ap psych c15--motivation and emotion
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
drive reduction theory
our behavior is motivated by biological needs
when our body is not in homeostasis, we have a need that creates a drive
arousal theory
we seek an optimum level of excitement or arousal
some people are thrill seekers who are especially susceptible to becoming bored (boredom susceptability)
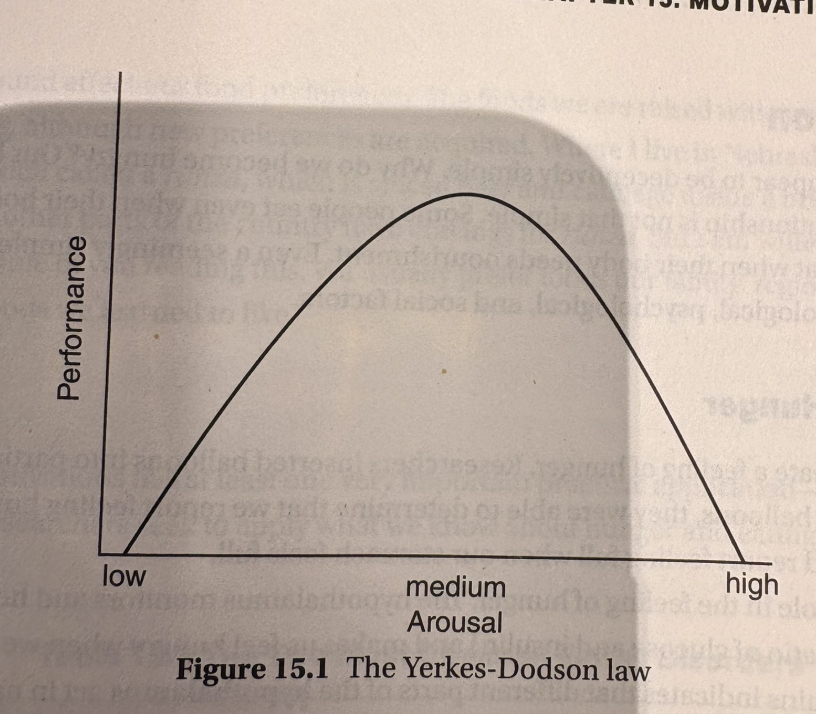
however, most people have an optimum level of arousal that determines their best level of performance. sometimes, even if our arousal is high, we cannot perform difficult tasks (Yerks Dodson law, pg. 143)
opponent process theory of motivation
we have a baseline state that we are usually at and may do something pleasurable to leave that state but eventually desire to return (drinking)
incentive theory
behavior is pulled by a desire (an incentive)
self-determination theory
we need intrinsic things (rewards we get internally) to be motivated
biological basis of hunger
our hypothalamus monitors our body to help us feel hungry when we need to eat
the lateral hyp. causes a species to eat, while the ventromedial hyp. causes a species to stop eating. these two work together to keep us balanced
ghrenlin communicates hunger to the brain, and leptin signals the brain that you have sufficient stored energy and are thus not hungry (both are hormones)
sexual motivation
sexual response cycle chart (pg 146)
twin studies indicate a genetic influence on sexual orientation since a twin is much more likely to be gay if the other twin is gay

social motivation
we are motivated to achieve things that are more complex, like our goals (achievement motivation)
intrinsic vs. extrinsic motivation
intrinsic motivation: rewards we get internally, like satisfaction
extrinsic motivation: external rewards like good grades
management theory
studies of management styles show two basic attitudes that affect how managers do their jobs
theory x—managers believe that employees will work only if they are rewarded with benefits or receive punishment
theory y—managers believe that managers are internally motivated to do good work
lewin’s motivational conflict theory
sometimes we have conflicts about what choice to make, there are four types
approach-approach conflict: choosing between two really good things (go to hawaii or go to NYC)
avoidance-avoidance: choose b/t two bad things
approach-avoidance: one event or goal has pros and cons
multiple approach-avoidance: multiple events or goals have pros and cons (BU vs. BC)
two factor theory
both our physical responses and our cognitive appraisal of them (our mental interpretations) combine to cause any particular emotional response. so, i scream when i see a car about to hit me because my heart races AND my cognitive label of the event is that it is scary