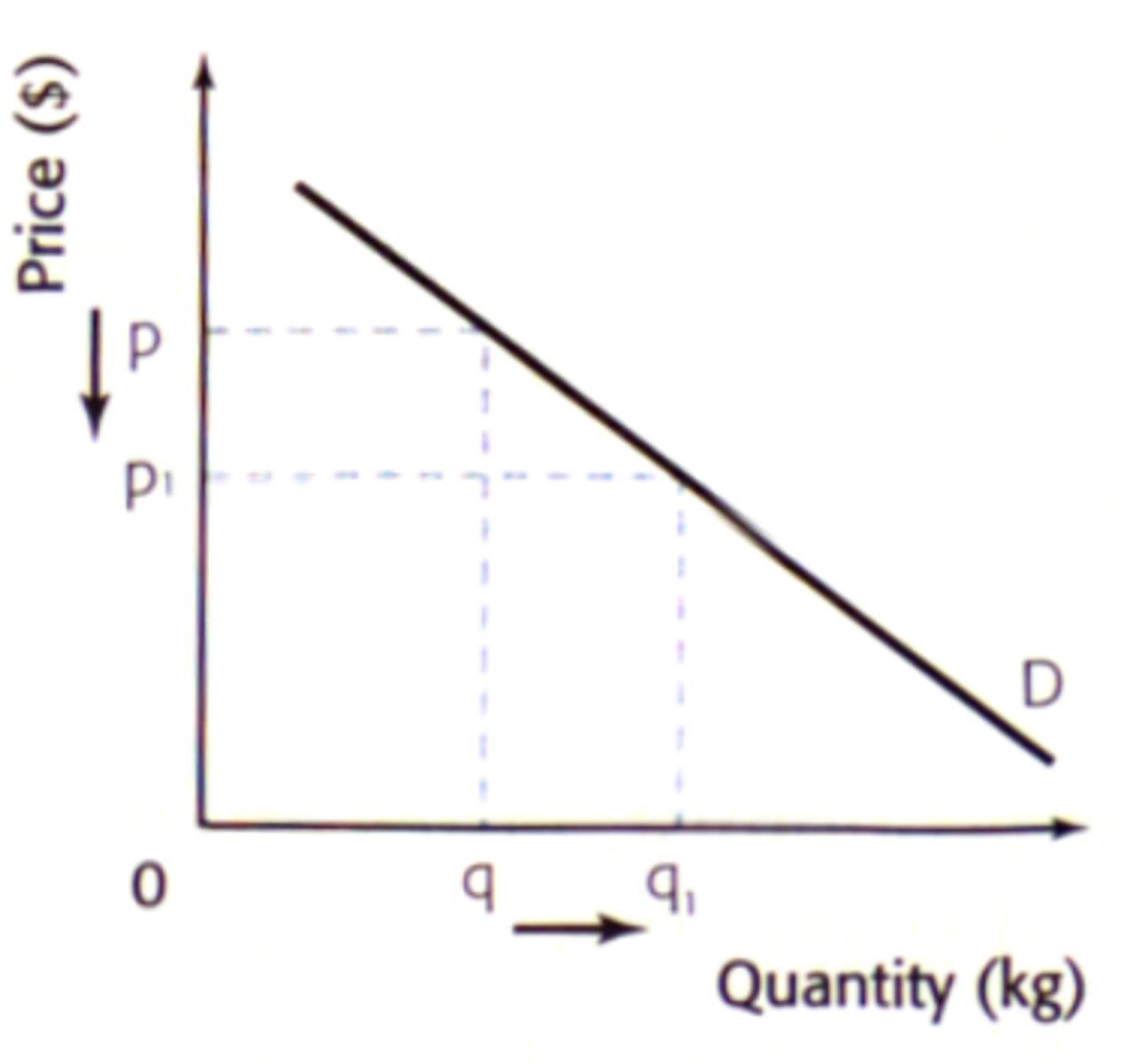
Law of demand
there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
The income effect
as the price of a good decreases, the consumer's purchasing power increases, causing an increase in quantity demanded for the good
The substitution effect
the price of a good rises, making other similar goods relatively cheaper, prompting consumers to swap the pricier item with a more economical alternative
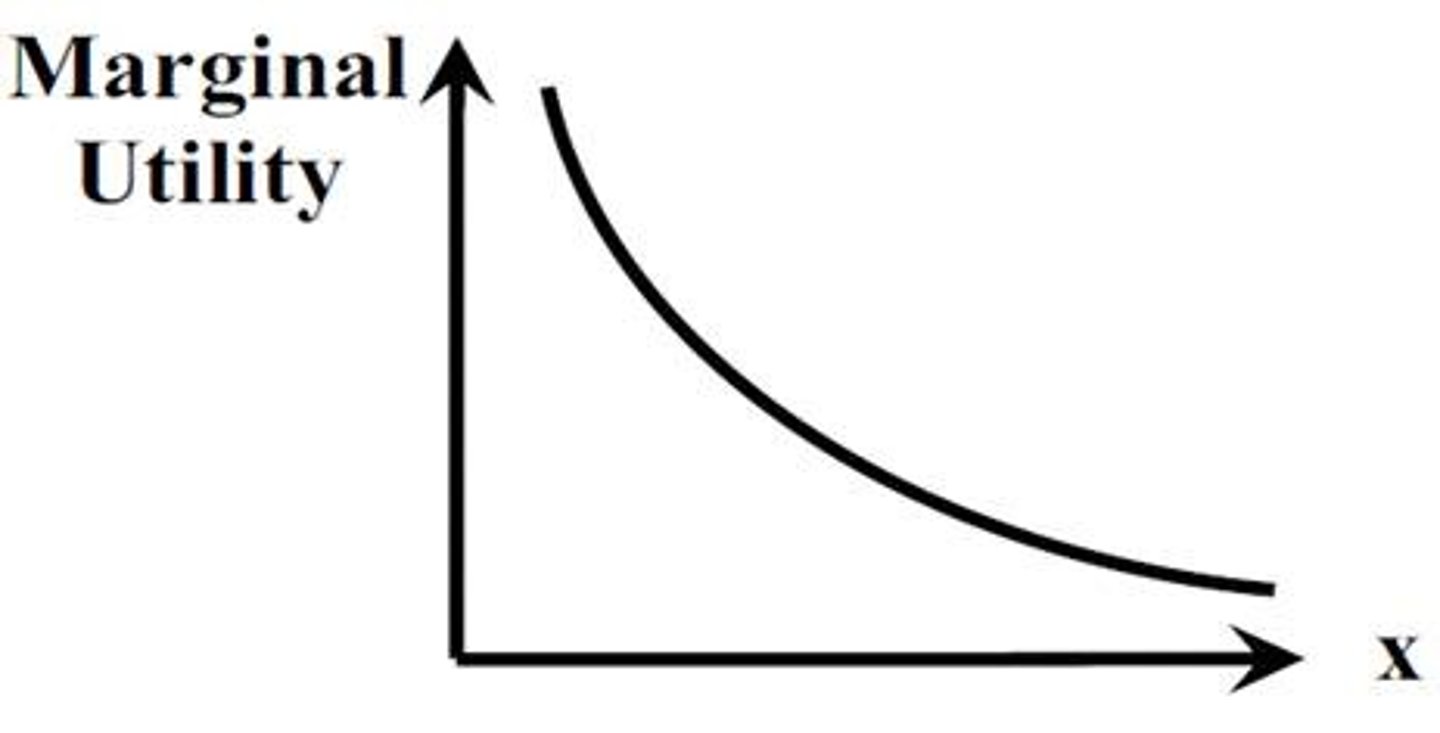
Law of diminishing marginal utility
as a person receives more of a good, the additional (or marginal) utility from each additional unit of the good decline
Non-price determinants of demand
Variables that can influence demand
[Income, Preferences, Prices of related goods, Number of consumers and Future price expectations]
Normal goods
Goods for which demand goes up when income is higher and for which demand goes down when income is lower.
Inferior goods
Goods for which demand tends to fall when income rises.
Substitute goods
Products or services that can be used in place of each other.
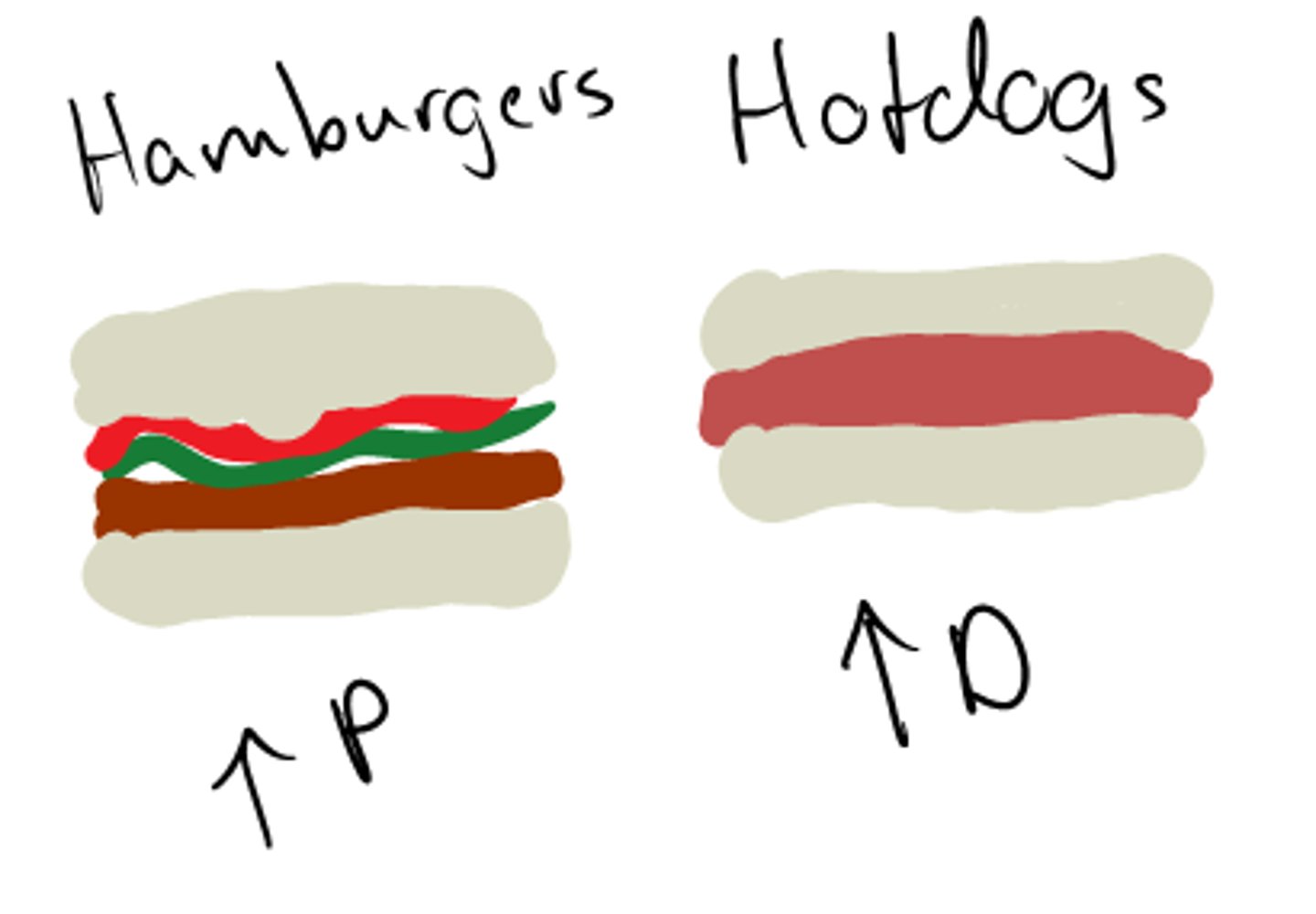
Complementary goods
Products and services that are used together. When the price of one falls, the demand for the other increases.