Tissue 2 - kidney, bone
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms

overall morphology of the kidney (large lagnification)
capsule
cortex - outer shell
medulla
papilla
calyx
pelvis
hilus (the point of entry and exit of blood vessels and nerves)
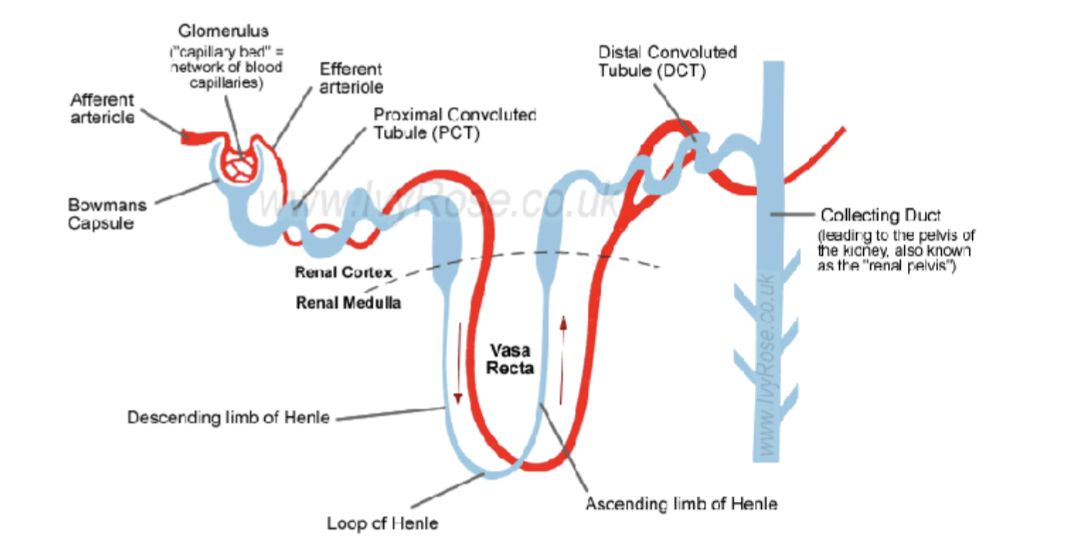
smallest unit in kidney
nephron = renal corpuscle + renal tubule
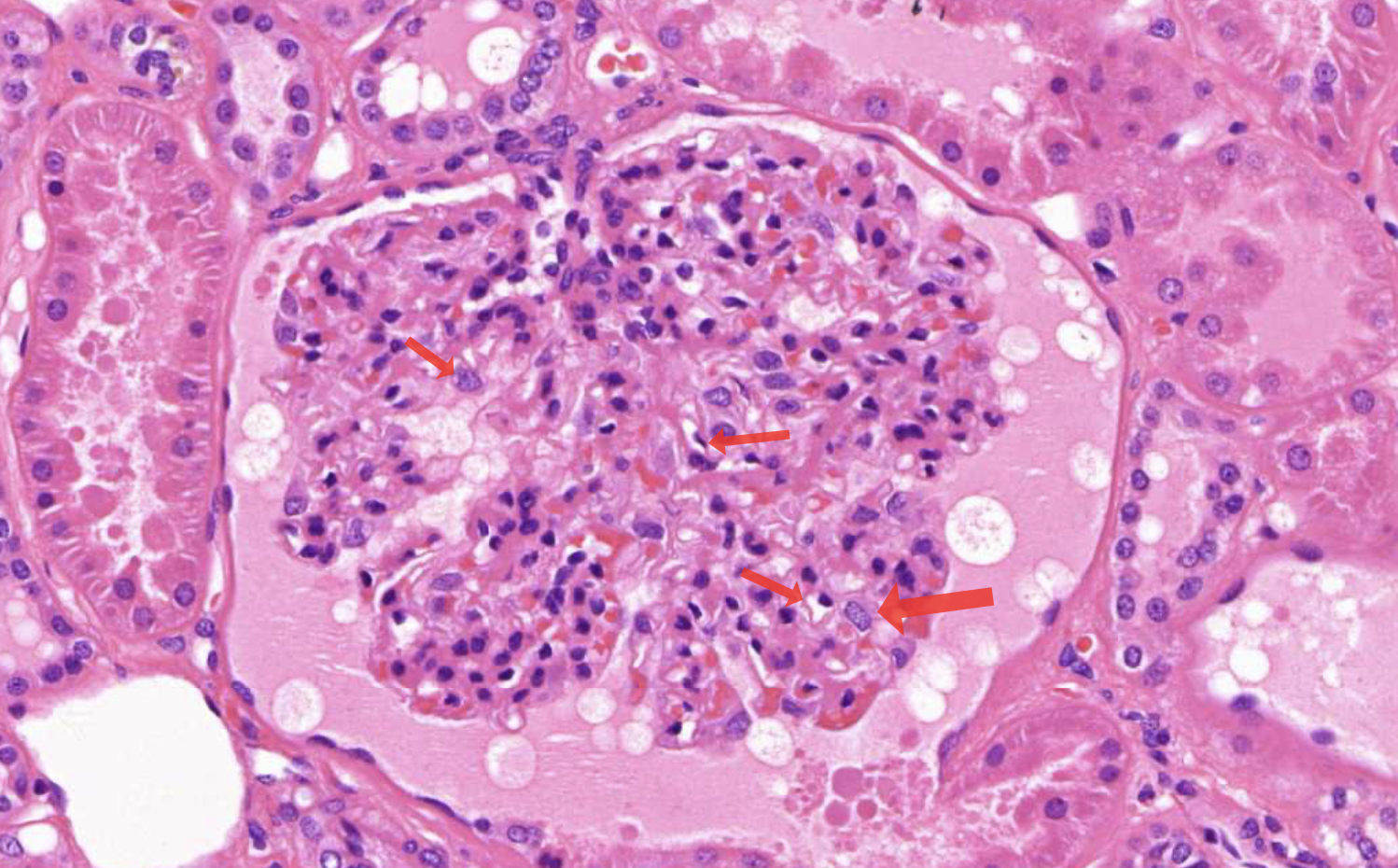
bowmans space - urinary space
simple squamous epithelium
bowmans capsule/glomerulus
fenestrated capillaries - fenestratins are pores that allow larger molecules to pass through the capillary wall
endothelial cells - 1st stage of filtration of blood to primary urine
besement membrane - 2nd
podocytes - 3rd stage
mesangial cells - provide structural support (dark irregular nuclei, surrounded by deep pink material)
vascular pole
affarent and effeent arteriole
juxtaglomerular apparatus
macula densa - regulate blood pressure and filtration rate
juxtaglomerular cells - secrete enzymes renin
urinary pole - proximal tubuli
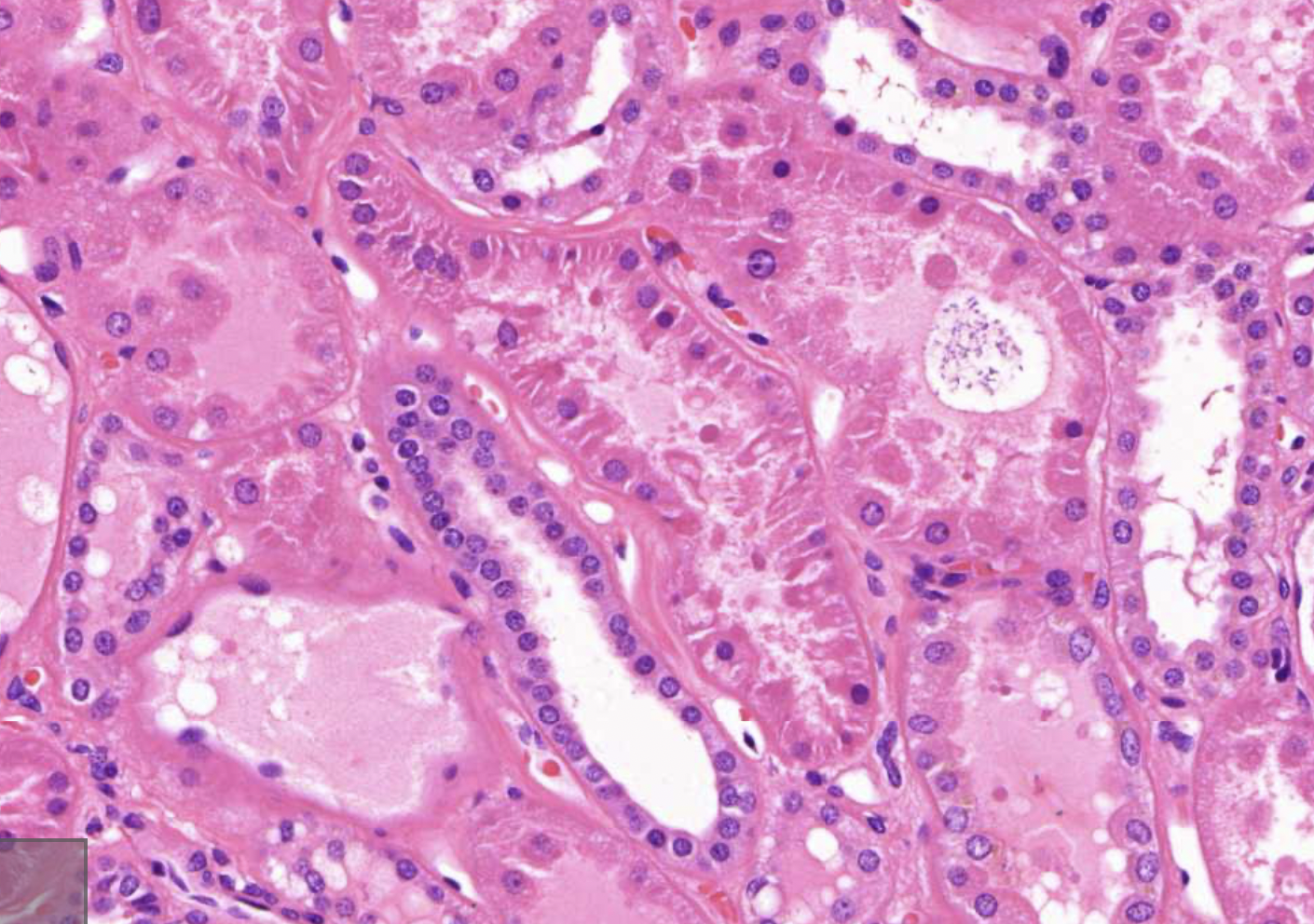
proximal tubuli (simple columnar epithelium) - remove small proteins from the primary urine, major site of reabsorption
distal tubuli (simple cuboidal epithelium) - reabsorbs Ca, sodium, Cl, regulates pH in the urine
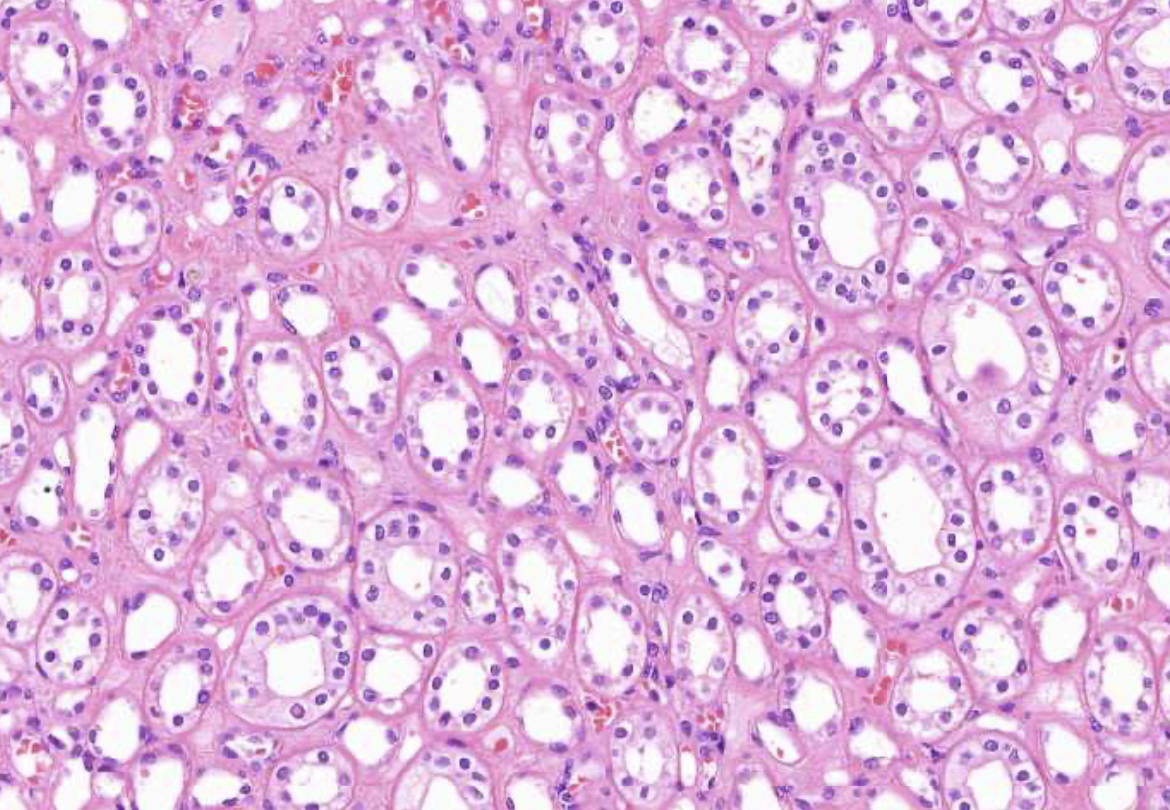
loop of henley/collectin ducts (simple cuboidal epithelium) - reabsoprtion of water and ions
blood vessels around - Vasa Recta
Describe the way blood and urine is transported thrpugh kidney + video
black staining in nephrons
PASM - methenamine
silver/black - basement membrane
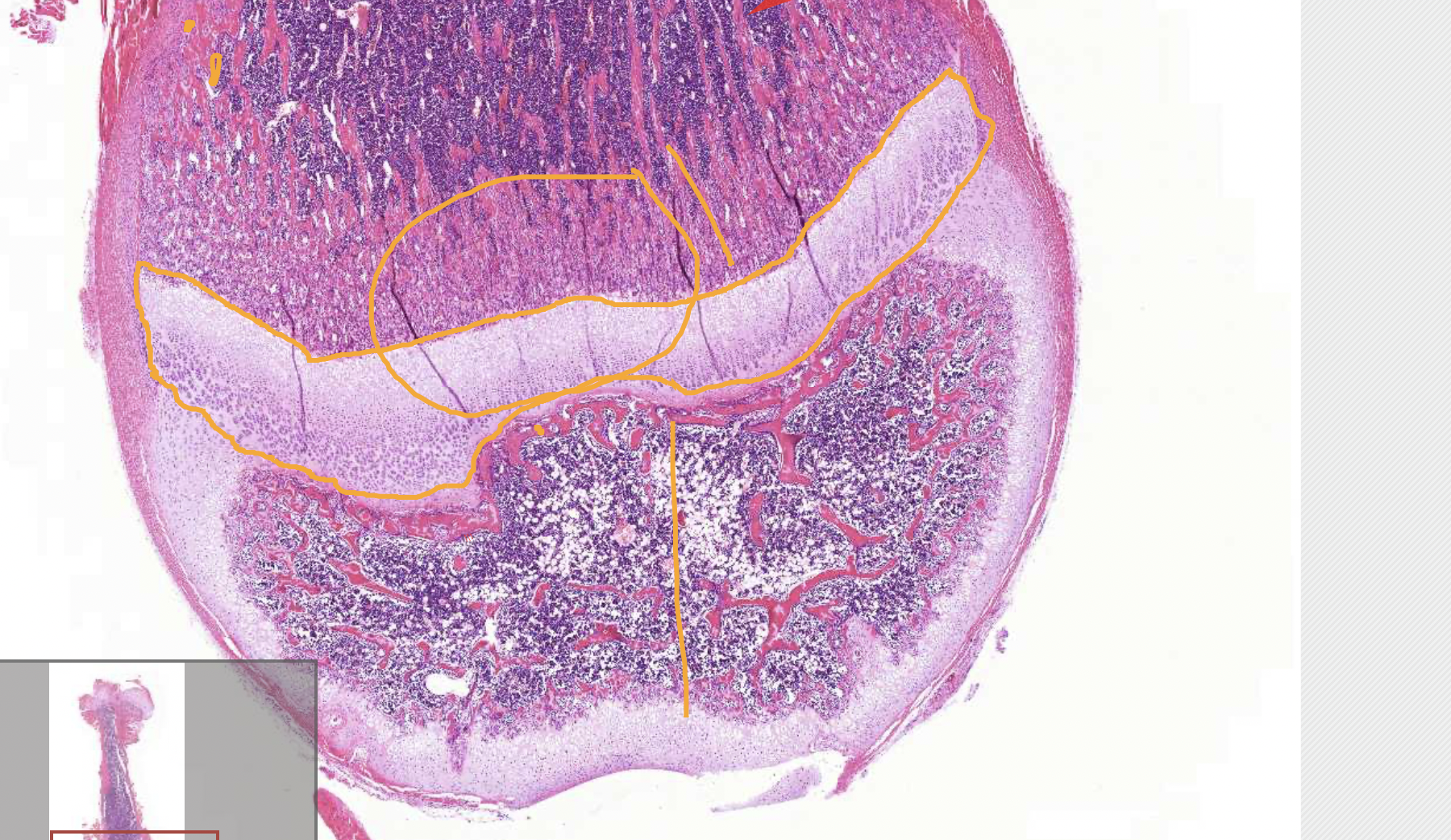
primary region of ossification (deeper in the bone)
secondary region of ossification (outer) - helps to not disturb the joint with growth
cortical/compact bone - dense, important for bone strength
trabecular bone - harbour precursor bone cells, haemopoietic cells (red marrow) and fat cells (yellow marow)
growth plate - longitudinal growth (cartilage then bone)
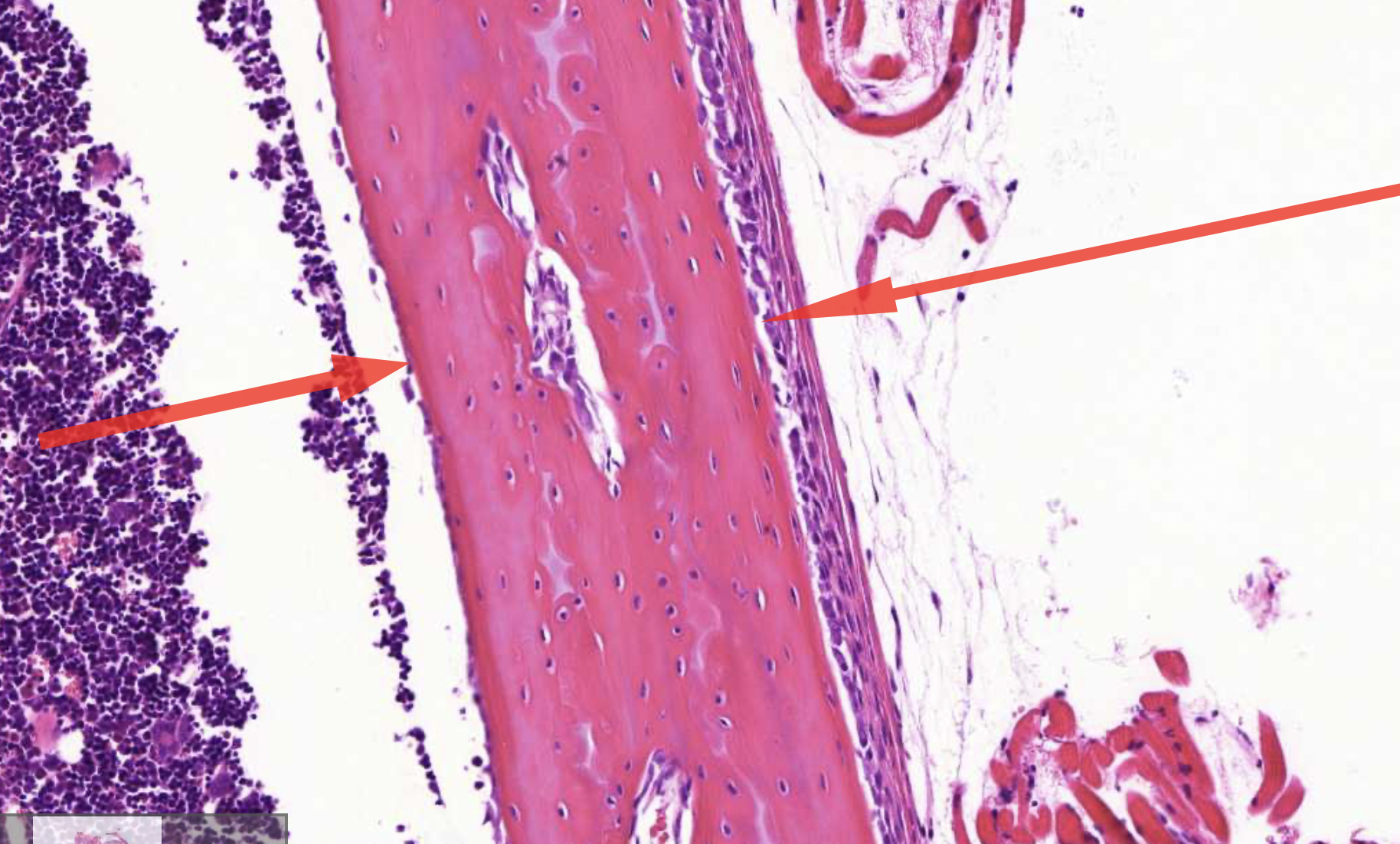
endosteum - inside or cortical bone
peristeum - outside or cortical bone
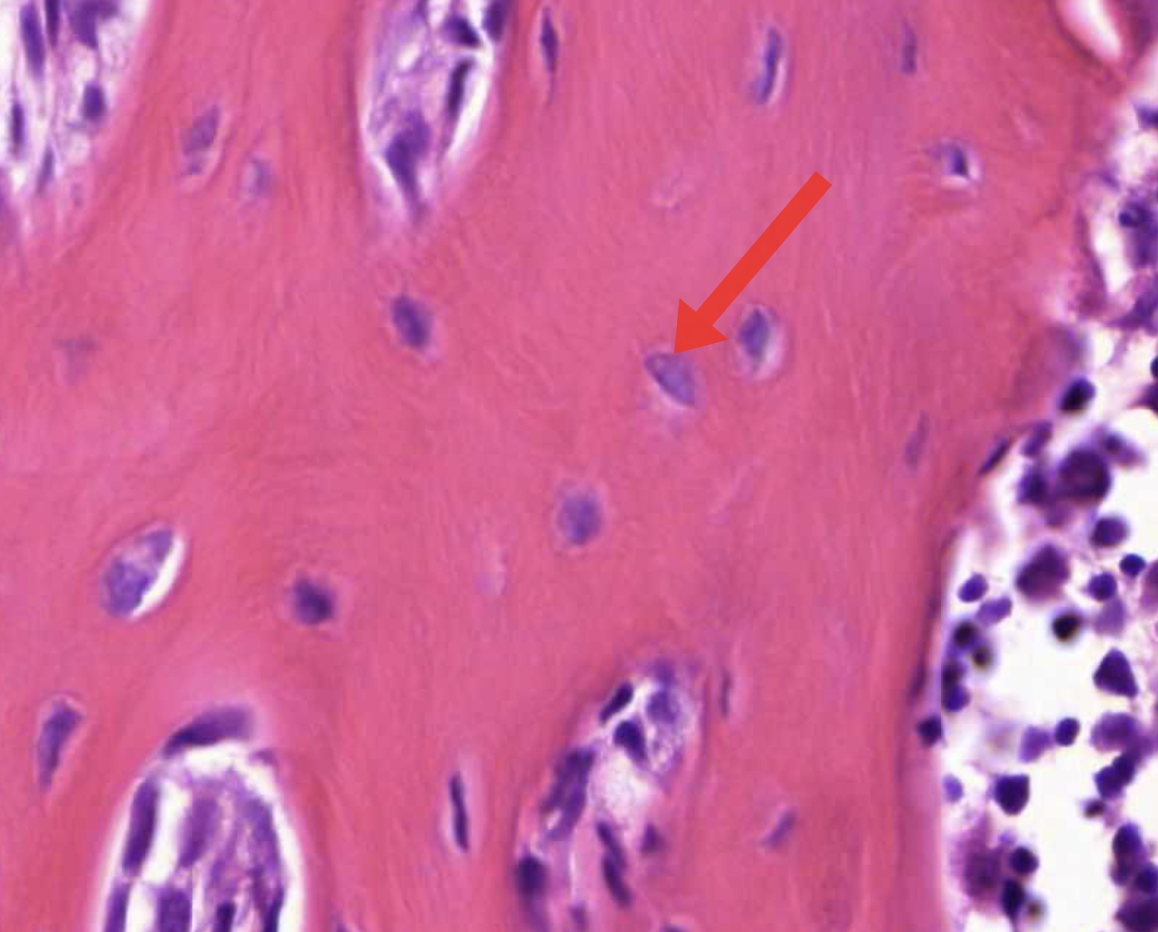
osteocyte - sense mechanical forces, orchestrate bone remodelling, maintain bone respnse
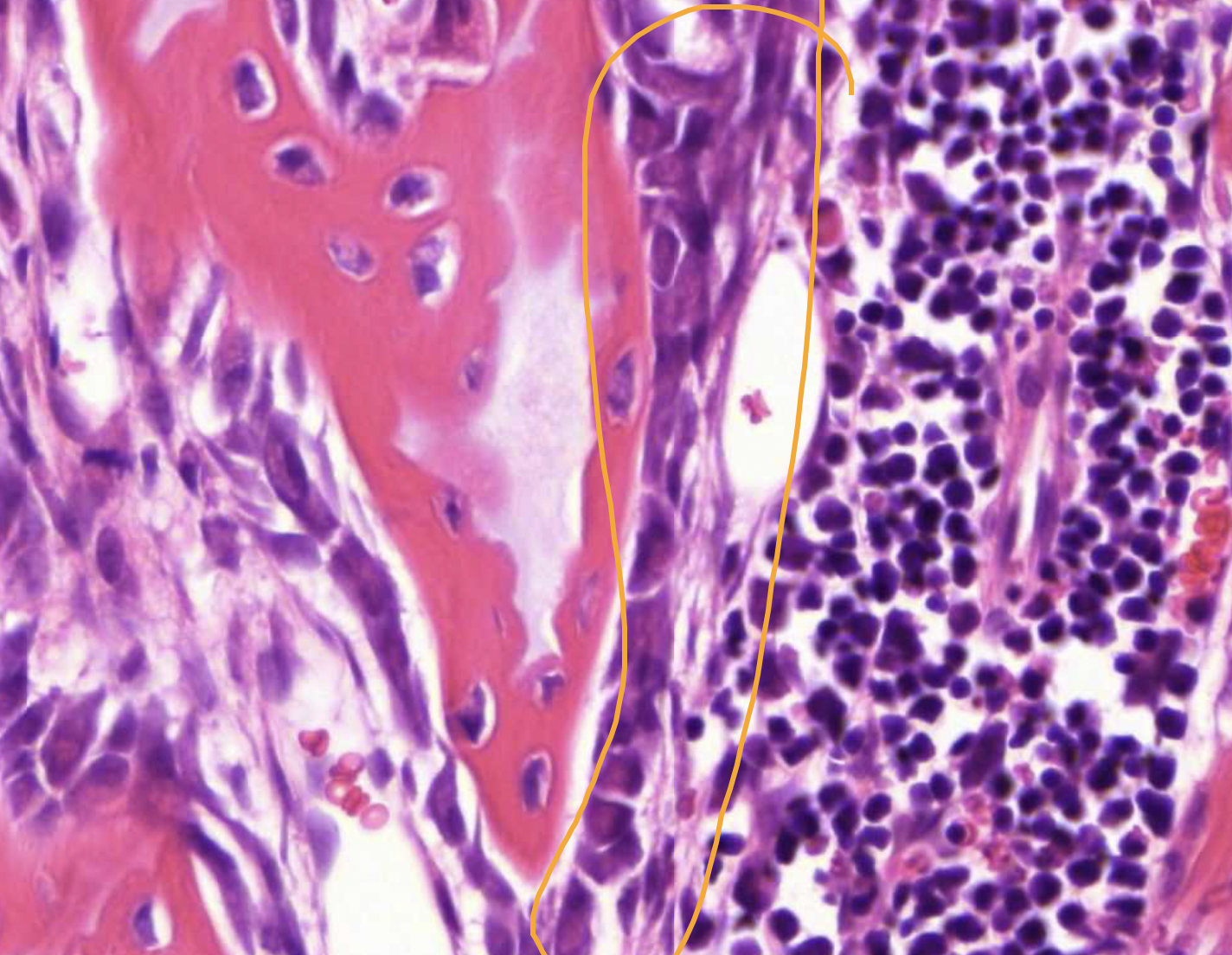
osteoblasts - bone formation, can embed themselves in bone matrix and differentiate into osteocytes
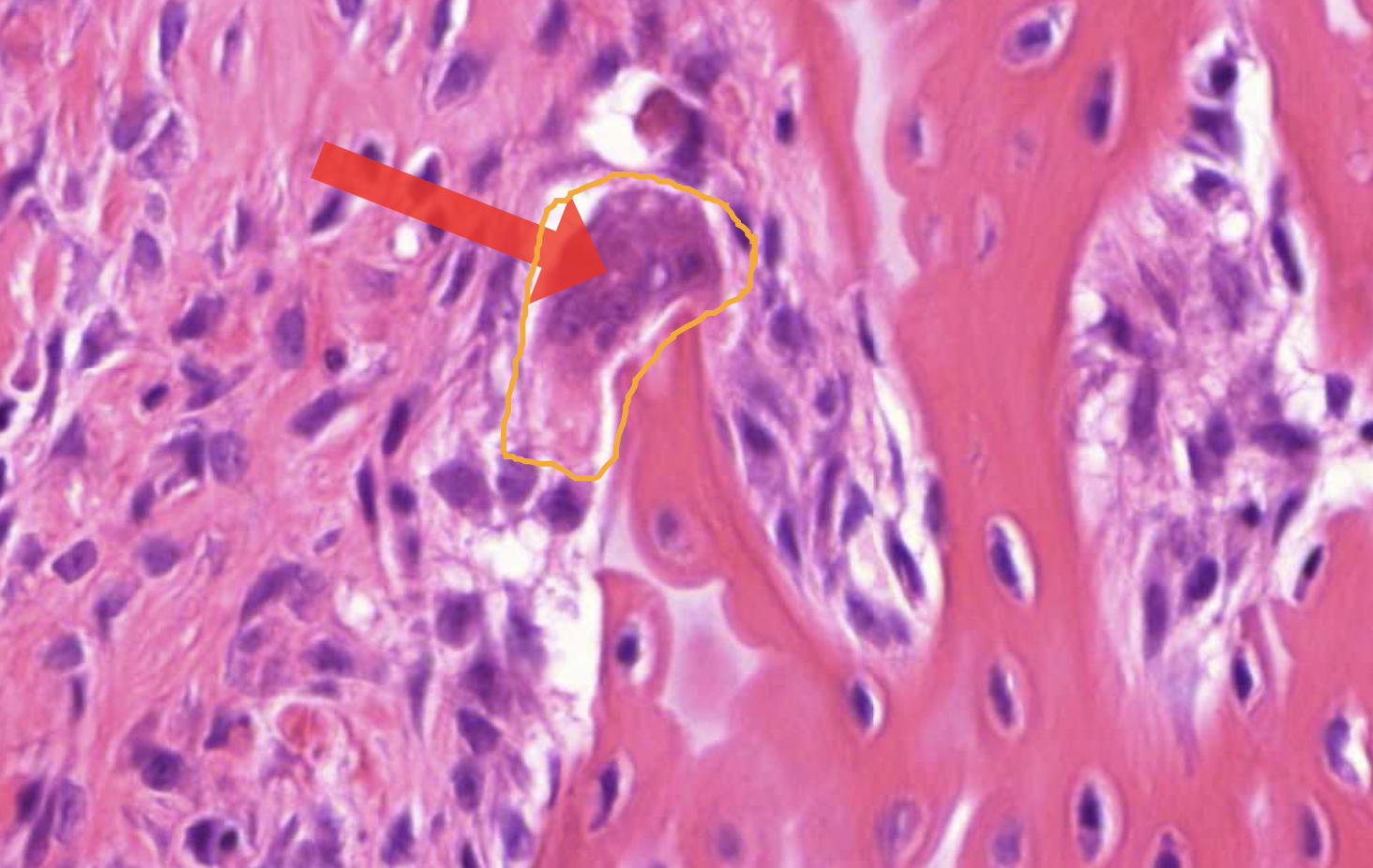
osteoclast - bone resorption (in cavities, multinuclei)
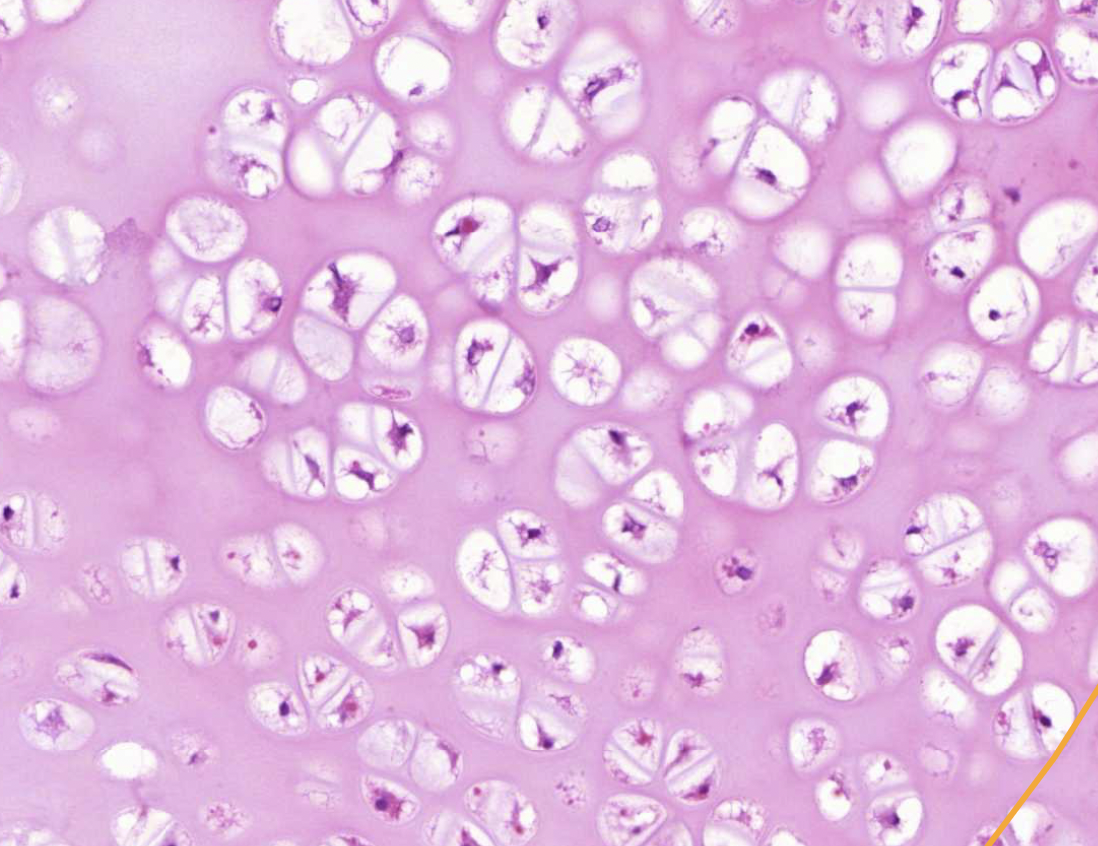
chondrocytes - secrete cartilage matrix
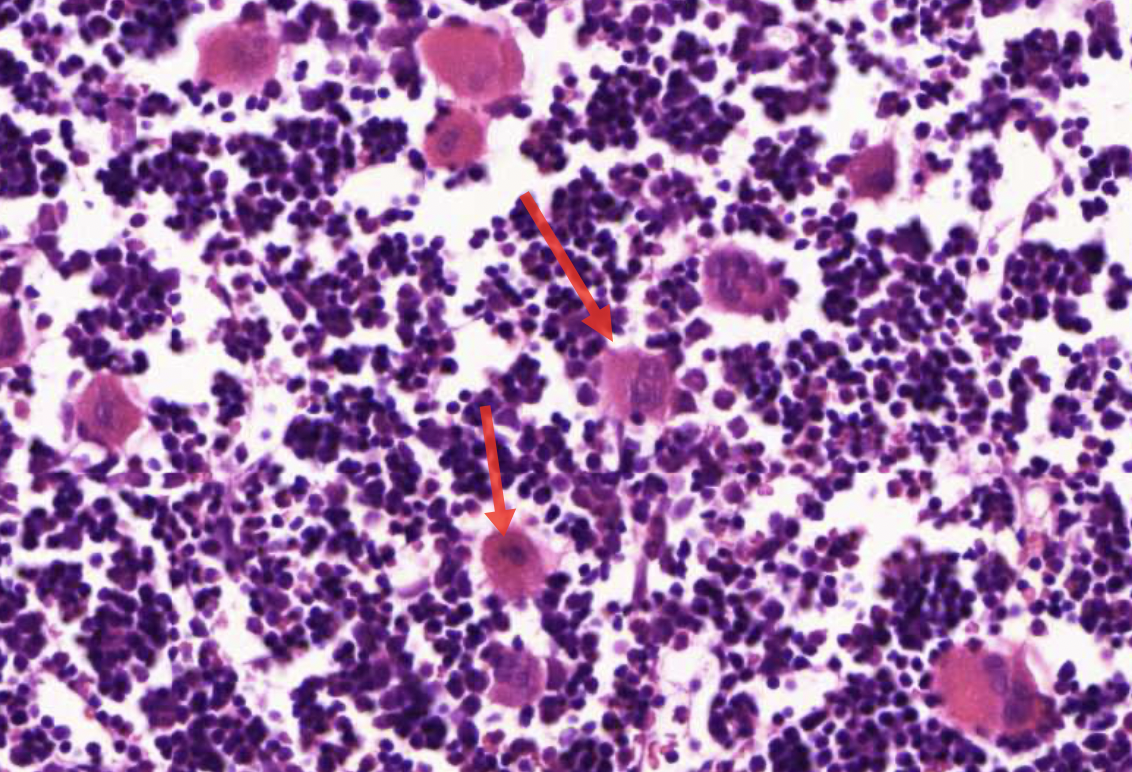
megacaryocytes - production of blood thrombocytes - for blood clotting
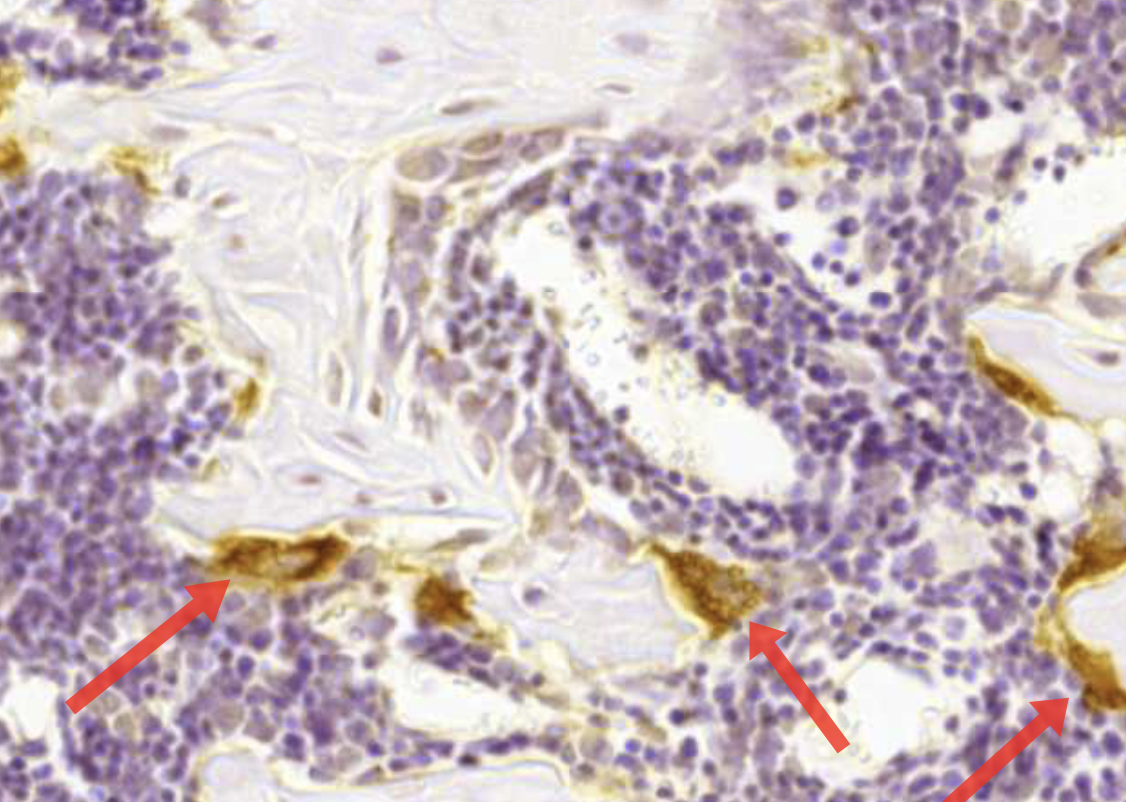
TRAP - stain for osteclasts
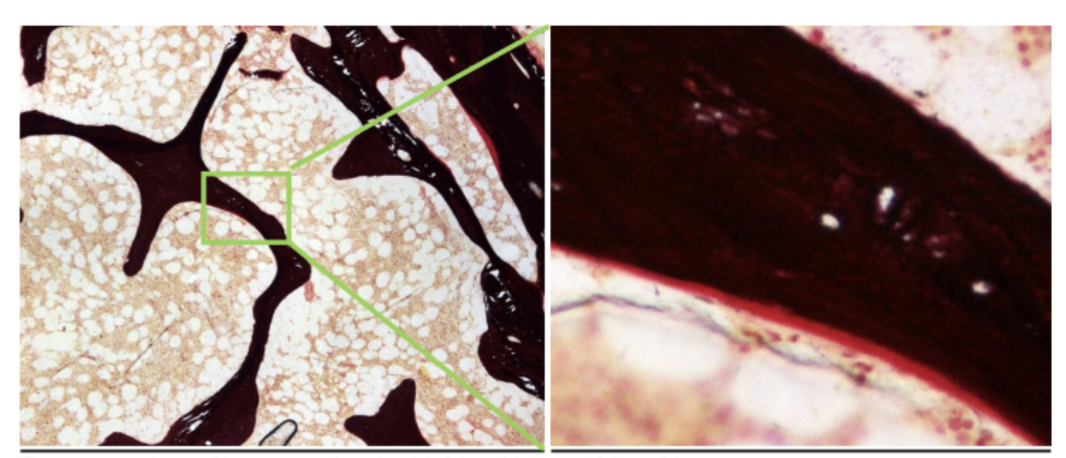
calcified matrix - black, newly formed collagen 1 - red