Physiology: Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Arteries and Veins
Arteries: Accept blood from the ventricles of the heart.
Arterioles: Small arteries (control flow)
Micro circulation: connects arterioles to venules
Venuels: small veins, collect blood from micro circulation
Veins: delivers blood to the atria of the heart.
Systemic vs Pulmonary
Pulmonary
circulculation from the right side of the heart and gains oxygen from the lungs
Pulmonary arteries have deoxygenated blood
Pulmonary veins have oxygenated blood
Systemic:
Delivers O2 to the rest of the body
Systemic arteries have oxygenated blood
Systemic veins have deoxygenated blood
Mean Arterial Pressure:
the arterial pressure averaged over the cardiac cycle
Pulse pressure: Difference in systolic and diastolic pressure.
Diastolic pressure + 1/3(Pulse Pressure)
Blood Pressure
Diastolic pressure: 80mmHg - relaxation of the heart
Systolic pressure: 120mmHg - contraction of the heart
Blood Pressure: systolic/diastolic
Cardiac Output
Heart rate: Number of contractions per unit time (70 beats/min)
Stroke Volume: Volume pumped by a ventricle in one contraction (70-80ml)
Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume pumped
Frank-Staring law
Increased venous return stretches the ventricle and increases force production until cardiac output matches venous return.
Heart Beat (Electrical signal)
Action Potential (AP) starts at the SA node
AP conducted through atrial muscle
AP is delayed at the AV node before entering the Bundle of His. (Conduction through the Bundle of His and Purkinje fibres is extremely rapid).
The ventricle depolarise from endo to epicardium and from apex to base.
Autorhythmicity
Some cells have an intrinsic rhythmicity which generates a pacemaker potential.
Cardiac Pacemakers
The sinoatrial node - fastest pacemaker (90-100 beats/min), is the normal pacemaker
The atrioventricular node - (40-60 beats/min)
Bundle of His - (15-30 beats/min)
Neural Control of Heart Rate
Agentd that alter heart rate are chronotopic
Positive chronotropic agents increase heart rate. (Adrenaline + Noradrenaline act on B-adrenergic receptors on the heart)
Negative Chronotropic agents slow the heart rate. (Acetylcholine cts on M-cholinergic receptors on the heart).
Heart Valves
Two valves between the atria and ventricles: atrioventricular valves.
Valves between the ventricles and arteries: semilunar valves
Heart valves prevent back flow
Venticricular Pressure - ECG
After the P wave atrial contraction lightly increases ventricular pressure
Following the QRS complex ventricular contraction greatly increases ventricular pressure.
Sound one occurs during ventricular pressure rise
Sound 2 occurs during fall in ventricular pressure.
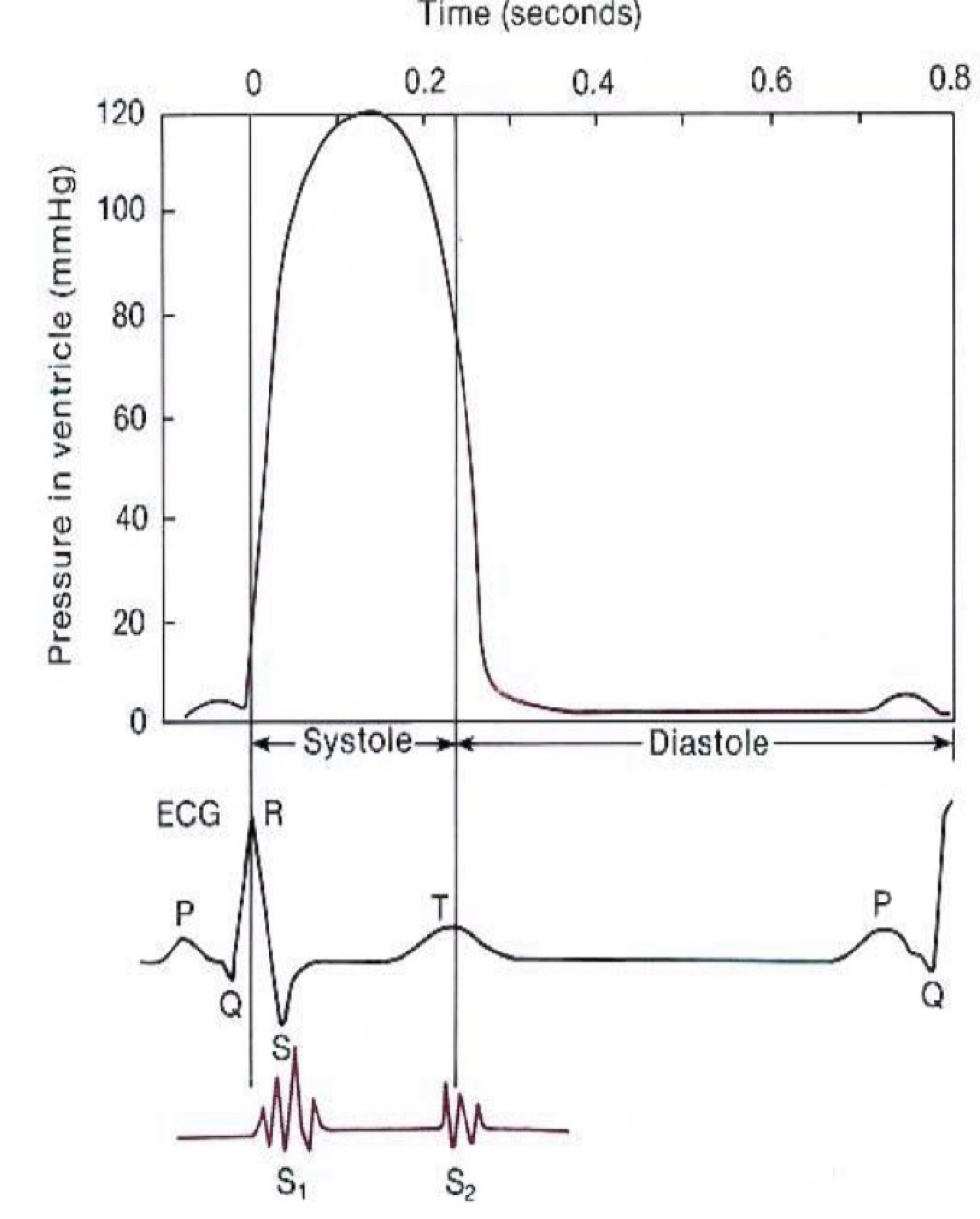
Ventricular Volume
During Diastole the ventricle fill with blood.
Atrial systole adds more blood
Isovolumic contraction: when all valves are closed.
Transport across capillaries
lipid soluble substance pass across the cell membranes (O2, CO2, ethanol)
Small-medium sized water soluble substances diffuse between endothelial cells. (Water, Na+, Cl-, Ca+, ure, glucose, ADH, insulin).
Large substances can be moved by pinocytosis.
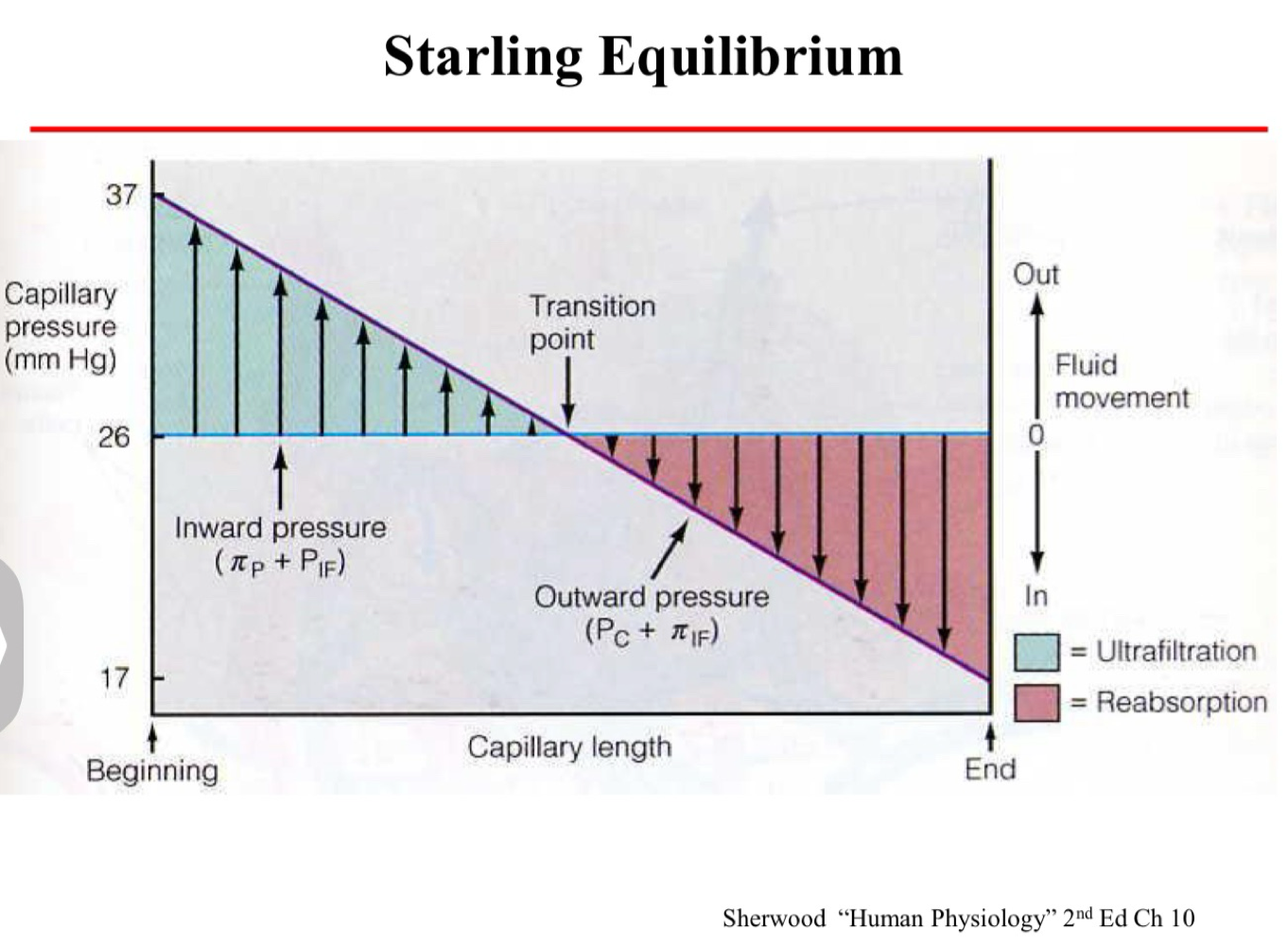
Plasma Filtration
Fluid (hydrostatic) pressure inside the capillaries pushes plasma out.
Plasma proteins stay in capillary so total solute concentration is higher in plasma than in interstitial fluid.
Colloidal osmotic pressure pulls interstitial fluid in
Plasma Osmotic Pressure
Total osmotic pressure of blood includes all solutes including salts: 6000mmHg. (Both interstitial fluid and plasma)
Colloid osmotic pressure of blood is due to the osmotic activity of proteins mostly albumin = 25mmHg. (Plasma)
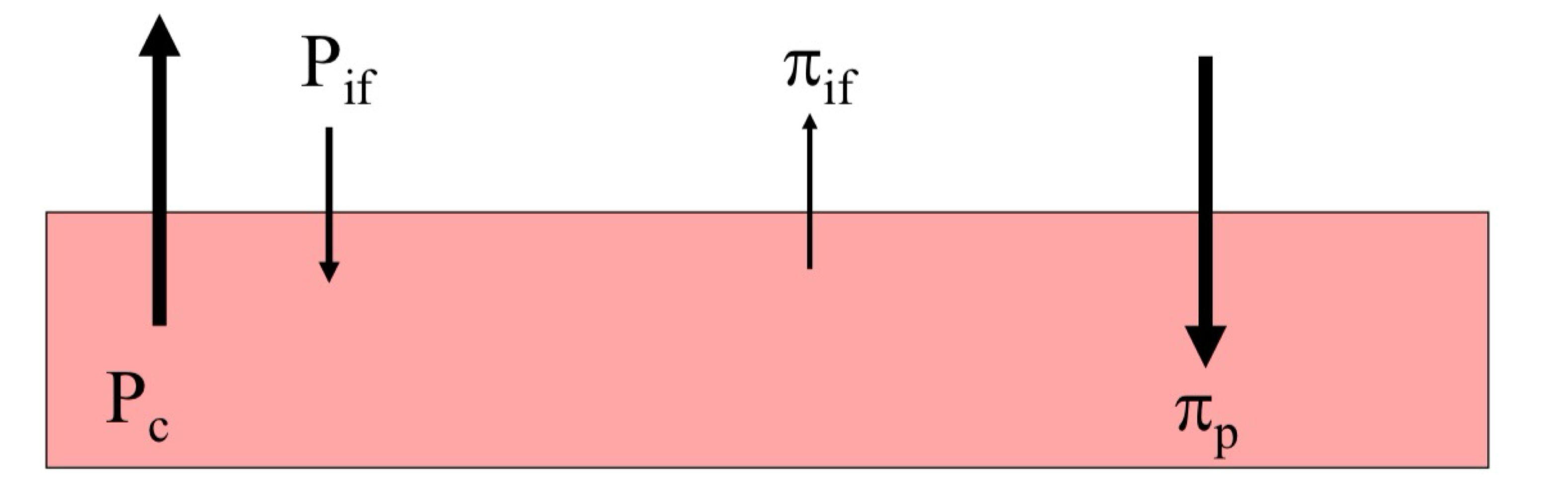
Fluid Pressure
Fluid pressure difference between the capillary (Pc) and interstitial fluid (Pif) pushes fluid out
Oncoming (colloid osmotic) pressure between the capillary (πp) and interstitial fluid(πif), pulls fluid in.
Starling Equilibrium
Increased filtration vs Increased absorption
Increased filtration:
vasodilation
Arterial Hypertension
Venous Hypertension
Increased plasma leakage
Plasma protein deficiency
Increased Absorption
Vasoconstriction
Arterial hypotension
Venous Hypotension
Dehydration
Haemorrhage