6.1 Aromatic compounds, carbonyls and acids
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
What is the molecular formula of benzene? (1)
C₆H₆
Describe the Kekulé model of benzene. (2)
- A six-membered ring
- with alternating single and double bonds between carbon atoms
Describe the delocalised model of benzene. (4)
- Each carbon atom donates a p-orbital electron
- to form a ring of delocalised electrons above and below the plane
- The ring is planar with bond angles of 120°
- and has σ-bonds between C-C and C-H
What evidence disproves the Kekulé model? (3)
- All C-C bond lengths in benzene are equal
- Benzene does not undergo electrophilic addition without a catalyst
- Enthalpy change of hydrogenation is less than expected, showing extra stability
How are substituent positions numbered on a benzene ring? (2)
- Use the lowest possible numbers
- List different substituents in alphabetical order
What is the name of the aromatic compound with a methyl group attached to benzene? (1)
Methylbenzene
What is the name of the aromatic compound with a carboxylic acid group attached to benzene? (1)
Benzenecarboxylic acid
NOTE: also known as benzoic acid
What is the name of the aromatic compound with an aldehyde group attached to benzene? (1)
Benzaldehyde
What is the first step of electrophilic substitution in benzene? (2)
- The delocalised ring attracts an electrophile,
- which accepts a pair of π electrons to form a covalent bond.
Why is the first step of electrophilic substitution the rate-determining step? (2)
- It is slow
- because it involves breaking the stability of the delocalised electron ring.
What happens after the unstable intermediate forms in electrophilic substitution? (1)
The intermediate releases a H⁺ ion to form a stable product.
Why is benzene unreactive compared to alkenes? (1)
Because it is stabilised by its delocalised ring of electrons.
What is needed to make benzene react with an electrophile? (1)
A catalyst is needed to generate the electrophile and speed up the reaction.
What are the conditions required for nitration of benzene? (2)
- 50°C
- concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst (H₂SO₄)
- reflux
What is the electrophile in nitration of benzene? (1)
NO₂⁺
What is the reaction for the generation of the NO₂⁺ electrophile? (1)
HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ → NO₂⁺ + HSO₄⁻ + H₂O
Draw a reaction mechanism for the nitration of benzene. (5)
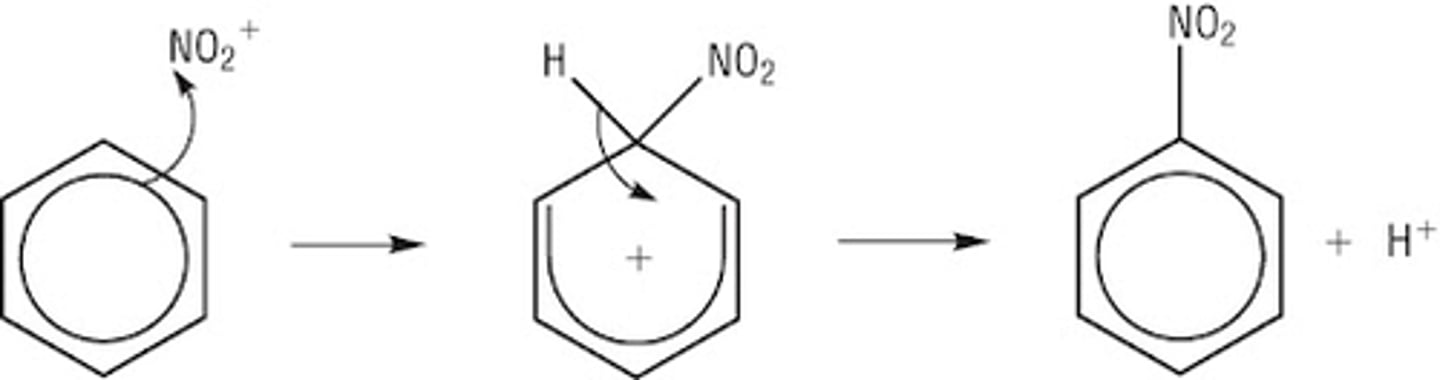
What is halogenation of benzene? (1)
The substitution of a hydrogen atom on benzene with a halogen atom using a halogen carrier catalyst.
What are the conditions for chlorination of benzene? (2)
- rtp,
- halogen carrier catalyst (FeCl₃ or AlCl₃)
What is the electrophile in chlorination? (1)
Cl⁺
What are the conditions for bromination? (2)
- rtp,
- halogen carrier catalyst (FeBr₃ or AlBr₃)
What is the electrophile in bromination? (1)
Br⁺
Draw a reaction mechanism for the chlorination of benzene. (5)
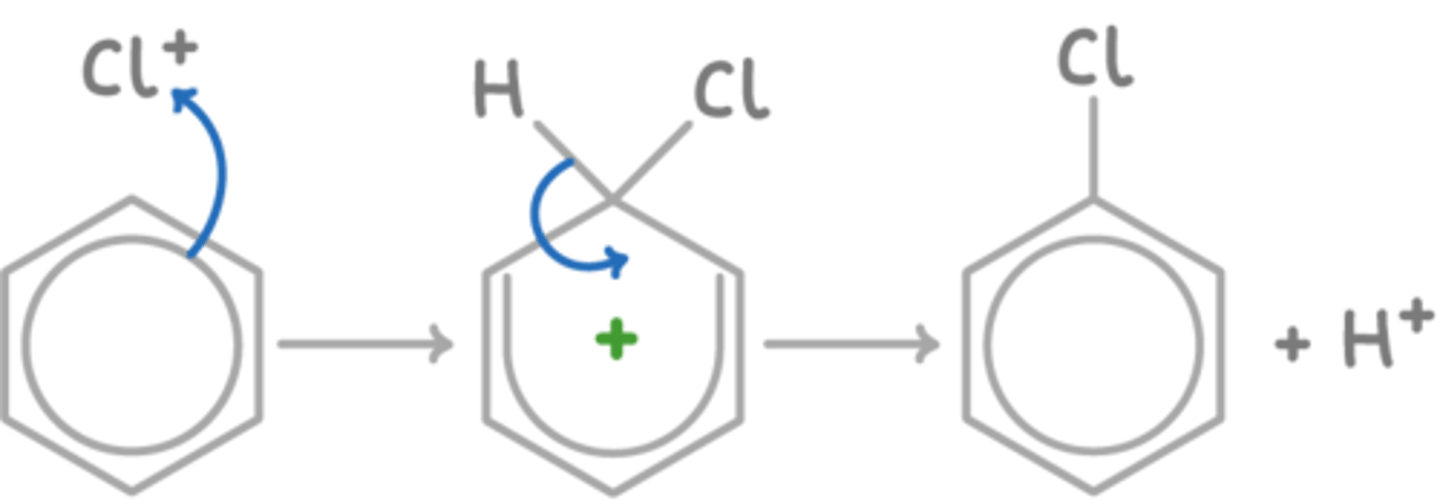
What is a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction? (3)
- An electrophilic substitution reaction
- where a hydrogen on benzene is replaced with an alkyl group
- using a haloalkane and a Lewis acid catalyst.
What are the reagents for alkylation? (1)
Haloalkane (R-X)
What are the conditions for alkylation? (1)
- Room temperature and pressure (rtp)
- halogen carrier catalyst (FeBr₃ or AlBr₃)
What is the electrophile in alkylation? (1)
R⁺
What is a Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction? (1)
- An electrophilic substitution reaction
- where a hydrogen on benzene is replaced with an acyl group
- using an acyl chloride and a Lewis acid catalyst.
What are the reagents for acylation? (1)
Acyl chloride (R-COCl)
What are the conditions for acylation? (1)
- 60°C for 30 mins under reflux,
- AlCl₃ or FeCl₃ catalyst,
- anhydrous conditions
What is the electrophile in acylation? (1)
R-C⁺=O
Why are Friedel-Crafts alkylations and acylations important in synthesis? (1)
They form new C-C covalent bonds
Why is benzene less reactive than alkenes? (3)
- Benzene has delocalised π electrons in a stable π system,
- resulting in lower electron density
- and less susceptibility to electrophilic attack.
Why does benzene require a catalyst for electrophilic substitution? (2)
- Benzene cannot induce a dipole in a halogen
- due to its low electron density and stable π system.
Why are alkenes more reactive than benzene? (2)
- Alkenes contain a double carbon bond with localised electrons in a π-bond,
- giving them a higher electron density.
What allows alkenes to undergo electrophilic addition more easily than benzene? (2)
- The high electron density in the π bond allows alkenes to induce dipoles
- and attract electrophiles without a catalyst.
What is phenol? (1)
Phenol is a benzene with a hydroxyl group (-OH).
Why is phenol more reactive than benzene? (3)
- The lone pair of p-orbital electrons on the oxygen in the -OH group is delocalised into the benzene ring,
- increasing electron density
- and making it more susceptible to electrophilic attack.
Why is phenol considered a weak acid? (1)
Phenol partially dissociates in aqueous solution.
What does phenol react with due to its weak acidity? (2)
- It reacts with strong bases
- such as group 1 hydroxides.
Write an equation for the reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide. (1)
C₆H₅OH + NaOH → C₆H₅O⁻Na⁺ + H₂O
Does phenol react with weak bases like group 1 carbonates? (1)
No
What happens when phenol reacts with bromine water? (1)
Phenol undergoes triple substitution to form 2,4,6-tribromophenol.
What happens when phenol reacts with dilute nitric acid? (2)
- Phenol undergoes single substitution
- to form a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol.
NOTE: No catalyst is needed
Write the equation for nitration of phenol with dilute nitric acid. (1)
C₆H₅OH + HNO₃ → C₆H₄(NO₂)OH + H₂O
What happens when phenol reacts with concentrated nitric acid? (2)
- Phenol undergoes triple substitution
- to form 2,4,6-trinitrophenol.
NOTE: No catalyst is needed
What effect does the -OH group have on the benzene ring in phenol? (4)
- The lone pair of p-orbital electrons from the oxygen in the -OH group is delocalised into the electron ring.
- activates the benzene ring,
- increasing electron density
- and making it more susceptible to electrophilic attack.
What are 2- and 4- directing groups? (2)
- Electron donating groups
- such as -OH and -NH₂.
What are 3- directing groups? (1)
- Electron withdrawing groups
- such as -NO₂.
What effect do electron donating groups have on the π system? (1)
They push more electrons onto the π system.
What effect do electron withdrawing groups have on the π system? (1)
They withdraw electrons from the π system.
How do directing groups influence electrophilic substitution? (1)
They direct electrophiles to positions 2-, 4- or 3- relative to their position on the ring.
Why is knowledge of directing groups important? (1)
- It helps predict substitution patterns
- and design the synthesis of desired products.
What is formed when an aldehyde is oxidised? (1)
A carboxylic acid
What are the reagents and conditions for oxidation of an aldehyde? (1)
- Acidified potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇/H⁺),
- under reflux
What is the general equation for the oxidation of an aldehyde. (1)
aldehyde + [O] → carboxylic acid
What type of reagent is NaBH₄? (1)
A reducing agent
What does NaBH₄ reduce carbonyl compounds to? (1)
Alcohols
What does the hydride ion (H⁻) from NaBH₄ attack during the reaction? (1)
The δ⁺ carbon atom in the carbonyl group
What happens after the hydride ion attacks the carbonyl compound? (1)
An intermediate is formed and then protonated
What is the final product of the reduction of a carbonyl compound by NaBH₄? (1)
An alcohol
What is a general equation for the reduction of a carbonyl compound using NaBH₄. (1)
carbonyl + 2[H] → alcohol
Draw a reaction mechanism for the reduction of ethanal by NaBH₄. (5)
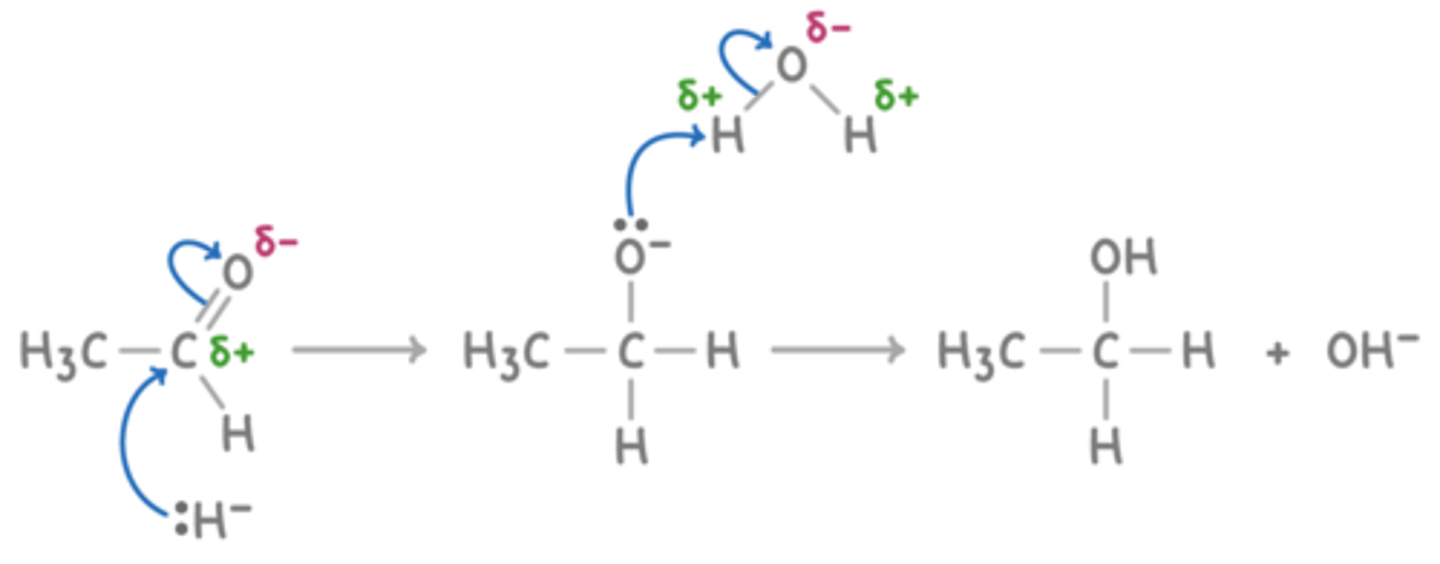
What type of acid is hydrogen cyanide? (1)
A weak acid
What is the role of hydrogen cyanide in reactions with carbonyl compounds? (1)
It allows further carbon atoms to be added to the molecule
What part of the carbonyl compound does the cyanide ion attack? (1)
The δ⁺ carbon atom in the carbonyl group
What is formed after the cyanide ion attacks the carbonyl compound? (1)
An intermediate, which is then protonated
What is the final product when a carbonyl compound reacts with hydrogen cyanide? (1)
A hydroxynitrile
Draw a reaction mechanism for the nucleophilic addition of HCN to propanone. (5)
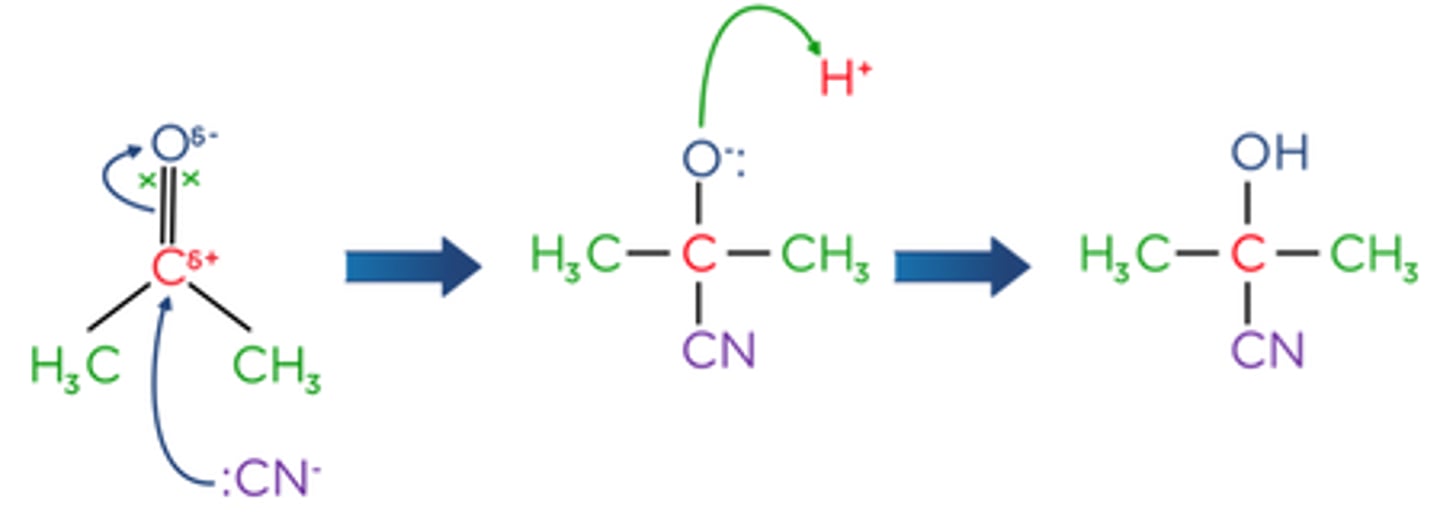
What is Brady's solution (2,4-DNP) used to test? (3)
- It is used to test for ketones and aldehydes.
- Positive result: Orange precipitate forms
- Negative result: No precipitate forms
What is the purpose of the precipitate formed from Brady's solution? (1)
It is used as a derivative for the carbonyl compound.
How can the carbonyl compound be identified using the derivative? (2)
- Purify the precipitate by recrystallisation
- Compare the melting point of the crystalline derivative to known data.
What is Tollen's reagent used to test? (2)
- It is used to test for aldehydes
- Positive result: forms a silver mirror
What is the ionic equation for the reaction in Tollen's reagent? (1)
Ag⁺ (aq) + e⁻ → Ag (s)
What functional group do carboxylic acids contain? (1)
-COOH
Why are smaller carboxylic acids very soluble in water? (1)
The polar -COOH group can form hydrogen bonds with water
Why does solubility of carboxylic acids decrease with increasing chain length? (1)
The molecule becomes more non-polar
Are carboxylic acids strong or weak acids? (1)
Weak acids
Weak acids
How do carboxylic acids behave in aqueous solutions? (1)
They partially ionise
Write the general reaction of a carboxylic acid with a metal. (1)
carboxylic acid + metal → metal salt + hydrogen
Write the general reaction of a carboxylic acid with a metal oxide. (1)
carboxylic acid + metal oxide → metal salt + water
Write the general reaction of a carboxylic acid with a metal hydroxide. (1)
carboxylic acid + metal hydroxide → metal salt + water
Write the general reaction of a carboxylic acid with a metal carbonate. (1)
carboxylic acid + metal carbonate → metal salt + water + carbon dioxide
What are the reagents and conditions for forming an ester from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol? (2)
- Gently heat
- with an acid catalyst (e.g. concentrated H₂SO₄)
What are the products when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol? (2)
- An ester
- water
Write a word equation for methanol reacting with ethanoic acid. (1)
methanol + ethanoic acid → methyl ethanoate + water
What is an acid anhydride? (2)
- A derivative of a carboxylic acid
- where the -OH group is replaced by a carbonyl group
What are the reagents and conditions for ester formation using an acid anhydride? (3)
- Acid anhydride and alcohol,
- gently heated
- an acid catalyst (e.g. concentrated H₂SO₄)
What is acid hydrolysis of esters? (1)
Breaking an ester down into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
What are the conditions required for acid hydrolysis of esters? (2)
- Heat
- Aqueous acid
What is alkali hydrolysis of esters? (1)
Breaking an ester down into an alcohol and a carboxylate salt
What are the conditions required for alkali hydrolysis of esters? (2)
- Heat
- Aqueous alkali
What is an acyl chloride? (2)
- A derivative of a carboxylic acid
- where the hydroxyl group is replaced by a chlorine atom
How can an acyl chloride be made from a carboxylic acid? (1)
React with SOCl₂
What is a general equation for the production of an acyl chloride from a carboxylic acid? (1)
SOCl₂ → acyl chloride + SO₂ + HCl
What are the products when an acyl chloride reacts with an alcohol? (2)
- Ester
- HCl
Why does using an acyl chloride with alcohol give a higher ester yield? (1)
Because the reaction is not reversible
What are the products when an acyl chloride reacts with phenol? (1)
- Ester
- HCl
Why is the acyl chloride method needed to esterify phenol? (1)
Because phenol does not react easily with carboxylic acids
What are the products when an acyl chloride reacts with water? (2)
- Carboxylic acid
- HCl